National Forest System Management: Overview and Issues for Congress
Changes from September 5, 2019 to May 18, 2023
This page shows textual changes in the document between the two versions indicated in the dates above. Textual matter removed in the later version is indicated with red strikethrough and textual matter added in the later version is indicated with blue.
National Forest System Management: Overview, Appropriations, and Issues for Congress
Contents
- Background
- Organization
- Management of the National Forest System
- Overview and Land Management Planning
- Planning Regulations
- National Forest System Uses
- Fish and Wildlife Habitat
- Outdoor Recreation
- Mineral and Energy Development
- Range
- Timber
- Watersheds
- Wilderness and Other Special Land Designations
- Other Uses
- Forest Health Conditions
- Insect, Disease, and Wildfire Risk
- Issues
- Discussion
- Appropriations
- Wildfire Funding
- Land Acquisition and Disposal
- Issues for Congress
Figures
Summary
National Forest System Management: May 18, 2023 Overview and Issues for Congress Katie Hoover The 193 million acres of the National Forest System (NFS) comprise 154 national forests, 20 Specialist in Natural national grasslands, and several other federal land designations. Management of the NFS is one Resources Policy of the three principal responsibilities of the Forest Service (FS), an agency within the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA). Most NFS lands are concentrated in the western United Anne A. Riddle States, although FS administers more federal land in the East than all other federal agencies Analyst in Natural combined. The Secretary of Agriculture has various authorities to acquire or dispose of NFS Resources Policy lands, although these authorities are often constrained by geography or other factors.
The original forest reserves were established to improve and protect federal forests and
watersheds and to provide a source of timber. Today, the NFS'’s statutory mission is to provide a variety of uses and values—timber production, watershed management, livestock grazing, energy and mineral development, outdoor recreation, fish and wildlife habitat management, and wilderness—without impairing the productivity of the land. Comprehensive land and resource management plans for each NFS unit (also known as forest plans) inform decisions on how those uses will be balanced and desired resource conditions. Although there is not a statutory mandate to generate revenue, FS is authorized to charge fees for many of the uses and services available on NFS lands and to use that revenue in various ways. In FY2018, FS generated a total of $283.4 million in revenue; timber harvests were the single largest source of revenue (57%). Growing demands for the various uses, values, and services have led to conflicts over the location and timing of activities.
Many have concern that degraded forest ecological conditions in the NFS are increasing the risk of insect or disease infestation or uncharacteristic wildfires, among other forest health concerns. Many have particular concern regarding accumulated levels of forest biomass (e.g., vegetation), which fuel fires and can facilitate insect or disease transmission, known as hazardous fuels without impairing the productivity of the land. Comprehensive land and resource management plans for each NFS unit (also known as forest plans) describe the desired resource conditions for the plan area and set a framework for associated land management projects. While preparing forest plans and projects, FS must comply with laws of general applicability that govern federal agency actions, including the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA; P.L. 91-109). NEPA requires FS to identify the potential environmental impacts of a proposed action (i.e., a forest plan or project) before making a final decision about that action. Congress has sometimes sought to expedite the NEPA process for certain FS actions, such as through passage of the Healthy Forests Restoration Act (HFRA; P.L. 108-148); HFRA authorized activities intended to expedite the NEPA process for certain projects to reduce wildfire risk and restore NFS lands.
NFS lands are administered for sustained yields of multiple uses, including fish and wildlife purposes, outdoor recreation, mineral and energy development, range (livestock grazing), timber production, and watershed protection, and for natural, scenic, scientific, and historical values, including wilderness preservation. Congress did not specify that FS should prioritize one use over any other use, instead specifying that FS is to pursue “harmonious and coordinated management of the various resources, each with the other ... in perpetuity of a high-level annual or regular periodic output ... without impairment of the productivity of the land.” Demand for the various uses and resources provided by the NFS—and the sometimes incompatible nature of those resources and uses—has led to conflicts over the location and timing of activities. Although revenue generation is not a stated statutory purpose of the NFS, FS is authorized to charge fees and otherwise collect revenue from many of the uses and services it provides, such as grazing, recreation, and timber harvesting. This revenue may be used to offset agency costs for specific activities, shared with the communities containing the NFS land, or deposited into the General Treasury, depending on the use, location, and varying statutory requirements. In FY2022, FS generated a total of $280.0 million; timber harvests were the single largest source of revenue (44%).
Many have concerns regarding the ecological condition of the NFS. Of particular concern is an accumulation of forest biomass (e.g., vegetation), which can fuel and accelerate fires and can facilitate insect or disease transmission; these are known as hazardous fuels. Degraded forest ecosystems may be more susceptible to mortality in response to disturbances (e.g., wildfires, wind or ice storms, flooding, insect and disease infestations) or may take longer to recover. Some research indicates that climate variability is reshaping forest landscapes by altering the frequency, intensity, and timing of disturbance events in ways that may modify or permanently impair the NFS’s lands and resources. Forest restoration projects aim to improve forest conditions and include activities such as post-disturbance reforestation (e.g., reestablishing forest cover). Forest restoration projects that remove or modify hazardous fuels are sometimes referred to as treatments and are generally intended to reduce the risk of uncharacteristic wildfire and facilitate postfire recovery.
FS reports about 63 million acres of NFS lands were at high or very high wildfire hazard potential in FY2022. In the same year, FS reports the agency completed hazardous fuel treatments on 3.2 million acres on NFS and adjacent lands. FS must comply with several statutory reporting requirements on the agency’s progress toward various forest restoration metrics. The reporting has varied over time, complicating analysis and Congress’s ability to conduct oversight. FS and other stakeholders have identified administrative process barriers and funding as two of many factors impeding progress toward forest restoration goals, and FS has proposed to increase the scale, scope, and implementation of projects to restore the resilience and resistance of NFS lands. There is disagreement, however, about how to achieve those objectives while ensuring compliance with other statutory requirements.
Congressional Research Service
link to page 6 link to page 6 link to page 7 link to page 9 link to page 10 link to page 10 link to page 11 link to page 12 link to page 13 link to page 15 link to page 16 link to page 17 link to page 19 link to page 19 link to page 20 link to page 20 link to page 21 link to page 22 link to page 23 link to page 24 link to page 24 link to page 26 link to page 27 link to page 28 link to page 29 link to page 31 link to page 33 link to page 8 link to page 22 link to page 8 link to page 18 link to page 32 link to page 34 National Forest System Management: Overview and Issues for Congress
Contents
Background ..................................................................................................................................... 2
National Forest System Establishment and Modification ......................................................... 2 Organization of the National Forest System ............................................................................. 3
Management of the National Forest System.................................................................................... 5
Land and Resources Management Planning ............................................................................. 6
Forest Plans ......................................................................................................................... 6 Project Planning .................................................................................................................. 7
National Environmental Policy Act........................................................................................... 8 Healthy Forests Restoration Act ................................................................................................ 9
HFRA Insect and Disease Designation Areas .................................................................... 11 NEPA Categorical Exclusions Established in HFRA ........................................................ 12
National Forest System Uses ......................................................................................................... 13
Fish and Wildlife Habitat ........................................................................................................ 15 Outdoor Recreation ................................................................................................................. 15 Mineral and Energy Development .......................................................................................... 16 Range and Grazing Management ............................................................................................ 16 Timber ..................................................................................................................................... 17 Watersheds .............................................................................................................................. 18 Wilderness and Other Special Land Designations .................................................................. 19 Other Uses ............................................................................................................................... 20
Forest Health Conditions on the National Forest System .............................................................. 20
Hazardous Fuels and Forest Restoration ................................................................................. 22
FS Goals and Strategies for Forest Restoration ................................................................ 23
Issues ....................................................................................................................................... 24
Pace and Scale of Project Implementation ........................................................................ 25 Reporting .......................................................................................................................... 27
Issues for Congress ........................................................................................................................ 29
Figures Figure 1. Map of the National Forest System .................................................................................. 4 Figure 2. FS Harvest Volume and Value, FY1940-FY2022 .......................................................... 18
Tables Table 1. The National Forest System (NFS) .................................................................................... 4 Table 2. FS Revenue, FY2018-FY2022 ........................................................................................ 14 Table 3. Selected Forest Service (FS) Statutory Reporting Requirements .................................... 28
Contacts Author Information ........................................................................................................................ 30
Congressional Research Service
National Forest System Management: Overview and Issues for Congress
Congressional Research Service
National Forest System Management: Overview and Issues for Congress
compliance with other statutory requirements.
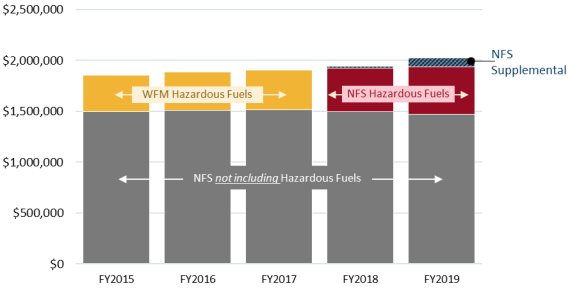
In FY2019, FS received a total of $2.02 billion to fund NFS management, approximately 29% of the $6.94 billion the agency received in discretionary appropriations. These figures reflect $854.3 million in emergency-designated supplemental appropriations provided to FS to respond to hurricanes and wildfires, of which $85.0 million was allocated to the NFS account. The NFS account includes several subaccounts, programs, and activities, many of which reflect the different ways in which the lands are used. The largest is Hazardous Fuels, which received 23% of the NFS appropriation in FY2019. This program funds activities to remove, modify, or manipulate vegetation to reduce the wildfire risk. Prior to FY2018, this program was funded through a different FS discretionary account. The addition of this program is one reason NFS appropriations have increased by 35% since FY2015.
Many also are concerned about the cost of wildfires. Although many wildfire management activities are funded separately from NFS management, some are concerned about the rising proportion of fire suppression and other fire-related costs on the rest of FS's budget. In FY2019, wildfire management-related activities accounted for 59% of the agency's total discretionary appropriation. Wildfire costs vary annually and are difficult to predict, and FS is authorized to transfer money out of other discretionary accounts to cover suppression costs; this is often referred to as fire borrowing. To address some of these concerns, the 115th Congress enacted a new mechanism for funding wildfire suppression (commonly referred to as the wildfire funding fix), which is available starting in FY2020.
The National Forest System (NFS) is administered by the Forest Service (FS) in the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA).11 The 193-million-acre NFS comprises national
T forests, national grasslandsgrasslands, and various other designations across 43 states and Puerto Rico.2
Rico.2 Although 87% of NFS lands are in the West, the FS administers more federal land in the East (26 million acres) than all other federal agencies combined. NFS lands are administered for sustained yields of multiple uses, including outdoor recreation (camping, hiking, hunting, sightseeing, etc.), livestock grazing, timber harvesting, watershed protection, and fish and wildlife habitats.
Ownership and use of the NFS—and federal lands more generally—have stirred controversy for decades. Competing public values concerning the NFS raise many questions and issues: how uses should be balanced and prioritized, whether and where Congress should designate areas for special purposes, and when and how FS should collect and distribute fees or other revenue for land and resource uses, among others. Congress continues to examine these questions through legislative proposals, program oversight, and annual appropriations. The 115th117th Congress, for example, enacted several legislative changes affecting management of the NFS.
This report provides an overview of the history and management of the NFS, including a discussion of the statutory framework for making land management plans and decisions. This report also includes an overview of two laws: the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) and the Healthy Forests Restoration Act (HFRA).3 These laws, among others, establish procedures relevant to FS’s decisionmaking processes and authorize specific forest management activities. In addition, the report discusses the multiple uses of the NFS and the revenue generated by those activities and the ecological condition of the NFS. It concludes with a discussion of the overarching issues regarding NFS management that Congress often debates.
Forest Service and National Forest System Appropriations
The Forest Service (FS) receives both discretionary and mandatory appropriations. Although it is an agency within the U.S. Department of Agriculture, FS receives its discretionary appropriations through Title III of regular Interior, Environment, and Related Agencies appropriations bil s. Separately, FS receives mandatory appropriations under multiple authorizing statutes. Laws authorizing mandatory appropriations allow FS to spend money without further action by Congress, and the budget authority for several of these mandatory spending accounts is dependent on revenue generated by activities in the National Forest System (NFS). NFS management is funded primarily through FS’s NFS discretionary account, although funding also comes from other discretionary accounts (e.g., Capital Improvement and Maintenance, Wildland Fire Management) and mandatory accounts (e.g., Reforestation Trust Fund, National Parks and Public Land Legacy Restoration Fund). FS budget requests and Interior Appropriations Subcommittee documents typically allocate monies in each account among various subaccounts and, in some cases, among specific programs and activities. FS further allocates its appropriations—at the account, subaccount, and program activity levels—among the nine FS regions, five research stations, two service centers and laboratories, and national headquarters office in Washington, DC. Once the funds have been allocated to the regions and programs, the money is then further allocated to each NFS unit. This can make analyzing appropriations by region or by forest challenging.
1 Management of the National Forest System (NFS) is one of the Forest Service’s (FS’s) three principal responsibilities. The other two principal responsibilities are providing assistance programs to nonfederal forest owners and conducting forestry research programs. FS also provides international forestry assistance.
2 The NFS is defined at 16 U.S.C. §1609(a). U.S. Department of Agriculture, U.S. Forest Service, Land Areas Report (LAR)—as of September 30, 2022, Table 1, at http://www.fs.usda.gov/land/staff/lar/LAR2022/lar2022index.html. Hereinafter referred to as FS, Land Areas Report, 2022. The LAR includes several additional land designations in the NFS, such as research and experimental forests or areas. This includes a 140-acre experimental forest in the U.S. Virgin Islands.
3 The National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA): P.L. 91-190, 42 U.S.C. §§4321-4347. The Healthy Forests Restoration Act (HFRA): P.L. 108-148, 16 U.S.C. §§6501 et seq.
Congressional Research Service
1
National Forest System Management: Overview and Issues for Congress
Background
National Forest System Establishment and Modification example, enacted several legislative changes affecting management of the NFS. For more information on those changes, see CRS Report R45696, Forest Management Provisions Enacted in the 115th Congress, by Katie Hoover et al.
This report provides an overview of the history and management of the NFS, including a discussion of the statutory framework for making land management plans and decisions as well as for acquiring or disposing of system lands. The report also discusses the multiple uses of the NFS and the revenue generated by those activities, appropriations to manage the NFS, and wildfire management issues and costs. It concludes with a discussion of the issues that Congress often debates regarding NFS management.
Background
In 1891, Congress granted the President the authority (now repealed) to establish forest reserves from the public domain.34 Six years later, Congress stated that the forest reserves were
to improve and protect the forest within the reservation, or for the purpose of securing favorable conditions of water flows, and to furnish a continuous supply of timber for the use and conditions of water flows, and to furnish a continuous supply of timber for the use and necessities of the citizens of the United States.4
5
Initially, the reserves were administered by the Division of Forestry in the Department of the Interior'Interior’s General Land Office. In 1905, this division was combined with the USDA Bureau of Forestry (renamed the Forest Service), and the administration of the 56 million acres of forest reserves was transferred to the new agency within USDA.56 In 1907, the reserves were renamed national forests.6
7
In 1906 and 1907, President Theodore Roosevelt more than doubled the acreage of the forest reserves. In response, Congress limited the authority of the President to add to the system in certain states in 1907.78 In 1910, Congress continued the limitation, but then in 1911, Congress passed the Weeks Act to authorize additions to the NFS through the purchase of private lands.8 9 Presidential authority to proclaim new national forests was terminated in 1976.910 Under the Weeks Act and other authorities, the system has continued to grow,NFS grew from 154 million acres in 1919 to 193 million acres in 2018. This growth has resulted from purchases and donations of private land and from transfers of other federal lands, primarily from the Bureau of Land Management (BLM, within the Department of the Interior). For more information on FS's authority to acquire lands, see the "Land Acquisition and Disposal" section of this report.
Organization
The NFS includes 154 national forests with 188.42022. The size of the NFS has been over 190 million acres since 1981.
Today, the Secretary of Agriculture has numerous authorities to add lands to the NFS through acquisitions or land exchanges.11 Often, though, the acquisitions are restricted to land within or contiguous to the proclaimed exterior boundaries of a national forest.12 The President (and, in some cases, the Secretary of Agriculture or the Chief of the Forest Service) also has the authority to change NFS unit names, combine NFS units for administration purposes, establish new national forests from existing NFS lands, and make mostly minor NFS boundary adjustments.13 Today, establishing a new national forest (from lands not already in the NFS) or significantly modifying the boundaries of an existing national forest requires an act of Congress.
4 Public domain lands consist of lands ceded by the original states or obtained from a foreign sovereign through purchase, treaty, or other means (e.g., the Louisiana Purchase in 1803). Public domain lands may be governed by different laws than acquired federal lands, which were obtained from private entities or states.
5 Organic Administration Act, Act of June 4, 1897, formerly codified at 16 U.S.C. §471 (now repealed). 6 The Transfer Act, Act of February 1, 1905 (P.L. 58-33, 16 U.S.C. §475). 7 Act of March 4, 1907, ch. 2907, 34 Stat. 1269 (P.L. 59-242). 8 Act of March 4, 1907, ch. 2907, 34 Stat. 1271 (P.L. 59-242), see 16 U.S.C. §471 note. The act limited the presidential authority to establish national forests in Colorado, Idaho, Montana, Oregon, Washington, and Wyoming. Roosevelt proclaimed additional reserves after it was enacted by Congress but before he signed it into law.
9 Act of March 1, 1911 (P.L. 61-435, 16 U.S.C. §515). 10 The authority for the President to establish national forests was codified at 16 U.S.C. §471 and was repealed by §704(a) of the Federal Land Policy and Management Act of 1976 (FLPMA; P.L. 94-579).
11 For more comprehensive information on the authority of FS and the other federal land management agencies to acquire lands, see CRS Report RL34273, Federal Land Ownership: Acquisition and Disposal Authorities.
12 The proclaimed exterior boundaries of the NFS are the formally identified geographic boundaries around lands that have been set aside and reserved for national forest purposes. These proclaimed exterior boundaries of an NFS unit may encompass areas larger than the actual boundary of an established national forest.
13 16 U.S.C. §473.
Congressional Research Service
2
link to page 8 link to page 8 link to page 8 National Forest System Management: Overview and Issues for Congress
The Secretary also has numerous authorities to convey NFS land out of federal ownership, all constrained in various ways and seldom used.14 Often, the authority requires the federal government to dispose of the land at fair market value or, in the case of land exchanges, requires that the lands be in the same state and of equal value (although value may be partially equalized by a cash payment). In addition to these standing authorities for FS to acquire, exchange, or dispose of land, Congress has sometimes enacted laws directing FS to acquire or dispose of particular parcels where no standing authority exists and, in other cases, to direct or facilitate land transactions.
National Forest System Land Status and Committee Jurisdiction
Lands were added to the National Forest System (NFS) in different ways. The national forests in the western United States were primarily established through a presidential proclamation or order reserving lands from the public domain, whereas the national forests in the eastern United States were primarily acquired under the Weeks Act (P.L. 61-435, 16 U.S.C. §515) authority. The national grasslands were acquired and transferred into the NFS pursuant to the Bankhead-Jones Farm Tenant Act of 1937 (7 U.S.C. §§1010 et seq.). Other NFS units were added in other ways, including through acts of Congress. The different origination status of NFS lands has implications regarding congressional jurisdiction. The House Committee on Natural Resources and the Senate Committee on Energy and Natural Resources have jurisdiction over the NFS units established from the public domain, whereas the House Committee on Agriculture and the Senate Committee on Agriculture, Nutrition, and Forestry have jurisdiction over the NFS other than those areas created from the public domain.
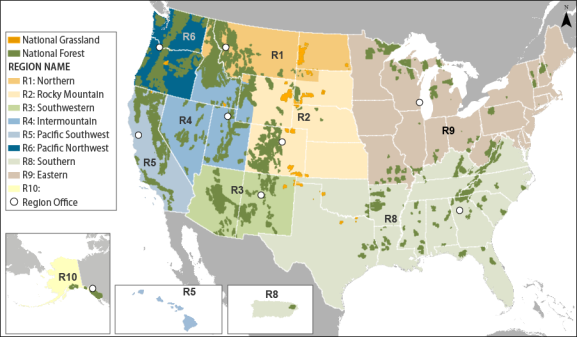
Organization of the National Forest System15 The NFS includes 154 national forests with 188.5 million acres (98% of the system), 20 national grasslands with 3.8 million acres (2%), and 110 other areas—such as a national grassland prairie, land utilization projects, purchase units, and research and experimental areas—with 0.8 million acres (<1%).1016 FS may combine units for administrative purposes, and each is administered by a forest supervisor. The NFS units are arranged into nine administrative regions, each headed by a regional forester. The nine regional foresters report to the NFS deputy chief, who reports to the chief of the Forest Service. The chief has traditionally been a career employee of the agency. The chief reports to the Secretary of Agriculture through the Under Secretary for Natural Resources and Environment.
The NFS regions are often referred to by number rather than by namename. Table 1 identifies the number, states encompassed, and acreage for each of the regions. NFS lands are concentrated in the seven western FS regions (see Figure 1). Inholdings, shown inin Table 1, are lands (primarilyare nonfederal lands (often private) within the designated boundaries of the national forests (and other NFS units) that are not administered by the FS. Inholdings sometimes pose difficulties for FS land management, because the agency does not regulate their development and use, which may be incompatible with desired uses of the federal lands, and constraints on access across inholdings may limit access to some federal lands. Many private landowners, however, object to the idea of possible federal restrictions on the use of their lands and especially to unfettered public access across their lands.
14 For more comprehensive information on the authority of FS and the other federal land management agencies to dispose of lands, see CRS Report RL34273, Federal Land Ownership: Acquisition and Disposal Authorities.
15 36 C.F.R. Part 200. 16 FS, Land Areas Report, 2022.
Congressional Research Service
3
link to page 8
National Forest System Management: Overview and Issues for Congress
Table 1. The National Forest System (NFS)
States/Territories
Forest Service Region
Containing NFS Lands
NFS Acreagea
Region Name
No. States
Federal
Inholdings
Total
Northern
1
ID, MT, ND, SD
25,610,100
2,541,357
28,151,457
Rocky Mountain
2
CO, KS, NE, SD, WY
22,057,859
2,548,962
24,606,821
Southwestern
3
AZ, NM
20,531,012
1,659,267
22,190,279
Intermountain
4
ID, NV, UT, WY
31,907,911
2,230,224
34,138,135
Pacific Southwest
5
CA, HI
20,241,198
3,404,725
23,645,922
Pacific Northwest
6
OR, WA
24,977,877
3,005,659
27,983,535
Southern
8
AL, AR, FL, GA, KY, LA, MS, NC, OK,
13,442,574
13,017,169
26,459,743
PR, SC, TN, TX, VA
Eastern
9
IL, IN, ME, MI, MN, MO, NH, NY, OH,
12,183,703
9,993,137
22,176,840
PA, VT, WI, WV
Alaska
10
AK
22,141,063
1,803,153
23,944,217
National Forest System
193,093,298
40,203,654
233,296,950
Source: U.S. Department of Agriculture, U.S. Forest Service (FS), Land Areas Report (LAR)—as of September 30, 2022restrictions on the use of their lands and especially to unfettered public access across their lands.
|
Forest Service Region |
|
| |||
|
Region Name |
No. |
States |
Federal |
Inholdings |
Total |
|
Northern |
1 |
ID, MT, ND, SD |
25,555,164 |
2,586,950 |
28,142,114 |
|
Rocky Mountain |
2 |
CO, KS, NE, SD, WY |
22,055,096 |
2,550,999 |
24,606,095 |
|
Southwestern |
3 |
AZ, NM |
20,530,154 |
1,660,545 |
22,190,699 |
|
Intermountain |
4 |
ID, NV, UT, WY |
31,896,356 |
2,348,250 |
34,244,606 |
|
Pacific Southwest |
5 |
CA, HI |
20,203,102 |
3,440,879 |
23,643,981 |
|
Pacific Northwest |
6 |
OR, WA |
24,967,936 |
3,013,215 |
27,988,151 |
|
Southern |
8 |
AL, AR, FL, GA, KY, LA, MS, NC, OK, PR, SC, TN, TX, VA |
13,419,773 |
12,079,988 |
25,499,761 |
|
Eastern |
9 |
IL, IN, ME, MI, MN, MO, NH, NY, OH, PA, VT, WI, WV |
12,174,918 |
10,001,182 |
22,176,100 |
|
Alaska |
10 |
AK |
22,138,560 |
1,791,001 |
23,929,561 |
|
National Forest System |
192,948,059 |
39,473,009 |
232,421,068 |
||
Source: U.S. Department of Agriculture, U.S. Forest Service, Land Areas Report (LAR)—as of September 30, 2018, Tables 1 and 2, at http://www.fs.fed.us/usda.gov/land/staff/lar/LAR2018/lar2018index.html.
lar/LAR2022/lar2022index.html. Notes: In 1966, Region 7 (the Lake States Region) was merged with Region 9 (the Northeastern Region) to form the current Region 9 (Eastern Region). Although this merger left 9 regions, the numbering sequence skips 7 and ends with 10, as shown in the table. Idaho, Wyoming, and South Dakota are each split into two regions. Regions include states that do not contain NFS lands.
a. , which are not listed in the table. a. Federal is federally owned land managed by the FS. Inholdings are private and other government lands within NFS
boundaries that are not administered or regulated by the FS.
FS. Figure 1. Map of the National Forest System |
 |
Source: Prepared by CRS from data available from FS Geodata Clearinghouse, at
|
Management of the National Forest System
Overview and Land Management Planning
http://data.fs.usda.gov/geodata/. Notes: Alaska, Hawaii, and Puerto Rico are presented in multiple scales.
Congressional Research Service
4
National Forest System Management: Overview and Issues for Congress
Management of the National Forest System The management goals for the national forests were articulated in Section 1 of the Multiple-Use Sustained-Yield Act of 1960,1117 which states:
It is the policy of the Congress that the national forests are established and shall be administered for outdoor recreation, range, timber, watershed, and wildlife and fish purposes. The purposes of this Act are declared to be supplemental to, but not in derogation of, the purposes for which the national forests were established as set forth in the Act of June 4, 1897.... The establishment and maintenance of areas as wilderness are consistent with the purposes and provisions of this Act.
Act.
The act directs management of the lands and resources of the national forests to be in the combination of uses that best meets the needs of the American people. Management of the resources is to be coordinated for multiple use—considering the relative values of the various resources but not necessarily maximizing dollar returns nor requiring that any one particular area be managed for all or even most uses. The act also calls for sustained yield—a high level of resource outputs maintained in perpetuity but without impairing the productivity of the land. Other statutes that apply to all federal agencies or actions—such as the Administrative Procedure Act (APA),12 National Environmental Policy Act of 1969 (NEPA),13 and
FS planning and management are guided primarily by the Forest and Rangeland Renewable Resources Planning Act of 1974 (RPA) and the National Forest Management Act of 1976 (NFMA).18 Together, these laws encourage foresight in the use of the nation’s forest resources and establish a long-range planning process for the management of the NFS. RPA assessments are published approximately every 10 years, and the assessments report the status and trends of the renewable resources on all forests and rangelands in the United States.19
Other laws also govern NFS management, such as the HFRA and the Federal Land Policy and Management Act.20 Some laws pertain to NFS management in specific areas. For example, NFS management in Alaska (Region 10, which covers over 10% of the NFS), is subject to provisions in the Alaska National Interest Lands Conservation Act and the Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act (ANCSA).21 FS also must comply with laws of general applicability that govern federal agency actions, such as the Administrative Procedure Act, NEPA, the Endangered Species Act of 1973 (ESA), and the National Historic Preservation Act (NHPA).22
17 Act of June 12, 1960, P.L. 86-517, 16 U.S.C. §§528-531. Other laws govern the management of some of the other NFS units. For example, the national grasslands are managed pursuant to the provisions in the Bankhead-Jones Farm Tenant Act (7 U.S.C. §§1010-1012).
18 The Forest and Rangeland Renewable Resources Planning Act of 1974 (RPA): P.L. 93-378, 16 U.S.C. §§1600 et seq. The National Forest Management Act of 1976 (NFMA): P.L. 94-588; 16 U.S.C. §1600 et seq.
19 For more information, see FS’s RPA website at http://www.fs.usda.gov/research/inventory/rpaa. The following is the most recent publication—as of the date of this report—associated with the decennial RPA assessments, and includes data on a variety of forest resource statistics. Sonja Oswalt, W. Brad Smith, and Patrick Miles, et al., Forest Resources of the United States, 2017: A Technical Document Supporting the Forest Service Update of the 2020 RPA Assessment. FS, GTR-WO-97, 2019, at https://www.fs.usda.gov/treesearch/pubs/57903.
20 Federal Land Policy and Management Act (FLPMA), P.L. 94-579, 43 U.S.C. §§1701 et seq. 21 Alaska National Interest Lands Conservation Act (ANILCA; 16 U.S.C. §§3101 et seq.); and Alaska Native Claims and Settlement Act (ANCSA; P.L. 92-203, 43 U.S.C. §§1601 et seq.).
22 Administrative Procedure Act (P.L. 79-404, 5 U.S.C. §§500 et seq.); NEPA (P.L. 91-190, 42 U.S.C. §§4321–47); Endangered Species Act (ESA; P.L. 93-205, 16 U.S.C. §§1531-1544); National Historic Preservation Act (NHPA; P.L. 89-665, 54 U.S.C. §§300101 et seq.).
Congressional Research Service
5
link to page 11 National Forest System Management: Overview and Issues for Congress
Land and Resources Management Planning FS engages in two different levels of planning for managing the NFS: unit-level planning and project-level planning.23 At the unit level, NFMA requires FS to prepare and update comprehensive land and resource management plans (i.e., forest plans).24 These forest plans establish the framework for guiding project-level planning and decisionmaking within the NFS unit.
FS promulgated regulations to implement the statutory planning requirements and establish the procedures to develop, amend, and revise forest plans at 36 C.F.R. Part 219, referred to as the planning rule. The planning rule has been revised several times, in part to incorporate new priorities as presidential administrations changed.25 The Obama Administration promulgated final planning regulations in 2012 (2012 planning rule).26 The 2012 planning rule established an adaptive, three-phase planning framework to emphasize ecological sustainability, landscape-scale restoration, and science-based decisions informed by public values. Plans are to also account for the potential impacts of climate change.
Forest Plans
Forest plans guide FS’s 1973 (ESA)14—as well as many other FS-specific statutes, also apply.
FS planning and management are guided primarily by the Forest and Rangeland Renewable Resources Planning Act of 1974 (RPA) and the National Forest Management Act of 1976 (NFMA).15 Together, these laws encourage foresight in the use of the nation's forest resources and establish a long-range planning process for the management of the NFS. RPA assessments are published approximately every 10 years, and the assessments report the status and trends of the renewable resources on all forests and rangelands in the United States.16
Planning Regulations
NFMA requires that the FS prepare a comprehensive land and resource management plan for each NFS unit, often called a "forest plan."17 Forest plans guide management of the plan area by identifying desired resource conditions on the ground; determining the suitability of lands for various uses;on the ground and specifying the objectives, standards, and guidelines for NFS activities and uses. Plans are to be revised at least every 15 years to address changing conditions, management goals, and public use.18 The plans must use an interdisciplinary approach, including economic analysis and the identification of costs and benefits of all resource uses. The plans must also be developed and revised with input from the public.
Regulations (often called the planning rules) to establish the procedures to develop, amend, and revise forest plansactivities and uses in the plan area.27 Forest plans provide management direction and are programmatic in nature, meaning they “provide a framework for future proposed actions.”28 Specific on-the-ground actions to accomplish those management objectives are referred to as projects, discussed in the next section (see “Project Planning”).29
23 36 C.F.R. §219.2. 24 FS’s implementing regulations are promulgated at 36 C.F.R. pt. 219 subpt. A. For more information on FS policies, guidance, and instruction for implementing the forest planning requirements, see FS, Forest Service Manual (FSM), ch. 1920, Land Management Planning (2015) (hereinafter FSM_1920), at https://www.fs.usda.gov/cgi-bin/Directives/get_dirs/fsm?1900!..; and FS, Land Management Planning Handbook, Forest Service Handbook (FSH) 1909.12, ch. 20, (2015) (hereinafter FSH 1909.12_20), at https://www.fs.usda.gov/cgi-bin/Directives/get_dirs/fsh?1909.12!... Forest plans is inclusive of plans for all NFS units, including grasslands and others.
25 The first planning regulations were issued in 1979 and then revised in 1982, 2000, 2005, 2008, and 2012. The were issued in 1979 and then revised in 1982, 2000, 2005, 2008, and 2012.19 The Clinton Administration'’s 2000 regulations (2000 planning rule) would have increased emphasis on ecological sustainability during the forest planning process.20 (65 Federal Register 67514, November 9, 2000). The George W. Bush Administration delayed implementation of the Clinton regulations three times out of concerns about implementation and the emphasis on biological sustainability, and then replaced themthe regulations before they went into effect. The Bush Administration promulgated final rules in 2005 (2005 planning rule) to balance ecological sustainability with economic and social considerations.21 (70 Federal Register 1022, January 5, 2005). The 2005 planning rule also would have also exempted forest plans from NEPA and ESA requirements. InterestsInterested parties successfully challenged the 2005 planning rule, arguing that the new rules reduced environmental protection without adequate public comment and ESA consideration.22consideration (Citizens for Better Forestry v. USDA, 481 F.Supp. 2d 1059 (N.D.Cal., 2007)). The Bush Administration reissued the 2005 rule as a proposed rule to provide for the court-ordered public comment and issued new final rules in 2008 (2008 planning rule).23, 73 Federal Register 21467, April 21, 2008). The court also invalidated the 2008 planning rule for violating NEPA and ESA (Citizens for Better Forestry v. USDA, 632 F.Supp. 2d 968 (N.D.Cal., 2009)). In 2009, FS reverted to using 1982 procedures. For more information on the history of the planning regulations as well as the status of the current rule, see https://www.fs.usda.gov/planningrule.
26 77 Federal Register 21260 (April 9, 2012). In 2016, FS amended the rule to clarify the plan amendment process and procedures, among other technical amendments (81 Federal Register 90723, December 15, 2016). The regulations are codified at 36 C.F.R. part 219.
27 36 C.F.R. §§219.2(b), 219.7(e). 28 50 C.F.R. §402.02. 29 36 C.F.R. §219.2(b).
Congressional Research Service
6
National Forest System Management: Overview and Issues for Congress
Forest plans generally do not authorize individual actions or projects, nor do they commit FS to take any specific action.30 Forest plans may, however, constrain FS from authorizing future projects or activities in specific areas.31
NFMA requires FS to revise forest plans at least every 15 years to address changing conditions, management goals, and public use.32 However, forest plans may be amended at any time.33 Amendments can address new information, changed resource conditions, or other altered circumstances. Plan amendments vary in scale and scope; some amendments may apply broadly across the entire NFS unit covered by the plan area, whereas other amendments may apply narrowly to a specific resource or area within the NFS unit.34 At times, FS has amended several forest plans simultaneously to address changing conditions across larger geographic scales and covering multiple NFS units. The time it takes to complete a plan amendment varies considerably, depending on the scope and nature of the amendment. Although FS guidance documents envision plan developments or revisions being completed within four years,35 plan revisions take seven years to complete on average.36 When developing forest plans, FS also must comply with laws of general applicability that govern federal agency actions, such as ESA, NEPA, NHPA, and others.
FS has developed 128 plans to guide the management of 110 NFS administrative units, with some plans covering multiple NFS units. As of March 2023, FS reports that 99 plans require revision (meaning they are older than 15 years).37
Project Planning
Projects are the on-the-ground actions that implement the forest plan prepared for a particular unit. Projects are defined in regulation as “an organized effort to achieve an outcome on NFS lands identified by location, tasks, outputs, effects, times, and responsibilities for execution.”38 Projects may include activities such as timber harvests, trail maintenance, or the issuance of special use authorizations for pipelines across NFS lands, among many others. Projects must comport with the resource objectives established in the forest plans.39
Projects must be planned, evaluated, and implemented in accordance with FS procedures that prescribe how to comply with applicable statutory requirements, such as those regarding NEPA implementation. The timing and scope of review for a given project may vary based on the
30 Forest plans must include a list of projects that may be proposed within three to five years after the plan is adopted, but the plan must explicitly state that the inclusion of those possible projects is not a commitment to those actions. 36 C.F.R. §§219.7(f)(1), FSH 1909.12_20, supra note 9. See specifically §22.34 – Proposed and Possible Actions. It is possible for a project to be approved concurrently with a forest plan, but the project is not considered a plan component or part of the plan. FSH 1909.12_20, supra note 9, at 28.
31 FSH 1909.12_20, supra note 9. See specifically §22.13 – Standards and §22.14 – Guidelines. 32 16 U.S.C. §1604(f)(5)(A). Annual appropriations laws have included a provision specifying that the Secretary of Agriculture is not considered to violate the requirements of RPA/NFMA solely because a forest plan has not been revised within 15 years, if the Secretary acts in good faith to update such plans. See, e.g., Further Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2020, P.L. 116-94, div. D, §407, 133 Stat. 2534 (2019) (codified at 16 U.S.C. §1604 note).
33 16 U.S.C. §1604(f)(4). For more information on plan amendments, see FSH 1909.12_20, supra note 9, at 18. 34 36 C.F.R. §219.13. 35 FSH 1909.12_20, supra note 9, at 5. 36 FS, FY2024 Budget Justification, March 2023, p. 30a-104, at https://www.fs.usda.gov/about-agency/budget-performance.
37 FS, FY2024 Budget Justification, March 2023, p. 30a-104, at https://www.fs.usda.gov/about-agency/budget-performance.
38 36 C.F.R. §219.19. 39 50 C.F.R. §219.15.
Congressional Research Service
7
link to page 16 National Forest System Management: Overview and Issues for Congress
specific statutory authority underpinning each project’s implementation, the types of resources at the site that could be affected, and the level of those potential effects. In some circumstances, a project may be planned concurrently with a plan amendment to ensure compliance.
National Environmental Policy Act Broadly, NEPA requires federal agencies to identify the environmental impacts of a proposed action before making a final decision about that action.40 How a federal agency demonstrates compliance with NEPA depends on the level of the proposal’s impacts.41
• A proposed action that would significantly affect the “quality of the human
environment” requires the preparation of an environmental impact statement (EIS) leading to a record of decision.42
• If the impacts are uncertain, an agency may prepare an environmental assessment
(EA) to determine whether an EIS is necessary or whether a finding of no significant impact (FONSI) may be issued through a decision notice.
• Under NEPA implementing regulations, categorical exclusions (CEs) refer
broadly to categories of actions that do not individually or cumulatively have a significant effect on the environment and hence are excluded from the requirement to prepare an EIS or an EA.43
For actions that require an EA or EIS, an agency generally must evaluate the impacts of the proposed action and reasonable alternatives to it, including the alternative of taking no action (i.e., a no-action alternative). The analysis included in the EIS or EA/FONSI is used to inform the agency’s decisionmaking process regarding the proposal. In its agency-specific procedures implementing NEPA, each federal agency has identified and listed actions it is authorized to approve that normally require an EIS (or an EA resulting in a FONSI) or that can be approved using a CE.44
FS identified CEs based on past experience with similar actions, referred to as administrative CEs for purposes of this report.45 Some CEs have been explicitly established in statute by Congress, as discussed in the “NEPA Categorical Exclusions Established in HFRA” section of this report. Since these CEs were established in statute, they do not necessarily reflect actions that have been shown to have no environmental effects, individually or cumulatively. FS regulations also provide for and identify the resource conditions in which a normally excluded action may have the potential for a significant environmental effect and may warrant further analysis in an EA or EIS.46 The presence of these resource conditions is termed extraordinary circumstances. For example, FS has identified the presence of flood plains, municipal watersheds, endangered
40 P.L. 91-109, 42 U.S.C. §§4321-4347. 41 NEPA established the Council on Environmental Quality (CEQ) in the Executive Office of the President, and CEQ issued broad, generic regulations regarding NEPA implementation. These regulations include requiring all federal agencies to adopt and supplement the CEQ regulations as necessary to include detail relevant to actions that agency is authorized to approve (see CEQ, “Regulations for Implementing the Procedural Provisions of the National Environmental Policy Act,” in 40 C.F.R. Parts 1500-1508 (43 Federal Register 55990, November 28, 1978). 42 42 U.S.C. §4332(2)(C). 43 See 40 C.F.R. §1508.4. 44 FS regulations implementing NEPA are codified at 36 C.F.R. Part 220 and supplement both the CEQ regulations and Department of Agriculture (USDA) regulations implementing NEPA at 7 C.F.R. Part 1b. For more information on FS NEPA implementation, see also FSM 1950 and FSH 1909.15, at https://www.fs.usda.gov/im/directives/.
45 For more information on FS categorical exclusions (CEs), see FSH 1909.15_30 (2023). 46 36 C.F.R. §220.6(b).
Congressional Research Service
8
National Forest System Management: Overview and Issues for Congress
species or their habitat, wilderness areas, inventoried roadless areas, and archaeological sites, among others, as potential extraordinary circumstances that may preclude the use of a CE for an otherwise eligible project.47
An agency’s procedures to implement NEPA may serve as an umbrella compliance process. For example, within the framework of determining the resources affected and the level of effects of a given proposal, the agency’s NEPA process would identify project impacts that may trigger additional environmental review and consultation requirements under ESA and NHPA, among other laws. If compliance with NEPA was waived for a given category of action, the requirements triggered by impacts to those resources under other federal laws would still apply.
Healthy Forests Restoration Act HFRA, among other purposes, was intended to expedite the planning and review process for hazardous fuel reduction and forest restoration projects on NFS lands.48 Hazardous fuel reduction projects are intended to reduce the risk of catastrophic wildfire by removing or modifying the availability of vegetation, or biomass (e.g., trees, shrubs, grasses, needles, leaves, and twigs), that fuels a wildland fire through various methods and measures (this vegetation is often referred to as hazardous fuels).
HFRA defined hazardous fuel reduction projects (HFRA projects) as methods and measures for reducing hazardous fuels, including prescribed fire, wildland fire use, and various mechanical (e.g., pruning or thinning, which is the removal of small-diameter trees) or other methods.49 HFRA has been amended several times, in many cases defining a certain activity as an HFRA project. For example, the definition of an HFRA project was expanded in 2018 to include the installation of fuel breaks (e.g., measures that change fuel characteristics in an attempt to modify the potential behavior of future wildfires) and fire breaks (e.g., natural or constructed barriers to stop, or establish an area to work to stop, the spread of a wildfire).50 More recently, the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA) specified that certain forest management activities implemented using IIJA funds are to be considered HFRA projects.51
HFRA projects can be developed and implemented using a potentially expedited planning and review process, in specified areas. This includes HFRA projects conducted in the wildland-urban interface (WUI).52 HFRA projects also may be conducted on specified areas within a municipal
47 36 C.F.R. §220.6. 48 U.S. Congress, Senate Committee on Agriculture, Nutrition, and Forestry, Healthy Forests Restoration Act of 2003, report to accompany H.R. 1904, 108th Cong., 1st sess., 2003, S.Rept. 108-121; and U.S. Congress, House Committee on the Judiciary, Healthy Forests Restoration Act of 2003, report to accompany H.R. 1904, 108th Cong., 1st sess., 2003, H.Rept. 108-96.
49 In 16 U.S.C. §6511(2), HFRA defines authorized hazardous fuel reduction projects by referencing the definition of appropriate tools in USDA and Department of the Interior, A Collaborative Approach for Reducing Wildland Fire Risks to Communities and the Environment: 10-Year Comprehensive Strategy Implementation Plan, May 2002, p. 18, at http://www.forestsandrangelands.gov/resources/plan/documents/11-23-en.pdf. HFRA further defines authorized hazardous fuels reduction projects and requirements in 65 U.S.C. §6512.
50 The Stephen Sepp Wildfire Suppression Funding and Forest Management Activities Act (P.L. 115-141, Division O, §203). Hereinafter referred to as the FY2018 omnibus.
51 The Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA; P.L. 117-58) specified in §40803(k) that mechanical thinning, timber harvesting, thinning, prescribed fire, and fuel break installation projects conducted using funds authorized and appropriated from IIJA shall be considered authorized hazardous fuels reduction projects pursuant to HFRA (16 U.S.C. §6592k). Some may refer to IIJA as the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, or BIL.
52 HFRA defines the wildland urban interface (WUI) in 16 U.S.C. §6511(16) as an area within or adjacent to an at-risk community (as defined in 16 U.S.C. §6511(1)) with a community wildfire protection plan (CWPP), or an area within a (continued...)
Congressional Research Service
9
National Forest System Management: Overview and Issues for Congress
watershed and with moderate or significant departure from the historical fire regimes (see shaded text box); on wind-, ice-, insect-, or disease-damaged land, or land at risk of insect or disease damage; or on lands with threatened and endangered species habitat threatened by wildfire.53 HFRA explicitly excluded projects that would occur on designated wilderness areas, wilderness study areas, or areas that otherwise prohibit vegetation removal by an act of Congress or presidential proclamation.54
HFRA projects must be consistent with the land and resource management plan in place for the area. Certain covered projects—basically, any HFRA project except those in response to or anticipation of wind, ice, insect, or disease damage—must focus on thinning, prescribed fire, or removing small-diameter trees to modify fire behavior, while maximizing large or old-growth tree retention (if retention promotes fire resiliency).55 The HFRA authorities are available for projects covering up to a cumulative total of 20 million acres of federal land.56
Fire Regime Condition Class
Fire regime condition class is a classification that describes the relative change between the historical (prior to modern human intervention) frequency and intensity of fire patterns across a vegetated landscape and the current fire patterns. More specifically, •
fire regime describes fire’s relative frequency and severity in an ecosystem, and
•
condition class describes the degree of departure from reference historical conditions.
Fires in landscapes classified into Fire Regime 1 occur every 0-35 years, and the fires are of low to mixed severity. Fire Regime II also has a frequency of 0-35 years, but the fires are severe, resulting in stand replacement of over 75% of the dominant overstory vegetation. Fire Regime III has a frequency of fire that ranges from 35 to 200 years, and the fires are of low to mixed severity. Fire Regime IV also has a frequency ranging from 35 to 200 years, but the fires are severe. Fire Regime V has a frequency of more than 200 years and includes fires of any severity. With respect to departure from reference historical conditions, Condition Class 1 represents no or minimal departure;
Condition Class 2 represents a moderate departure and declining ecological integrity; Condition Class 3 describes a high departure and poor ecological integrity. For more information, see S. Barrett et al., Interagency Fire Regime Condition Class (FRCC) Guidebook Version 3.0, 2010, at http://www.landfire.gov/frcc/frcc_guidebooks.php. The Healthy Forest Restoration Act (HFRA) authorizes certain activities in areas classified as Condition Class 2 or 3 in Fire Regimes I, II, and III. HFRA’s definition of these terms (see 16 U.S.C. §6511) is largely consistent with the above descriptions, except that HFRA defines Fire Regime III as mixed severity fires with a return frequency of 35-100 years instead of 35-200 years. At the time of enactment, the return frequency for Fire Regime III was defined as 35-100+ years and the classification scale has been refined as data availability, data reliability, and modeling capacity have improved.
HFRA also directed FS to establish a specific administrative review process (sometimes referred to as a pre-decisional objection process) and set forth requirements for judicial review for HFRA projects.57 Congress later directed FS to apply the administrative review procedures for HFRA
specified distance to an at-risk community without a CWPP and with specified characteristics (e.g., steep slopes). In other sources, the WUI is more generally defined as the area where structures and other human development meet or intermingle with undeveloped wildland vegetation. For more information on the WUI, see FS, The 2010 Wildland-Urban Interface of the Conterminous United States, 2015, at https://www.fs.usda.gov/research/treesearch/48642; V. C. Radeloff et al., “The Wildland-Urban Interface in the United States,” Ecological Applications, vol. 15, no. 3 (2005), pp. 799-805; 66 Federal Register 751-777; and CRS Report RS21880, Wildfire Protection in the Wildland-Urban Interface.
53 16 U.S.C. §6512(a). 54 16 U.S.C. §6512(d). 55 16 U.S.C. §6512(e)(1)(B). 56 16 U.S.C. §6512(c). 57 FS’s procedures for administrative review of HFRA projects are promulgated at 36 C.F.R. §218 Subpart C and for judicial review are at 36 C.F.R. §218.14.
Congressional Research Service
10
National Forest System Management: Overview and Issues for Congress
projects to non-HFRA projects.58 As a result, all FS projects fall under the same pre-decisional objection process, although there are some differences between HFRA and non-HFRA projects. For example, the Chief of the Forest Service may declare a non-HFRA project an emergency situation and proceed directly to implementation after the publication of the decision document.
HFRA’s planning procedures have been amended several times since enactment. For example, IIJA authorized the Secretary of Agriculture to issue an Emergency Situation Determination for NFS lands and to take specified emergency actions to mitigate and provide relief from threats to natural resources and human health and safety.59 The authorized emergency actions include timber salvage harvests, removal of hazard trees, hazardous fuel reduction projects, and reforestation activities, among others. IIJA also established procedures related to the planning and implementation of those actions, including limiting environmental reviews to the action and no-action alternatives for activities planned using an EA or EIS. Secretary of Agriculture Tom Vilsack invoked this authority in January 2023.60
HFRA Insect and Disease Designation Areas
The Agricultural Act of 2014 (the 2014 farm bill) added Section 602 to HFRA and authorized the establishment of landscape-scale insect and disease treatment areas within the NFS, by state, as requested by the state governor and then designated by the Chief of the Forest Service.61 To be eligible for this insect and disease treatment area designation, the NFS area must be experiencing declining forest health based on annual forest health surveys, at risk of experiencing substantial tree mortality over the next 15 years, or in an area in which hazard trees pose an imminent risk to public safety. In total, FS has designated approximately 75 million acres nationwide.62 (Hereinafter this report refers to these designated areas as I&D areas.)
Congress further authorized FS to prioritize projects in the designated I&D areas and plan and implement those projects through a potentially expedited process. In some states, all eligible lands were designated. In those states, the expedited project planning procedures are thus broadly available, but any prioritization benefit is effectively nullified.
58 Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2012, P.L. 112-74 §428. 59 IIJA §40807(a)-(f), 16 U.S.C. §6592c. The authority to issue an Emergency Situation Determination was previously established (see 36 C.F.R. §218.21). IIJA expanded the authority in part by defining specific authorized emergency actions.
60 FS, “Using Emergency Authorities to Support the Wildfire Crisis Strategy,” press release, February 10, 2023, at https://www.fs.usda.gov/inside-fs/leadership/using-emergency-authorities-support-wildfire-crisis-strategy and FS, Summary of Inflation Reduction Act provisions and Authorized Emergency Actions, Briefing Paper, January 2023.
61 Agricultural Act of 2014 (the 2014 farm bill), P.L. 113-79 §8204, 16 U.S.C. §6591a. Some may refer to this as the HFRA Section 602 Authority. The term “landscape-scale” is not specifically defined, but the law references subwatersheds as an example, and further defines subwatersheds as the sixth-level of the System of Hydrologic Unit Codes of the United States Geological Survey.
62 The 2014 farm bill required FS to make the initial designations within 60 days of enactment (April 8, 2014) and authorized FS to designate additional areas as needed. FS evaluated state requests against eligibility criteria and generally designated areas that met at least one of the criteria. The 75.3 million acres of designated areas include state requests and additional designations made as of April 2023 (From FS, Report to Congress on Section 8204 of the Agricultural Act of 2014, provided to CRS from FS legislative affairs on April 21, 2023). For more information, including state designation maps, see the Forest Service web page on Insect and Disease Area Designations at http://www.fs.usda.gov/managing-land/farm-nill/area-designations.
Congressional Research Service
11
National Forest System Management: Overview and Issues for Congress
NEPA Categorical Exclusions Established in HFRA
Several amendments have expanded HFRA’s project planning authorities. In particular, several laws have amended HFRA to establish statutory CEs for certain projects. Selected examples include the following:63
• Insect and Disease CE (this may also be referred to as the Section 603 CE or the
Farm Bill CE):64 This CE can be used for certain hazardous fuel reduction projects or projects that are intended to reduce the risk or extent of insect or disease infestations. Projects must be located in I&D areas within the WUI or outside of the WUI in specified areas.65 The authority to initiate projects using this CE is set to expire at the end of FY2023.66
• Wildfire Resilience CE (this may also be referred to as the Section 605 CE):67
This CE can be used for certain hazardous fuel reduction projects located in I&D areas within the WUI or outside of the WUI in specified areas.68 This CE is similar to the Insect and Disease CE, except the Wildfire Resilience CE directs FS to prioritize projects located within the WUI and limits projects outside of the WUI to areas that contain very high wildfire hazard potential.69
• Greater Sage-Grouse and Mule Deer Habitat CE:70 This CE can be used for
vegetation management projects that protect, restore, or improve habitat for the greater sage-grouse and/or mule deer in designated I&D areas within a sagebrush steppe ecosystem.
• Fuel Breaks CE:71 This CE is for forest management projects with a primary
purpose of establishing or maintaining linear fuel breaks up to 1,000 feet in width contiguous with or incorporating existing linear features, such as roads, water infrastructure, transmission and distribution lines, and pipelines on federal land.
These CEs contain other similar statutory requirements. For example, projects using the CE generally have project size limitations (ranging from 3,000-4,500 acres), road construction
63 For more information on FS’s CEs, see FSH 1909.15-30 (2023). 64 The 2014 farm bill (P.L. 113-79 §8204) added a new section 603 to HFRA and established the Insect and Disease CE; the 2018 farm bill (P.L. 115-334 §8407b) amended the CE to include hazardous fuel reduction projects, 16 U.S.C. §6591b.
65 The Insect and Disease CE may apply to projects outside the WUI but in fire regime groups I, II, or III and condition classes 2 or 3.
66 16 U.S.C. §6591a(d)(2). 67 The FY2018 omnibus (P.L. 115-141, Division O, §202) added a new Section 605 to HFRA and established the Wildfire Resilience CE, 16 U.S.C. §6591d.
68 The Wildfire Resilience CE may apply to projects outside the WUI but in fire regime groups I, II, or III and condition classes 2 or 3 that contain very high wildfire hazard potential.
69 Wildfire Hazard Potential (WHP) is an index that reflects the relative potential for a wildfire to occur that would then be difficult to suppress or contain. WHP was originally developed by Dillon, G.K.; J. Menakis; and F. Fay, 2015, “Wildland Fire Potential: A Tool for Assessing Wildfire Risk and Fuels Management Needs,” pp 60-76, In Keane, R. E.; Jolly, M.; Parsons, R.; and Riley, K. Proceedings of the large wildland fires conference; May 19-23, 2014; Missoula, MT. Proc. RMRS-P-73. Fort Collins, CO: USDA, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, at http://firelab.org/project/wildfire-hazard-potential. The FY2018 omnibus directed FS to scale the WHP for community use; see http://www.wildfirerisk.org.
70 The 2018 farm bill (P.L. 115-334 §8611) added a new Section 606 to HFRA and established the Sage-Grouse/Mule Deer CE, 16 U.S.C. §6591e.
71 IIJA (P.L. 117-58, §40806) established the Fuel Breaks CE. The legislation did not directly amend HFRA but was codified under HFRA at 16 U.S.C. §6592b(b).
Congressional Research Service
12
National Forest System Management: Overview and Issues for Congress
requirements (generally prohibiting construction of new permanent roads and specifying decommissioning of temporary roads within a specified time frame), and geographic constraints (e.g., prohibited from occurring in designated wilderness areas). The planning process for projects using the CEs must consider best available science, maximize the retention of old-growth and large trees, and be developed through a collaborative process. In addition, projects using the CEs must be consistent with the underlying forest plan.
In addition to these HFRA CEs, FS has other statutory CEs. Some pertain to specific activities, such as issuing certain types of oil and gas leases, grazing permits, or special use authorizations.72 Other laws have established statutory CEs for specific geographic areas. For example, there are two statutory CEs pertaining to activities located within the Lake Tahoe Basin area.73
Notwithstanding the establishment of these statutory CEs, FS’s administrative CEs remain viable options for FS planning and decisionmaking.74
National Forest System Uses As noted above, NFS lands are administered for sustained yields of multiple uses, including fish and wildlife purposes; outdoor recreation; mineral and energy development; range (livestock grazing); timber production; watershed protection; and for natural, scenic, scientific, and historical values, including wilderness preservation.75 Congress did not specify that FS should prioritize one use over any other use; reportedly, Congress specifically listed the uses in alphabetical order to avoid conferring any implied prioritization for management of the NFS.76 The various uses of NFS lands are to be balanced in the “combination that will best meet the needs of the American people” with the “harmonious and coordinated management of the various resources, each with the other ... in perpetuity of a high-level annual or regular periodic output ... without impairment of the productivity of the land.”77 These uses are discussed in more detail in the following sections.
Although revenue generation is not a stated statutory purpose of the NFS, FS is authorized to charge fees for many of the uses and services it provides. This revenue may be used to offset agency costs for specific activities, shared with the communities containing the NFS land, or
72 For more information, see FSH 1909.15-30 (2023), pp. 19-27, 30-31. 73 The Lake Tahoe Basin Hazardous Fuels Reduction Project CE was established by the FY2009 Omnibus Appropriations Act (P.L. 111-8), see FSH 1909.15-30 (2023), p.27. The Lake Tahoe Basin Forest Management Activities CE was established by the Water Infrastructure Improvements for the Nation Act (WIIN, P.L. 114-322), see FSH 1909.15-30 (2023), p.31.
74 Administrative CEs refer to the category of actions FS has previously identified as not having an individual or cumulative effect on the environment as listed in FSH 1909.15_30 (2023).
75 The management mission for the national forests was established pursuant to the Multiple-Use Sustained Yield Act of 1960 (MUSY; Act of June 12, 1960; P.L. 86-517, 16 U.S.C. §§528-531). Other laws govern the management of some other NFS units. The uses specified for the NFS in MUSY (16 U.S.C. §528) did not specifically include energy and mineral or natural scenic, scientific, or historical values, though other statutes authorized those uses for the NFS. For example, The Wilderness Act of 1964, P.L. 88-577, §4; 16 U.S.C. §529, added wilderness preservation as a use for designated areas within the NFS.
76 MUSY listed the multiple uses as “outdoor recreation, range, timber, watershed, and wildlife and fish purposes” (16 U.S.C. §528,). Con H. Schallau and Richard M. Alston, “The Commitment to Community Stability: A Policy or Shibboleth?,” Environmental Law, vol. 17, no. 3 (1987), p. 469, at https://www.jstor.org/stable/43265802. 77 16 U.S.C. §531.
Congressional Research Service
13
link to page 18 National Forest System Management: Overview and Issues for Congress
deposited into the General Treasury, depending on the use, location, and varying statutory requirements.78 See the text box below for further background on NFS revenue considerations.
In FY2022, FS generated a total of $280.0 million.79 Over the past 10 years, FS revenue has ranged from a low of $220.2 million in FY2020 to a high of $293.9 million in FY2021. Table 2 lists the revenue generated by type for the previous five years (FY2018-FY2022). The single largest source of revenue for FS over FY2018-FY2022 was the sale of timber. The next largest source of revenue was recreation, followed by fees associated with the use or occupancy of NFS lands.
Table 2. FS Revenue, FY2018-FY2022
(nominal dollars in millions)
FY2018
FY2019
FY2020
FY2021
FY2022
Timber
160.2
147.5
124.1
138.7
123.4
Recreation
84.7
90.3
55.3
110.7
106.2
Land Use
32.4
31.3
34.6
38.4
44.3
Grazing
5.8
5.4
5.6
5.1
5.3
Minerals
0.3
1.0
0.6
1.0
0.9
Total
$283.4
$275.5
$220.2
$293.9
$280.0
Source: U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, All Service Receipts (ASR), Final Receipts Summary Report (ASR-04), at https://www.fs.usda.gov/main/pts/securepayments/projectedpayments. Notes: Data are provided in nominal dol ars and totals may not add due to rounding. Timber revenue is amounts col ected under several different authorities for the sale of timber and certain other forest products and also reflects deposits or credits to several different special funds or accounts. Recreation revenue is amounts col ected for all types of recreation, including user fees col ected under the Federal Lands Recreation Enhancement Act (P.L. 108-447, as amended). Land use revenue is amounts col ected for the use or occupancy of NFS lands, such as for communication or energy transmission lines, but excludes col ections associated with minerals or recreational uses. Grazing revenue is amounts col ected for grazing fees in the NFS, with both the eastern and western grazing fees combined. Minerals revenue is amounts col ected from the sale of minerals (including quartz crystals) and permit fees. It includes mineral lease and permit fees col ected by DOI on acquired lands having
NFS status but does not include any mineral revenue derived from NFS land that was established from the public domain.
National Forest System Management: Financial Considerations
Management decisions for national forests are not based on financial optimization for the federal government. In the 1960s, Congress debated adding profitability as a goal for national forest management but ultimately defined multiple use to mean considering “the relative values of the various resources, [but] not necessarily the combination of uses that wil give the greatest dol ar return or the greatest unit output” (16 U.S.C. §531(a)). Although the Forest Service (FS) considers management costs and efficiencies during the development of forest plans and projects, it considers these financial factors relative to other ecological and social factors. More specifically, FS regulations stipulate that forest plans “guide management of [National Forest System] lands so that they are ecologically sustainable and contribute to social and economic sustainability . . and have the capacity to provide people and communities . . a range of social, economic, and ecological benefits for the present and into the future” (36 C.F.R. §217.1(c)). Policies that contribute to economic stability or provide economic benefits to communities surrounding the national forests may not be financial optimal for the federal government. At various times, goals of contributing to community stability or otherwise supporting timber-dependent communities have shaped FS policies and
78 For information on the requirements to share certain revenues with the states and counties containing NFS lands, see CRS Report R41303, The Secure Rural Schools and Community Self-Determination Act: Background and Issues.
79 FS, All Service Receipts: Receipts Summary Report, FY2022, ASR-04.
Congressional Research Service
14
National Forest System Management: Overview and Issues for Congress
decisions. At times, these considerations have led FS to make decisions that would not be financially optimal for the federal government, such as below-cost timber sales. This decisionmaking model can appear inefficient in comparison to the models of some private actors, especial y those that manage their lands to optimize timber production or financial returns. Sources: Con H. Schallau and Richard M. Alston, “The Commitment to Community Stability: A Policy or Shibboleth?,” Environmental Law, vol. 17, no. 3 (1987), pp. 429-481, at https://www.jstor.org/stable/43265802; David Wear, “Chapter 12: Public Timber Supply Under Multiple-Use Management,” in Forests in a Market Economy, eds. Erin Sil s and Karen Abt (Boston: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2003), pp. 203-220; Robert W. Wolf, “National Forest Timber Sales and the Legacy of Gifford Pinchot: Managing a Forest and Making it Pay,” University of Colorado Law Review, vol. 60, no. 4 (1989), pp. 1063-1064.
Fish and Wildlife Habitat The NFS contains important fish and wildlife habitats as well as botanically significant resources, which contribute ecological, recreational, economic, and cultural benefits to the nation. These resources include fishable streams, lakes, wetlands, and wildlife—such as elk, bighorn sheep, and wild turkey—which are enjoyed by a variety of recreational users. The NFS provides habitat for commercial species (e.g., salmon) and opportunities for subsistence uses. In addition, the NFS contains over 400 species of plants and animals listed as threatened or endangered and 3,500 that have been designated as sensitive and require special management.
Outdoor Recreation Recreational activities on NFS lands include camping, fishing, hiking, horseback riding, hunting, skiing, snowboarding, wildlife viewing, and more.80 Private companies also provide additional recreational opportunities on the NFS through recreation special use authorizations for downhill ski resorts, campgrounds, resorts, marinas, recreational events, outfitters, and guides. FS reports more than 156 million annual recreational visits to the NFS in FY2021.81
Some recreation uses, such as the use of off-highway vehicles and snowmobiles in the NFS, have generated controversy.82 FS travel management regulations established a planning process for each NFS unit and designated which roads and trails were available for motorized use.83 These motor vehicle use maps are generally updated annually.84
Recreation on NFS lands also generates significant revenue for FS. In FY2022, recreation receipts totaled $106.2 million (38% of the total revenue generated).85 In 2004, the Federal Lands Recreation Enhancement Act established a recreation fee program for FS (and the other federal land management agencies).86 The program was set to expire in FY2014 but has been reauthorized several times, and was most recently extended through the end of FY2024.87 The act authorizes different kinds of fees, outlines criteria for establishing fees, prohibits certain fees, and
80 FS, FY2020 Budget Justification, p. 58, at https://www.fs.usda.gov/about-agency/budget-performance. 81 FS, FY2024 Budget Justification, p. 30a-90. 82 See CRS Report R42920, Motorized Recreation on Bureau of Land Management and Forest Service Lands. 83 70 Federal Register 68264, November 9, 2005, and 73 Federal Register 74689, December 9, 2008. The regulations are available at 36 C.F.R. Part 212. For more information, see https://www.fs.usda.gov/recreation/programs/ohv/.
84 A motor vehicle use map is generally available in the “maps and publications” section of the website for each NFS unit.
85 FS, All Service Receipts: Receipts Summary Report, FY2022, ASR-04. 86 P.L. 108-447. 87 P.L. 117-328, Division G, Title IV, §421 extended the program to October 1, 2024.
Congressional Research Service
15
link to page 24 National Forest System Management: Overview and Issues for Congress
allows FS to use collections without further appropriation. While Congress sought to make the actual users pay fees, some users object, arguing that the fees amount to paying twice (once through taxation) to support the agency. Congress may consider allowing the recreation fee program to sunset or may consider extending the program again, with or without modifications.88
Mineral and Energy Development Much of the NFS is open to mineral and energy resource exploration and development. Oil, natural gas, and coal exploration and production is governed by the Mineral Leasing Act of 1920, which also requires the Bureau of Land Management (BLM) to manage the subsurface rights to virtually all federal lands, including NFS lands.89 Development of other minerals from FS lands, such as hardrock minerals (e.g., gold, silver, copper) and other salable minerals (e.g., sand, gravel, clay) are governed by the General Mining Law of 1872 and the Materials Act of 1947, respectively.90 FS reports approximately 4.2 million acres underlying NFS lands were leased for oil, gas, coal, and other mineral operations in 2022.91 NFS lands contain an estimated 4,000 federal oil and gas wells and approximately 75,000 mining claims. Receipts and royalties generated for energy and mineral activities are collected by the Office of Natural Resources Revenue in the Department of the Interior and are distributed for a variety of purposes.92
Renewable energy projects—such as solar and wind projects—are also allowed on NFS lands, generally through a special use authorization (SUA, discussed in the “Other Uses” section). FS approved a utility-scale wind power facility SUA in 2012, which began operation in 2017.93
Range and Grazing Management Range management includes the use of NFS rangelands for livestock grazing as well as for the management of wild horses and burros, which are protected under the Wild Free-Roaming Horses and Burros Act of 1971.94 Management of wild horses and burros on NFS (and BLM) lands has generated controversy, and issues for Congress have included concerns regarding management of their population, among others. FS estimates there were approximately 8,900 wild horses and 1,200 burros on NFS lands in 2022, approximately four times the appropriate management level.95
88 For further information on the Federal Lands Recreation Enhancement Act, see CRS In Focus IF10151, Federal Lands Recreation Enhancement Act: Overview and Issues and CRS Report RL33730, Recreation Fees Under the Federal Lands Recreation Enhancement Act.
89 30 U.S.C. §§181 et seq. CRS Report R46278, Policy Topics and Background Related to Mining on Federal Lands. 90 General Mining Law of 1872 (17 Stat. 91); Materials Act of 1947: P.L. 80-281. 91 FS, FY2024 Budget Justification, p. 30a-95. 92 For more information, see CRS Report R46537, Revenues and Disbursements from Oil and Natural Gas Production on Federal Lands.
93 See, for example, “Deerfield Wind Begins Operation,” Vermont Business Magazine, December 2017, at https://vermontbiz.com/news/2017/december/29/deerfield-wind-begins-operation.
94 16 U.S.C. §§1331 et seq. For more information on wild horses and burros, see CRS In Focus IF11060, Wild Horse and Burro Management: Overview of Costs.
95 These estimates are taken from “USDA Forest Service Wild Horse and Burro Program,” at https://www.blm.gov/sites/default/files/docs/2022-09/USFS%20Update.pdf. This document is posted on the BLM website for the National Wild Horse and Burro Advisory Board, under “Materials from Past Advisory Board Meetings, USDA Forest Service Update.”
Congressional Research Service
16
link to page 22 National Forest System Management: Overview and Issues for Congress
In FY2022, approximately 74 million acres of the NFS were under permit for livestock grazing in FY2022.96 Permits generally cover a 10-year period and may be renewed automatically while the agency processes a backlog of grazing allotments and permits needing evaluation.97 Fees for grazing on federal lands—FS and BLM—are generally charged under a formula established by law in 1978.98 For 2023, the federal grazing fee is $1.35 per head month, the minimum fee allowed under the law.99
Timber100 One of the first uses of the early forest reserves was to “furnish a continuous supply of timber.”101 The first chief of FS, Gifford Pinchot, initially believed the agency could eventually become self-supporting through the production of timber, although he eventually abandoned the idea.102 FS timber sales and revenue generation were negligible until the 1950s, when the post-World War II housing boom, combined with declining competition from private timber sales, led to increasing NFS timber sales (see Figure 2). For many years after, FS was a major provider of timber for the wood products industry, generally selling between 10 billion and 12 billion board feet of timber annually.103 Since the 1990s, FS timber production has decreased to levels similar to the era before the 1950s.104 The decline is attributable to a multitude of factors, including (but not limited to) changing legislative directives and related forest management policies and practices—such as increased planning and procedural requirements—as well as changing market dynamics for wood products, public preferences, and litigation.
For the last 15 years, timber harvest volume has remained relatively constant between 2.0 and 3.0 billion board feet harvested annually, with a value between approximately $100 and $250 million. In FY2022, approximately 2.6 billion board feet were harvested from FS lands, at a value of approximately $142.2 million.105
96 FS, FY2024 Budget Justification, p. 30a-91. 97 In FY2022, FS reports a backlog of 12% of active grazing permits require evaluation for renewal (FS, FY2024 Budget Justification, p. 30a-91). The authority to automatically renew leases was granted in P.L. 108-108, §325 and has been extended in annual appropriations law. See, for example, P.L. 117-328, Division G, §415.
98 Public Rangelands Improvement Act of 1978, P.L. 95-514, 43 U.S.C. §§1901, 1905. The formula has been continued indefinitely through an executive order issued by President Reagan in 1986 (Executive Order 12548, 51 Federal Register 5985, February 19, 1986).
99 The 2023 grazing fee is in effect from March 1, 2023, through February 29, 2024. This is the same fee as charged by the agencies for 2022 (in effect through February 28, 2023). Head month is defined as one month’s use and occupancy of the range by one animal, except for sheep and goats (36 C.F.R. §222.50). For more information on fees, see CRS Report RS21232, Grazing Fees: Overview and Issues.
100 For more information on timber harvesting on federal lands, see CRS Report R45688, Timber Harvesting on Federal Lands.
101 Organic Administration Act, Act of June 4, 1897, 16 U.S.C. §473. 102 Harold K. Steen, The U.S. Forest Service: A History (University of Washington Press, 1976), p. 91. 103 A board foot is a volume measurement, representing a unit of wood measuring 12 inches by 12 inches by 1 inch. Harvest volume is also sometimes reported as cubic feet. During the period when FS was harvesting 10 billion to 12 billion board feet annually, the revenue was less than the total cost of NFS management.
104 The decrease in timber production, and revenue generation, also led to a decrease in the revenue-sharing payments made to counties containing NFS land. Congress enacted an alternative payment system in response. For more information, see CRS Report R41303, The Secure Rural Schools and Community Self-Determination Act: Background and Issues.
105 Data reflect the cut volume and value (FS, Forest Cut and Sold Reports, at https://www.fs.usda.gov/forestmanagement/products/cut-sold/index.shtml). Cut value refers to the appraised value of the timber after it is (continued...)
Congressional Research Service
17
National Forest System Management: Overview and Issues for Congress
Figure 2. FS Harvest Volume and Value, FY1940-FY2022
Source: CRS. FY1977-FY2022 data: Forest Service, Forest Products Cut and Sold Reports, at https://www.fs.usda.gov/forestmanagement/products/cut-sold/index.shtml. FY1940-FY1976 data: Forest Service Legislative Affairs Office. Notes: MMBF stands for mil ion board feet. 1,000 mil ion board feet equals 1 bil ion board feet. A board foot is a unit of wood measuring 12 inches by 12 inches by 1 inch. Cut value has been converted to FY2022 dol ars using Bureau of Labor Statistics Historical Consumer Price Index, All Urban Customers, fiscal year averages.
FS may harvest timber for a number of reasons, including as a tool to achieve various land and resource management objectives (i.e., hazardous fuels reduction, watershed management, and many others), commercial timber production, or a combination of objectives. Some special timber harvest authorities address NFS timber harvesting under specified circumstances related to forest restoration. For example, FS may combine contracts for restoration activities with timber harvesting to offset some of the restoration costs (stewardship contracting) or may authorize states, counties, and federally recognized Indian tribes to sell NFS timber as part of forest restoration projects (the Good Neighbor authority).106 FS also may harvest trees damaged or killed in fires or other disturbance events, called salvage harvesting. Salvage harvesting may capture some of the economic value of the federal resources and generate revenue to fund other restoration activities, and in some cases may facilitate forest restoration and recovery.
Watersheds Protecting watershed health was one of the original purposes of the national forests. This includes the management of surface water and groundwater resources as well as water uses and rights on NFS lands. Nearly one-fifth of the nation’s water originates on NFS lands.107 In addition, watersheds support ecological services such as productive soils, biological diversity, and fish and wildlife habitat, including spawning and rearing habitat for sport and commercial fish species. Watersheds also provide flood control benefits.
harvested. The cut value reported in any given fiscal year may not be reflected in the collection of timber revenue for that same fiscal year for various reasons (e.g., because revenue may be collected at various times throughout a timber sale contract, which may be executed over several years).
106 For more information, see CRS In Focus IF11179, Stewardship End Result Contracting: Forest Service and Bureau of Land Management, by Anne A. Riddle and CRS In Focus IF11658, The Good Neighbor Authority on Federal Lands.
107 FS, “Watershed,” at http://www.fs.usda.gov/naturalresources/watershed/index.shtml.
Congressional Research Service
18
National Forest System Management: Overview and Issues for Congress
FS established the Watershed Condition Framework (WCF) in 2011 to assess, classify, and prioritize the conditions of the watersheds containing significant portions of NFS lands. The 115th Congress codified the WCF program in statute.108 The initial assessment—completed in FY2011—classified conditions on approximately 15,000 watersheds based on 12 biophysical and ecological indicators indicating the degree of watershed functionality or integrity.109 Watersheds that were in good condition were classified as functioning (52% in the initial 2011 assessment), watersheds in fair condition were classified as functioning at risk (43%), and watersheds in poor condition were classified as having impaired function (3%).110 FS reports that, in FY2022, 54% of the watersheds were in functioning condition, 44% were functioning at risk, and 3% had impaired function.111 FS reports that, in FY2021, FS completed work across 287,600 acres in 10 priority watersheds and restored more than 21,000 acres of lakes and 2,390 miles of stream habitat.112
In FY2012, FS began developing watershed restoration action plans to identify projects and activities to improve the condition of priority watersheds. Watershed restoration activities may include a range of forestry or land management practices, such as decommissioning roads, reforestation, or restoring or enhancing stream habitat, among others. Under the WCF, FS is expected to actively monitor and track progress on watershed condition improvements.
Wilderness and Other Special Land Designations Congress has also provided management direction within the NFS by creating special designations for certain areas. Some of these designations—wilderness areas, wild and scenic rivers, and national trails—are part of larger management systems affecting several federal land management agencies.113
The NFS also includes several other types of land designations. The NFS contains many national game refuges and wildlife preserves, national recreation areas and scenic areas, national monuments, and other congressionally designated areas.114 Resource development and use is generally more restricted in these specially designated areas than on general NFS lands, and specific guidance is typically provided with each designation.
Questions persist over the extent to which FS should protect the approximately 58.2 million acres of FS inventoried roadless areas (IRAs): areas where roads and timber harvesting are restricted
108 P.L. 115-334, Title VIII, §8405. The 115th Congress also established a water source protection program (§8404). For more information on these changes, see CRS Report R45696, Forest Management Provisions Enacted in the 115th Congress, pp. 30-31.
109 For more information on the classification process, see FS, Watershed Condition Classification Technical Guide, FS-978, 2011, at https://www.fs.usda.gov/naturalresources/watershed/condition_framework.shtml.
110 Figures as reported do not add to 100%. FS, FY2015 Budget Justification, p. 5-9, at https://www.fs.usda.gov/about-agency/budget-performance. FS may also reports these categories as condition class I (functioning), condition class II (functioning at risk), and condition class III (impaired function). For more information on the watershed condition framework, see Forest Service, Watershed Condition Framework, FS-977, 2011, at https://www.fs.usda.gov/sites/default/files/Watershed_Condition_Framework.pdf.
111 Figures do not add to 100% due to rounding. Data provided by FS on March 31, 2023. 112 FS, FY2023 Budget Justification, p. 85, at https://www.fs.usda.gov/about-agency/budget-performance. 113 For more information on wilderness, see CRS Report RL31447, Wilderness: Overview, Management, and Statistics and CRS Report R41610, Wilderness: Issues and Legislation. For more information on wild and scenic rivers, see CRS Report R45890, Wild and Scenic Rivers: Designation, Management, and Funding and CRS Report R42614, The National Wild and Scenic Rivers System: A Brief Overview. For more information on national trails, see CRS Report R43868, The National Trails System: A Brief Overview. For more information on other federal land designations, see CRS Report R43429, Federal Lands and Related Resources: Overview and Selected Issues for the 118th Congress.
114 FS, Land Areas Report, 2018. For more information, see CRS Report R41285, Congressionally Designated Special Management Areas in the National Forest System.
Congressional Research Service
19
National Forest System Management: Overview and Issues for Congress
by certain FS regulations.115 Controversy over the designation and protection of such areas has resulted in multiple FS rulemakings on the topic, many of which were litigated, over more than two decades. The IRA designation originated in 2001 (2001 rule), through a rulemaking initiated by the Clinton Administration, although the George W. Bush Administration delayed implementation of the Clinton rule and issued an alternative policy. After both were litigated, the 2001 rule remained largely in place.116 In 2020, FS, under the Trump Administration, issued a rule exempting the Tongass National Forest in Alaska from the 2001 rule.117 In 2023, the Biden Administration rescinded the Trump Administration rule, restoring the applicability of the 2001 rule to the Tongass.118
Other Uses NFS lands are also used for other purposes and services supporting national policies and federal land laws. These uses or activities may be permitted on NFS lands under various authorities, collectively referred to as special use authorizations (SUAs), as noted earlier. SUAs allow uses of NFS lands for various purposes, ranging from commercial filming to ski resort operation, among others. For example, the Secretary of Agriculture is authorized to issue a type of SUA called rights-of-way (ROW) for the use and occupancy of NFS lands.119 The ROW allow for the specific use of NFS lands for: various types of water infrastructure; infrastructure for the storage, transportation, or distribution of liquids, gases (with specified exceptions), and solid materials; electricity generation, transmission, and distribution infrastructure; communications systems infrastructure; roads, trails, highways, canals, tunnels and other means of transportation in general; and other “necessary” systems and facilities which are in the public interest.120
Forest Health Conditions on the National Forest System Forest health generally refers to the ability of forest ecosystems to respond to disturbance events (e.g., wildfires, ice or wind storms, insect and disease infestations, timber harvests).121 Forest ecosystems have inherent characteristics that enhance their capability to survive such events (resistance) or facilitate recovery after disturbance (resilience). Some ecosystems are adapted to specific disturbances occurring at regular intervals (e.g., different fire regimes). For example, some forest ecosystems are adapted to relatively frequent (e.g., up to every 35 years) but low-intensity wildfires to burn surface fuels (e.g., needles, leaves), reduce competition, and return
115 For more information, see CRS Report R46504, Forest Service Inventoried Roadless Areas (IRAs). 116 During the period the 2001 rule was being litigated, FS issued state-specific rules for the states of Colorado and Idaho, which supersede the 2001 rule in those states.
117 Forest Service, “Special Areas; Roadless Area Conservation; National Forest System Lands in Alaska,” 85 Federal Register 68688, October 29, 2020. For more information, see CRS Report R46505, The Alaska Roadless Rule: Eliminating Inventoried Roadless Areas (IRAs) in the Tongass National Forest.
118 Forest Service, “Special Areas; Roadless Area Conservation; National Forest System Lands in Alaska,” 88 Federal Register 5252, January 27, 2023.
119 FLPMA (P.L. 94-579, Title V, 43 U.S.C. §§1761 et seq.) and the regulations are codified at 36 C.F.R. §251 Subpart B. For more information on FS ROWs and special use authorizations, see https://www.fs.usda.gov/specialuses/.
120 These purposes are summarized from 43 U.S.C. §1761(a). 121 Disturbance is defined as “any relatively discrete event in time that disrupts ecosystems, community, or population structure and changes resources, substrate availability, or the physical environment.” Steward T. A. Pickett and P. S. White, The Ecology of Natural Disturbance and Patch Dynamics (Orlando: Academic Press, 1985). Disturbance events may be unplanned (e.g., precipitation events) or planned (e.g., harvest, prescribed fire).
Congressional Research Service
20
National Forest System Management: Overview and Issues for Congress
nutrients to the soil, among other benefits. Other forest ecosystems are adapted to infrequent but high intensity wildfires.
Degraded forest ecosystems, however, may be more susceptible to mortality in response to disturbances or may take longer to recover. Different disturbances may also interact and exacerbate the effects of other events in a feedback loop. For example, a prolonged drought may impair a tree’s resistance to an insect or disease infestation, or may make a tree more susceptible to damage during a wildfire. In addition, some research indicates that climate variability is reshaping forest landscapes by altering the frequency, intensity, and timing of disturbance events in ways that may exceed the resistance and resilience capacity of many forests.122 Many are concerned that degraded forest ecological conditions in the NFS are increasing the risk of insect or disease infestation or uncharacteristic wildfires, among other forest health concerns.
Forest restoration projects generally aim to improve forest conditions, such as improving watershed functioning or otherwise facilitating ecological resilience and resistance. Other forest restoration activities also include post-disturbance reforestation (i.e., reestablishing forest cover).123 FS estimated around 1.5 million acres of NFS lands were in need of reforestation at the end of FY2020.124 Wildfires were the largest driver of this reforestation backlog (81%); timber harvests were the second-largest driver (10%).125
FS reports forest health conditions on the NFS using several interrelated metrics.126 For example, FS developed and uses the WCF to assess the agency’s status and progress toward improving watershed functionality or integrity across the NFS. FS increased the number of NFS watersheds functioning properly by 1% (180 watersheds) from FY2011 to FY2022, decreased the number of watersheds functioning at risk by 1% (161 watersheds), and decreased the number of impaired watersheds by less than <1% (18 watersheds).127 FS also reports the NFS acreage at risk for fire or insect, disease, or pest infestation. In 2023, FS published an inventory of old-growth and mature forests on NFS and BLM lands.128 The rest of this section discusses forest health issues and challenges, such as those related to implementing, reporting, and assessing forest restoration activities.
122 James M. Vose, David L. Peterson, and Toral Patel-Weynard, Effects of Climate Variability and Change on Forest Ecosystems: A Comprehensive Science Synthesis for the U.S., FS, PNW-GTR-870, 2012, at http://www.treesearch.fs.usda.gov/research/treesearch/42610.
123 The Repairing Existing Public Lands by Adding Necessary Trees (REPLANT) Act, enacted as IIJA, Division G, Title III, §§70301 et seq; 16 U.S.C. §1600 note, requires FS to conduct reforestation on NFS lands impacted by unplanned disturbance events (e.g., wildfire), directs FS to prioritize reforestation needs, and requires annual reports to Congress on reforestation needs and accomplishments.
124 FS, NFS Reforestation Strategy, FS-1198, July 2022, p. 30, at https://www.fs.usda.gov/managing-land/forest-management/vegetation-management/reforestation.
125 Other events such as windstorms, hurricanes, and insect and disease infestation contribute to 8% of the reforestation backlog. NFS Reforestation Strategy, p. 9.
126 Forest health is difficult to measure. See, for example, D. J. Rapport, R. Costanza, and A. J. McMichael, “Assessing Ecosystem Health,” Trends in Ecology and Evolution, vol. 13, no. 10 (October 1998), pp. 397-402.
127 Calculations done by CRS using: FY2011 data downloaded from FS’s Watershed Condition Framework website (at http://www.fs.usda.gov/naturalresources/watershed/condition_framework.shtml) and FY2022 data provided by FS legislative affairs on March 31, 2023.
128 Forest Service, Mature and Old-Growth Forests: Definition, Identification, and Initial Inventory on Lands Managed by the Forest Service and Bureau of Land Management, FS-1215a, April 2023. The report fulfills requirements established in a Biden administration executive order. Executive Office of the President, “Strengthening the Nation’s Forests, Communities, and Local Economies,” 87 Federal Register 24851, April 27, 2023.
Congressional Research Service
21
National Forest System Management: Overview and Issues for Congress
Forest Health: Federal vs. Nonfederal Forests
Forest health is often perceived by some as a larger problem for federal forests relative to other forests. Although this perception may be true—particularly across some measures, such as mortality or biomass density—it also may be an example of information availability bias: more information is available on forest health measures across federal forests due to greater levels of public access, availability for research, and scrutiny. Some studies have identified examples where forest health outcomes appear to be better on federal forests relative to private forests, however, or on public forests (federal, state, or local) relative to private forests. For example, watersheds with higher concentrations of federal compared to private forests had improved watershed conditions, and streams flowing through federal forests had higher water quality than streams flowing through nonfederal forests. Other studies have found that public forests tend to be more structurally complex than the more production-style forests on private lands; presumably, this complexity provides public forests with the interrelated benefits of biodiversity and resiliency. However, more research on the influence of ownership trends on various forest management objectives is needed to draw definitive conclusions. Sources: Kirsten Gallo et al., Northwest Forest Plan—the First 10 Years: Preliminary Assessment of the Condition of Watersheds, FS, PNW-GTR-647, 2005, at https://www.fs.fed.us/pnw/pubs/pnw_gtr647.pdf; Shannon Hubler, High Level Indicators of Oregon’s Forested Streams, Oregon Department of Environmental Quality, DEQ09-LAB-0041-TR, 2009, at https://www.oregon.gov/deq/FilterDocs/10-LAB-003.pdf; Vivian Griffey et al., “Ownership Patterns Drive Multi-Scale Forest Structure Patterns across a Forested Region in Southern Coastal Oregon, USA,” Forests, vol. 12, no. 1 (2021).
Hazardous Fuels and Forest Restoration In addition to general concerns about overall ecological conditions and fire, insect, and disease risk across the NFS, many have particular concerns regarding an accumulation of forest biomass resulting from a century of aggressive wildfire suppression and other land management practices. This biomass—dead and dying trees, heavy undergrowth, and dense stands of small trees—is often referred to as hazardous fuels. Hazardous fuels can significantly affect wildfire behavior, and contribute to wildfires becoming more intense, severe, and difficult to contain. Dense stands of trees may also facilitate the transmission of insect and disease infestations.
Projects that remove or modify these fuels are called treatments, and are intended to reduce the risk of catastrophic wildfire and facilitate post-fire recovery (see the HFRA section for more information on treatments and related authorities). Treatments include removing small-diameter trees (called thinning) or the deliberate use of fire in specific areas within prescribed conditions (called prescribed burning) to reduce fuel loads. Treatments may have broader forest restoration benefits as well.
For FY2022, FS reported about 63 million acres of NFS lands were at high or very high wildfire hazard potential—or, in other words, at high or very high risk for wildfires that would be difficult to contain.129 FS reported that hazardous fuels reduction projects, or treatments, were completed on 3.2 million acres of NFS lands in FY2022, a decrease relative to the 3.7 million acres treated in FY2021.130 At that pace, it would take nearly 20 years to eliminate the backlog of treatment needs, not accounting for maintaining treated areas to the desired resource conditions. In addition, some estimate that hazardous fuels are accumulating three times faster than the rate of treatment.131
129 FS, FY2024 Budget Justification, p. 30a-192. 130 FS, FY2024 Budget Justification, pp. 30a-155 and 30-232a. 131 USDA, Office of the Inspector General (OIG), FS Wildland Fire Activities - Hazardous Fuels Reduction, 08601-004-41, July 2016, hereinafter referred to as OIG, FS Hazardous Fuels.
Congressional Research Service
22
National Forest System Management: Overview and Issues for Congress
Mitigating Wildfire Risk
Wildfire is an ecological process, and wildfires wil occur in forests—and other vegetated landscapes—regardless of their ecological conditions. Some wildfires cannot be prevented or mitigated in certain ecosystems. For example, some ecosystems (e.g., lodgepole pines in the Rocky Mountain region) are adapted to high-severity, stand-replacing fires, and these fires are crucial to ecosystem functioning (e.g., the high temperatures from fires release the seeds to facilitate propagation). In forests adapted to low-severity fires, however, a high-severity fire could have damaging ecological impacts. Degraded forest ecosystems may contribute and benefit from fire, whereas some functioning ecosystems may be severely damaged by fires. Because of this, the overarching forest health concern related to wildfire is the extent to which the pattern of fire frequency and severity deviates from the historical fire regime. Therefore, a forest health objective of many forest managers and scientists is to reduce the risk of uncharacteristic fire rather than to reduce the risk of fire generally. Relatedly, another forest health objective is to facilitate the return of historic fire patterns specific to the forest type or, in some cases, to facilitate adaptation to a different fire regime based on changing climatic conditions. An interrelated objective is to reduce the potential for damaging impacts to the areas and communities surrounding forests when fires do occur.
FS Goals and Strategies for Forest Restoration
IIJA directed FS (and DOI) to conduct forest restoration treatments to improve the fire regime condition class on 10 million acres of federal and Indian land identified as having a very high wildfire hazard potential by September 30, 2027 (five years after enactment).132 In January 2022, Secretary Vilsack announced a 10-year strategy for wildfire risk mitigation (referred to as the Wildfire Crisis Strategy in this report).133 According to the strategy, FS intends to treat up to an additional 20 million acres of NFS lands over the 10-year period.134 Because the acreage goal is expressed as an “additional” amount, it is not clear if there is a more concrete acreage goal. At FS’s current pace of treatment (3.2 million acres treated in FY2022), FS could presumably complete treatments on 32 million acres over 10 years. In any case, it is not clear if achieving treatments on 20-30 million acres over the next 10 years would result in meaningful progress toward eliminating the backlog of 63 million acres of NFS lands in need of treatment.
As part of the Wildfire Crisis Strategy, FS intends to increase the scale, scope, and implementation of forest management projects generally, and forest restoration treatments specifically, in part by using HFRA planning authorities. For example, FS intends to use Secretary Vilsack’s Western Fireshed Emergency Action Determination to expedite project planning and environmental analysis across 28 million acres of high-risk and post-fire recovery areas in several western states.135 FS also identified the need for a “paradigm shift” in land management across FS and other partners to facilitate increasing and sustaining fuel treatment accomplishments.136
132 IIJA, §40803(b). 133 USDA, “Secretary Vilsack Announces New 10 Year Strategy to Confront the Wildfire Crisis,” press release, January 18, 2022, at https://www.fs.usda.gov/news/releases/secretary-vilsack-announces-new-10-year-strategy-confront-wildfire-crisis. See also FS, Wildfire Crisis Strategy, FS-1187a, January 2022. For more information, including links to the strategy documents and implementation plans and press announcements, see FS’s Confronting the Wildfire Crisis website at https://www.fs.usda.gov/managing-land/wildfire-crisis.
134 The Wildfire Crisis Strategy also identifies a goal of FS supporting treatment on up to an additional 30 million acres of non-NFS lands. FS, Wildfire Crisis Strategy, FS-1187a, January 2022 and FS, Wildfire Crisis Implementation Plan, FS-1187b, January 2022.
135 FS, “Using Emergency Authorities to Support the Wildfire Crisis Strategy,” press release, February 10, 2023, at https://www.fs.usda.gov/inside-fs/leadership/using-emergency-authorities-support-wildfire-crisis-strategy and FS, Summary of Inflation Reduction Act provisions and Authorized Emergency Actions, Briefing Paper, January 2023.
136 FS, Wildfire Crisis Strategy, FS-1187a, January 2022, p.4.
Congressional Research Service
23
National Forest System Management: Overview and Issues for Congress
The underlying goals and strategies for increasing project implementation are not necessarily new. For example, in 2018, FS outlined a “shared stewardship” approach to address land management concerns at a landscape-scale and across ownership boundaries.137 The Wildfire Crisis Strategy appears to build upon the shared stewardship approach by expanding the scale of existing agreements to “execute priority projects quickly and efficiently while we grow FS institutional capacity.”138
Issues Many forest health issues have been ongoing for decades. For example, concerns about deteriorating forest conditions and high fuel levels across all federal lands were raised after wildfires in Yellowstone National Park in 1988. In the 1990s, several reviews—including those by congressionally chartered commissions and the Government Accountability Office (GAO)—recommended that the federal land management agencies create long-term strategies for addressing forest health and reducing hazardous fuels. In the 2000s, GAO and the USDA Office of the Inspector General (OIG), among others, raised concerns with FS’s strategies for addressing forest health and implementation of the hazardous fuels reduction program. Some of these reports are listed below.
• In 1994, the congressionally chartered National Commission on Wildfire
Disasters recommended federal land management agencies invest more in reducing hazardous fuels in high-risk ecosystems and observed that “the question is no longer if policy-makers will face disastrous wildfires and their enormous costs, but when.”139
• In 1995, a FS study recommended the agency increase hazardous fuel treatments
to up to 3 million acres per year by 2005.140
• In 1999, GAO recommended FS develop a strategy to identify long-term options
for reducing fuels to address forest health issues and mitigate wildfire risk.141
• In 2002, GAO recommended FS—and the other land management agencies—
improve processes for identifying lands, resources, and communities at high wildfire risk.142
• In 2006, the USDA OIG raised concerns with FS’s hazardous fuels reduction
program and recommended FS develop guidance and controls to identify,
137 FS, Toward Shared Stewardship Across Landscapes: An Outcome-Based Investment Strategy, FS-118, 2018, at https://www.fs.usda.gov/sites/default/files/toward-shared-stewardship.pdf (hereinafter referred to as FS, Shared Stewardship). For more information, see FS’s Shared Stewardship website at https://www.fs.usda.gov/working-with-us/shared-stewardship.
138 FS, “Achieving Our Mission Through Keystone Agreements,” press release, March 27, 2023, at https://www.fs.usda.gov/inside-fs/leadership/achieving-our-mission-through-keystone-agreements.
139 The commission was established by the Wildfire Disaster Recovery Act of 1989 (P.L. 101-286) after the 1988 wildfires in Yellowstone. R. Neil Sampson, chair, Report of the National Commission on Wildfire Disasters, Washington, DC, 1994.
140 FS, Course to the Future: Positioning Fire and Aviation Management, May 1995. 141 U.S. Government Accountability Office (GAO), Western National Forests: A Cohesive Strategy is Needed to Address Catastrophic Wildfire Threats, RCED-99-65, April 2, 1999, at https://www.gao.gov/products/RCED-99-65.
142 GAO, Severe Wildland Fires: Leadership and Accountability Needed to Reduce Risks to Communities and Resources, GAO-02-259, January 31, 2002.
Congressional Research Service
24
National Forest System Management: Overview and Issues for Congress
prioritize, implement, monitor, and report on hazardous fuels reduction projects and funding.143
• A 2016 OIG report assessed FS’s progress toward implementing the
recommendations from that 2006 report and found continued issues with FS prioritizing, tracking, and reporting of hazardous fuels reduction projects.144
• A 2019 GAO report examined FS’s and DOI’s fuel reduction methods and
progress and identified several factors affecting agency efforts to implement fuel reduction projects, including the existing backlog of treatment needs.145
Concerns about NFS ecological health raise several issues about FS’s management. Two specific issues—FS reporting and the pace and scale of project implementation—are discussed in more depth below.
Pace and Scale of Project Implementation
Concerns about FS project implementation have been ongoing since at least 2001.146 FS and others identify administrative process barriers as one of many factors impeding progress toward their forest restoration goals.147 More specifically, some identify federal agency decisionmaking processes as preventing FS from implementing projects at their desired pace and scale, particularly related to NEPA compliance, public involvement, and administrative and judicial challenges to agency decisions.148 For some, these administrative process barriers include concerns about the time and costs associated with NEPA compliance, public involvement, and litigation. For others, the administrative process barriers include concerns about FS’s administrative capacities (e.g., funding, staffing, and training) for both completing NEPA requirements and for implementing projects.
Several studies have examined FS’s NEPA compliance, public involvement, and litigation rates, though many studies date back decades and may not represent current conditions.149 Examining
143 USDA Office of Inspector General (OIG), Implementation of the Healthy Forests Initiative, 08601-6-AT, September 2006.
144 OIG, FS Hazardous Fuels. 145 GAO, Wildland Fire: Federal Agencies’ Efforts to Reduce Wildland Fuels and Lower Risk to Communities and Ecosystems, GAO-20-52, December, 2019, at https://www.gao.gov/products/gao-20-52. Hereinafter referred to as GAO-20-52.
146 For example, in 2001 Congress asked GAO to evaluate the extent to which administrative or judicial challenges impeded FS’s implementation of fuel management projects. The 2003 report found that approximately 24% of the fuel reduction decisions signed in FY2001 and FY2002 were appealed (GAO, Forest Service: Information on Appeals and Litigation Involving Fuels Reduction Activities, GAO-04-52, October, 2003, at https://www.gao.gov/assets/250/240305.pdf). A later GAO analysis found that 20% of the fuel management projects identified for implementation in FY2006 through FY2008 were challenged through appeals or objections GAO, Forest Service: Information on Appeals, Objections, and Litigation Involving Fuel Reduction Activities, Fiscal Years 2006 through 2008, GAO-10-337, March 4, 2010, at https://www.gao.gov/products/GAO-10-337.
147 See, for example, House Committee on Natural Resources, Resilient Federal Forests Act of 2017, House Report, 115th Cong., 1st sess., October 25, 2017, H.Rept. 115-370 (hereinafter referred to as H.Rept. 115-370), FS, The Process Predicament: How Statutory, Regulatory, and Administrative Factors Affect National Forest Management, 2002, at https://www.fs.usda.gov/projects-policies/documents/Process-Predicament.pdf, and FS, “National Environmental Policy Act Compliance,” 84 Federal Register 114, June 13, 2019. 148rule for violating NEPA and ESA,24 and in 2009 the FS reverted to using 1982 procedures. The Obama Administration promulgated final planning regulations in 2012 (2012 planning rule).25 The 2012 planning rule establishes an adaptive, three-phase planning framework to emphasize ecological sustainability, landscape-scale restoration, and science-based decisions informed by public values. Plans are to also account for the potential impacts of climate change.
The FS has developed 130 plans to guide the management of 110 administrative units of the NFS (some plans cover multiple NFS units). FS reports that approximately 85 plans require revision (meaning they are older than 10 years (31) or 15 years (54)).26 Thirty plans are under revision in FY2019.27 Of those under revision, four are using the 1982 procedures to conduct the revisions; the others are using the procedures established in the 2012 planning rule.
National Forest System Uses
As noted above, NFS lands are administered for sustained yields of multiple uses, including fish and wildlife purposes, outdoor recreation, mineral and energy development, range (livestock grazing), timber, and watershed management. Wilderness was added as a use in 1964.28 The various uses of NFS lands are to be balanced in the "combination that will best meet the needs of the American people" with the "harmonious and coordinated management of the various resources, each with the other ... in perpetuity of a high-level annual or regular periodic output ... without impairment of the productivity of the land."29 These uses are discussed in more detail in the following sections.
Although revenue generation is not a stated statutory purpose of the NFS, FS is authorized to charge fees for many of the uses and services it provides. This revenue may be used to offset agency costs for specific activities, shared with the communities containing the NFS land, or deposited into the General Treasury, depending on the use, location, and varying statutory requirements.30 In FY2018, the FS generated a total of $283.4 million.31 Table 2 lists the revenue generated by type for FY2014-FY2018. The single largest source of revenue for the FS over FY2010-FY2014 was the sale of timber. The next largest source of revenue was recreation, followed by fees associated with the use or occupancy of NFS lands.
|
FY2014 |
FY2015 |
FY2016 |
FY2017 |
FY2018 |
|||||||||||
|
Timber |
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||
|
Recreation |
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||
|
Land Use |
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||
|
Grazing |
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||
|
Minerals |
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||
|
Total |
|
|
|
|
|
Source: U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, All Service Receipts (ASR), Final Receipts Summary Report (ASR-04), available from https://www.fs.usda.gov/main/pts/securepayments/projectedpayments.
Notes: Data are provided in nominal dollars. Timber revenue is amounts collected under several different authorities for the sale of timber and certain other forest products and also reflects deposits or credits to several different special funds or accounts. Recreation revenue is amounts collected for all types of recreation, including user fees collected under the Federal Lands Recreation Enhancement Act (P.L. 108-447, as amended). Land use revenue is amounts collected for the use or occupancy of NFS lands, such as for communication or energy transmission lines, but excludes collections associated with minerals or recreational uses. Grazing revenue is amounts collected for grazing fees in the NFS, with both the eastern and western grazing fees combined. Minerals revenue is amounts collected from the sale of minerals (including quartz crystals) and permit fees. It includes mineral lease and permit fees collected by DOI on acquired lands having NFS status but does not include any mineral revenue derived from NFS land that was established from the public domain.
Fish and Wildlife Habitat
The NFS contains important fish and wildlife habitats as well as botanically significant resources, which contribute ecological, recreational, economic, and cultural benefits to the nation. These resources include fishable streams, lakes, wetlands, and wildlife—such as elk, bighorn sheep, and wild turkey—which are enjoyed by a variety of recreational users. In addition, the NFS contains over 400 species of plants and animals listed as threatened or endangered and 3,500 that have been designated as sensitive and require special management.
Outdoor Recreation
FS reports that outdoor recreation is the "single greatest use of the national forests," with more than 150 million annual recreational visits. Recreational activities on NFS lands include camping, fishing, hiking, horseback riding, hunting, skiing, snowboarding, wildlife viewing, and more.32 Private companies also provide additional recreational opportunities on the NFS through recreation special use authorizations for downhill ski resorts, campgrounds, resorts, marinas, recreational events, outfitters, and guides.
Some recreation uses, such as the use of off-highway vehicles and snowmobiles in the NFS, have generated controversy.33 In 2004, the FS chief identified unmanaged recreation—"increasing use of the national forests for outdoor activities ... including the use of off-highway vehicles"—as one of the four major threats to the ecological integrity of NFS lands.34 FS published regulations in 2005 regarding the use of off-highway vehicles as part of an effort to address roads and trails management generally on NFS lands (known as travel management) and amended its internal policy in 2008.35 The agency conducted a travel management planning process for each NFS unit and designated which roads and trails were available for motorized use.36 These motor vehicle use maps are generally updated annually.37
Recreation on NFS lands also generates significant revenue for the FS. In FY2018, recreation receipts totaled $84.7 million (30% of the total revenue generated).38 In 2004, the Federal Lands Recreation Enhancement Act established a recreation fee program for the FS (and the other federal land management agencies).39 The program was set to expire in 2014 but has been reauthorized several times, and was most recently extended through September 30, 2020.40 The act authorizes different kinds of fees, outlines criteria for establishing fees, prohibits certain fees, and allows the FS to use collections without further appropriation. While Congress sought to make the actual users pay fees, some users object, arguing that the fees amount to paying twice (once through taxation) to support the agency. Congress may consider allowing the recreation fee program to sunset or may consider extending the program again, with or without modifications.41
Mineral and Energy Development
Much of the NFS is open to mineral and energy resource exploration and development. Oil, natural gas, and coal exploration and production is governed by the Mineral Lands Leasing Act of 1920, which also requires the BLM to manage the subsurface rights to virtually all federal lands, including NFS lands.42 Approximately 5.3 million acres underlying NFS lands are currently leased for oil, gas, coal, and geothermal operations.43 NFS lands contain an estimated 4,000 federal oil and gas wells and approximately 75,000 mining claims. Receipts and royalties generated for energy and mineral activities are collected by the Office of Natural Resources Revenue in the Department of the Interior and are distributed for a variety of purposes.44
Renewable energy projects—such as solar and wind projects—are also allowed on NFS lands, generally through a special use authorization (SUA, discussed in the "Other Uses" section). FS has not approved any solar projects to date. FS approved a utility-scale wind power facility SUA in 2012, which began operation in 2017.45
Range
Range management includes the use of NFS rangelands for livestock grazing as well as for the management of wild horses and burros, which are protected under the Wild Free-Roaming Horses and Burros Act of 1971.46 Management of wild horses and burros on NFS (and BLM) lands has generated controversy, and issues for Congress have included concerns regarding management of their population, among others. FS estimates there were approximately 9,300 wild horses and burros on NFS lands in 2018, approximately four times the appropriate management level.47
Of the 93 million acres of NFS lands identified as available for such use during the planning process, approximately 74 million acres were under permit for livestock grazing in FY2017.48 Permits generally cover a 10-year period and may be renewed automatically while the agency processes a backlog of grazing allotments and permits needing evaluation.49 Fees for grazing on federal lands—FS and BLM—are generally charged under a formula established by law in 1978.50 For 2019, the federal grazing fee is $1.35 per head month, the minimum fee allowed under the law.51
Timber52
One of the first uses of the early forest reserves was to "furnish a continuous supply of timber."53 The first chief of the FS, Gifford Pinchot, initially believed the agency could eventually become self-supporting through the production of timber, although he eventually abandoned the idea.54 FS timber sales and revenue generation were negligible until the 1950s, when the post-World War II housing boom, combined with declining competition from private timber sales, led to increasing NFS timber sales (see Figure 2). For many years after, the FS was a major provider of timber for the wood products industry, generally selling between 10 billion and 12 billion board feet of timber annually (about 20%-25% of total U.S. wood supply).55 Since the 1990s, FS timber production has decreased, totaling around 2 billion board feet annually since FY1999.56 In 2011, NFS supplied 2% of U.S. wood and paper products.57 The decline is attributable to a multitude of factors, including (but not limited to) changing legislative directives and related forest management policies and practices—such as increased planning and procedural requirements—as well as changing market dynamics for wood products, public preferences, and litigation.
For the last 15 years, harvest volume has remained relatively constant around 2.0 billion board feet harvested annually, with a slight upward trend over the last few years. Starting in FY2005, the price of lumber dropped significantly, mostly in response to instability in the U.S. housing market. This drop contributed to the value of FS harvests declining annually from FY2005 through FY2010, although the value has been modestly increasing since then. In FY2018, approximately 2.8 billion board feet were harvested from FS lands, at a value of approximately $188.8 million.58
|
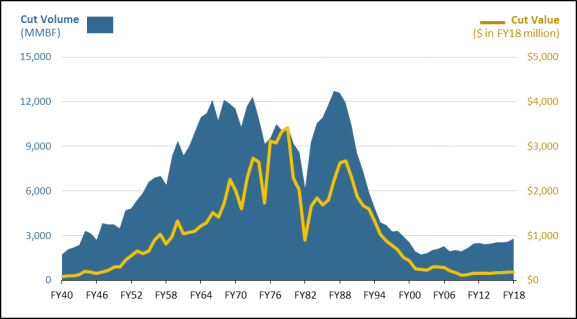 |
Notes: MMBF stands for million board feet. 1,000 million board feet equals 1 billion board feet. A board foot is a unit of wood measuring 12 inches by 12 inches by 1 inch. |
The FS is increasingly using timber harvests as a tool to achieve various land and resource management objectives or in the context of larger restoration objectives—such as enhancing ecosystem or watershed conditions—in addition to timber production. For example, the FS may enter into stewardship contracts: contracts for restoration activities (e.g., thinning to reduce potential wildfire fuels) that include the sale of commercial timber to offset some of the stewardship costs.59 The FS may also harvest trees damaged or killed in fires or other disturbance events, called salvage harvesting. Salvage harvesting may capture some of the economic value of the federal resources and generate revenue to fund other restoration activities, and in some cases may facilitate forest restoration and recovery.
Watersheds
Protecting watershed health was one of the original purposes of the national forests. This includes the management of surface and groundwater resources as well as water uses and rights on NFS lands. Nearly one-fifth of the nation's water originates on NFS lands.60 In addition, watersheds support ecological services such as productive soils, biological diversity, and fish and wildlife habitat, including spawning and rearing habitat for sport and commercial fish species. Watersheds also provide flood control benefits.
The FS established the Watershed Condition Framework (WCF) in 2011 to assess, classify, and prioritize the conditions of the watersheds containing significant portions of NFS lands. The 115th Congress codified the WCF program in statute.61 The initial assessment—completed in FY2011—classified conditions on approximately 15,000 watersheds based on 12 biophysical and ecological indicators indicating the degree of watershed functionality or integrity.62 Watersheds that were in good condition were classified as functioning (52% in the initial 2011 assessment), watersheds in fair condition were classified as functioning at risk (43%), and watersheds in poor condition were classified as having impaired function (3%).63 FS reports that, in FY2018, 53% of the watersheds were in functioning condition, 44% were functioning at risk, and 3% had impaired function.64
In FY2012, the FS began developing watershed restoration action plans to identify projects and activities to improve the condition of priority watersheds. Watershed restoration activities may include a range of forestry or land management practices, such as decommissioning roads, reforestation, or restoring or enhancing stream habitat, among others. Under the WCF, FS is expected to actively monitor and track progress on watershed condition improvements.
Wilderness and Other Special Land Designations
Congress has also provided management direction within the NFS by creating special designations for certain areas. Some of these designations—wilderness areas, wild and scenic rivers, and national trails—are part of larger management systems affecting several federal land management agencies.65
The NFS also includes several other types of land designations. The NFS contains many national game refuges and wildlife preserves, national recreation areas and scenic areas, national monuments, and other congressionally designated areas.66 Resource development and use is generally more restricted in these specially designated areas than on general NFS lands, and specific guidance is typically provided with each designation.
Management to preserve or develop FS roadless areas (areas that have been reviewed for wilderness designation but have not been designated as wilderness by Congress) continues to be controversial. Questions persist over the extent to which FS should manage to protect the wilderness characteristics of the approximately 58.5 million acres of roadless areas by prohibiting or permitting certain uses to occur. In 2001, President Clinton proposed a new rule to prohibit most road construction and timber harvesting in these areas. President George W. Bush delayed implementation of the Clinton rule and proposed an alternative policy. Both were litigated; however, the Clinton roadless rule remains intact after the Supreme Court refused to review a lower court's decisions in 2012.67 In 2018, the Forest Service initiated a rulemaking process to develop a new roadless rule specific to the national forests in the state of Alaska.68
Other Uses
NFS lands are also used for other purposes and services supporting national policies and federal land laws. These uses or activities may be permitted on NFS lands under various authorities, collectively referred to as special use authorizations (SUAs), as noted earlier. SUAs allow uses of NFS lands for various purposes, ranging from commercial filming to ski resort operation, among others. For example, the Secretary of Agriculture is authorized to issue a type of SUA called rights-of-way (ROW) for the use and occupancy of NFS lands.69 The rights-of-way allow for the specific use of NFS lands for: various types of water infrastructure; infrastructure for the storage, transportation, or distribution of liquids, gases (with specified exceptions), and solid materials; electricity generation, transmission, and distribution infrastructure; communications systems infrastructure; roads, trails, highways, canals, tunnels and other means of transportation in general; and other "necessary" systems and facilities which are in the public interest.70 The 115th Congress directed FS to initiate rulemaking regarding the SUA process for telecommunications sites and also addressed management of electricity transmission SUAs.71
Forest Health Conditions
Forest health generally refers to the ability of forest ecosystems to respond to disturbance events (e.g., wildfires, ice or wind storms, insect and disease infestations, timber harvests).72 Forest ecosystems have inherent characteristics that enhance their capability to survive such events (resistance) or facilitate recovery after disturbance (resilience). Some ecosystems are adapted to specific disturbances occurring at regular intervals. For example, some forest ecosystems are adapted to relatively frequent (e.g., up to every 35 years) but low-intensity wildfires to burn surface fuels (e.g., needles, leaves), reduce competition, and return nutrients to the soil, among other benefits. Other forest ecosystems are adapted to infrequent but high intensity wildfires.
Degraded forest ecosystems, however, may be more susceptible to mortality in response to disturbances or may take longer to recover. Different disturbances may also interact and exacerbate the effects of other events in a feedback loop. For example, a prolonged drought may impair a tree's resistance to an insect or disease infestation, or may make a tree more susceptible to damage during a wildfire. In addition, some research indicates that climate variability is reshaping forest landscapes by altering the frequency, intensity, and timing of disturbance events in ways that may exceed the resistance and resilience capacity of many forests.73
Insect, Disease, and Wildfire Risk
Many are concerned that degraded forest ecological conditions in the NFS are increasing the risk of insect or disease infestation or uncharacteristic wildfires, among other forest health concerns. Many have particular concerns regarding an accumulation of forest biomass resulting from a century of aggressive wildfire suppression and other land management practices.74 This biomass—dead and dying trees, heavy undergrowth, and dense stands of small trees—is often referred to as hazardous fuels. Hazardous fuels can significantly affect wildfire behavior, and contribute to wildfires becoming more intense, severe, and difficult to contain. Dense stands of trees may also facilitate the transmission of insect and disease infestations.
Projects that remove or modify these fuels are called treatments, and are intended to reduce the risk of catastrophic wildfire and facilitate post-fire recovery. Treatments include removing small-diameter trees (called thinning) or the deliberate use of fire in specific areas within prescribed conditions (called prescribed burning) to reduce fuel loads. Treatments may have broader forest restoration benefits as well, such as improving watershed functioning and facilitating ecological resilience and resistance.
FS has identified around 52 million-58 million acres of NFS lands at high or very high fire risk or insect infestation and in need of treatments.75 FS reports that it accomplishes around 2 million-6 million acres of treatments annually.76 At that pace, it would take between 9 and 29 years to eliminate the backlog of treatment needs, which does not account for maintaining already treated areas to the desired resource conditions. Some estimate that hazardous fuels are accumulating three times faster than the rate of treatment.77 To address these concerns, FS has proposed to increase the scale, scope, and implementation of forest management projects generally, and forest restoration treatments specifically.78 In addition, FS has several authorities to partner with stakeholders in various ways, as elements of a "shared stewardship" approach to address land management concerns at a landscape-scale and across ownership boundaries.79
Issues
FS and others identify administrative process barriers as one of many factors impeding progress toward their forest restoration goals.80 More specifically, some identify federal agency decisionmaking processes as preventing the agencies from implementing projects at their desired pace and scale, particularly related to implementation of the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) and opportunities for the public to challenge agency decisions administratively and judicially.81 Others may point to FS-specific implementation issues related to NEPA as contributing to planning delays more than involvement from the public or administrative or judicial challenges.82 Other stakeholders identify other administrative barriers—such as inadequate program funding levels and training—as preventing FS from implementing project planning requirements in a more efficient manner.
The 115th Congress enacted several provisions aimed to improve agency efficiencies by expanding the applicability of procedures intended to expedite the planning and review process for projects, such as hazardous fuel reduction and forest restoration projects.83 For example, proponents of this approach contend that expanding the use of Healthy Forests Restoration Act (HFRA) authorities and allowing federal agencies to plan more projects over larger areas under NEPA Categorical Exclusions (CEs) would expedite project implementation and allow FS and BLM to achieve progress toward their restoration goals.84 As such, in June 2019, FS announced proposed changes to its NEPA regulations—including the establishment of new CEs—to increase efficiency.85 Some, however, contend that changes made to the FS decisionmaking processes—such as through the establishment of CEs—are changing the basic legal framework for federal forest management and making it increasingly difficult for citizens to participate or challenge government decisions.86 In addition, some stakeholders contend that expanding the use of these authorities could result in environmental impacts that exacerbate forest health concerns.87
Discussion
Many forest health issues have been ongoing for decades. For example, concerns about deteriorating forest conditions and high fuel levels were raised after wildfires in Yellowstone National Park in 1988. In the 1990s, several reviews—including those by congressionally chartered commissions and the Government Accountability Office (GAO)—recommended that land management agencies create long-term strategies for addressing forest health and reducing hazardous fuels. In the 2000s, GAO and the USDA Office of the Inspector General (OIG), among others, raised concerns with FS's strategies for addressing forest health and implementation of the hazardous fuels reduction program. Some of these reports are listed below.
- In 1994, the congressionally chartered National Commission on Wildfire Disasters recommended federal land management agencies invest more in reducing hazardous fuels in high-risk ecosystems and observed that "the question is no longer if policy-makers will face disastrous wildfires and their enormous costs, but when."88
- In 1995, a FS study recommended the agency increase hazardous fuel treatments to up to 3 million acres per year by 2005.89
- In 1999, GAO recommended FS develop a strategy to identify long-term options for reducing fuels to address forest health issues and mitigate wildfire risk.90
- In 2002, GAO recommended FS—and the other land management agencies—improve processes for identifying lands, resources, and communities at high wildfire risk.91
- In 2006, the USDA OIG raised concerns with FS's hazardous fuels reduction program and recommended FS develop guidance and controls to identify, prioritize, implement, monitor, and report on hazardous fuels reduction projects and funding.92
- A 2016 OIG report assessed FS's progress toward implementing the recommendations from that 2006 report and found continued issues with FS prioritizing, tracking, and reporting of hazardous fuels reduction projects.93
Concerns about FS project implementation also have been ongoing. For example, in 2001 Congress asked GAO to evaluate the extent to which administrative or judicial challenges impeded FS's implementation of fuel management projects. The report found that approximately 24% of the fuel reduction decisions signed in FY2001 and FY2002 were appealed.94 A similar GAO analysis found that 20% of the fuel management projects identified for implementation in FY2006 through FY2008 were challenged through appeals or objections.95 In addition, several academic studies examining FS NEPA implementation suggest that projects that are more complex—in terms of scale and scope—are more likely to be challenged.96 These studies also found that other project characteristics (e.g., timber harvests, forest plans) and factors related to staffing, documentation, and implementation of the public involvement requirements affect the likelihood of project challenges.
HFRA, passed in 2003, included provisions intended to expedite implementation of hazardous fuels reduction projects. Despite these provisions, the extent of NFS areas in need of treatment has continued to increase, and FS continues to look for ways to increase the pace of project implementation. To some, this implies that the HFRA approach to streamline agency decisionmaking has not been successful. To others, it implies that the HFRA approach needs to be more broadly applied, as it was in legislation enacted during the 115th Congress.97
Appropriations
The FS receives both discretionary and mandatory appropriations. Although it is an agency within the USDA, the FS receives its discretionary appropriations through Title III of regular Interior, Environment, and Related Agencies appropriations bills.98 Separately, annual mandatory appropriations are provided under existing authorizing statutes. Laws authorizing mandatory appropriations allow the FS to spend money without further action by Congress, and the budget authority for several of these mandatory spending accounts is dependent on revenue generated by activities in the NFS. In FY2019, the FS received $7.32 billion in total funding, of which $6.94 billion (95%) was discretionary funds and an estimated $377.4 million (5%) was mandatory funds.99
The NFS account, one of the FS's largest discretionary accounts, funds the management of the NFS.100 Several mandatory accounts also fund NFS activities; however, this report focuses on discretionary appropriations. In FY2019, Congress appropriated $2.02 billion to the NFS discretionary account, which reflects $1.94 billion in regular appropriations plus an additional $85.0 million in emergency-designated supplemental appropriations.101 On average over the last five fiscal years, the NFS account has received approximately 28% of total FS discretionary funding.
FS budget requests and Interior Appropriations Subcommittee documents typically allocate monies in each account among various subaccounts and, in some cases, among specific programs and activities. The FS further allocates its appropriations—at the account, subaccount, and program activity levels—among the nine FS regions, five research stations, two service centers and laboratories, and the national headquarters office in Washington, DC. Once the funds have been allocated to the regions and programs, the money is then further allocated to each NFS unit. This can make analyzing appropriations by region or by forest challenging.
The NFS account includes several subaccounts, programs, and activities, many of which reflect the different ways national forests are used. The NFS subaccounts are described below, in descending order of FY2019 budget authority (see Table 3).102 The activities funded through each subaccount are listed, along with information on the FY2019 appropriation. For purposes of this report, regular appropriations refers to the appropriations provided in the Consolidated Appropriations Act, FY2019 (P.L. 116-6), and supplemental appropriations refers to any appropriations provided in the Additional Supplemental Appropriations for Disaster Relief Act, 2019 (P.L. 116-20).
- Hazardous Fuels funds activities to remove, modify, or manipulate vegetation to reduce the likelihood of uncharacteristically intense wildland fire. Prior to FY2018, this program was funded through the Wildland Fire Management account. (FY2019: $467.5 million [$435.0 million regular plus $32.5 million supplemental], 23% of NFS).
- Forest Products funds activities to analyze, prepare, offer, award, and administer timber sales, stewardship contracts, and special forest products permits on NFS lands (FY2019: $407.3 million [$368.0 million regular plus $39.3 million supplemental], 20% of NFS).
- Recreation, Heritage, and Wilderness funds activities related to the management of recreation opportunities on the NFS, administering recreation special use authorizations, supporting the protection of heritage resources, and protection of designated wilderness areas and wild and scenic rivers (FY2019: $260.0 million, 13% of NFS).
- Land Management Planning, Assessment, and Monitoring funds the development, maintenance, and revision of the forest plans (FY2019: $180.0 million, 9% of NFS).
- Vegetation and Watershed Management funds restoration-related management activities to improve forest and rangeland conditions, fish and wildlife habitat, water quality, quantity, and timing of stream flows, among others (FY2019: $188.6 million [$180.0 million regular plus $8.6 million supplemental], 10% of NFS).
- Wildlife and Fish Habitat Management funds activities to restore, recover, and maintain wildlife and fish—particularly rare animal and plant species—and their habitats on NFS lands (FY2019: $137.0 million, 7% of NFS).
- Law Enforcement Operations responds to emergencies, investigates illegal activities (such as illegal drug activities), and conducts crime prevention activities on NFS lands (FY2019: $131.0 million, 6% of NFS).
- Landownership Management provides funds for the basic land management or real estate activities necessary to support all NFS programs, such as granting special use authorizations for energy transmission corridors and processing land exchanges (FY2019: $79.5 million [$75.0 million regular plus $4.5 million supplemental], 4% of NFS).
- Minerals and Geology Management funds the administration of mineral operations on NFS lands, management and mitigation of abandoned mine lands, management of geologic resources and hazards, and management of environmental compliance and restoration related to mineral activities (FY2019: $75.0 million, 4% of NFS).
- Grazing Management funds the administration of livestock grazing use permits on the NFS and implementing environmental reviews of all FS grazing allotments as statutorily mandated (FY2019: 57.0 million, 3% of NFS).103
- Collaborative Forest Landscape Restoration Program Fund (CFLRP), authorized in 2009,104 funds 23 landscape-scale restoration projects for 10 years in priority landscapes (FY2019: $40.0 million, 2% of NFS).
|
NFS Subaccount |
FY2015 |
FY2016 |
FY2017 |
|
|
|
— |
— |
— |
$430.0 |
$467.5 |
|
Forest Products |
$339.1 |
$359.8 |
$367.8 |
$366.4 |
$407.3 |
|
Recreation, Heritage, and Wilderness |
$261.7 |
$261.7 |
$264.6 |
$259.0 |
$260.0 |
|
$188.8 |
$185.0 |
$182.9 |
$179.3 |
$180.0 |
|
Vegetation and Watershed Management |
$184.7 |
$184.7 |
$184.7 |
$192.4 |
$188.6 |
|
Wildlife and Fish Habitat Management |
$140.5 |
$140.5 |
$140.5 |
$137.6 |
$137.0 |
|
Law Enforcement Operations |
$126.7 |
$126.7 |
$126.2 |
$129.2 |
$131.0 |
|
Minerals and Geology Management |
$76.4 |
$76.4 |
$75.6 |
$74.2 |
$75.0 |
|
Landownership Management |
$77.7 |
$77.7 |
$73.7 |
$79.5 |
$79.5 |
|
Grazing Management |
$55.4 |
$56.9 |
$56.9 |
$56.9 |
$57.0 |
|
CFLRP |
$40.0 |
$40.0 |
$40.0 |
$40.0 |
$40.0 |
|
$3.4 |
— |
— |
— |
— |
|
Total, NFS |
$1,494.3 |
$1,509.4 |
$1,513.3 |
1,944.4 |
2,023.0 |
Source: CRS. Data compiled from detailed funding tables prepared by the House Committee on Appropriations. Additional data on the funding allocation from the FY2018 and FY2019 supplemental appropriations was provided by the FS legislative affairs office.
Notes: Data are presented in nominal dollars and reflect any emergency or supplemental appropriations. CFLRP = Collaborative Forest Landscape Restoration Program.
a. Data includes $20.7 million in emergency-designated supplemental appropriations provided in the Further Additional Supplemental Appropriations for Disaster Relief Requirements Act, 2018 enacted as Division B of the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018 (P.L. 115-123).
b. Data includes $85.0 million in emergency-designated supplemental appropriations provided in the Additional Supplemental Appropriations for Disaster Relief Act, 2019 (P.L. 116-20).
c. Prior to FY2018, Hazardous Fuels funding was provided in FS's Wildland Fire Management account.
d. Prior to FY2017, this program was funded in two separate subaccounts. This table reports the total of those two subaccounts for FY2015 and FY2016.
e. Management of the Valles Caldera National Preserve was transferred to the National Park Service in FY2015.
Table 3 provides appropriations data for the NFS subaccounts over the last five fiscal years (FY2015 through FY2019). Over that time, appropriations to the NFS account averaged $1.61 billion annually. Appropriations increased 35% from FY2015 ($1.49 billion) to FY2019 ($2.02 billion). However, much of this increase is due to a structural change (discussed below) in the account as well as supplemental funding provided in both FY2018 and FY2019. Funding for most of the subaccounts was relatively constant over the five-year period, either increasing or decreasing by no more than 3%. An exception is the Forest Products subaccount, which increased by 20% over the five year period. A portion of that increase can be attributed to the $39.3 million in supplemental funding for Forest Products provided in FY2019.
The addition of the Hazardous Fuels subaccount, which previously had been funded in the FS's Wildland Fire Management account, was a significant structural change that was implemented in FY2018. Table 4 provides more detail on the funding for Hazardous Fuels management across accounts over the FY2015-FY2019 time period; this activity received $404.8 million annually on average over those five years, and also received supplemental funding in FY2019. Notwithstanding the additional FY2018 and FY2019 funds in the NFS account for the newly created Hazardous Fuels subaccount, appropriations to the NFS account averaged $1.51 billion annually and increased by 2% from FY2015 to FY2019. Further, much of that increase is attributed to the supplemental funding provided in FY2019 (see Figure 3).
|
FS Account |
FY2015 |
FY2016 |
FY2017 |
FY2018 |
|
|
Wildland Fire Management |
$361.7 |
$375.0 |
$390.0 |
— |
— |
|
National Forest System |
— |
— |
— |
$430.0 |
$467.5 |
Source: CRS. Data compiled from detailed funding tables prepared by the House Committee on Appropriations. Additional data on the funding allocation from the FY2018 and FY2019 supplemental appropriations was provided by the FS legislative affairs office.
Notes: Data are presented in current dollars and reflect any emergency or supplemental appropriations.
a. Data includes $32.5 million in emergency-designated supplemental appropriations provided for Hazardous Fuels in the Additional Supplemental Appropriations for Disaster Relief Act, 2019 (P.L. 116-20).
Wildfire Funding
The FS receives appropriations to conduct wildfire management activities—preparedness, suppression, and site rehabilitation—on NFS lands through its Wildland Fire Management (WFM) account.105 In addition, FS receives funding for other wildfire-related purposes in its State and Private Forestry account. Combined, total funding for wildfire-related purposes has accounted for more than half of the FS discretionary appropriation over the past five years (FY2015-FY2019). For FY2019, FS received $4.09 billion for wildfire-related purposes, which included a supplemental appropriation of $720.0 million.
Congress has been concerned about the cost of WFM generally and suppression activities specifically. Suppression activities include all of the work associated with extinguishing or confining fires on NFS lands (and other federal or nonfederal lands under fire protection agreements with the FS). Suppression costs vary annually and are difficult to predict, and may be high even during years of relatively mild wildfire activity. Due to the emergency nature of fire control activities, FS is authorized to transfer money out of other discretionary accounts if suppression funds become depleted; this is often referred to as fire borrowing.106 In response, Congress has typically enacted supplemental appropriations to repay the transferred funds and/or to replenish the agency's wildfire accounts.
Congress has expressed concern about the impact of fire borrowing on other NFS management activities and about the increasing portion of the FS budget going toward suppression funding. Wildfire spending—like all discretionary spending—is currently subject to procedural and budgetary controls.107 In the past, Congress has sometimes—but not always—effectively waived some of these controls for certain wildfire spending. This situation prompted the 115th Congress to enact a new mechanism or process for suppression funding in the form of an adjustment to the discretionary spending limit; this mechanism is commonly referred to as the wildfire funding fix.108 The wildfire funding fix starts in FY2020 and allows Congress to provide additional funding above a specified baseline level for suppression purposes that is effectively outside of the discretionary spending limits, up to a specified annual maximum. This wildfire adjustment is available annually from FY2020 through FY2027, although the statutory limits for discretionary spending are currently only in effect until FY2021.
Land Acquisition and Disposal109
As noted above, in 1891, the President was authorized to reserve lands from the public domain as forest reserves, but this authority was subsequently limited by Congress.110 However, many presidential proclamations and executive orders have modified NFS boundaries and changed names, including establishing new national forests from existing NFS lands. National forests in the East generally were established between 1910 and 1951. Today, establishing a new national forest or significantly modifying the boundaries of an existing national forest requires an act of Congress.
The Secretary of Agriculture has numerous authorities to add lands to the NFS, through acquisitions or land exchanges. Often, though, the acquisitions are restricted to land within or contiguous to the proclaimed exterior boundaries of a national forest (e.g., inholdings). The first and broadest authority is in the Weeks Act of 1911, which allows the Secretary to purchase "such forested, cut-over, or denuded lands within the watersheds of navigable streams ... [for] the regulation of the flow of navigable streams or for the production of timber."111
Additional authorities are provided by the Bankhead-Jones Farm Tenant Act of 1937,112 which authorized the Secretary to acquire submarginal lands and lands not suitable for cultivation. Under this authority, the FS acquired and established the 20 national grasslands and six land utilization projects that account for 2% of the NFS. Other laws authorize land acquisition for the NFS, typically in specific areas or for specific purposes. For example, the Secretary is authorized to acquire access corridors to NFS lands across nonfederal lands.113
The Secretary also has numerous authorities to convey NFS land out of federal ownership, all constrained in various ways and seldom used. Often, the authority requires the federal government to dispose of the land at fair market value, or in the case of land exchanges, requires that the lands be in the same state and of equal value (although value may be partially equalized by a cash payment). Some of the disposal authorities are designed to allow FS to convey land that is no longer needed for a federal purpose or that might be chiefly valuable for another purpose. For example, the Weeks Act authorizes the disposal of land better suited for other uses, such as agriculture or mining.114 Some of the authorities specify particular circumstances where they can be used, such as the conveyance of NFS land to relieve encroachments due to erroneous surveys or for educational purposes.115
In addition to these standing authorities for FS to acquire or dispose of land, Congress has sometimes enacted laws directing FS to acquire or dispose of particular parcels where no standing authority exists and, in other cases, to direct or facilitate land transactions.
Issues for Congress
Congress considers many issues regarding NFS management. Current debates tend to focus more on particular issues that involve land and resource allocation and valuation, such as balancing increasing demands for commodity and noncommodity uses and services from the NFS. Simultaneously, public interest in how these resource allocation decisions are made and the lands are used has increased. NFS management and administration has thus become more complex and contentious. However, these controversies often derive from questions about the fundamental management principles of multiple use and sustained yield.
The meaning and application of the dual concepts of multiple use and sustained yield have been debated since Congress first authorized the reservation of federal land.116 The debates generally revolve around questions such as these:
- Is multiple use achieved through adjacent or sequential allowance of single resource uses or by simultaneous application of several uses?
- Is sustained yield management to provide a regular flow of products for human use or to assure the maintenance of the biological productivity of the forest resources?
When these management principles were established, Congress conferred considerable discretion on the FS to make those decisions. As concerns arose and persisted about the agency's interpretation of multiple use and sustained yield, Congress began to restrict that discretion by enacting legislation specifying that certain uses occur (or not occur) in specified areas.117 However, Congress has not enacted legislation directly addressing the concepts of multiple use or sustained yield across the entire NFS.
Therefore, conflicts arise as users and land managers attempt to balance multiple uses and services and produce a sustained yield of resources from the NFS. Congress often considers legislation to prioritize various uses over others or to define or specify levels of production. For example, Congress has considered legislation to prioritize timber production over other uses in certain areas or to specify a certain annual output of timber production.118
There are several ongoing concerns regarding wildfire management, including the total federal costs of wildfire management, the strategies and resources used for wildfire management, and the impact of wildfire on both the quality of life and the economy of communities surrounding wildfire activity. Fire control expenditures continue to climb, affecting the implementation of other programs (and thus affecting NFS uses) through personnel and funds transferred to fire control. The wildfire funding fix provides a mechanism to fund control activities and potentially reduce the impact of fire transfers on the agency but does not address the factors driving cost increases. It is unclear when, whether, and how costs can be contained.
Author Contact Information
Footnotes
| 1. |
Management of the National Forest System (NFS) is one of the Forest Service's (FS's) three principal responsibilities. The other two principal responsibilities are providing assistance programs to nonfederal forest owners and conducting forestry research programs. FS also provides international forestry assistance. |
| 2. |
The NFS is defined at 16 U.S.C. 1609(a). U.S. Department of Agriculture, U.S. Forest Service, Land Areas Report (LAR)—as of September 30, 2018, Table 1, at http://www.fs.fed.us/land/staff/lar/LAR2018/lar2018index.html. Hereinafter referred to as FS, Land Areas Report, 2018. The LAR includes several additional land designations in the NFS, such as research and experimental forests or areas. This includes a 140-acre experimental forest in the U.S. Virgin Islands. |
| 3. |
Public domain lands consist of lands ceded by the original states or obtained from a foreign sovereign through purchase, treaty, or other means (e.g., the Louisiana Purchase in 1803). Public domain lands may be governed by different laws than acquired federal lands, which were obtained from private entities or states. |
| 4. |
Organic Administration Act, Act of June 4, 1897 (16 U.S.C. §473). |
| 5. |
The Transfer Act, Act of February 1, 1905 (P.L. 58-33, 16 U.S.C. §§472, 554). |
| 6. |
Act of March 4, 1907 (P.L. 59-242, 16 U.S.C. §499). |
| 7. |
Act of March 4, 1907 (P.L. 59-242, 16 U.S.C. §499). The act limited the presidential authority to establish national forests in Colorado, Idaho, Montana, Oregon, Washington, and Wyoming. Roosevelt proclaimed additional reserves after it was enacted but before he signed it into law. |
| 8. |
Act of March 1, 1911 (P.L. 61-435, 16 U.S.C. §480). |
| 9. |
Federal Land Policy and Management Act of 1976, Act of October 21, 1976 (P.L. 94-579, 43 U.S.C. §§1701 et seq.). |
| 10. |
FS, Land Areas Report, 2018. |
| 11. |
Act of June 12, 1960, P.L. 86-517, 16 U.S.C. §§528-531. Other laws govern the management of some of the other NFS units. For example, the national grasslands are managed pursuant to the provisions in the Bankhead-Jones Farm Tenant Act (50 Stat. 525, 7 U.S.C. §§1010-1012). |
| 12. |
P.L. 79-404, 5 U.S.C. §§500 et seq. |
| 13. |
P.L. 91-190, 42 U.S.C. §§4321-4347. For more information on the National Environmental Policy Act, see CRS Report RL33152, The National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA): Background and Implementation, by Linda Luther, and CRS Report R45696, Forest Management Provisions Enacted in the 115th Congress, by Katie Hoover et al., pp. 3-4. |
| 14. |
P.L. 93-205, 16 U.S.C. §§1531-1544. For more information on the Endangered Species Act, see CRS Report RL31654, The Endangered Species Act: A Primer, by Pervaze A. Sheikh. |
| 15. |
The Forest and Rangeland Renewable Resources Planning Act of 1974 (RPA): P.L. 93-378, 16 U.S.C. §§1600 et seq. The National Forest Management Act of 1976 (NFMA): P.L. 94-588; 16 U.S.C. §1601 et al. |
| 16. |
The following is the most recent publication—as of the date of this report—associated with the decennial RPA assessments, and includes data on a variety of forest resource statistics. Sonja Oswalt, W. Brad Smith, and Patrick Miles, et al., Forest Resources of the United States, 2017: A Technical Document Supporting the Forest Service Update of the 2020 RPA Assessment. USDA, FS, GTR-WO-97, 2019, at https://www.fs.usda.gov/treesearch/pubs/57903. |
| 17. |
16 U.S.C. §1604. |
| 18. |
16 U.S.C. §1604(f)(5)(A). Annual appropriations laws have included a provision specifying that the Secretary of Agriculture is not considered to be in violation of the requirements of RPA/NFMA solely because a forest plan has not been revised within 15 years, as long as the Secretary is acting in good faith to update such plans. See, for example, §407 of Title IV of P.L. 116-6, the Consolidated Appropriations Act, FY2019. |
| 19. |
For more information on the history of the planning regulations as well as the status of the current rule, see https://www.fs.usda.gov/planningrule. |
| 20. |
65 Federal Register 67514 (November 9, 2000). |
| 21. |
70 Federal Register 1022 (January 5, 2005). |
| 22. |
Citizens for Better Forestry v. USDA, 481 F.Supp. 2d 1059 (N.D.Cal., 2007). |
| 23. |
73 Federal Register 21467 (April 21, 2008). |
| 24. |
Citizens for Better Forestry v. USDA, 632 F.Supp. 2d 968 (N.D.Cal., 2009). |
| 25. |
77 Federal Register 21260 (April 9, 2012). In 2016, FS amended the rule to clarify the plan amendment process and procedures, among other technical amendments (81 Federal Register 90723). The regulations are codified at 36 C.F.R. part 219. |
| 26. |
Data as of March 14, 2018, and from "Status of Plans" document posted on https://www.fs.fed.us/emc/nfma/index.htm (retrieved August 12, 2019). |
| 27. |
FS, FY2020 Budget Justification, p. 67, available from https://www.fs.fed.us/about-agency/budget-performance. |
| 28. |
The Wilderness Act of 1964, P.L. 88-577, §4; 16 U.S.C. §529. |
| 29. |
16 U.S.C. §531. |
| 30. |
For information on the requirements to share certain revenues with the states and counties containing NFS lands, see CRS Report R41303, Reauthorizing the Secure Rural Schools and Community Self-Determination Act of 2000, by Katie Hoover. |
| 31. |
FS, All Service Receipts: Receipts Summary Report, FY2018, ASR-04. |
| 32. |
FS, FY2020 Budget Justification, p. 58. |
| 33. |
See CRS Report R42920, Motorized Recreation on Bureau of Land Management and Forest Service Lands, by Carol Hardy Vincent and Katie Hoover. |
| 34. |
|
| 35. |
70 Federal Register 68264, November 9, 2005, and 73 Federal Register 74689, December 9, 2008. The regulations are available at 36 C.F.R. Part 212. |
| 36. |
|
| 37. |
A motor vehicle use map is generally available in the "maps and publications" section of the website for each NFS unit. |
| 38. |
FS, All Service Receipts: Receipts Summary Report, FY2013, ASR-04. |
| 39. | |
| 40. |
P.L. 116-6 extended the program to October 1, 2020. P.L. 113-235. |
| 41. |
For further information on the Federal Lands Recreation Enhancement Act, see CRS In Focus IF10151, Federal Lands Recreation Enhancement Act: Overview and Issues, by Carol Hardy Vincent, and CRS Report RL33730, Recreation Fees Under the Federal Lands Recreation Enhancement Act, by Carol Hardy Vincent. |
| 42. |
30 U.S.C. §181 et seq. For more information, see CRS In Focus IF10127, Energy and Mineral Development on Federal Land, by Marc Humphries. |
| 43. |
Forest Service, FY2020 Budget Justification, p. 73, at http://www.fs.fed.us/about-agency/budget-performance. |
| 44. |
For more information on energy and mineral revenue, see CRS Report R43891, Mineral Royalties on Federal Lands: Issues for Congress, by Marc Humphries. |
| 45. |
See, for example, "Deerfield Wind Begins Operation," Vermont Business Magazine, December 2017, https://vermontbiz.com/news/2017/december/29/deerfield-wind-begins-operation. |
| 46. |
16 U.S.C. §§1331 et seq. For more information on wild horses and burros, see CRS In Focus IF11060, Wild Horse and Burro Management: Overview of Costs, by Carol Hardy Vincent. |
| 47. |
This estimate was provided to CRS by the FS on December 17, 2018. |
| 48. |
These figures were provided to CRS by the FS on November 30, 2018. For discussion on grazing trends on NFS lands, see CRS Report R44932, Statistics on Livestock Grazing on Federal Lands: FY2002 to FY2016, by Carol Hardy Vincent. |
| 49. |
The authority to automatically renew leases is provided in multiple laws. They include P.L. 113-291, §3023 and P.L. 108-108, §325, as extended most recently through FY2019 by P.L. 116-6, §420. |
| 50. |
Public Rangelands Improvement Act of 1978, P.L. 95-514, 43 U.S.C. §§1901, 1905. The formula has been continued indefinitely through an executive order issued by President Reagan in 1986 (Executive Order 12548, 51 Federal Register 5985, February 19, 1986). |
| 51. |
The 2019 fee took effect March 1, 2019, and will be in effect through February 29, 2020. Head month is defined as one month's use and occupancy of the range by one animal, except for sheep and goats (36 C.F.R. §222.50). For more information on fees, see CRS Report RS21232, Grazing Fees: Overview and Issues, by Carol Hardy Vincent. |
| 52. |
For more information on timber harvesting on federal lands, see CRS Report R45688, Timber Harvesting on Federal Lands, by Anne A. Riddle. |
| 53. |
Organic Administration Act, Act of June 4, 1897, 16 U.S.C. 473. |
| 54. |
Harold K. Steen, The U.S. Forest Service: A History (University of Washington Press, 1976), p. 91. |
| 55. |
A board foot is volume measurement, representing a unit of wood measuring 12 inches by 12 inches by 1 inch. Harvest volume is also sometimes reported as cubic feet. During the period when FS was harvesting 10 to 12 billion board feet annually, the revenue was less than the total cost of NFS management. |
| 56. |
The decrease in timber production, and revenue generation, also led to a decrease in the revenue-sharing payments made to counties containing NFS land. Congress enacted an alternative payment system in response. For more information, see CRS Report R41303, Reauthorizing the Secure Rural Schools and Community Self-Determination Act of 2000, by Katie Hoover. |
| 57. |
Sonja Oswalt, W. Brad Smith, and Patrick Miles, et al., Forest Resources of the United States, 2012: A Technical Document Supporting the Forest Service Update of the 2010 RPA Assessment. Forest Service (FS), U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), GTR-WO-91, 2014. |
| 58. |
Data reflects the cut volume and value (FS, Forest Cut and Sold Reports, at http://www.fs.fed.us/forestmanagement/products/sold-harvest/cut-sold.shtml). Cut value refers to the appraised value of the timber after it is harvested. The cut value reported in any given fiscal year may not be reflected in the collection of timber revenue for that same fiscal year for various reasons (for example, because revenue may be collected at various times throughout a timber sale contract, which may be executed over several years). |
| 59. |
Stewardship contracting was first authorized on a temporary basis in 1999, extended several times, and then permanently authorized by the Agricultural Act of 2014 (2014 farm bill, P.L. 113-79, Title VIII). Stewardship contracts may include sales of other forest products (such as Christmas trees). For more information, see CRS In Focus IF11179, Stewardship End Result Contracting: Forest Service and Bureau of Land Management, by Anne A. Riddle. |
| 60. |
FS, "Watershed, Fish, Wildlife, Air and Rare Plants," at http://www.fs.fed.us/biology/watershed/#focus. |
| 61. |
P.L. 115-334, Title VIII, §8405. The 115th Congress also established a water source protection program (§8404). For more information on these changes, see CRS Report R45696, Forest Management Provisions Enacted in the 115th Congress, by Katie Hoover et al., pp. 30-31. |
| 62. |
For more information on the classification process, see FS, Watershed Condition Classification Technical Guide, FS-978, 2011, available from https://www.fs.fed.us/naturalresources/watershed/condition_framework.shtml. |
| 63. |
FS, FY2015 Budget Justification, p. 5-5, at http://www.fs.fed.us/about-agency/budget-performance. For more information on the watershed condition framework, see Forest Service, Watershed Condition Framework, FS-977, 2011, https://www.fs.fed.us/sites/default/files/Watershed_Condition_Framework.pdf. |
| 64. |
Figures were provided by FS on August 20, 2019. |
| 65. |
For more information on wilderness, see CRS Report RL31447, Wilderness: Overview, Management, and Statistics, by Anne A. Riddle and Katie Hoover, and CRS Report R41610, Wilderness: Issues and Legislation, by Katie Hoover and Sandra L. Johnson. For more information on wild and scenic rivers, see CRS Report R45890, Wild and Scenic Rivers: Designation, Management, and Funding, by Anne A. Riddle and CRS Report R42614, The National Wild and Scenic Rivers System: A Brief Overview, by Sandra L. Johnson and Laura B. Comay. For more information on national trails, see CRS Report R43868, The National Trails System: A Brief Overview, by Mark K. DeSantis and Sandra L. Johnson. For more information on other federal land designations, see CRS Report R43429, Federal Lands and Related Resources: Overview and Selected Issues for the 116th Congress, coordinated by Katie Hoover. |
| 66. |
FS, Land Areas Report, 2018. For more information, see CRS Report R41285, Congressionally Designated Special Management Areas in the National Forest System, by Katie Hoover. |
| 67. |
Wyoming v. Department of Agriculture, 133 S.Ct. 417 (2012). |
| 68. |
FS, "Roadless Area Conservation; National Forest System Lands in Alaska," 83 Federal Register 169, August 30, 2018. |
| 69. |
|
| 70. |
These purposes are summarized from 43 U.S.C. §1761(a). |
| 71. |
For information on the specific provisions, see CRS Report R45696, Forest Management Provisions Enacted in the 115th Congress, by Katie Hoover et al., pp. 32-36. |
| 72. |
Disturbance is defined as "any relatively discrete event in time that disrupts ecosystems, community, or population structure and changes resources, substrate availability, or the physical environment." Steward T.A. Pickett and P.S. White, The Ecology of Natural Disturbance and Patch Dynamics (Orlando: Academic Press, 1985). Disturbance events may be unplanned (e.g., precipitation events) or planned (e.g., harvest, prescribed fire). |
| 73. |
James M. Vose, David L. Peterson, and Toral Patel-Weynard, Effects of Climate Variability and Change on Forest Ecosystems: a Comprehensive Science Synthesis for the U.S., Forest Service, PNW-GTR-870, Portland, OR, 2012, http://www.treesearch.fs.fed.us/pubs/42610. |
| 74. |
For a more detailed discussion on forest biomass and fuels, see CRS Report R40811, Wildfire Fuels and Fuel Reduction, by Katie Hoover. |
| 75. |
Range is an estimate based on several reported measures for lands in need of some type of forest restoration treatment. See for example, FS, Toward Shared Stewardship Across Landscapes: An Outcome-Based Investment Strategy, FS-118, 2018, https://www.fs.fed.us/sites/default/files/toward-shared-stewardship.pdf (hereinafter referred to as FS, Shared Stewardship), reporting approximately 52 million acres at high to very high fire risk and/or above-normal levels of insect and disease mortality, see p. 11. |
| 76. |
Range is an estimate based on several reported measures for FS acres treated annually. See for example, in FS, Shared Stewardship, the authors estimate about 1.9 million acres of NFS lands are treated annually to reduce hazardous fuels (see p. 12) and also report that around 6 million acres of NFS were treated to reduce fire risk and improve forest conditions per year for FY2016 and FY2017 (see p. 23). |
| 77. |
USDA, Office of the Inspector General (OIG), FS Wildland Fire Activities - Hazardous Fuels Reduction, 08601-004-41, July 2016, hereinafter referred to as OIG, FS Hazardous Fuels. |
| 78. |
See, for example, FS, Shared Stewardship. |
| 79. |
FS, Shared Stewardship. |
| 80. |
See, for example, House Committee on Natural Resources, Resilient Federal Forests Act of 2017, House Report, 115th Cong., 1st sess., October 25, 2017, H.Rept. 115-370 (hereinafter referred to as H.Rept. 115-370), FS, The Process Predicament: How Statutory, Regulatory, and Administrative Factors Affect National Forest Management, 2002, https://www.fs.fed.us/projects/documents/Process-Predicament.pdf, and FS, "National Environmental Policy Act Compliance," 84 Federal Register 114, June 13, 2019. |
| 81. | See, for example, U.S. Congress, House Committee on Natural Resources, Subcommittee on Oversight and Investigations, Exploring Solutions to Reduce Risks of Catastrophic Wildfire and Improve Resiliency of National Forests, Oversight hearing, |
| 82. |
See, for example, Audrey Bixler et al., Administrative and Judicial Review of NEPA Decisions: Risk Factors and Risk Minimizing Strategies for the Forest Service, University of Oregon Ecosystem Workforce Program, Working Paper Number 66, 2016 (hereinafter referred to as Bixler et al. 2016); Michael J. Mortimer et al., "Environmental and Social Risks: Defensive NEPA in the U.S. Forest Service," Journal of Forestry, vol. 109, no. 1 (2011), pp. 27-33; or Marc J. Stern, "The meaning of the National Environmental Policy Act within the U.S. Forest Service," Journal of Environmental Management, vol. 91 (2010), pp. 1371-1379. |
| 83. |
For more discussion on these provisions, see CRS Report R45696, Forest Management Provisions Enacted in the 115th Congress, by Katie Hoover et al. |
| 84. |
P.L. 108-148, 16 U.S.C. §§6501 et seq. See, for example, H.Rept. 115-370, Dissenting Views. |
| 85. |
FS, "National Environmental Policy Act Compliance," 84 Federal Register 114, June 13, 2019. |
| 86. |
See, for example, S.Hrg. 115-112 (e.g., letter submitted by Center for Biological Diversity); H.Rept. 115-370, Dissenting Views; or Martin Nie and Peter Metcalf, "National Forest Management: The Contested Use of Collaboration and Litigation," Environmental Law Reporter, vol. 46 (2016), pp. 10281-10298. |
| 87. |
See, for example, H.Rept. 115-370, Dissenting Views. |
| 88. |
The commission was established by the Wildfire Disaster Recovery Act of 1989 (P.L. 101-286) after the 1988 wildfires in Yellowstone. R. Neil Sampson, chair, Report of the National Commission on Wildfire Disasters, Washington, DC, 1994. |
| 89. |
FS, Course to the Future: Positioning Fire and Aviation Management, May 1995. |
| 90. |
U.S. Government Accountability Office (GAO), Western National Forests: A Cohesive Strategy is Needed to Address Catastrophic Wildfire Threats, RCED-99-65, April 2, 1999, https://www.gao.gov/products/RCED-99-65. |
| 91. |
GAO, Severe Wildland Fires: Leadership and Accountability Needed to Reduce Risks to Communities and Resources, GAO-02-259, January 31, 2002. |
| 92. |
USDA Office of Inspector General (OIG), Implementation of the Healthy Forests Initiative, 08601-6-AT, September 2006. |
| 93. |
OIG, FS Hazardous Fuels. |
| 94. |
The report identified a total of 818 signed decisions with fuel reductions as an activity. Of those 818, 194 decisions were appealed. Because more than one appeal may occur per decision, the total number of appeals was higher (285). GAO, Forest Service: Information on Appeals and Litigation Involving Fuels Reduction Activities, GAO-04-52, October, 2003, https://www.gao.gov/assets/250/240305.pdf. An earlier GAO report found that through July 2001, 20 (1%) of the 1,671 hazardous fuel reductions projects identified for implementation for FY2001 were challenged. GAO, Forest Service: Appeals and Litigation of Fuel Reduction Projects, GAO-01-1114R, August 31, 2001, https://www.gao.gov/products/GAO-01-1114R. |
| 95. |
The report found that from FY2006 through FY2008, FS issued 1,312 decisions involving fuel reduction activities that were subject to appeal or objections, and 266 of those decisions were challenged. An additional 103 decisions were not subject to appeal or objections. Of the total 1,312 decisions, 29 (2%) were litigated in court. Some of the differences between the report findings may be attributable to the lack of a uniform definition for "hazardous fuels reduction projects." GAO, Forest Service: Information on Appeals, Objections, and Litigation Involving Fuel Reduction Activities, Fiscal Years 2006 through 2008, GAO-10-337, March 4, 2010, https://www.gao.gov/products/GAO-10-337. |
| 96. |
For a review of 27 studies examining various aspects of FS NEPA implementation, see Bixler et al., 2016. |
| 97. |
For more information, see CRS Report R45696, Forest Management Provisions Enacted in the 115th Congress, by Katie Hoover et al. |
| 98. |
The FS has received additional discretionary monies through supplemental appropriations bills. In addition, Congress has used continuing appropriations resolutions to maintain funding for the agency when regular appropriations bills have not been enacted before the start of the fiscal year and, in some cases, to provide full-year funding. For more information, see CRS In Focus IF11169, Forest Service: FY2019 Appropriations and FY2020 Request, and CRS Report R44934, Interior, Environment, and Related Agencies: Overview of FY2019 Appropriations. |
| 99. |
FS discretionary figures for FY2019 reflect $854.3 million in supplemental appropriations provided through the Additional Supplemental Appropriations for Disaster Relief Act, 2019 (P.L. 116-20). Discretionary figures are from detailed funding tables prepared by the House Committee on Appropriations. Estimated mandatory figures were derived from the FS FY2020 Budget Justification and are subject to change. |
| 100. |
The other main FS discretionary accounts include Forest and Rangeland Research, State and Private Forestry, Capital Improvement and Maintenance, Land Acquisition, Wildland Fire Management, and several other relatively smaller accounts. |
| 101. |
The $1.94 billion was provided through the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2019 (P.L. 116-6) and the $85.0 million was provided through the Additional Supplemental Appropriations for Disaster Relief Act, 2019 (P.L. 116-20). The supplemental funds were designated as emergency spending. FY2019 funding was also provided through two continuing resolutions because P.L. 116-6 was not enacted until February 15, 2019, and there was a lapse in appropriations and partial government shutdown from December 22, 2018, through January 25, 2019. |
| 102. |
This list reflects the main subaccounts as of the FY2019 appropriation. Because Congress has restructured the NFS subaccounts in the past and may do so in the future, this list may or may not reflect the same subaccounts in future appropriations. |
| 103. |
Rescissions Act of 1995, P.L. 104-14 §504. |
| 104. |
The Collaborative Forest Landscape Restoration Program was first authorized in FY2009, and was authorized to receive $40.0 million annually, subject to appropriations (P.L. 111-11, Title IV). The program was extended through FY2023 and the authorization was increased to $80.0 million annually, subject to appropriations (P.L. 115-334, Title VII, §8629). |
| 105. |
Suppression activities were also previously funded through a separate account, the FLAME Wildfire Suppression Reserve Fund, but no appropriations were provided in FY2019. The FLAME Suppression Reserve Fund was established by the Federal Land Assistance, Management, and Enhancement Act of 2009 (P.L. 111-88, 43 U.S.C. §1748a). The authorization specifies that the account will be terminated after three consecutive years without an appropriation or obligation. |
| 106. |
Transfer authority is granted in the Interior, Environment, and Related Agencies annual appropriations bill, specifically in the administrative provisions for the FS. The accounts from which funds were transferred have historically been reimbursed in the following year's appropriations act. |
| 107. |
P.L. 112-25. For more information on discretionary spending limits, see CRS Report R41965, The Budget Control Act of 2011, by Bill Heniff Jr., Elizabeth Rybicki, and Shannon M. Mahan. |
| 108. |
P.L. 115-141, Division O, §102(a), 2 U.S.C. §901(b)(2)(f). For more information, see CRS Report R45696, Forest Management Provisions Enacted in the 115th Congress, by Katie Hoover et al., pp. 20-21, or CRS Report R45778, Exceptions to the Budget Control Act's Discretionary Spending Limits, by Megan S. Lynch. |
| 109. |
For more comprehensive information on the authority of the FS and the other federal land management agencies to acquire or dispose of lands, see CRS Report RL34273, Federal Land Ownership: Acquisition and Disposal Authorities, by Carol Hardy Vincent et al. |
| 110. |
16 U.S.C. §471, now repealed. |
| 111. |
Act of March 1, 1911, P.L. 61-435 as amended; 16 U.S.C. §§515 et seq. |
| 112. |
P.L. 75-210, 7 U.S.C. §1010. |
| 113. |
FLPMA, 43 U.S.C. §1715(a). |
| 114. |
16 U.S.C. §516. |
| 115. |
16 U.S.C. §§479a, 521. |
| 116. | U.S. Congress, House Committee on Interior and Insular Affairs, Multiple Use and Sustained Yield: Changing Philosophies for Federal Land Management, the proceedings and summary of a workshop convened in March 1992, prepared by Congressional Research Service, |
| 117. |
163 For example, Congress has established several Special Management Areas in the NFS with specified uses. See CRS Report R41285, Congressionally Designated Special Management Areas in the National Forest System |
| 118. | .
164 See for example, H.R. 2613 from the |