The Defense Budget and the Budget Control Act: Frequently Asked Questions
Changes from July 13, 2018 to September 27, 2019
This page shows textual changes in the document between the two versions indicated in the dates above. Textual matter removed in the later version is indicated with red strikethrough and textual matter added in the later version is indicated with blue.
The Defense Budget and the Budget Control
Act: Frequently Asked Questions
Updated September 27, 2019
Congressional Research Service
https://crsreports.congress.gov
R44039
The Defense Budget and the Budget Control Act: Frequently Asked Questions
Summary
Act: Frequently Asked Questions
Contents
- Background
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the debate over defense spending caps?
- How does the BCA affect defense spending?
- What are the BCA limits on defense discretionary spending?
- Does the BCA limit Overseas Contingency Operations (OCO) funding?
- What are the BCA limits on the Department of Defense (DOD)?
- How have the defense spending caps changed over time?
- What is a sequester?
- Can the National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) trigger a sequester?
- How has defense discretionary spending changed since enactment of the BCA?
- What are the Administration's plans for defense spending?
- Acknowledgements
Figures
Summary
Enacted on August 2, 2011, the Budget Control Act of 2011 as amended (P.L. 112-25, P.L. 112-240, , P.L. 112240, P.L. 113-67, , P.L. 114-74, P.L. 115-123, and P.L. 115-123116-37) sets limits on defense and
nondefense discretionary spending. As part of an agreement to increase the statutory limit on
public debt, the BCA aimed to reduce annual federal budget deficits by a total of at least $2.1
trillion from FY2012 through FY2021, with approximately half of the savings to come from
defense.
The spending limits (or capscaps) apply separately to defense and nondefense discretionary budget authoritybudget
authority. Budget authority is authority provided by law to a federal agency to obligate money for goods
and services. The caps are enforced by a mechanism called sequestrationsequestration. Sequestration
automatically cancels previously enacted appropriations (a form of budget authority) by an
amount necessary to reach prespecified levels. The defense spending limits apply to national
defense (budget function 050) but not to funding designated for Overseas Contingency
Operations (OCO) or emergencies.
as emergency requirements.
Some defense policymakers and officials argue the BCA spending restrictions impede the
Department of Defense'’s (DOD'’s) ability to adequately prepareresource military personnel and
equipment for operations and other national security requirements. Others argue the limits are
necessary to curb rising deficits and debt.
After lawmakers did not reach a deficit-reduction deal and triggered steeper reductions to the initial BCA caps, Congress repeatedly amended the legislation to raise the spending limits. Most recently, President Donald Trump on February 9, 2018, signed into law the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018 (P.L. 115-123). The bill amended the BCA to increase discretionary defense spending caps by the largest amounts to date—by $80 billion to $629 billion in FY2018 and by $85 billion to $647 billion in FY2019. It did not change the spending limits for FY2020 and FY2021.
The annual federal budget deficit decreased from $1.1 trillion (6.8% of Gross Domestic Product) in FY2012 to $665 billion (3.5% of GDP) in FY2017, but is projected to increase to $1.1 trillion (4.9% of GDP) in FY2021. Meanwhile, federal debt held by the public has increased from $11.3 trillion (70.4% of GDP) in FY2012 to $14.7 trillion (76.5% of GDP) in FY2017, and is projected to further increase to $19 trillion (83.1
Congress has repeatedly amended the legislation to raise the spending limits with two-year
budget agreements. Most recently, on August 2, 2019, President Donald Trump signed into law
the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2019 (BBA 2019; P.L. 116-37). The bill amended the BCA to
increase defense discretionary spending caps by the largest amount to date—by $90.3 billion, to
$666.5 billion in FY2020; and by $81.3 billion, to $671.5 billion in FY2021. BBA 2019 also
specified nonbinding Overseas Contingency Operations/Global War on Terrorism (OCO/GWOT)
defense funding targets of $71.5 billion for FY2020 and $69 billion for FY2021.
The annual federal budget deficit decreased from $1.1 trillion (6.7% of Gross Domestic Product)
in FY2012 to $779 billion (3.9% of GDP) in FY2018, but is projected to increase to $1 trillion
(4.5% of GDP) in FY2021. Meanwhile, federal debt held by the public has increased from $11.3
trillion (70.3% of GDP) in FY2012 to $15.7 trillion (77.8% of GDP) in FY2018, and is projected
to further increase to $18.8 trillion (82.4% of GDP) in FY2021.
Congressional Research Service
The Defense Budget and the Budget Control Act: Frequently Asked Questions
Contents
Background ..................................................................................................................................... 1
Frequently Asked Questions ............................................................................................................ 3
What is the debate over defense spending caps? ....................................................................... 3
How does the BCA affect defense spending? ........................................................................... 4
What are the BCA limits on defense discretionary spending? .................................................. 5
How did the Bipartisan Budget of Act of 2019 change BCA defense caps? ............................. 6
Does the BCA limit Overseas Contingency Operations (OCO) funding? ................................ 6
How have the defense spending caps changed over time? ........................................................ 7
What is sequestration?............................................................................................................... 9
Do BCA caps apply to the Department of Defense (DOD)? ..................................................... 9
Can the National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) trigger sequestration?.......................... 9
How has defense discretionary spending changed since enactment of the BCA? .................. 10
Figures
Figure 1. Outlays by Budget Enforcement Act Category, FY2001-FY2024 ................................... 2
Figure 2. Changes to BCA Limits on National Defense (050) Discretionary Budget
Authority, FY2012-FY2021 ......................................................................................................... 8
Figure 3. National Defense (050) Discretionary Outlays, FY1962-FY2024.................................. 11
Tables
Table 1. BCA Limits on National Defense (050) Discretionary Base Budget Authority ................ 5
Table 2. BBA 2019 OCO Spending Targets .................................................................................... 7
Contacts
Author Information........................................................................................................................ 13
Acknowledgments ......................................................................................................................... 13
Congressional Research Service
The Defense Budget and the Budget Control Act: Frequently Asked Questions
Background
% of GDP) in FY2021.
Background
National defense is one of 20 major functions used by the Office of Management and Budget
(OMB) to organize budget data―and the largest in terms of discretionary spending. The national
defense budget function (identified by the numerical notation 050) comprises three subfunctions:
Department of Defense (DOD)-Military (051); atomic energy defense activities primarily of the
Department of Energy (DOE) (053); and other defense-related activities (054) such as Federal
Bureau of Investigation (FBI) counterintelligence activities.11 Discretionary spending is, for the
most part, provided by annual appropriations bills and the focus of Congress'’s efforts to fund the
federal government. By contrast, mandatory (or direct) spending, which includes entitlement
programs such as Social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid, is generally governed by existing
statutory criteria.2
2
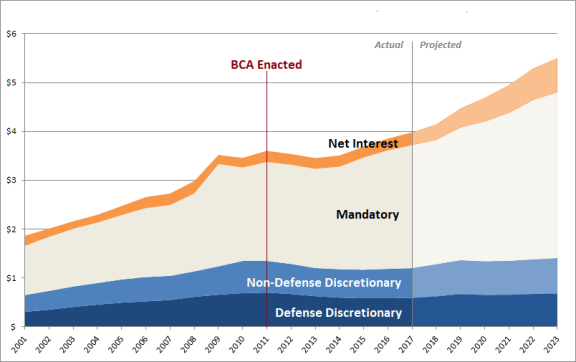
Since the terrorist attacks of September 11, 2001, outlaysoutlays—money spent by a federal agency from
funds provided by Congress—for discretionary defense defense discretionary programs in nominal dollars (not adjusted
for inflation) has almosthave more than doubled from $306 billion in FY2001 to $590623 billion in FY2017. FY2018.3
Defense discretionary outlays are projected to reach $655721 billion in FY2021.4 Yet as a percentage
of total federal outlays, discretionary defensefederal outlays, defense discretionary outlays declined over this period from 16.4% in
FY2001 to 14.8% in FY201715.2% in FY2018. They are projected to further decrease to 13.214.9% in FY2021, as
mandatory programs and net interest consume a larger share of the total (see Figure 1).3
).5
Between FY2009 and FY2012, annual federal budget deficits topped $1 trillion and averaged 8.5. In FY2009, the
deficit reached 9.8% of Gross Domestic Product (GDP), the highest level since World War II. 6
The deficits arewere attributable in part to reduced tax revenues from the 2007-2009 recession and
increased spending from the economic stimulus package known as the American Recovery and
Reinvestment Act of 2009 (P.L. 111-5).4).7 As part of an agreement to increase the statutory limit on
public debt, the Budget Control Act of 2011 (P.L. 112-25) aimed to reduce annual federal budget
deficits by a total of at least $2.1 trillion from FY2012 through FY2021, with approximately half
of the savings to come from defense.
Congress has previously used budget enforcement mechanisms—such as a statutory limit on
annual appropriations for discretionary activities—to mandate a specific budgetary policy or to obtain a fiscal objective. The BCA amended the Balanced Budget and Emergency Deficit Control Act of 1985 (P.L. 99-177
1
See CRS In Focus IF10618, Defense Primer: The National Defense Budget Function (050), by Christopher T. Mann.
See CRS Report 98-721, Introduction to the Federal Budget Process, coordinated by James V. Saturno.
3 Office of Management and Budget, Historical Tables, Table 8.7, Outlays for Discretionary Programs: 1962-2024, at
https://www.whitehouse.gov/omb/historical-tables/.
4 Congressional Budget Office, 10-Year Budget Projections, Table 1-5, CBO’s Baseline Projections of Discretionary
Spending, Adjusted to Exclude the Effects of Timing Shifts, August 2019, at https://www.cbo.gov/about/products/
budget-economic-data#3.
5 Office of Management and Budget, Historical Tables, Table 8.1, Outlays by Budget Enforcement Act Category:
1962-2024, at https://www.whitehouse.gov/omb/historical-tables/; and Congressional Budget Office, 10-Year Budget
Projections, Table 1-1, CBO’s Baseline Budget Projections, by Category, and Table 1-5, CBO’s Baseline Projections of
Discretionary Spending, Adjusted to Exclude the Effects of Timing Shifts, August 2019, at https://www.cbo.gov/about/
products/budget-economic-data#3. For more information on mandatory spending trends, see CRS Report R44763,
Present Trends and the Evolution of Mandatory Spending, by D. Andrew Austin.
6 Office of Management and Budget, Historical Tables, Table 1.3, Summary of Receipts, Outlays, and Surpluses or
Deficits (-) in Current Dollars, Constant (FY 2012) Dollars, and as Percentages of GDP: 1940-2024, at
https://www.whitehouse.gov/omb/historical-tables/.
7 CRS Report R44874, The Budget Control Act: Frequently Asked Questions, by Grant A. Driessen and Megan S.
Lynch.
2
Congressional Research Service
1
The Defense Budget and the Budget Control Act: Frequently Asked Questions
obtain a fiscal objective. The BCA amended the Balanced Budget and Emergency Deficit Control
Act of 1985 (P.L. 99-177) by reinstating spending limits on discretionary budget authority
beginning in FY2012.58 Congress provides budget authority by law to federal agencies to obligate
money for goods and services. Congress does not directly control outlaysoutlays, which occur when
obligations are liquidated, primarily through issuing checks, transferring funds, or disbursing
cash.69 For spending limits in FY2012 and FY2013, the BCA originally specified separate "security" and "nonsecurity"
“security” and “nonsecurity” categories. The security category was broad in scope and included
budget accounts of the Department of Defense (DOD), the Department of Homeland Security
(DHS), the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), the National Nuclear Security Administration,
the intelligence community management account, and international affairs (budget function
150).710 After the Joint Select Committee on Deficit Reduction did not reach a deficit-reduction
deal and triggered backup budgetary enforcement measures of steeper reductions to the initial
BCA caps beginning in FY2013, the "security"“security” category was revised to the narrower "defense" “defense”
category, which included only discretionary programs in the national defense budget function
(050).
(050).
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions What is the debate over defense spending caps?
The discretionary spending limits established by the Budget Control Act of 2011 (P.L. 112-25) )
have been a point of contention since enactment.
Critics of the legislation argue reductions to defense investments "“present a grave and growing
danger to our national security."8”11 They also note the spending restrictions disproportionately
affect defense programs, which in FY2017 accounted for 16% of budgetary resources (excluding
net interest payments) and 49% of BCA spending reductions.912 The late Senator John McCain and
Representative William "Mac"Mac Thornberry, the former chairs of the Senate and House Armed Services
Committees, respectively, have said the law has "“failed."10 Defense Secretary James Mattis has said: "Let me be ”13 In 2019, Representative Adam Smith,
chairman of HASC, introduced the Relief from Sequestration Act of 2019 (H.R. 2110) “to repeal
the automatic cuts in both discretionary and mandatory spending triggered by the 2011 Budget
Control Act’s sequestration.”14 Former Defense Secretary James Mattis has said: “Let me be
clear: As hard as the last 16 years of war have been on our military, no enemy in the field has
done as much to harm the readiness of U.S. military than the combined impact of the BCA's ’s
defense spending caps, worsened by operating for ten10 of the last 11 years under continuing
resolutions of varied and unpredictable duration."
”
Proponents of BCA argue its limits are necessary in light of recurring deficits and growing federal debt: "The spending caps put in place by the BCA, and the punitive nature of the sequestering that follows if they are exceeded, are well-designed measures that encourage responsible spending."11 Representative Mark Meadows, chair of the House Freedom Caucus, which opposed the latest budget deal to raise the spending caps, said, "I want to fund our military, but at what cost? Should we bankrupt our country in the process?"12 Lawrence Korb, an Assistant Secretary of Defense during the Reagan Administration, said the BCA has "affected defense capability somewhat," but noted Congress has blunted the law's impact by increasing the caps and by exempting from the restrictions funding for Overseas Contingency Operations (OCO), allowing the Department of Defense (DOD) to use such funds for base-budget activities.13
debt.15 Representative Mark Meadows, a former chairman of the House Freedom Caucus who has
repeatedly opposed budget deals to raise the spending caps, has said, “I want to fund our military,
but at what cost? Should we bankrupt our country in the process?”16 Lawrence Korb, an assistant
secretary of defense during the Reagan Administration, said the BCA has “affected defense
11
Open letter from eighty-five national security experts and former government officials: Elliot Abrams, David
Adesnik, and Michael Auslin, et al. to John Boehner, then-speaker of the House, and Mitch McConnell, Senate
Majority Leader, et al., February 24, 2015. Document on file with the author.
12 Frederico Bartels, “America’s defense budget is yet again held hostage by Congress,” The Hill, November 2, 2017, at
http://thehill.com/opinion/national-security/358385-congress-needs-to-do-its-job-and-properly-fund-americas-defense.
13 Former Sen. John McCain, “Restoring American Power: Recommendations for the FY2018-FY2022 Defense
Budget,” white paper, January 16, 2017; and Ben Werner, “Thornberry: Budget Control Act Limits on Defense
Spending Could End Soon,” USNI News, September 6, 2017, at https://news.usni.org/2017/09/06/thornberry-budgetcontrol-act-limits-defense-spending-end-soon.
14 The legislation was introduced and referred to the House Budget Committee on April 4, 2019. See also Adam Smith,
“Chairman Smith Reintroduces Legislation to End Sequestration,” press release, April 4, 2019, at
https://adamsmith.house.gov/2019/4/chairman-smith-reintroduces-legislation-to-end-sequestration. For more on
sequestration, see the “What is sequestration?” section later in this report.
15 See, for example, Michael Shindler, “Don’t Let Defense Wreck the Budget,” Real Clear Defense, February 23, 2017,
at https://www.realcleardefense.com/articles/2017/02/23/dont_let_defense_wreck_the_budget_110857.html. For more
information on deficits and debt, see CRS Report R44383, Deficits, Debt, and the Economy: An Introduction, by Grant
A. Driessen.
16 Rep. Mark Meadows, “Rep. Meadows’ Statement on Budget Agreement,” press release, February 9, 2018, at
https://meadows.house.gov/news/documentsingle.aspx?DocumentID=815. Final House roll call vote results for the
Bipartisan Budget Act of 2019 at http://clerk.house.gov/evs/2019/roll511.xml.
Congressional Research Service
3
The Defense Budget and the Budget Control Act: Frequently Asked Questions
capability somewhat,” but noted Congress has blunted the law’s impact by increasing the caps
and by exempting from the restrictions funding for Overseas Contingency Operations (OCO),
allowing the Department of Defense (DOD) to use such funds for regular, or base, budget
activities.17
Attempts to fully repeal BCA have not succeeded.18Attempts to fully repeal BCA have not succeeded.14 Lawmakers have enacted increases to the
defense and nondefense sending caps for each year from FY2013 to FY2019.15
-FY2021.19 How does the BCA affect defense spending?
The Budget Control Act of 2011 (P.L. 112-25) contained several measures intended to reduce
deficits by a total of at least $2.1 trillion from FY2012 to FY2021, with approximately half of the
savings to come from defense.1620 A key component of the legislation set limits on discretionary
budget authority to reduce projected spending by $0.9 trillion over the period. As backup
budgetary enforcement measures, the BCA also required at least $1.2 trillion in additional savings
if a congressionally mandated panel, the Joint Select Committee on Deficit Reduction, did not
reach agreement on a deficit-reduction plan. The spending limits (or capscaps) apply separately to
defense and nondefense discretionary budget authority.1721 The caps are enforced by a mechanism
called sequestrationcalled sequestration, which automatically cancels previously enacted spending by an amount
necessary to reach prespecified levels.1822 The defense discretionary spending limits apply to
national defense (budget function 050) but not to funding designated for Overseas Contingency Operations (OCO) or emergencies.19 Because the committee
Operations/Global War on Terrorism (OCO/GWOT) or as emergency requirements.23 Because the
Committee did not agree on a plan to reduce the deficit, the BCA required steeper reductions to
the discretionary spending limits each year from FY2013 through FY2021 (see Table 1).20
).24
Lawrence J. Korb, “Trump’s Defense Budget,” Center for American Progress, February 28, 2018, at
https://www.americanprogress.org/issues/security/news/2018/02/28/447248/trumps-defense-budget/.
18 Rep. Mike Turner, “Trump Calls for Repeal of Sequestration; Turner: Repeal Gains Groundswell of Support,” press
release, March 1, 2017, https://turner.house.gov/media-center/press-releases/trump-calls-for-repeal-of-sequestrationturner-repeal-gains-groundswell.
19 The BCA was amended by the American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012 (ATRA; P.L. 112-240), the Bipartisan Budget
Act of 2013 (BBA 2013; P.L. 113-67, referred to as the Murray-Ryan agreement), the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2015
(BBA 2015; P.L. 114-74), the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018 (BBA 2018; P.L. 115-123), and the Bipartisan Budget
Act of 2019 (BBA 2019; P.L. 116-37). For more information, see CRS Insight IN11148, The Bipartisan Budget Act of
2019: Changes to the BCA and Debt Limit, by Grant A. Driessen and Megan S. Lynch.
20 Congressional Budget Office, Letter from then-Director Douglas W. Elmendorf to then-Speaker of the House John
Boehner and then-Majority Leader of the Senate Harry Reid, “CBO Estimate of the Impact on the Deficit of the Budget
Control Act of 2011,” August 1, 2011, at http://www.cbo.gov/sites/default/files/cbofiles/ftpdocs/123xx/doc12357/
budgetcontrolactaug1.pdf.
21 Legislation amending the BCA included equal increases to defense and nondefense discretionary spending caps until
the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018 (P.L. 115-123), which included a larger increase to defense than nondefense. For
more on the so-called parity principle, see CRS In Focus IF10657, Budgetary Effects of the BCA as Amended: The
“Parity Principle”, by Grant A. Driessen. For more on the “security” category that predated the “defense” category,
see the “Background” section above.
22 For more information on sequestration, see CRS Report R42972, Sequestration as a Budget Enforcement Process:
Frequently Asked Questions, by Megan S. Lynch.
23 For more information on the national defense budget function, see the “Background” section above. For more
information on OCO, see CRS Report R44519, Overseas Contingency Operations Funding: Background and Status, by
Brendan W. McGarry and Emily M. Morgenstern.
24 These automatic reductions to the original BCA limits are often referred to as sequestration but technically are not
because Congress can allocate funding within the caps.
17
Congressional Research Service
4
The Defense Budget and the Budget Control Act: Frequently Asked Questions
What are the BCA limits on defense discretionary spending?
What are the BCA limits on defense discretionary spending?
Congress has repeatedly amended the Budget Control Act of 2011 (P.L. 112-25)) to revise the
discretionary spending limits.21 Table 1 depicts the limits , mostly recently with the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2019 (P.L. 11637).25 Table 1 depicts the limits as amended (in bold and shaded) for the defense category, which
includes discretionary programs of the national defense budget function (050) and excludes
funding for Overseas Contingency Operations (OCO) or emergencies.22
(OCO), emergencies, and certain other activities.26 Table 1. BCA Limits on National Defense (050) Discretionary Base Budget Authority
(in billions of dollars)
National Defense |
2012 |
2013 |
2014 |
2015 |
2016 |
2017 |
2018 |
2019 |
2020 |
2021 |
||||||||||
|
Budget Control Act of 2011 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||
|
BCA after automatic revision |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||
|
American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||
|
Bipartisan Budget Act of 2013 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||
|
Bipartisan Budget Act of 2015 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||
|
Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sources: CBORelief Act of 2012
555
518
497
511
522
535
548
561
575
589
Bipartisan Budget Act of
2013
555
518
520
521
523
536
549
562
576
590
Bipartisan Budget Act of
2015
555
518
520
521
548
551
549
562
576
590
Bipartisan Budget Act of
2018
555
518
520
521
548
551
629
647
576
590
555
518
520
521
548
551
629
647
667
672
Bipartisan Budget Act of
2019
Sources: Congressional Budget Office, letter to the Honorable John A. Boehner and Honorable Harry Reid
estimating the impact on the deficit of the Budget Control Act of 2011, August 2011; CBO, Final Sequestration
Report for Fiscal Year 2012, January 2012; CBO, Final Sequestration Report for Fiscal Year 2013, March 2013; CBO,
Final Sequestration Report for Fiscal Year 2014, January 2014; CBO, Final Sequestration Report for Fiscal Year 2016, ,
December 2015, CBO, Sequestration Update Report: August 2017, August 2017; CBO, Cost Estimate for Bipartisan
Budget Act of 2018, February 2018.
, CBO, Sequestration Update Report: August 2019; P.L. 116-37.
Notes: Bold and shaded figures indicate statutory changes. Figures do not include funding for Overseas
Contingency Operations (OCO), emergencies, or disaster reliefand certain other activities. The BCA as amended provided for "security" and "nonsecurity"
“security” and “nonsecurity” categories in FY2012 and FY2013: italicized figures denote CRS estimates of budget
authority for defense and nondefense categories in those years. Small changes in budget authority beginning in
FY2016 are caused by adjustments in the annual proportional allocations of automatic enforcement measures as
calculated by OMB: for more information on these adjustments, see CBO, Estimated Impact of Automatic Budget
Enforcement Procedures Specified in the Budget Control Act, September 2011. This table is an abridged version of
one that originally appeared in CRS Report R44874, The Budget Control Act: Frequently Asked Questions, by [author name scrubbed] and [author name scrubbed].
Does the BCA limit Overseas Contingency Operations (OCO) funding?
The BCA stipulates that certain discretionary funding, such as appropriations designated as Overseas Contingency Operations (OCO) or emergency requirements, allow for an upward adjustment of the discretionary limits. OCO funding is therefore described as "exempt" from the discretionary spending limits. The BCA does not define what constitutes OCO funding. Instead, it includes a requirement that Congress designate OCO spending on an account-by-account basis, and that the President subsequently designate the spending as such. Further, the BCA does not limit the level or amount of spending that may be designated as OCO.23
The designation of funding for OCO/Global War on Terrorism (GWOT) has shifted over time, reflecting different viewpoints about the extent, nature, and duration of conflicts in countries such as Afghanistan, Iraq, and Syria.24 Recently, Congress and the President , by Grant
A. Driessen and Megan S. Lynch.
25
The BCA was amended by the American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012 (ATRA; P.L. 112-240), the Bipartisan Budget
Act of 2013 (BBA 2013; P.L. 113-67, referred to as the Murray-Ryan agreement), the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2015
(BBA 2015; P.L. 114-74), the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018 (BBA 2018; P.L. 115-123), and the Bipartisan Budget
Act of 2019 (BBA 2019; P.L. 116-37).
26 For more on the “security” category that predated the “defense” category, see the “Background” section above.
Congressional Research Service
5
The Defense Budget and the Budget Control Act: Frequently Asked Questions
How did the Bipartisan Budget of Act of 2019 change BCA defense
caps?
On August 2, 2019, President Trump signed the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2019 (BBA 2019; P.L.
116-37). BBA 2019 raised discretionary spending limits set by the BCA for FY2020 and
FY2021—the final two years the BCA discretionary caps are in effect. The act also extended
mandatory spending reductions through FY2029 and suspended the statutory debt limit until
August 1, 2021.27
BBA 2019 raised the federal government’s discretionary spending limits, as set by the BCA, from
$1.119 trillion for FY2020 and $1.145 trillion for FY2021 to $1.288 trillion for FY2020 and to
$1.298 trillion for FY2021. The act increased FY2020 defense discretionary funding levels
(excluding OCO) by the largest amount to date—$90.3 billion in FY2020, from $576.2 billion to
$666.5 billion—and nondefense funding by $78.3 billion, from $543.2 billion to $621.5 billion.
The FY2021 adjustments are slightly lower, with an increase of $81.3 billion in defense
discretionary funding, from $590.2 billion to $671.5 billion, and an increase of $71.6 billion for
nondefense funding, from $554.9 billion to $626.5 billion.
Does the BCA limit Overseas Contingency Operations (OCO)
funding?
The BCA stipulates that certain discretionary funding, such as appropriations designated for
Overseas Contingency Operations/Global War on Terrorism (OCO/GWOT) or as emergency
requirements, allow for an upward adjustment of the discretionary limits. OCO funding is
therefore described as “exempt” from the discretionary spending limits. The BCA does not define
what constitutes OCO funding. Instead, the BCA includes a requirement that Congress designate
OCO spending on an account-by-account basis, and that the President subsequently designate the
spending as such. Further, the BCA does not limit the level or amount of spending that may be
designated for OCO.28
Debate over what should constitute OCO or emergency activities and expenses has shifted over
time, reflecting differing viewpoints about the extent, nature, and duration of U.S. military
operations in Afghanistan, Iraq, Syria, and elsewhere.29 Recently, Congress and the President
have designated funding for OCO that includes activities previously in the DOD base budget.25regular, or base, DOD
budget.30 By designating OCO funding for ongoing activities not directly related to contingency operations as OCO
operations, Congress and the President can effectively increase topline defense, foreign affairs,
and other related discretionary spending, without triggering sequestration.31
27
For more information on the BBA 2019, see CRS Insight IN11148, The Bipartisan Budget Act of 2019: Changes to
the BCA and Debt Limit, by Grant A. Driessen and Megan S. Lynch.
28
The Bipartisan Budget Act of 2015 (P.L. 114-74) established non-binding targets for OCO spending in FY2016 and
FY2017.
29 For more information on OCO funding, see CRS Report R44519, Overseas Contingency Operations Funding:
Background and Status, by Brendan W. McGarry and Emily M. Morgenstern.
30 The term base budget is generally used to refer to funding for planned or regularly occurring costs to man, train and
equip the military. This is used in contrast to amounts needed to fund contingency operations or DOD response to
emergencies or disaster relief.
Section 1501 of the National Defense Authorization Act for FY2017 (P.L. 114-328) stipulates that certain
amounts designated as OCO are to be used for base budget requirements. Such amounts would not be counted against
31
Congressional Research Service
6
The Defense Budget and the Budget Control Act: Frequently Asked Questions
Like the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2015 (BBA 2015; P.L. 114-74), BBA 2019 also established
targets for OCO/GWOT funding for the next two fiscal years.32 BBA 2019 set the defense
OCO/GWOT target at $71.5 billion for FY2020 and $69 billion for FY2021, and the nondefense
OCO/GWOT target at $8 billion for both FY2020 and FY2021.33 (See Table 2.)
Table 2. BBA 2019 OCO Spending Targets
(in millions of dollars of budget authority)
Category
FY2020
FY2021
Defense
71,500
69,000
Nondefense
8,000
8,000
79,500
77,000
Total
Source: Bipartisan Budget Act of 2019 (BBA 2019; P.L. 116-37).
How have the defense spending caps changed over time?
and other related discretionary spending, without triggering sequestration.26
The Trump Administration's initial FY2019 DOD budget request, released on February 12, 2018, included $89.0 billion designated for OCO. In a budget amendment published April 13, 2018, the Administration removed the OCO designation from $20.0 billion of funding in the initial request, in effect, shifting that amount into the base budget request after Congress agreed to raise the spending caps. In a statement on the budget amendment, White House Office of Management and Budget Director Mick Mulvaney said the FY2019 budget request fixes "long-time budget gimmicks" in which OCO funding has been used for base budget requirements. Beginning in FY2020, "the Administration proposes returning to OCO's original purpose by shifting certain costs funded in OCO to the base budget where they belong," he wrote.27
What are the BCA limits on the Department of Defense (DOD)?
Department of Defense (DOD)-Military activities (budget subfunction 051) historically constitute approximately 95% of the national defense budget (function 050).28 Although the BCA does not establish limits on subfunctions (051, 053 and 054), the BCA limits on national defense have, in practice, been proportionally applied to subfunctions. CRS estimates the BCA limits on DOD-Military base budget activities at approximately $600 billion in FY2018, $617 billion in FY2019, $549 billion in FY2020, and $564 billion in FY2021.
How have the defense spending caps changed over time?
The Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018 (P.L. 115-123), enacted on February 9, 2018, amended the BCA to raise defense discretionary spending caps for FY2018 and FY2019, with increases more than three times larger than previous changes (see Figure 2). To date, CRS estimates Congress has amended the Budget Control Act of 2011 (P.L. 112-25)) to
increase discretionary defensedefense discretionary spending limits by a total of $264approximately $435 billion (thus
lowering their deficit-reduction effect by a corresponding amount). The increases over previous
caps break down as follows:
$85 $26 billion (155%) in FY2013; $23 billion (5%) in FY2014; $10 billion (2%) in FY2015; $25%) in FY2019;$80billion (155%) in FY2016;%) in FY2018;- $15 billion (3%) in FY2017;
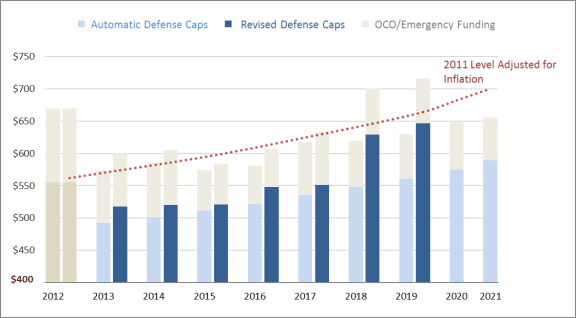
$25$80 billion (515%) in FY2018; $85%) in FY2016;$10billion (215%) in FY2019; $90%) in FY2015;$23billion (516%) inFY2014FY2020; and $81; and$26billion (514%) in FY2021.34 the BCA limits. See also OMB, “Presidential Designation of Funding as an Emergency Requirement: Multiple Accounts in the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2017, for the Department of Agriculture, Department of Homeland Security, Department of Housing and Urban Development, Department of the Interior, Department of Transportation, and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration,” press release, May 2017, at https://www.whitehouse.gov/sites/whitehouse.gov/files/omb/budget/amendments/ Emergency%20Funding%20Transmittal%20Package%205.5.17.pdf. 32 In FY2017, OCO funding for defense and nondefense exceeded the targets set in BBA 2015. See P.L. 114-74 and Office of Management and Budget, OMB Sequestration Update Report to the President and Congress for Fiscal Year 2020, August 20, 2019, at https://www.whitehouse.gov/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/ Sequestration_Update_August_2019.pdf. 33 In the Senate, the use of the OCO/GWOT designation for funds appropriated for FY2020 and FY2021 may be subject to a point of order under section 208 of the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2019 (BBA 2019; P.L. 116-37). If the point of order were made, it would require a vote of three-fifths of all Senators to retain the designation. For more information, see CRS Report R42388, The Congressional Appropriations Process: An Introduction, coordinated by James V. Saturno. 34 This figure is based on a CRS estimate of changes to the defense category. The BCA initially provided for “security” and “nonsecurity” categories. See notes to Table 1 and the Background section. Congressional Research Service 7 The Defense Budget and the Budget Control Act: Frequently Asked Questions%) in FY2013.29
Figure 2. Changes to BCA Limits on National Defense (050) Discretionary Budget
|
 |
|
), and Bipartisan Budget Act of 2019 (BBA 2019; P.L. 116-37. OCO funding reflects
DOD levels and does not include appropriations for hurricane relief, avian flu and Ebola assistance, Iron Dome,
missile defeat, and other purposes. CBO baseline excludes funding for operations in Afghanistan and Iraq and for
similar activities.
In 2011, the Congressional Budget Office (CBO) estimated discretionary budget authority for the
national defense budget function (050), excluding funding for Overseas Contingency Operations
(OCO), would total $6.26 trillion over the 10-year period from FY2012 through FY2021,
assuming the 2011 level would grow at the rate of inflation (see Figure 2).30).35 Based on this benchmark, level,
CRS estimates the automatic reductions to the initial caps of the BCA would have decreased projected discretionary defensedefense discretionary base budget
authority by approximately $868 billion0.86 trillion (14%) to $5.39 trillion over the decade—and the caps as
amended would reduce projected defense discretionary base budget authority by approximately $604 billion (10%) to $5.65 trillion over the period.31
What is a sequester?
A sequester provides for the enforcement of budgetary limits established in law through the automatic cancellation of previously enacted spending, making largely across-the-board reductions to nonexempt programs, activities, and accounts. A sequester is implemented through a sequestration order issued by the President as required by law. The purpose of sequestration is to deter enactment of legislation violating the spending limits or, in the event that such legislation is enacted violating these spending limits, to automatically reduce spending to the limits specified in law. Each statutory limit—defense and nondefense—is separately enforced so that the breach of
$0.43 trillion (7%) to $5.83 trillion over the period.36 Note, however, that these figures do not
35
Congressional Budget Office, The Budget and Economic Outlook: An Update, Table 1-6, Illustrative Paths for
Discretionary Budget Authority Subject to the Caps Set in the Budget Control Act of 2011, August 2011. Document on
file with the author.
36 These take into account the small changes in budget authority caused by adjustments in the annual proportional
Congressional Research Service
8
The Defense Budget and the Budget Control Act: Frequently Asked Questions
take into account funding for OCO, emergencies, and certain other activities. Defense OCO
funding is projected at approximately $0.77 trillion over the same period, and DOD has
acknowledged using OCO funding for base budget activities.
What is sequestration?
Sequestration provides for the enforcement of budgetary limits established in law through the
automatic cancellation of previously enacted spending, making largely across-the-board
reductions to nonexempt programs, activities, and accounts. A sequester is implemented through a
sequestration order issued by the President as required by law. The purpose of sequestration is to
deter enactment of legislation violating the spending limits or, in the event that such legislation is
enacted violating these spending limits, to automatically reduce spending to the limits specified in
law. Each statutory limit—defense and nondefense—is separately enforced so that the breach of
the limit for one category is enforced by a sequester of resources only within that category.37
the limit for one category is enforced by a sequester of resources only within that category.32
The absence of legislation to reduce the federal budget deficit by at least $1.2 trillion triggered the sequestration process
sequestration in 2013. In accordance with the Budget Control Act of 2011 (P.L. 112-25), then-President. 112-25), thenPresident Barack Obama ordered the sequestration of budgetary resources across nonexempt
federal government accounts on March 1, 2013—five months into the fiscal year. DOD was
required to apply a $37 billion sequester to $528 billion in available (subfunction 051) budgetary
resources—a reduction of 7%.
Can the National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) trigger a sequester?
Do BCA caps apply to the Department of Defense (DOD)?
Department of Defense (DOD)-Military activities (budget subfunction 051) historically constitute
approximately 95% of the national defense budget (function 050).38 Although the BCA does not
establish limits on subfunctions (051, 053 and 054), the BCA limits on national defense have, in
practice, been proportionally applied to subfunctions. CRS estimates the BCA limits on DODMilitary base budget activities at approximately $638 billion in FY2020 and $643 billion in
FY2021.
Can the National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) trigger
sequestration?
Legislation authorizing discretionary appropriations, such as the National Defense Authorization
Act (NDAA), does not provide budget authority and therefore cannot trigger a sequester for sequestration for
violating discretionary spending limits.3339 A sequester will occur only if either the defense or
nondefense discretionary spending limits are exceeded in enacted appropriations bills.34
How has defense discretionary spending changed since enactment 40
allocations of automatic enforcement measures as calculated by OMB, as well as changes to the FY2014 defense cap
from P.L. 112-240. See notes to Table 1.
37 This paragraph was contributed by Megan S. Lynch, CRS Specialist on Congress and the Legislative Process. See
CRS Report R42972, Sequestration as a Budget Enforcement Process: Frequently Asked Questions, by Megan S.
Lynch.
38 See CRS In Focus IF10618, Defense Primer: The National Defense Budget Function (050), by Christopher T. Mann.
39 For more information on the NDAA, see CRS In Focus IF10516, Defense Primer: Navigating the NDAA, by
Brendan W. McGarry and Valerie Heitshusen.
40 See CRS Report R42972, Sequestration as a Budget Enforcement Process: Frequently Asked Questions, by Megan
S. Lynch.
Congressional Research Service
9
The Defense Budget and the Budget Control Act: Frequently Asked Questions
How has defense discretionary spending changed since enactment
of the BCA?
of the BCA?
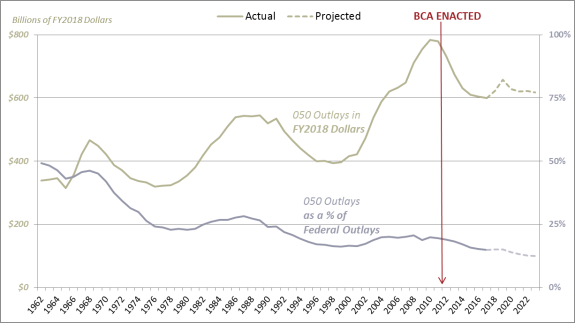
Nominal defense discretionary outlaysoutlays, including funding for Overseas Contingency Operations
(OCO), decreased from $671 billion in FY2012 to $590623 billion in FY2017FY2018, a decline of $80 48
billion (127%). They are projected to reach $655721 billion in FY2021, a decline of $16an increase of $51 billion (2%) 8%)
from FY2012.3541 Adjusting for inflation (in constant FY2018FY2019 dollars), defense discretionary
outlays peaked at $784806 billion in FY2010 during the height of the U.S.-led wars in Iraq and
Afghanistan (see Figure 3).36).42 Following enactment of the BCA, defense discretionary outlays
decreased from $734755 billion in FY2012 to $599635 billion in FY2017FY2018, a decline of $135119 billion (18
(16%) in inflation-adjusted dollars. Despite a projected uptick in FY2018 and FY2019, theyThey are projected to reach $620693 billion in FY2021, $114 62
billion (168%) less than the FY2012 level in inflation-adjusted dollars. The figure also shows
defense discretionary outlays as a percentage of all federal outlays. Over the past half century,
federal outlays devoted to discretionary defensedefense discretionary programs have trended downward from nearly
half (49%) of total outlays in FY1962 during the Vietnam War, to 19% in FY2012 after enactment
of the BCA, to 15% in FY2017. They are projected to further decline to 13% in FY2021, as mandatory spending and net interest consume a larger share of all federal outlays (see also Figure 1).37
Similarly, discretionary defense outlays as a share of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) have
trended downward, from 9.12% of GDP in 1968FY1968, to 4.2% of GDP in FY2012 after enactment of
the BCA, to 3.1% of GDP in FY2017FY2018. By FY2021—the last year of the BCA limits—CBO projects discretionary defense outlays to decline to 2.9discretionary
caps—CBO projects defense discretionary outlays at 3.2% of GDP. 44
% of GDP.38
The deficit-reduction effects of the BCA have been offset by other factors affecting the federal
budget.45 The federal budgetbudget.39 While the deficit decreased from $1.1 trillion (6.87% of Gross Domestic
Product) in FY2012 to $665779 billion (3.59% of GDP) in FY2017, itFY2018, but is projected to increase to $1.1
trillion (4.95% of GDP) in FY2021.4046 Over the same period, federal debt held by the public has
44
Office of Management and Budget, Historical Tables, Table 8.4, Outlays by Budget Enforcement Act Category as
Percentages of GDP: 1962-2024, and Congressional Budget Office, Over the same period, federal debt held by the public has increased from $11.3 trillion (70.4% of GDP) in FY2012 to $14.7 trillion (76.5% of GDP) in FY2017 and is projected to further increase to $19 trillion (83.1% of GDP) in FY2021.41
What are the Administration's plans for defense spending?
The Trump Administration has proposed increasing defense spending beyond the statutory limits of the Budget Control Act of 2011 (P.L. 112-25) as amended. The President's FY2019 budget request proposed increasing caps on defense discretionary base budget authority by $84 billion (15%) to $660 billion in FY2020 and by $87 billion (15%) to $677 billion in FY2021. It also proposed defense funding for Overseas Contingency Operations (OCO) totaling $73 billion in FY2020 and $66 billion in FY2021.42
Acknowledgements
This is an update to a report originally authored by [author name scrubbed], former CRS Specialist in Defense Readiness and Infrastructure. It references research previously compiled by [author name scrubbed], former CRS Specialist in U.S. Defense Policy and Budget; [author name scrubbed], CRS Analyst in Public Finance; and [author name scrubbed], CRS Specialist on Congress and the Legislative Process. [author name scrubbed], Research Assistant, helped compile the graphics.
Author Contact Information
Footnotes
| 1. |
See CRS In Focus IF10618, Defense Primer: The National Defense Budget Function (050), by [author name scrubbed]. |
| 2. |
See CRS Report 98-721, Introduction to the Federal Budget Process, coordinated by [author name scrubbed]. |
| 3. |
|
| 4. |
CRS Report R44874, The Budget Control Act: Frequently Asked Questions, by [author name scrubbed] and [author name scrubbed]. |
| 5. |
OMB, Final Sequestration Report to the President and Congress for Fiscal Year 2018, April 6, 2018, at https://www.whitehouse.gov/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/2018_final_sequestration_report_april_2018_potus.pdf. |
| 6. |
See CRS Report 98-721, Introduction to the Federal Budget Process, coordinated by [author name scrubbed]. |
| 7. |
OMB, Final Sequestration Report to the President and Congress for Fiscal Year 2012, January 18, 2012, at https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/sites/default/files/omb/assets/legislative_reports/sequestration/sequestration_final_jan2012.pdf. |
| 8. |
Open letter from eighty-five national security experts and former government officials: Elliot Abrams, David Adesnik, and Michael Auslin, et al. to John Boehner, then-speaker of the House, and Mitch McConnell, Senate Majority Leader, et al., February 24, 2015. |
| 9. |
Frederico Bartels, "America's defense budget is yet again held hostage by Congress," The Hill, November 2, 2017, at http://thehill.com/opinion/national-security/358385-congress-needs-to-do-its-job-and-properly-fund-americas-defense. See also Footnote 4. |
| 10. |
Senator John McCain, "Restoring American Power: Recommendations for the FY2018-FY2022 Defense Budget," January 16, 2017, at https://www.mccain.senate.gov/public/index.cfm/2017/1/restoring-american-power-sasc-chairman-john-mccain-releases-defense-budget-white-paper; and Ben Werner, "Thornberry: Budget Control Act Limits on Defense Spending Could End Soon," USNI News, September 6, 2017, at https://news.usni.org/2017/09/06/thornberry-budget-control-act-limits-defense-spending-end-soon. |
| 11. |
Michael Shindler, "Don't Let Defense Wreck the Budget," Real Clear Defense, February 23, 2017, at https://www.realcleardefense.com/articles/2017/02/23/dont_let_defense_wreck_the_budget_110857.html. For more information on deficits and debt, see CRS Report R44383, Deficits and Debt: Economic Effects and Other Issues, by [author name scrubbed]. |
| 12. |
Mark Meadows, "Rep. Meadows' Statement on Budget Agreement," press release, February 9, 2018, at https://meadows.house.gov/news/documentsingle.aspx?DocumentID=815. Final roll call vote results for the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018 at http://clerk.house.gov/evs/2018/roll069.xml. |
| 13. |
Lawrence J. Korb, "Trump's Defense Budget," Center for American Progress, February 28, 2018, at https://www.americanprogress.org/issues/security/news/2018/02/28/447248/trumps-defense-budget/. |
| 14. |
Congressman Mike Turner, "Trump Calls for Repeal of Sequestration; Turner: Repeal Gains Groundswell of Support," press release, March 1, 2017, https://turner.house.gov/media-center/press-releases/trump-calls-for-repeal-of-sequestration-turner-repeal-gains-groundswell. |
| 15. |
The BCA was amended by the American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012 (ATRA; P.L. 112-240), the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2013 (BBA 2013; P.L. 113-67, referred to as the Murray-Ryan agreement), the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2015 (BBA 2015; P.L. 114-74), and the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018 (BBA 2018; P.L. 115-123). For more information on the effect of each, see CRS Insight IN10861, Discretionary Spending Levels Under the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018, by [author name scrubbed] and [author name scrubbed]. |
| 16. |
CBO, Letter from then-Director Douglas W. Elmendorf to then-Speaker of the House John Boehner and then-Majority Leader of the Senate Harry Reid, "CBO Estimate of the Impact on the Deficit of the Budget Control Act of 2011," August 1, 2011; http://www.cbo.gov/sites/default/files/cbofiles/ftpdocs/123xx/doc12357/budgetcontrolactaug1.pdf. |
| 17. |
Legislation amending the BCA included equal increases to defense and nondefense discretionary spending caps until the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018 (P.L. 115-123), which included a larger increase to defense than nondefense. For more on the so-called parity principle, see CRS In Focus IF10657, Budgetary Effects of the BCA as Amended: The "Parity Principle", by [author name scrubbed]. For more on the "security" category that predated the "defense" category, see the "Background" section above. |
| 18. |
For more information on sequestration, see CRS Report R42972, Sequestration as a Budget Enforcement Process: Frequently Asked Questions, by [author name scrubbed]. |
| 19. |
For more information on the national defense budget function, see the "Background" section above. For more information on OCO, see CRS Report R44519, Overseas Contingency Operations Funding: Background and Status, coordinated by [author name scrubbed] and [author name scrubbed]. |
| 20. |
These automatic reductions to the original BCA limits are often referred to as sequestration but technically are not because Congress can allocate funding within the caps. See footnote 18. |
| 21. |
See footnote 15. |
| 22. |
For more on the "security" category that predated the "defense" category, see the "Background" section above. |
| 23. |
The Bipartisan Budget Act of 2015 (P.L. 114-74) established non-binding targets for OCO spending in FY2016 and FY2017. |
| 24. |
See CRS Report R44519, Overseas Contingency Operations Funding: Background and Status, coordinated by [author name scrubbed] and [author name scrubbed]. |
| 25. |
|
| 26. |
Section 1501 of National Defense Authorization Act for FY2017 (P.L. 114-328) stipulates that certain amounts designated as OCO are to be used for base budget requirements. Such amounts would not be counted against the BCA limits. See also OMB, "Presidential Designation of Funding as an Emergency Requirement: Multiple Accounts in the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2017, for the Department of Agriculture, Department of Homeland Security, Department of Housing and Urban Development, Department of the Interior, Department of Transportation, and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration," press release, May 4, 2017, at https://www.whitehouse.gov/sites/whitehouse.gov/files/omb/budget/amendments/Emergency%20Funding%20Transmittal%20Package%205.5.17.pdf |
| 27. |
DOD, Defense Budget Overview: United States Department of Defense Fiscal Year 2019 Budget Request, originally published February 12, 2018, and revised February 13, 2018; OMB, Estimate #1-FY2019 Budget Amendments, April 18, 2018; and OMB, Addendum to the FY2019 Budget, February 12, 2018. |
| 28. |
See CRS In Focus IF10618, Defense Primer: The National Defense Budget Function (050), by [author name scrubbed]. |
| 29. |
|
| 30. |
CBO, The Budget and Economic Outlook: An Update, Table 1-6, Illustrative Paths for Discretionary Budget Authority Subject to the Caps Set in the Budget Control Act of 2011, August 2011. |
| 31. |
|
| 32. |
This paragraph was contributed by [author name scrubbed], CRS Specialist on Congress and the Legislative Process. See CRS Report R42972, Sequestration as a Budget Enforcement Process: Frequently Asked Questions, by [author name scrubbed]. |
| 33. |
For more information on the NDAA, see CRS In Focus IF10516, Defense Primer: Navigating the NDAA, by [author name scrubbed] and [author name scrubbed]. |
| 34. |
See CRS Report R42972, Sequestration as a Budget Enforcement Process: Frequently Asked Questions, by [author name scrubbed]. |
| 35. |
See footnote 3. |
| 36. |
See footnote 3 and OMB, Historical Tables, Table 10.1, Gross Domestic Product and Deflators Used in the Historical Tables: 1940–2023. |
| 37. |
See footnote 3. |
| 38. |
OMB, Historical Tables, Table 8.4, Outlays by Budget Enforcement Act Category as Percentages of GDP. See CBO references in footnote 3. |
| 39. |
For example, CBO in 2018 increased projected deficits compared to a previous estimate due to recent tax and spending legislation, including the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (P.L. 115-97), Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018 (P.L. 115-123), and the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2018 (P.L. 115-141). |
| 40. |
OMB, Historical Tables, Table 1.3, Summary of Receipts, Outlays, and Surpluses or Deficits in Current Dollars, Constant (FY2009) Dollars, and as Percentages of GDP, 1940-2023. See CBO references in footnote 3. |
| 41. |
|
| 42. |
OMB, Budget of the U.S. Government for Fiscal Year 2019, Table S-7. Proposed Discretionary Caps for 2019 Budget, https://www.whitehouse.gov/wp-content/uploads/2018/02/budget-fy2019.pdf#page=146. |