The POWER Initiative: Energy Transition as Economic Development
Changes from November 20, 2019 to September 8, 2022
This page shows textual changes in the document between the two versions indicated in the dates above. Textual matter removed in the later version is indicated with red strikethrough and textual matter added in the later version is indicated with blue.
Contents
- Introduction
- Background
- The POWER+ Plan
- The POWER Initiative
- POWER Elements in the Current Administration
- The EDA Assistance to Coal Communities (ACC) Program
- Abandoned Mine Land (AML) Reclamation Investments
- The ARC's POWER Initiative
- About the ARC
- Scope and Activities
- Funding History
- Policy Considerations
- Concluding Notes
Figures
Summary
: Energy Transition as
September 8, 2022
Economic Development
Julie M. Lawhorn
With the decline of the U.S. coal industry, managing the economic effects of energy transition
Analyst in Economic
has become a priority for the federal government. The Partnerships for Opportunity and
Development Policy
Workforce and Economic Revitalization (POWER) Initiative, and the broader POWER Plus Plan
of which it was a part, represent the U.S. government'’s efforts to ease the economic effects of energy transition in coal industry-dependent communities in the United States, and especially in
Appalachia. Launched in 2015 by the Obama Administration as a multi-agency effort utilizing various existing programs, the POWER Plus plan received partial backing through appropriations for Fiscal Year 2016 (FY2016) to the Appalachian Regional Commission, the Economic Development Administration, and for abandoned mine land reclamation.
While certain proposed provisions of POWER Plus were never enacted or funded, other elements of the POWER Initiative continuehave continued under the Trump Administrationand Biden Administrations. Continuing programs include the Assistance to Coal Communities program (now part of the Assistance to Energy Communities initiative) within the Economic Development Administration, the POWER Initiative under the Appalachian Regional Commission (the only program to retain the original branding), and a funding program for abandoned mine land reclamation. Of these efforts, the Appalachian Regional Commission'Commission’s POWER Initiative is the largest of the initiative'’s economic development programs, having funded nearly $150 million in projects (out of over $600 over $319 million in proposed projects) since it was first launched in FY2016. The Appalachian Regional Commission'’s POWER Initiative is regionally targeted to declining coal communities in Appalachia, unlike the Economic Development Administration'’s Assistance to Coal Communities (now the Assistance to Energy Communities) program, which has a national scope. To date, the initiative has reportedly leveraged approximately $772 million1.5 billion of private investment into the Appalachian regional economy. This report provides background on the origins, development, and activities of the POWER Initiative.
Introduction
Congressional Research Service
link to page 4 link to page 4 link to page 5 link to page 6 link to page 7 link to page 7 link to page 8 link to page 10 link to page 11 link to page 12 link to page 14 link to page 15 link to page 17 link to page 11 link to page 14 link to page 6 link to page 8 link to page 10 link to page 15 link to page 15 link to page 19 The POWER Initiative: Energy Transition as Economic Development
Contents
Introduction ..................................................................................................................................... 1 Background ..................................................................................................................................... 1
The POWER+ Plan ................................................................................................................... 2 The POWER Initiative .............................................................................................................. 3
POWER Elements in the Current Administration ........................................................................... 4
The EDA Assistance to Coal Communities (ACC) Program .................................................... 4 Abandoned Mine Land Economic Revitalization (AMLER) Reclamation Program ................ 5
The ARC’s POWER Initiative......................................................................................................... 7
About the ARC .......................................................................................................................... 8 Scope and Activities .................................................................................................................. 9 Funding History ....................................................................................................................... 11
Policy Considerations .................................................................................................................... 12 Concluding Notes .......................................................................................................................... 14
Figures Figure 1. Map of the Appalachian Regional Commission ............................................................... 8 Figure 2. Distribution of ARC POWER Initiative Projects, 2016-2022 (to date) .......................... 11
Tables Table 1. POWER+ Plan, FY2015 Roll Out ..................................................................................... 3 Table 2. ACC Program Funding, FY2015-FY2022 ......................................................................... 5 Table 3. AMLER Reclamation Appropriations, FY2016-FY2022 .................................................. 7 Table 4. ARC POWER Initiative Appropriations, FY2016-FY2022 and FY2023 Request .......... 12 Table 5. ARC POWER Initiative Grant Awards, FY2016-FY2022 .............................................. 12
Contacts Author Information ........................................................................................................................ 16
Congressional Research Service
The POWER Initiative: Energy Transition as Economic Development
Introduction The U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) has forecast U.S. coal production to decline through 2050, with the sharpest reduction to occur by the mid-2020s.11 Consequently, the coal industry'industry’s decline has contributed to economic distress in coal-dependent communities, including increased unemployment and poverty rates.2
2
In response, the Obama Administration launched the Partnerships for Opportunity and Workforce and Economic Revitalization (POWER) Plus Plan, which addressed the coal sector'’s decline through funding for (1) economic stabilization, (2) social welfare efforts, and (3) environmental efforts. The economic elements were organized within the POWER Initiative, a multi-agency federal initiative to provide economic development funding and technical assistance to address economic distress caused by the effects of energy transition principally in coal communities. Although the initiative began as a multi-agency effort as part of the POWER Plus Plan, the POWER Initiative currently operates as a funded program administered by the Appalachian Regional Commission (ARC) in its 420423-county service area.
This report considers the background of the POWER Initiative and the broader effort of which it was originally a part, the POWER Plus Plan. It broadly surveys the state of POWER elements in the current administration, including elements of the initiative in the Economic Development Administration (EDA), the Appalachian Regional Commission (ARC)ARC, and funded efforts for abandoned mine land reclamation. The Appalachian Regional Commission'’s POWER Initiative program is the largest of these, and the only program to retain the POWER Initiative branding. This report considers its scope and activities as well as its funding history.
The POWER Initiative is supported by Congress as reflected by consistent annual appropriations. The POWER Initiative may also be of interest to Congress as an economic development program that actively facilitates and eases the repercussions of energy transition in affected communities in Appalachia. More broadly, in light of the projected continued decline of the coal industry, as well as proposals to address greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from hydrocarbon combustion, congressional interest in programs to address economic dislocations as a result of energy transition is likely to accelerate.
Background
Background The POWER Initiative was launched in 2015 as a multi-agency federal effort to provide grant funding and technical assistance to address economic and labor dislocations caused by the effects of energy transition—principally in coal communities around the United States.33 The POWER Initiative was a precursor to a broader effort known as the POWER Plus Plan (dubbed POWER+
1 U.S. Energy Information Administration, Annual Energy Outlook 2022: With Projections to 2050, March 3, 2022, Total Coal Production, reference case, https://www.eia.gov/outlooks/aeo/data/browser/#/?id=1-AEO2022®ion=0-0&cases=ref2022&start=2020&end=2050&f=A&linechart=~ref2022-d011222a.6-1-AEO2022&ctype=linechart&sourcekey=0 and https://www.eia.gov/outlooks/aeo/narrative/electricity/sub-topic-02.php.
2 Eric Bowen et al., An Overview of the Coal Economy in Appalachia, Appalachian Regional Commission, January 2018, https://www.arc.gov/assets/research_reports/CIE1-OverviewofCoalEconomyinAppalachia.pdf.
3 The White House, Office of the Press Secretary, “FACT SHEET: The Partnerships for Opportunity and Workforce and Economic Revitalization (POWER) Initiative,” press release, March 27, 2015, https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/the-press-office/2015/03/27/fact-sheet-partnerships-opportunity-and-workforce-and-economic-revitaliz.
Congressional Research Service
1
The POWER Initiative: Energy Transition as Economic Development
Initiative was a precursor to a broader effort known as the POWER Plus Plan (dubbed POWER+ by the Obama Administration).44 This latter plan was launched using preexisting funds, and was intended to develop an array of grant programs across multiple agencies to facilitate energy transition and ameliorate the negative effects of that transition. Most legislative elements of the POWER+ Plan were carried out under existing authorities rather than new legislation. Certain features continue to be active—particularly elements of the POWER Initiative within the ARC and the EDA.
The POWER+ Plan
The POWER+ Plan was organized to address three areas of concern:
1.1. economic diversification and adjustment for affected coal communities;2.2. social welfare for coal mineworkers and their families, and the accelerated clean- up of hazardous coal abandoned mine lands; and3.3. tax incentives to support the technological development and deployment of carbon capture, utilization, and sequestration technologies.5
5
The POWER+ Plan was proposed in the FY2016 President'’s Budget as a multi-agency approach to energy transition.66 As proposed, the POWER+ Plan involved the participation of the Department of Labor (DOL), the Appalachian Regional Commission (ARC), the Small Business Administration (SBA), the Economic Development Administration (EDA), the Department of Agriculture (USDA), the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), the Department of the Treasury, the Department of Energy (DOE), the Corporation for National and Community Service, and the Department of the Interior (DOI). The FY2016 President'’s Budget requested approximately $56 million in POWER+ Plan grant funds: (1) $20 million for the DOL; (2) $25 million for the ARC; (3) $6 million for the EDA; and (4) $5 million for the EPA. In addition, a portion of USDA rural development funds—$12 million in grants and $85 million in loans—were aligned to POWER+ Plan priorities. Also, the plan sought $1 billion for abandoned mine land reclamation and an additional $2 billion for carbon capture and sequestration technology investments.7
The POWER Initiative
The Obama Administration described the POWER Initiative as a "down payment" on the POWER+ Plan, and focused on the Plan'7
4 The White House, Office of the Press Secretary, “FACT SHEET: Administration Announces New Workforce and Economic Revitalization Resources for Communities through POWER Initiative,” press release, October 2015, https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/the-press-office/2015/10/15/fact-sheet-administration-announces-new-workforce-and-economic.
5 U.S. Office of Management and Budget (OMB), Investing in Coal Communities, Workers, and Technology: The POWER+ Plan, The President’s Budget: Fact Sheets on Key Issues Fiscal Year 2016, February 2, 2015, https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/sites/default/files/omb/budget/fy2016/assets/fact_sheets/investing-in-coal-communities-workers-and-technology-the-power-plan.pdf.
6 The POWER+ Plan involved a number of existing programs and initiatives administered by the participating agencies, and did not have an appropriations line item unto itself. An OMB fact sheet describes the specific funding measures proposed in the new budget among the participating agencies: OMB, Investing in Coal Communities, Workers, and Technology: The POWER+ Plan, The President’s Budget: Fact Sheets on Key Issues, Fiscal Year 2016, February 2, 2015, https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/sites/default/files/omb/budget/fy2016/assets/fact_sheets/investing-in-coal-communities-workers-and-technology-the-power-plan.pdf.. These funding requests were reflected in the FY2016 White House budget proposal: OMB, Fiscal Year 2016 Budget of the U.S. Government: Appendix, February 2, 2015, https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/BUDGET-2016-APP/pdf/BUDGET-2016-APP.pdf. See also The White House, Office of the Press Secretary, “FACT SHEET: Administration Announces New Workforce and Economic Revitalization Resources for Communities through POWER Initiative,” press release, October 2015, https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/the-press-office/2015/10/15/fact-sheet-administration-announces-new-workforce-and-economic.
7 OMB, Investing in Coal Communities, Workers, and Technology: The POWER+ Plan, The President’s Budget: Fact
Congressional Research Service
2
link to page 6 link to page 6 The POWER Initiative: Energy Transition as Economic Development
The POWER Initiative The Obama Administration described the POWER Initiative as a “down payment” on the POWER+ Plan, and focused on the Plan’s economic development elements using existing funding sources (Table 1).8.8 Those existing funding sources (or "“Targeted Funds" in” in Table 1) refer to funds that were set aside by the respective federal executive agency in support of the POWER+ Plan in FY2015. These funding amounts are only those funds made available initially, and do not account for additional appropriations or set-asides made available as the program progressed. The EDA was initially designated as the lead agency for the POWER Initiative, with significant funding elements from the ARC, SBA, and DOL. While led by the EDA, POWER Initiative grants were determined by the individual awarding agency. Grants were divided into two funding streams: (1) planning grants; and (2) implementation grants.
The POWER Initiative was announced in March 2015, with the first tranche of grants awarded in October 2016.99 With the exception of certain parts of the POWER Initiative and funding for reclaiming abandoned mine land (AML), broad elements of the POWER+ Plan were not enacted by Congress. Since the end of the Obama Administration, the ARC is the only federal agency with a POWER Initiative-designated program.
Table 1. POWER+ Plan, FY2015 Roll Out
as announced in March 2015
Agency
Program / Activity
Targeted Funds
Department of Commerce,
Assistance to Coal Communities,
$15 mil ion
Economic Development
Economic Adjustment Assistance,
Administration
and Partnership Planning
Department of Labor, Employment
Dislocated Worker National
$10-20 mil ion
and Training Administration
Emergency Grants
Small Business Administration
Regional Innovation Clusters and
$3 mil ion
Growth Accelerators
Appalachian Regional Commission
Technical Assistance and
$0.5 mil ion
Demonstration Projects
Source: The White House, Office of the Press Secretary, “as announced in March 2015
|
Agency |
Program / Activity |
Targeted Funds |
|
Department of Commerce, Economic Development Administration |
Assistance to Coal Communities, Economic Adjustment Assistance, and Partnership Planning |
$15 million |
|
Department of Labor, Employment and Training Administration |
Dislocated Worker National Emergency Grants |
$10-20 million |
|
Small Business Administration |
Regional Innovation Clusters and Growth Accelerators |
$3 million |
|
Appalachian Regional Commission |
Technical Assistance and Demonstration Projects |
$0.5 million |
Source: The White House, Office of the Press Secretary, "FACT SHEET: The Partnerships for Opportunity and Workforce and Economic Revitalization (POWER) Initiative,"” press release, March 27, 2015, https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/the-press-office/2015/03/27/fact-sheet-partnerships-opportunity-and-workforce-and-economic-revitaliz.
. Notes: The EPA, USDA, Department of the Treasury, Department of Energy, the Corporation for National and Community Service, and the Department of Interior were also noted as participating agencies, but did not initiallyinitial y contribute funding. Targeted funds refers to funds that were set aside by the respective federal agency in support of the POWER+ Plan in FY2015. These funding amounts are only those funds made available initially, and do not account for additional appropriations or set-asides made available as the program progressed.
Sheets on Key Issues, Fiscal Year 2016, February 2, 2015, https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/sites/default/files/omb/budget/fy2016/assets/fact_sheets/investing-in-coal-communities-workers-and-technology-the-power-plan.pdf.
8 The White House, Office of the Press Secretary, “FACT SHEET: The Partnerships for Opportunity and Workforce and Economic Revitalization (POWER) Initiative,” press release, March 27, 2015, https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/the-press-office/2015/03/27/fact-sheet-partnerships-opportunity-and-workforce-and-economic-revitaliz.
9 The White House, Office of the Press Secretary, “FACT SHEET: Administration Announces New Workforce and Economic Revitalization Resources for Communities through POWER Initiative,” press release, October 2015, https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/the-press-office/2015/10/15/fact-sheet-administration-announces-new-workforce-and-economic.
Congressional Research Service
3
The POWER Initiative: Energy Transition as Economic Development
POWER Elements in the Current Administration As of FY2022POWER Elements in the Current Administration
As of November 2019, the POWER Initiative exists solely as a funded program of the ARC, and is no longer a multi-agency initiative. However, certain other elements originally included in the POWER+ Plan and the POWER Initiative continue to receive appropriations and continue to be active, but they are not designated as such. by the Trump Administration.
These elements are discussed below.
The EDA Assistance to Coal Communities (ACC) Program
Program10 The EDA continues to receive appropriations for its Assistance to Coal Communities (ACC) program. The ACC program was a grant-making element launched as a part of the EDA'’s role in the POWER Initiative.
In FY2019,10 $30
In FY2022, $41.5 million was designated for the ACC program as part of appropriations to the EDA.1111 The FY2019FY2022 appropriations represent the fifthrepresented the eighth consecutive fiscal year of funding for the ACC program, and reflected 315the program,12 and reflect 300% growth from approximately $10 million appropriated in FY2015. (See CRS Report R46991, Economic Development Administration: An Overview of Programs and Appropriations (FY2011-FY2022), by Julie M. Lawhorn.12
While the ACC program FY2015. However, the Trump Administration's FY2017 Budget sought to eliminate the ACC program;13 and subsequent Administration Budget requests have proposed eliminating the EDA entirely, including the ACC program.14
While the ACC is an active outgrowth of the POWER Initiative and POWER+ Plan, it is no longer associated with the POWER Initiative and instead is identified as a separate program drawing on Economic Adjustment Assistance (EAA) funds.1513 Because it draws on EAA funding, 10 Following the initial implementation of the ACC program, EDA continued to allocate funding to coal-impacted communities. In FY2021, EDA allocated 10% ($300 million) of the $3 billion appropriation from the American Rescue Plan Act (ARPA, P.L. 117-2) to coal-impacted communities through the Coal Communities Commitment (CCC). The set-asides were made to the Build Back Better Regional Challenge (BBBRC) and Economic Adjustment Assistance Challenge (EAAC). The Initial Report to the President on Empowering Workers Through Revitalizing Energy Communities (April 2021), developed by President Biden’s Interagency Working Group (IWG), also recommended focused federal investments for coal-impacted communities. According to EDA, the CCC builds on this report. See EDA, “Coal Communities Commitment,” https://eda.gov/arpa/coal-communities/. The IWG’s report is available at https://netl.doe.gov/sites/default/files/2021-04/Initial%20Report%20on%20Energy%20Communities_Apr2021.pdf.
11 See the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2022, P.L. 117-103, and the accompanying explanatory statement, printed in the March 9, 2022, Congressional Record (pp. H1772-H1773), https://www.congress.gov/117/crec/2022/03/09/168/42/CREC-2022-03-09-bk3.pdf.
12 The Trump Administration’s FY2017 Budget sought to eliminate the ACC program. See U.S. Department of Commerce, Economic Development Administration: Fiscal Year 2017 Congressional Budget Request, February 9, 2016, pp. 36-38, http://www.osec.doc.gov/bmi/budget/FY17CBJ/EDA%20FY%202017%20Congressional%20Submission%202-8-16%20OMB%20cleared%20508%20Compliant.pdf. Subsequent Trump Administration Budget requests proposed eliminating the EDA entirely, including the ACC program. For FY2018, the Trump Administration requested $30 million in funding for the EDA to enable the “orderly closeout” of the agency: OMB, Budget of the U.S. Government Fiscal Year 2018: Appendix, May 23, 2017, pp. 181-183, https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/BUDGET-2018-APP/pdf/BUDGET-2018-APP.pdf. In FY2019, the EDA was also proposed for termination, and approximately $15 million was requested to enable its closeout: OMB, Budget of the U.S. Government Fiscal Year 2019: Appendix, February 12, 2018, pp. 182-183, https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/BUDGET-2019-APP/pdf/BUDGET-2019-APP.pdf. In the Trump Administration’s budget request for FY2020, $30 million was requested for the EDA’s closeout: OMB, Budget of the U.S. Government Fiscal Year 2020: Appendix, March 18, 2019, pp. 178-180, https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/BUDGET-2020-APP/pdf/BUDGET-2020-APP.pdf. In the Trump Administration’s budget request for FY2021, $32 million was requested for the EDA’s closeout; see OMB, Budget of the U.S. Government Fiscal Year 2021: Appendix, February 10, 2020, pp. 191-192, https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/BUDGET-2021-APP/pdf/BUDGET-2021-APP.pdf. For a summary of EDA appropriations, see CRS Report R46991, Economic Development Administration: An Overview of Programs and Appropriations (FY2011-FY2022), by Julie M. Lawhorn.
13 The White House, Office of the Press Secretary, “FACT SHEET: The Partnerships for Opportunity and Workforce and Economic Revitalization (POWER) Initiative,” press release, March 27, 2015,
Congressional Research Service
4
The POWER Initiative: Energy Transition as Economic Development
Because it draws on EAA funding, ACC investments may only be used for projects located in, or substantially benefiting, a community or region that meets EDA distress criteria.
EDA economic distress is defined as
" “An unemployment rate that is, for the most recent 24-month period for which data are available, at least one percentage point greater than the national average unemployment rate;-
Per capita income that is, for the most recent period for which data are available,
80 percent or less of the national average per capita income; or
-
A Special Need, as determined by EDA.
"16
”14
Table 2. ACC Program Funding, FY2015-FY2019
FY2022
in millions ($)
FY2015
FY2016
FY2017
FY2018
FY2019
FY2020
FY2021
FY2022
Funding for
$10.0
$15.0
$30.0
$30.0
$30.0
$30.0
$33.5
$41.5
ACC program
in millions ($)
|
FY2015 |
FY2016 |
FY2017 |
FY2018 |
FY2019 |
|
|
Funding for ACC program |
$10 |
$15 |
$30 |
$30 |
$30 |
Source: Compiled by CRS from Department of Commerce budget justification documents.
Notes: The ACC program was not identified as a specific appropriations line item until the FY2017 Department of Commerce budget justification, which sought to terminate its funding. However, that same document included past funding amounts for ACC in FY2015 and FY2016, which were included as set-asides within the EAA program. In FY2018 and FY2019-FY2021, funding for the ACC program was not requested as the Trump Administration proposed terminating the EDA and its programs.
Abandoned Mine Land (AML) Reclamation Investments
One of the pillarsEconomic Revitalization (AMLER) Reclamation Program One objective of the POWER+ Plan was funding for the social welfare of miners and for cleanup and reclamation of former mine and other coal-related "brownfield"“brownfield” sites. While certain legislative proposals for these purposes were never enacted,1715 Congress has approved annual funding since FY2016 for economic development grants to states for Abandoned Mine Land reclamation.18
reclamation activities. The Office of Surface Mining Reclamation and Enforcement (OSMRE) within the Department of the Interior is the federal office responsible for administering Abandoned Mine Land reclamation activities in coordination with eligible states and tribes.16
https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/the-press-office/2015/03/27/fact-sheet-partnerships-opportunity-and-workforce-and-economic-revitaliz.
14 13 C.F.R. §301.3. See also Economic Development Administration, Applying for EDA Investments: Eligibility Requirements and Criteria, https://www.eda.gov/archives/2016/how-to-apply/files/Eligibility-Requirements-and-Criteria.pdf. For additional information about area eligibility and measures of economic distress in EDA programs, see CRS In Focus IF12074, Areas of Economic Distress for EDA Activities and Programs, by Julie M. Lawhorn, Areas of Economic Distress for EDA Activities and Programs, by Julie M. Lawhorn.
15 See, for example, The Miners Protection Act, first introduced in 2015 as S. 1714. Versions of this bill, with the same scope and effect, have been reintroduced in the years since. For example, in the 116th Congress, the Revitalizing the Economy of Coal Communities by Leveraging Local Activities and Investing More (RECLAIM) Act of 2016, H.R. 4456, was introduced but was not enacted.
16 Funding launched in FY2016 was notable for providing grants for economic development purposes. Previously, grants had been made available to eligible states and tribes to address the hazards and environmental degradation posed by abandoned mine sites under the Surface Mining Control and Reclamation Act (SMCRA) of 1977 (P.L. 95-87). For
Congressional Research Service
5
The POWER Initiative: Energy Transition as Economic Development
Initially, OSMRE referred to this program as the “AML Pilot Program.” Later, the program was renamed as the Abandoned Mine Land Economic Revitalization (AMLER) Program.
The FY2016 appropriation of $90 million directed funds to be divided equally among the three Appalachian states with the greatest amount of unfunded AML needs (P.L. 114-13).19).17 The $105 million appropriated for FY2017 set aside $75 million to be divided this way, with the balance of that amount being available more broadly to other eligible AML reclamation applicants (P.L. 115-31).2031).18 FY2018 appropriations of $115 million set aside $75 million for the three states demonstrating the greatest unmet need (P.L. 115-141).21
).19
For FY2019, the Department of the Interior, Environment, and Related Agencies Appropriations Act, 2019, Division E of the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2019 (P.L. 116-6), ), appropriated $115 million, which was subdivided further: $75 million for the three Appalachian states with the greatest amount of unfunded needs; $30 million for the next three Appalachian states with the “subsequent greatest amount of unfunded needs”; and $10 million for federally recognized Indian Tribes.20
For FY2020, the Department of the Interior, Environment, and Related Agencies Appropriations Act, 2020, Division D of the Further Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2020 (P.L. 116-94), appropriated $115 million, which was subdivided further: $75 million for the three Appalachian states with the greatest amount of unfunded needs; $30 million for the next three Appalachian states with the "“subsequent greatest amount of unfunded needs"”; and $10 million for federally recognized Indian Tribes with AML programs.21
For FY2021, the Department of the Interior, Environment, and Related Agencies Appropriations Act, 2021, Division G of the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2021 (P.L. 116-260), appropriated $115 million, which was subdivided further: $75 million for the three Appalachian states with the greatest amount of unfunded needs; $30 million for the next three Appalachian states with the “subsequent greatest amount of unfunded needs”; and $10 million for federally recognized Indian tribes.22
For FY2022, the President’s budget requested $165 million for the AMLER program, a proposed increase of $50 million from the prior year appropriation.23 For FY2022, the Department of the Interior, Environment, and Related Agencies Appropriations Act, 2022, Division G of the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2022 (P.L. 117-103) appropriated $122.5 million, which was subdivided further: $79.9 million for the three Appalachian states with the greatest amount of unfunded needs; $32 million for the next three Appalachian states with the “subsequent greatest
more information on the AML economic development program, see Office of Surface Mining Reclamation and Enforcement, Report on Abandoned Mine Land Reclamation Economic Development Pilot Program (AML Pilot Program) for FY 2016–FY2018, April 19, 2019, https://www.osmre.gov/programs/AML/2016_2018_Annual_Report_AML_Economic_Development_Pilot_Program.pdf. See also Office of Surface Mining Reclamation and Enforcement, Reclaiming Abandoned Mine Lands, https://www.osmre.gov/programs/aml.shtm.
17 To clarify the effective date of certain provisions of the Border Patrol Agent Pay Reform Act of 2014, and for other purposes, P.L. 114-13.
18 Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2017, P.L. 115-31. 19 Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2018, P.L. 115-141. 20 Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2019, P.L. 116-6. 21 Further Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2020, P.L. 116-94. 22 Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2021, P.L. 116-260. 23 Office of Surface Mining Reclamation and Enforcement, Budget Justifications and Performance Information, Fiscal Year 2022, https://www.doi.gov/sites/doi.gov/files/fy2022-osmre-budget-justification.pdf.
Congressional Research Service
6
link to page 10 link to page 10 link to page 10 link to page 10 link to page 10 The POWER Initiative: Energy Transition as Economic Development
amount of unfunded needs”; and $10.7 million for federally recognized Indian tribes.24 The appropriation was $42.5 million less than requested, but increased the AMLER program by 6.5% from the previous year.
Table 3. AMLER Reclamation Appropriations, FY2016-FY2022
in millions ($)
FY2016
FY2017
FY2018
FY2019
FY2020
FY2021
FY2022
Total for AMLER
$90.0
$105.0
$115.0
$115.0
$115.0
$115.0
$122.5
reclamation
Total amount for the
$90.0
$75.0
$75.0
$75.0
$75.0
$75.0
$79.9
toprecognized Indian Tribes.22
|
FY2016 |
FY2017 |
FY2018 |
FY2019 |
|
|
Appropriations for AML reclamation |
$90 |
$105 |
$115 |
$115 |
|
$90 |
$75 |
$75 |
$75 |
Source: Data compiled and tabulated by CRS from: P.L. 114-13; P.L. 115-31; ; P.L. 115-141; P.L. 116-6; P.L. 116-94; P.L. 116-260; and P.L. 116-6.
Notes: For FY2019,P.L. 117-103. Notes: Beginning in FY2017, Congress provided tiers of funding not reserved for the three Appalachian states with the greatest amount of unfunded AML needs was further subdivided for the first time: $75 million . For example, in FY2018 Congress appropriated $75 mil ion for the three Appalachian states with the greatest amount of unfunded needs; $30 millionmil ion for the next three Appalachian states with the "“subsequent greatest amount of unfunded needs"”; and $10 millionmil ion for grants to federally recognized Indian Tribes.
The ARC' Subsequent appropriations laws specified a similar approach to al ocating funding among the eligible states and tribes. a. OSMRE periodically updates funding estimates for sites in the Abandoned Mine Land Inventory System
(AMLIS) inventory. The unfunded reclamation needs a state reports may vary from year to year. Thus, a state’s grant amount may change depending on their relative reporting of unfunded reclamation needs.
b. Each state or tribe eligible for an AMLER grant received one-third of the total grant amount for that year.
The ARC’s POWER Initiative s POWER Initiative
The Appalachian Regional Commission (ARC) is the only federal agency that continues to receive regular appropriated funding for energy transition activities under the POWER Initiative designation.23
24 Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2022, P.L. 117-103.
Congressional Research Service
7
link to page 11
The POWER Initiative: Energy Transition as Economic Development
designation.25 While the POWER Initiative was launched as a multi-agency effort, only the ARC chose to designate its contributions as the POWER Initiative.
About the ARC
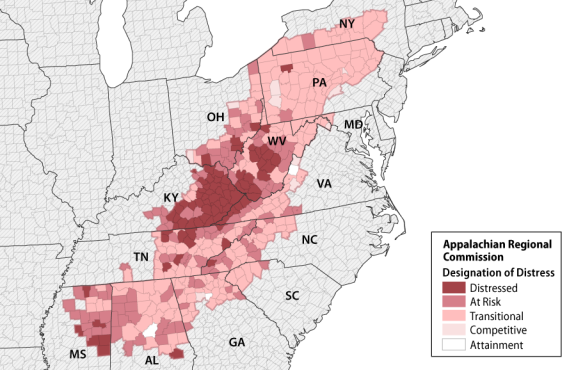
The ARC was established in 1965 to address economic distress in the Appalachian region (40 U.S.C. §14101-14704).2426 The ARC'’s jurisdiction spans 420423 counties in Alabama, Georgia, Kentucky, Ohio, New York, Maryland, Mississippi, North Carolina, Pennsylvania, South Carolina, Tennessee, Virginia, and West Virginia (Figure 1).
(Figure 1).
The ARC is a federal-state partnership, with administrative costs shared equally by the federal government and member states, while economic development activities are federally funded
25 It should be noted that while the ARC is generally classified as an independent federal agency, the federal regional commissions and authorities are unique in that although they are federally chartered organizations and draw on federal appropriations for their operations and activities, they are generally understood to be partnerships between the constituent states and the federal government. The vast majority of their staff and leadership are not federal employees. For more information, see CRS Report R45997, Federal Regional Commissions and Authorities: Structural Features and Function, by Julie M. Lawhorn.
26 Appalachian Regional Development Act of 1965, as amended, P.L. 89-4.
Congressional Research Service
8
link to page 15 The POWER Initiative: Energy Transition as Economic Development
government and member states, while economic development activities are federally funded through appropriations. Thirteen state governors and a federal co-chair oversee the ARC. The federal co-chair is appointed by the President with the advice and consent of the Senate.25
27 Scope and Activities
The ARC'’s POWER Initiative program prioritizes federal resources to projects and activities in coal communities that exhibit elements that
- produce multiple economic development outcomes (e.g., promoting regional economic growth; job creation; and/or employment opportunities for displaced workers);
- are specifically identified under state, local, or regional economic development plans; and
-
have been collaboratively designed by state, local, and regional stakeholders.
26
The ARC funds three28
For FY2022, the ARC will fund two classes of grants as part of the POWER Initiative: (1) implementation grants, with awards of up to $1.5 million; (2) technical assistance grants, with awards of up to $50,000; and (3) broadband deployment projects, with awards of up to $2.5 million.
For FY2019, $45 (with the exception for broadband deployment projects, which can have awards of up to $2.5 million),29 and (2) planning grants, with awards of up to $50,000. For FY2022, $65 million in grant funding was made available for the POWER Initiative (see Table 4), of which one-third, of which $15 million was reserved for broadband projects. 30
POWER investments are subject to the ARC'’s grant match requirements, which are linked to the Commission'Commission’s economic distress hierarchy.27
31 Those economic distress designations are, in descending order of distress
-
distressed (80% funding allowance, 20% grant match);
28 - at-risk (70%);
- transitional (50%);
- competitive (30%); and
- attainment (0% funding allowance).
32 at-risk (70%);
27 For more information about the ARC and the other federal regional commissions and authorities, see CRS Report R45997, Federal Regional Commissions and Authorities: Structural Features and Function, by Julie M. Lawhorn. See also, in summarized form, CRS In Focus IF11140, Federal Regional Commissions and Authorities: Overview of Structure and Activities, by Julie M. Lawhorn.
28 Appalachian Regional Commission (ARC), Partnerships for Opportunity and Workforce and Economic Revitalization (POWER) Initiative: Federal Fiscal Year 2022—Request for Proposals (RFP) for Project Grants, February 22, 2022, https://www.arc.gov/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/POWER-2022-RFP.pdf.
29 According to the FY2022 POWER RFP, to qualify for the broadband deployment funding, at least 65% of the broadband project’s budget “must be directed to the physical deployment of broadband infrastructure.” If more than 35% of proposed funds are directed to activities not directly associated with deployment of broadband infrastructure, then applicants may apply for funding under the guidelines for implementation projects and will not qualify for broadband deployment funding. See ARC, POWER, FY2022 RFP for Project Grants, February 22, 2022, p. 3, https://www.arc.gov/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/POWER-2022-RFP.pdf.
30 ARC, POWER, FY2022 RFP for Project Grants, February 22, 2022, p. 3, https://www.arc.gov/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/POWER-2022-RFP.pdf.
31 ARC, County Economic Status and Distressed Areas in Appalachia, https://www.arc.gov/classifying-economic-distress-in-appalachian-counties/.
32 The ARC uses an index-based classification system to compare each county within its jurisdiction with national averages based on: (1) three-year average unemployment rates; (2) per capita market income; and (3) poverty rates. These factors are calculated into a composite index value for each county, which are ranked and sorted into designated distress levels. Each distress level corresponds to a given county’s ranking relative to that of the U.S. as a whole. These designations are defined as, in descending order: distressed counties, or those with values in the “worst” 10% of U.S. counties; at-risk, which rank between worst 10% and 25%; transitional, which rank between worst 25% and best 25%; competitive, which rank between “best” 25% and best 10%; and attainment, or those which rank in the best 10%.
Congressional Research Service
9
link to page 11 link to page 14 The POWER Initiative: Energy Transition as Economic Development
transitional (50%); competitive (30%); and attainment (0% funding allowance).
Special allowances at the discretion of the commission may reduce or discharge matches, and match requirements may be met with other federal funds when allowed. Designations of county-level distress in the ARC'’s service area are represented inin Figure 1.
POWER investments are also aligned to the ARC'’s strategic plan. The current strategic plan, adopted in November 2015October 2021, prioritizes five investment goals:
1.1. entrepreneurial and business development;2.2. workforce development;3.3. infrastructure development;4.4. natural and cultural assets; and5.5. leadership and community capacity.29
33
Given its programmatic breadth, POWER investments may link to any one of these investment goals. POWER investment determinations are made according to annual objectives outlined in the request for proposals, as well as broader investment priorities, which are building a competitive workforce; fostering entrepreneurial activities; developing industry clusters in communities; and broadband.34 responding to substance abuse
responding to substance abuse.
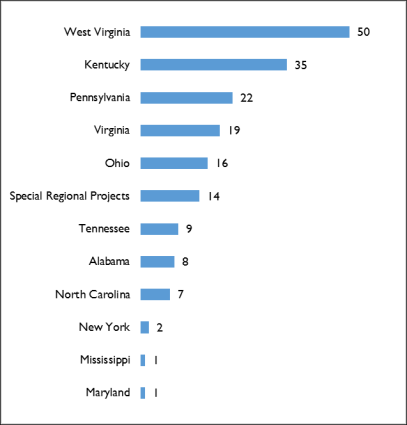
The ARC has designated $50 million annually ("activities in support of the POWER+ Plan"30) for POWER activities (Table 4). According to the ARC,31 over $148According to the ARC,35 over $319 million in investments have been made since FY20162015 through 185395 projects in 312358 counties across the ARC'’s service area, leveraging an estimated $772 million 1.5 billion of private investment. Figure 2 is a representation of the ARC'’s POWER Initiative projects tallied by state (for 2016-2022 (to date)).
33 ARC, Appalachia Envisioned: A New Era of Opportunity, ARC Strategic Plan for Fiscal Years 2022–2026, https://www.arc.gov/strategicplan/.
34 ARC, POWER, FY2022 RFP for Project Grants, February 22, 2022, pp. 2-3, https://www.arc.gov/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/POWER-2022-RFP.pdf.
35 ARC, ARC’s Partnerships for Opportunity and Workforce and Economic Revitalization (POWER) Initiative, accessed July 28, 2022, https://www.arc.gov/arcs-power-initiative/.
Congressional Research Service
10
link to page 15
The POWER Initiative: Energy Transition as Economic Development
Figure 2. Distribution of ARC POWER Initiative Projects, 2016-2022 (to date)
by state (and one additional category)
Source: Data retrieved from ARC website (https://www.arc.gov/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/POWER-Award-Summaries-by-State-as-of-May-2022.pdf) on September 6, 2022. Notestallied by state.
Data reflect the number of awards announced by ARC as of May 2022.
Funding History Funding History
While the POWER Initiative does not receive appropriations separate from that of the ARC as a whole, congressional intent is signaled in House Appropriations Committee reports, which specify amounts to be reserved for the POWER Initiative. In committee report language, it is generally described as activities "“in support of the POWER+ Plan."32
” or “in support of the POWER Initiative.”36
Table 4 shows appropriations set aside for the POWER Initiative from FY2016 to FY2022 and the FY2023 requested amounts, as well as the amounts of annual and supplemental appropriations for ARC as a whole.
36 See, for example: U.S. Congress, House Appropriations, Energy and Water Appropriations Bill, 2019, Report to accompany H.R. 5895, 115th Cong., 2nd sess., 2019, H.Rept. 115-697 (Washington: GPO, 2019), p. 159; and the explanatory statement accompanying the Energy and Water, Legislative Branch, and Military Construction and Veterans Affairs Appropriations Act, 2019 (P.L. 115-244), printed in the September 10, 2018, Congressional Record (p. H8038), vol. 164, no. 150, https://www.congress.gov/115/crec/2018/09/10/CREC-2018-09-10-pt1-PgH7946-2.pdf.
Congressional Research Service
11
link to page 15 link to page 11 The POWER Initiative: Energy Transition as Economic Development
Table 4. ARC POWER Initiative Appropriations, FY2016-FY2022
and FY2023 Request
in millions ($)
FY2023
FY2016
FY2017
FY2018
FY2019
FY2020
FY2021
FY2022
Request
Appropriations
$50
$50
$50
$50
$50
$55
$65
$72
reserved for POWER
Appropriations
$146
$152
$155
$165
$175
$180
$395
$235
for the ARC as a whole
Sources: Data compiled and tabulated by CRS from data provided by ARC and from shows appropriations set aside for the POWER Initiative from FY2016 to FY2019, and for the ARC as a whole.
|
FY2016 |
FY2017 |
FY2018 |
FY2019 |
|
|
Appropriations reserved for POWER |
$50 |
$50 |
$50 |
$50 |
|
Appropriations for the ARC as a whole |
$146 |
$152 |
$155 |
$165 |
Source: Data compiled and tabulated by CRS from committee reports associated with the following appropriations bills: fol owing annual appropriations bil s: P.L. 114-113 (FY2016); P.L. 115-31 (FY2017); P.L. 115-141141 (FY2018); P.L. 115-244 (FY2019).
The ARC received approximately $610 million (FY2019); P.L. 116-94 (FY2020); P.L. 116-260 (FY2021); and P.L. 117-103 (FY2022). The FY2022 amount includes $195 mil ion provided through annual appropriations (P.L. 117-103) and $200 mil ion from Division J, Title III of the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA, P.L. 117-58). The IIJA provided $200 mil ion for the ARC in each fiscal year from FY2022 through FY2026. The amount requested for FY2023 is from ARC FY2023 Performance Budget Justification (see https://www.arc.gov/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/FINAL-FY2023-ARC-Budget-Justification-Congressional.pdf).
To date, the ARC received approximately $1.2 billion in requests for POWER Initiative grant funding from FY2016 to FY2018 FY2022 (Table 5). This suggests that there was unmet demand for the POWER Initiative in the Appalachian region alone (the ARC'’s service area, as depicted in Figure 1).
Table 5. ARC POWER Initiative Grant Awards, FY2016-FY2022
FY2016-
FY2017
FY2018
FY2019
FY2020
FY2021
FY2022a
# Applications
216
231
140
174
188
167
Amount of
$280 mil ion
$329 mil ion
$120 mil ion
$164 mil ion
$173 mil ion
$153 mil ion
Funding Requested by Applicants
Awarded Funds
$91 mil ion
$49 mil ion
$47 mil ion
$45 mil ion
$57 mil ion
$77 mil ion
Table 5. ARC POWER Initiative Grant Awards, FY2016-FY2018
|
FY2016-FY2017 |
FY2018 |
|
|
# Applications |
216 |
231 |
|
Locally Requested Funds |
$280 million |
$329 million |
|
Awarded Funds |
$91 million |
$49 million |
Source: Data provided by the ARC and tabulated by CRS.
Source: Data provided by the ARC and tabulated by CRS. Notes: For FY2016 and FY2017, funding was combined into a single pot and awarded accordingly. In FY2018, funding was awarded through two competitive rounds. When this information was collected in 2019, three applications were reported to be in the final stages of review.
FY2021, the Commission voted to recommend 26 projects totaling $28,440,625 from the FY2021cycle for funding in FY2022. a. The FY2022 “Awarded Funds” amount reflects the amount of funding announced as of August 18, 2022.
Policy Considerations Policy Considerations
The Energy Information Administration (EIA) projects that coal production overall will continue to decline as a consequence of falling market demand.3337 In particular, the EIA forecasts coal to account for 24% of U.S. electric energy generation in 2019 and 2020, down from 28% in 2018.34
37 U.S. Energy Information Administration, Annual Energy Outlook 2022: With Projections to 2050, March 3, 2022. Total Coal Production, reference case, https://www.eia.gov/outlooks/aeo/data/browser/#/?id=1-AEO2022®ion=0-0&cases=ref2022&start=2020&end=2050&f=A&linechart=~ref2022-d011222a.6-1-AEO2022&ctype=linechart&
Congressional Research Service
12
link to page 15 The POWER Initiative: Energy Transition as Economic Development
account for 6% less generating capacity at the end of 2022 than at the end of 2021.38 By 2050, coal is projected to decline to 1710% of U.S. electricity generation, nuclear is projected to account for 12%, renewables 31(i.e., wind, solar) 36%, hydropower 5%, and natural gas 3934%, according to EIA projections.35
Coal'39
Coal’s decline is a function of market forces, particularly its higher cost relative to natural gas and renewable energy options.3640 In the future, under current policies, coal'’s cost disadvantage is expected to continue, and could be accelerated if policies are adopted to reduce GHG emissions that contribute to climate change.3741 Even with federal incentives to invest in carbon capture, utilization, and storage as a means to mitigate fossil fuel-related emissions, coal may still not be competitive in many situations. As a result of falling demand, noncompetitive coal producers and their communities are expected to face continued economic dislocation.
Should it wish to broaden or intensify federal efforts to address energy transition in local communities, Congress may have several options. In the past, Congress has demonstrated bipartisan interest in the federal government providing assistance to populations adversely affected by the ongoing energy transitions. It has done so through its appropriations for the ARC'ARC’s POWER Initiative, the EDA'’s ACC program, and the AMLAMLER investments.3842 In combination with evidence of unmet demand for federal assistance, as measured by unfunded requests to the ARC (Table 5), Congress may consider reviewing the balance among needs, appropriations, and effectiveness of past efforts.
Congress could conduct a review of the POWER Initiative and the efficacy of its performance and resources. This potential review suggests some particular considerations:
-
Geography: While the ACC is available for the nation as a whole, the ARC
's’s POWER Initiative is restricted to the ARC'’s service area in the Appalachian region. Congress may consider expanding the POWER Initiative to be available more broadly across the nation, or in a more targeted fashion as demonstrated by the ARC'’s program. Alternatively, funding could be made available nationwide to any eligible coal community, such as through other federal regional commissions and authorities and/or EDA regions. -
Funding: Projections of U.S. coal production (cited earlier) suggest that the
ongoing transition in U.S. energy systems may lead to further localized economic distress without the development of new regional opportunities. Congress may consider the level of funding for POWER Initiative programs in the context of those economic needs. Funding levels could be tied to the overall scale of the challenge, allocated to areas with the greatest need, and made in consideration of
sourcekey=0.
38 U.S. Energy Information Administration, Coal Will Account for 85% of U.S. Electric Generating Capacity Retirements in 2022, January 11, 2022, https://www.eia.gov/todayinenergy/detail.php?id=50838.
39 U.S. Energy Information Administration, Annual Energy Outlook 2022: With Projections to 2050, March 3, 2022. Total Coal Production, reference case, https://www.eia.gov/outlooks/aeo/data/browser/#/?id=1-AEO2022®ion=0-0&cases=ref2022&start=2020&end=2050&f=A&linechart=~ref2022-d011222a.6-1-AEO2022&ctype=linechart&sourcekey=0 and https://www.eia.gov/outlooks/aeo/narrative/electricity/sub-topic-02.php.
40 Howard Gruenspecht, The U.S. Coal Sector: Recent and Continuing Challenges, Brookings Institution, January 2019, https://www.brookings.edu/research/the-u-s-coal-sector/.
41 See, for example, Ed Crooks, “U.S. Coal Output Forecasted to Fall Despite Trump Revival Efforts,” Financial Times, January 26, 2019, https://www.ft.com/content/5c31c480-2036-11e9-b126-46fc3ad87c65.
42 See, for example: U.S. Congress, House Natural Resources, Energy and Mineral Resources, Climate Change: Preparing for the Energy Transition, 116th Cong., 1st sess., February 12, 2019, House Event 108873.
Congressional Research Service
13
The POWER Initiative: Energy Transition as Economic Development
challenge, allocated to areas with the greatest need, and made in consideration ofdata-driven evaluations of the program effectiveness. In assessing scale, Congress may consider macroeconomic factors as well as social and environmental policy objectives. -
Energy Type: Congress may also consider expanding the POWER Initiative
programand/or related programs beyond the coal industry to other energy industries or regions perceived to be in decline.43 For example, since FY2020, Congress has directed the EDA to allocate economic adjustment assistance funding to support transition efforts in nuclear closure communities. Congress may consider policies to support economically distressed communities impacted by other changes in the fossil fuel industry as wellFor example, economic strain and job losses following the closure of other electrical generating units, such as aging nuclear power plants,39may signal additional types of displacement. EIA forecasts anticipate a modest decline in nuclear power generation by 2050 as older, less efficient reactors are retired. Nuclear-industry communities may face similar issues of economic distress and labor dislocation. Congress may also consider other public policy goals, such as reducing GHGs, to assist in promoting renewable energy types and carbon capture technologies.
Should Congress consider such efforts, the ARC'’s POWER Initiative program could serve as a potential model to be scaled or replicated as needed. In addition, other models have also been proposed in bills introduced in the 116th Congress116th and 117th Congresses that would assist coal communities in transition.40
44 Concluding Notes
Although the POWER+ Plan was not enacted in its entirety, some of its legacy programs continue to receive annual appropriations and remain active. The persistence of such programs suggests support among many policymakers for federal efforts to rectify, or at least attenuate, economic distress as a consequence of energy transition. In addition, were Congress to pursue policy efforts reflective of broadening concern for climate issues,4145 a POWER Initiative-type program could be developed to also facilitate energy transition from fossil fuel-based energy sources to a mix of renewables and other alternatives.
Although the POWER+ Plan did not continue beyond the Obama administration, several constituent programs have continued to receive congressional backing, and applicant volume—at least in the case of the ARC'’s POWER Initiative—may suggest further demand for additional federal resources in addressing energy and economic transition issues. More broadly, these mechanisms could also be purposed to facilitate federal resources for other related issues, such as related to ecological/environmental resilience and adaptation.
The POWER Initiative, as originally conceived or in its current form as a program of the ARC, has not been subjected to a formal evaluationevaluated by the U.S. Government Accountability Office (GAO) or other research organization offor its effectiveness as either a mechanism for alleviating community economic distress caused by the declining coal industry, or economic development more broadly. One
43 See Martha T. Moore, Nuclear Plant Closures Bring Economic Pain to Cities and Towns, Pew Trusts, September 5, 2018, https://www.pewtrusts.org/en/research-and-analysis/blogs/stateline/2018/09/05/nuclear-plant-closures-bring-economic-pain-to-cities-and-towns.
44 For example, in the 166th Congress, H.R. 315 included provisions “To amend the Surface Mining Control and Reclamation Act of 1977 to authorize partnerships between States and nongovernmental entities for the purpose of reclaiming and restoring land and water resources adversely affected by coal mining activities before August 3, 1977, and for other purposes”; H.R. 4142, “To rebuild the Nation’s infrastructure, provide a consumer rebate to the American people, assist coal country, reduce harmful pollution, and for other purposes.” In the 117th Congress, H.R. 5376 included provisions to provide assistance to assistance to energy and industrial transition communities, including coal, oil and gas, and nuclear transition communities.
45 See H.Res. 112.
Congressional Research Service
14
The POWER Initiative: Energy Transition as Economic Development
recent GAO report mentioned the Assistance to Coal Communities program, but did not seek to analyze its activities or efficacy.46 Similarly, older GAO reports exist that feature the Abandoned Mine Land Reclamation program (prior to its current configuration),47 and the Appalachian Regional Commission,48 but may be of limited relevance when evaluating current programming, including more recent activities such as the POWER Initiative. Meanwhile, a number of anecdotal and media reports appear to tout the POWER Initiative’s success and viability.49 The ARC, for its part, reports that the POWER Initiative has “invested over $319 million in over 395 projects touching 358 counties across Appalachia.” According to the ARC, those investments are “projected to create or retain more than 36,600 jobs, and leverage more than $1.5 billion in additional private investment.”50
ARC completed three evaluations of the POWER Initiative. The FY2019 evaluation (Year 1) focused on early impacts, challenges, opportunities, and technical assistance needs associated with the implementation grants funded in or prior to FY2018.51 The FY2020 evaluation (Year 2) covered additional topics such as projects designed to address the impacts of substance use disorder (SUD); community capacity in counties in which multiple POWER projects have been implemented; and multistate projects. The FY2020 evaluation also evaluated early results of closed POWER projects.52 The FY2021 evaluation (Year 3) reported on indicators of change from the individual, business, and community levels.53 The evaluations highlight the varying scales of implementation and the range of activities supported by POWER Initiative awards (e.g., infrastructure, planning, broadband, workforce development, substance use disorder, or a combination of activities). Additionally, the evaluations note that POWER projects may have a range of timelines for implementation, which impacts the evaluators’ ability to uniformly measure outcomes. An FY2022 evaluation is in development.
46 U.S. Government Accountability Office, Economic Adjustment Assistance: Federal Programs Intended to Help Beneficiaries Adjust to Economic Disruption, GAO-19-85R, March 5, 2019, pp. 13-14, https://www.gao.gov/products/GAO-19-85R.
47 U.S. Government Accountability Office, Department of the Interior, Office of Surface Mining Reclamation and Enforcement: Abandoned Mine Land Program, GAO-09-208R, November 26, 2008, https://www.gao.gov/products/GAO-09-208R.
48 U.S. Government Accountability Office, Economic Development: Limited Information Exists on the Impact of Assistance Provided by Three Agencies, RCED-96-103, April 3, 1996, https://www.gao.gov/products/RCED-96-103.
49 See, for example: Brittany Patterson, Portal 31: How A Closed Mine Opened New Prospects For One Coal Town, WFPL.org, November 11, 2019, https://wfpl.org/portal-31-how-a-closed-mine-opened-new-prospects-for-one-coal-town/; and “A $1.5M Shot in the Arm for Workforce Development,” Independent Herald, November 12, 2019, https://www.ihoneida.com/2019/11/12/shot-arm-workforce-development/.
50 ARC, POWER Award Summaries by State as of May 2022, accessed September 6, 2022, https://www.arc.gov/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/POWER-Award-Summaries-by-State-as-of-May-2022.pdf, and ARC, ARC’s POWER Initiative, https://www.arc.gov/arcs-power-initiative/.
51 ARC, Chamberlin and Dunn, Success Factors, Challenges, and Early Impacts of the POWER Initiative: An Implementation Evaluation, October 2019, https://www.arc.gov/report/success-factors-challenges-and-early-impacts-of-the-power-initiative-an-implementation-evaluation/.
52 ARC, Chamberlin and Dunn, POWER Initiative Evaluation: Factors and Results of Project Implementation, September 2020, https://www.arc.gov/report/power-initiative-evaluation-factors-and-results-of-project-implementation/.
53 ARC, Chamberlin and Dunn, POWER Initiative Evaluation: The POWER of Change Stories of Results for Individuals, Businesses, and Communities, September 2021,
Congressional Research Service
15
The POWER Initiative: Energy Transition as Economic Development
Author Information
Julie M. Lawhorn
Analyst in Economic Development Policy
Acknowledgments
This report was originally written by former CRS Analyst Michael Cecire. Congressional clients seeking more information and analysis on the material covered in this report should contact the current author. Lance N. Larson, Analyst in Environmental Policy, provided substantive edits and assistance in updating the report.
Disclaimer
This document was prepared by the Congressional Research Service (CRS). CRS serves as nonpartisan shared staff to congressional committees and Members of Congress. It operates solely at the behest of and under the direction of Congress. Information in a CRS Report should not be relied upon for purposes other than public understanding of information that has been provided by CRS to Members of Congress in connection with CRS’s institutional role. CRS Reports, as a work of the United States Government, are not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Any CRS Report may be reproduced and distributed in its entirety without permission from CRS. However, as a CRS Report may include copyrighted images or material from a third party, you may need to obtain the permission of the copyright holder if you wish to copy or otherwise use copyrighted material.
Congressional Research Service
R46015 · VERSION 10 · UPDATED
16 distress caused by the declining coal industry, or economic development more broadly. One recent GAO report mentioned the Assistance to Coal Communities program, but did not seek to analyze its activities or efficacy.42 Similarly, older GAO reports exist that feature the Abandoned Mine Land Reclamation program (prior to its current configuration),43 and the Appalachian Regional Commission,44 but may be of limited relevance when evaluating current programming, including more recent activities such as the POWER Initiative. Meanwhile, a number of anecdotal and media reports appear to tout the POWER Initiative's success and viability.45 The ARC, for its part, reports that the POWER Initiative has "invested over $190 million in 239 projects touching 326 counties across Appalachia." According to the ARC, those investments are "projected to create or retain more than 23,000 jobs, and leverage more than $811 million in additional private investment."46
In the ARC's 2018 Performance and Accountability Report, the ARC reported that the annual outcome target for "Students, Workers, and Leaders with Improvements" in FY2018 was exceeded by 55% "likely due to" investments from the POWER Initiative; similarly, the ARC reported the outcome target for "Communities with Enhanced Capacity" in FY2018 was exceeded by 125%, "due in part to priorities established for the POWER Initiative." The same report also noted that the ARC launched a new monitoring and evaluation effort on the POWER Initiative in September 2018 encompassing "approximately 135 POWER grants" in FY2015-FY2017.47 The results of that assessment have not yet been released.
Author Contact Information
Footnotes
| 1. |
U.S. Energy Information Administration, Annual Energy Outlook 2019: With Projections to 2050, January 24, 2019. Total Coal Production, reference case: https://www.eia.gov/outlooks/aeo/data/browser/#/?id=1-AEO2019®ion=0-0&cases=ref2019&start=2017&end=2050&f=Q&linechart=~ref2019-d111618a.6-1-AEO2019&ctype=linechart&sourcekey=0. |
| 2. |
Eric Bowen et al., An Overview of the Coal Economy in Appalachia, Appalachian Regional Commission, January 2018, https://www.arc.gov/assets/research_reports/CIE1-OverviewofCoalEconomyinAppalachia.pdf. |
| 3. |
The White House, Office of the Press Secretary, "FACT SHEET: The Partnerships for Opportunity and Workforce and Economic Revitalization (POWER) Initiative," press release, March 27, 2015, https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/the-press-office/2015/03/27/fact-sheet-partnerships-opportunity-and-workforce-and-economic-revitaliz. |
| 4. |
The White House, Office of the Press Secretary, "FACT SHEET: Administration Announces New Workforce and Economic Revitalization Resources for Communities through POWER Initiative," press release, October 2015, https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/the-press-office/2015/10/15/fact-sheet-administration-announces-new-workforce-and-economic. |
| 5. |
U.S. Office of Management and Budget (OMB), Investing in Coal Communities, Workers, and Technology: The POWER+ Plan, The President's Budget: Fact Sheets on Key Issues Fiscal Year 2016, February 2, 2015, https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/sites/default/files/omb/budget/fy2016/assets/fact_sheets/investing-in-coal-communities-workers-and-technology-the-power-plan.pdf. |
| 6. |
The POWER+ Plan involved a number of existing programs and initiatives administered by the participating agencies, and did not have an appropriations line item unto itself. An OMB fact sheet describes the specific funding measures proposed in the new budget among the participating agencies: OMB, Investing in Coal Communities, Workers, and Technology: The POWER+ Plan, The President's Budget: Fact Sheets on Key Issues, Fiscal Year 2016, February 2, 2015, https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/sites/default/files/omb/budget/fy2016/assets/fact_sheets/investing-in-coal-communities-workers-and-technology-the-power-plan.pdf.. These funding requests were reflected in the FY2016 White House budget proposal: OMB, Fiscal Year 2016 Budget of the U.S. Government: Appendix, February 2, 2015, https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/BUDGET-2016-APP/pdf/BUDGET-2016-APP.pdf. See also The White House, Office of the Press Secretary, "FACT SHEET: Administration Announces New Workforce and Economic Revitalization Resources for Communities through POWER Initiative," press release, October 2015, https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/the-press-office/2015/10/15/fact-sheet-administration-announces-new-workforce-and-economic. |
| 7. |
OMB, Investing in Coal Communities, Workers, and Technology: The POWER+ Plan, The President's Budget: Fact Sheets on Key Issues, Fiscal Year 2016, February 2, 2015, https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/sites/default/files/omb/budget/fy2016/assets/fact_sheets/investing-in-coal-communities-workers-and-technology-the-power-plan.pdf. |
| 8. |
The White House, Office of the Press Secretary, "FACT SHEET: The Partnerships for Opportunity and Workforce and Economic Revitalization (POWER) Initiative," press release, March 27, 2015, https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/the-press-office/2015/03/27/fact-sheet-partnerships-opportunity-and-workforce-and-economic-revitaliz. |
| 9. |
The White House, Office of the Press Secretary, "FACT SHEET: Administration Announces New Workforce and Economic Revitalization Resources for Communities through POWER Initiative," press release, October 2015, https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/the-press-office/2015/10/15/fact-sheet-administration-announces-new-workforce-and-economic. |
| 10. |
U.S. Congress, House Committee on Appropriations, Making Further Continuing Appropriations for the Department of Homeland Security for Fiscal Year 2019, And for Other Purposes, Conference report to accompany H.J.Res. 31, 116th Cong., 1st sess., February 13, 2019, H.Rept. 116-9 (Washington: GPO, 2019), p. 610. |
| 11. |
Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2019, P.L. 116-6. |
| 12. |
U.S. Department of Commerce, Economic Development Administration: Fiscal Year 2019 Congressional Budget Request, February 12, 2018, pp. 51-55, http://www.osec.doc.gov/bmi/budget/FY19CBJ/EDA_FY2019_President%27s_Budget_FINAL.pdf. |
| 13. |
U.S. Department of Commerce, Economic Development Administration: Fiscal Year 2017 Congressional Budget Request, February 9, 2016, pp. 36-38, http://www.osec.doc.gov/bmi/budget/FY17CBJ/EDA%20FY%202017%20Congressional%20Submission%202-8-16%20OMB%20cleared%20508%20Compliant.pdf. |
| 14. |
For FY2018, the Trump Administration requested $30 million in funding for the EDA to enable the "orderly closeout" of the agency: OMB, Budget of the U.S. Government Fiscal Year 2018: Appendix, May 23, 2017, pp. 181-183, https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/BUDGET-2018-APP/pdf/BUDGET-2018-APP.pdf. In FY2019, the EDA was also proposed for termination, and approximately $15 million was requested to enable its closeout: OMB, Budget of the U.S. Government Fiscal Year 2019: Appendix, February 12, 2018, pp. 182-183, https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/BUDGET-2019-APP/pdf/BUDGET-2019-APP.pdf. In the Trump Administration's budget request for FY2020, $30 million was requested for the EDA's closeout: OMB, Budget of the U.S. Government Fiscal Year 2020: Appendix, March 18, 2019, pp. 178-180, https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/BUDGET-2020-APP/pdf/BUDGET-2020-APP.pdf. |
| 15. |
The White House, Office of the Press Secretary, "FACT SHEET: The Partnerships for Opportunity and Workforce and Economic Revitalization (POWER) Initiative," press release, March 27, 2015, https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/the-press-office/2015/03/27/fact-sheet-partnerships-opportunity-and-workforce-and-economic-revitaliz. |
| 16. |
13 C.F.R. §301.3. See also Economic Development Administration, Applying for EDA Investments: Eligibility Requirements and Criteria, https://www.eda.gov/archives/2016/how-to-apply/files/Eligibility-Requirements-and-Criteria.pdf. |
| 17. |
See, for example: The Miners Protection Act, first introduced in 2015 as S. 1714, which has been regularly reintroduced in the years since; and the Revitalizing the Economy of Coal Communities by Leveraging Local Activities and Investing More (RECLAIM) Act of 2016, H.R. 4456, which has also been regularly reintroduced but failed to gain enactment. |
| 18. |
Funding launched in FY2016 was notable for providing grants for economic development purposes. Previously, grants had been made available to eligible states and tribes to address the hazards and environmental degradation posed by abandoned mine sites under the Surface Mining Control and Reclamation Act of 1977 (P.L. 95-87). For more information on the AML economic development program, see Office of Surface Mining Reclamation and Enforcement, Report on Abandoned Mine Land Reclamation Economic Development Pilot Program (AML Pilot Program) for FY 2016–FY2018, April 19, 2019, https://www.osmre.gov/programs/AML/2016_2018_Annual_Report_AML_Economic_Development_Pilot_Program.pdf. See also Office of Surface Mining Reclamation and Enforcement, Reclaiming Abandoned Mine Lands, https://www.osmre.gov/programs/aml.shtm. |
| 19. |
To clarify the effective date of certain provisions of the Border Patrol Agent Pay Reform Act of 2014, and for other purposes, P.L. 114-13. |
| 20. |
Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2017, P.L. 115-31. |
| 21. |
Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2018, P.L. 115-141. |
| 22. |
Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2019, P.L. 116-6. |
| 23. |
It should be noted that while the ARC is generally classified as an independent federal agency, the federal regional commissions and authorities are unique in that although they are federally-chartered organizations and draw on federal appropriations for their operations and activities, they are generally understood to be partnerships between the constituent states and the federal government. The vast majority of their staff and leadership are not federal employees. For more information, see CRS Report R45997, Federal Regional Commissions and Authorities: Structural Features and Function, by Michael H. Cecire. |
| 24. |
Appalachian Regional Development Act of 1965, as amended, P.L. 89-4. |
| 25. |
For more information about the ARC and the other federal regional commissions and authorities, see CRS Report R45997, Federal Regional Commissions and Authorities: Structural Features and Function, by Michael H. Cecire. See also, in summarized form, CRS In Focus IF11140, Federal Regional Commissions and Authorities: Overview of Structure and Activities, by Michael H. Cecire. |
| 26. |
Appalachian Regional Commission (ARC), Partnerships for Opportunity and Workforce and Economic Revitalization (POWER) Initiative: Federal Fiscal Year 2019 – Request for Proposals (RFP) for Project Grants, January 7, 2019, https://www.arc.gov/images/grantsandfunding/POWER2019/RFP/POWER-RFP-2019.pdf. |
| 27. |
ARC, County Economic Status and Distressed Areas in Appalachia, https://www.arc.gov/appalachian_region/CountyEconomicStatusandDistressedAreasinAppalachia.asp. |
| 28. |
The ARC uses an index-based classification system to compare each county within its jurisdiction with national averages based on: (1) three-year average unemployment rates; (2) per capita market income; and (3) poverty rates. These factors are calculated into a composite index value for each county, which are ranked and sorted into designated distress levels. Each distress level corresponds to a given county's ranking relative to that of the U.S. as a whole. These designations are defined as, in descending order: distressed counties, or those with values in the "worst" 10% of U.S. counties; at-risk, which rank between worst 10% and 25%; transitional, which rank between worst 25% and best 25%; competitive, which rank between "best" 25% and best 10%; and attainment, or those which rank in the best 10%. |
| 29. |
ARC, Investing in Appalachia's Future: The Appalachian Regional Commission's Five-Year Strategic Plan for Capitalizing on Appalachia's Opportunities, 2016–2020, https://www.arc.gov/about/arc2016-2020strategicplan.asp. |
| 30. |
U.S. Congress, House Appropriations, Energy and Water Appropriations Bill, 2019, Report to accompany H.R. 5895, 115th Cong., 2nd sess., 2019, H.Rept. 115-697 (Washington: GPO, 2019), p. 159. |
| 31. |
ARC, Partnerships for Opportunity and Workforce and Economic Revitalization (POWER) Initiative, https://www.arc.gov/funding/POWER.asp. |
| 32. |
See, for example: U.S. Congress, House Appropriations, Energy and Water Appropriations Bill, 2019, Report to accompany H.R. 5895, 115th Cong., 2nd sess., 2019, H.Rept. 115-697 (Washington: GPO, 2019), p. 159. |
| 33. |
U.S. Energy Information Administration, Annual Energy Outlook 2019: With Projections to 2050, January 24, 2019. Total Coal Production, reference case: https://www.eia.gov/outlooks/aeo/data/browser/#/?id=1-AEO2019®ion=0-0&cases=ref2019&start=2017&end=2050&f=Q&linechart=~ref2019-d111618a.6-1-AEO2019&ctype=linechart&sourcekey=0. |
| 34. |
U.S. Energy Information Administration, Short Term Energy Outlook, August 2019, https://www.eia.gov/outlooks/steo/pdf/steo_full.pdf. |
| 35. |
U.S. Energy Information Administration, Annual Energy Outlook 2019: With Projections to 2050, January 24, 2019, https://www.eia.gov/outlooks/aeo/pdf/aeo2019.pdf. |
| 36. |
Howard Gruenspecht, The U.S. Coal Sector: Recent and Continuing Challenges, Brookings Institution, January 2019, https://www.brookings.edu/research/the-u-s-coal-sector/. |
| 37. |
See, for example, Ed Crooks, "U.S. Coal Output Forecasted to Fall Despite Trump Revival Efforts," Financial Times, January 26, 2019, https://www.ft.com/content/5c31c480-2036-11e9-b126-46fc3ad87c65. |
| 38. |
See, for example: U.S. Congress, House Natural Resources, Energy and Mineral Resources, Climate Change: Preparing for the Energy Transition, 116th Cong., 1st sess., February 12, 2019, House Event 108873. |
| 39. |
See Martha T. Moore, Nuclear Plant Closures Bring Economic Pain to Cities and Towns, Pew Trusts, September 5, 2018, https://www.pewtrusts.org/en/research-and-analysis/blogs/stateline/2018/09/05/nuclear-plant-closures-bring-economic-pain-to-cities-and-towns. |
| 40. |
For example, H.R. 315, "To amend the Surface Mining Control and Reclamation Act of 1977 to authorize partnerships between States and nongovernmental entities for the purpose of reclaiming and restoring land and water resources adversely affected by coal mining activities before August 3, 1977, and for other purposes"; H.R. 4142, "To rebuild the Nation's infrastructure, provide a consumer rebate to the American people, assist coal country, reduce harmful pollution, and for other purposes." |
| 41. |
See H.Res. 112. |
| 42. |
U.S. Government Accountability Office, Economic Adjustment Assistance: Federal Programs Intended to Help Beneficiaries Adjust to Economic Disruption, GAO-19-85R, March 5, 2019, pp. 13-14, https://www.gao.gov/products/GAO-19-85R. |
| 43. |
U.S. Government Accountability Office, Department of the Interior, Office of Surface Mining Reclamation and Enforcement: Abandoned Mine Land Program, GAO-09-208R, November 26, 2008, https://www.gao.gov/products/GAO-09-208R. |
| 44. |
U.S. Government Accountability Office, Economic Development: Limited Information Exists on the Impact of Assistance Provided by Three Agencies, RCED-96-103, April 3, 1996, https://www.gao.gov/products/RCED-96-103. |
| 45. |
|
| 46. |
ARC, POWER Initiative, accessed November 14, 2019, https://www.arc.gov/funding/power.asp. |
| 47. |
ARC, Fiscal Year 2018 Performance and Accountability Report, September 30, 2018, https://www.arc.gov/images/newsroom/publications/fy2018par/FY2018PerformanceAndAccountabilityReport.pdf. |