U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel: Overview and Developments since October 7, 2023
Changes from August 7, 2019 to November 16, 2020
This page shows textual changes in the document between the two versions indicated in the dates above. Textual matter removed in the later version is indicated with red strikethrough and textual matter added in the later version is indicated with blue.
Contents
- Background and Recent Trends
- Qualitative Military Edge (QME)
- Overview
- QME and U.S. Arms Sales to the Gulf
- U.S. Bilateral Military Aid to Israel
- The Current 10-Year Security Assistance Memorandum of Understanding (MOU)
- Foreign Military Financing (FMF) and Arms Sales
- Cash Flow Financing
- Early Transfer and Interest Bearing Account
- F-35 Joint Strike Fighter
- "Namer" Armored Personnel Carriers
- Excess Defense Articles
- Defense Budget Appropriations for U.S.-Israeli Missile Defense Programs
- Iron Dome
- Iron Dome's Performance
- Co-production and U.S. Funding
- David's Sling
- Overview
- Co-production and U.S. Funding
- The Arrow and Arrow II
- High Altitude Missile Defense System (Arrow III)
- Overview
- Emergency U.S. Stockpile in Israel
- Defense Budget Appropriations/Authorization for Anti-Tunnel Defense
- Aid Restrictions and Possible Violations
- Arms Sales and Use of U.S.-Supplied Equipment
- Human Rights Vetting (Leahy Law)
Use of U.S. Funds within Israel'U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel November 16, 2020 This report provides an overview of U.S. foreign assistance to Israel. It includes a review of past aid programs, data on annual assistance, and analysis of current issues. For general information Jeremy M. Sharp on Israel, see Israel: Background and U.S. Relations in Brief, by Jim Zanotti. Specialist in Middle Eastern Affairs Israel is the largest cumulative recipient of U.S. foreign assistance since World War II. Successive Administrations, working with Congress, have provided Israel with significant assistance in light of robust domestic U.S. support for Israel and its security; shared strategic goals in the Middle East; a mutual commitment to democratic values; and historical ties dating from U.S. support for the creation of Israel in 1948. To date, the United States has provided Israel $146 billion (current, or noninflation-adjusted, dollars) in bilateral assistance and missile defense funding. At present, almost all U.S. bilateral aid to Israel is in the form of military assistance, although from 1971 to 2007, Israel also received significant economic assistance. In 2016, the U.S. and Israeli governments signed their third 10-year Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) on military aid, covering FY2019 to FY2028. Under the terms of the MOU, the United States pledged to provide—subject to congressional appropriation—$38 billion in military aid ($33 billion in Foreign Military Financing grants plus $5 billion in missile defense appropriations) to Israel. This MOU followed a previous $30 billion 10-year agreement, which ran through FY2018. Israel is the first international operator of the F-35 Joint Strike Fighter, the Department of Defense’s fifth-generation stealth aircraft, considered to be the most technologically advanced fighter jet ever made. To date, Israel has purchased 50 F-35s in three separate contracts, funded with U.S. assistance. For FY2021, the Trump Administration requested $3.3 billion in FMF for Israel and $500 million in missile defense aid to mark the second year of the MOU. The Administration also requested $5 million in Migration and Refugee Assistance humanitarian funding for migrants to Israel. H.R. 7608 – State, Foreign Operations, Agriculture, Rural Development, Interior, Environment, Military Construction, and Veterans Affairs Appropriations Act, 2021 (which passed the House in July 2020) would, among other things, provide $3.3 billion in Foreign Military Financing (FMF) for Israel. H.R. 7617 – The Defense, Commerce, Justice, Science, Energy and Water Development, Financial Services and General Government, Labor, Health and Human Services, Education, Transportation, Housing, and Urban Development Appropriations Act, 2021 (which passed the House in July 2020) would provide $500 million in joint U.S.-Israeli missile defense cooperation (of which $73 million for Iron Dome, $177 million for David’s Sling, $77 million for Arrow III, and $173 million for Arrow II). Congressional Research Service link to page 5 link to page 6 link to page 7 link to page 9 link to page 10 link to page 12 link to page 13 link to page 13 link to page 14 link to page 15 link to page 16 link to page 17 link to page 17 link to page 18 link to page 20 link to page 21 link to page 21 link to page 22 link to page 22 link to page 23 link to page 25 link to page 27 link to page 28 link to page 29 link to page 29 link to page 30 link to page 31 link to page 32 link to page 33 link to page 33 link to page 35 link to page 35 link to page 36 link to page 36 link to page 36 link to page 38 link to page 39 link to page 41 link to page 41 link to page 41 link to page 42 link to page 42 U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel Contents Background and Recent Trends ....................................................................................................... 1 U.S. Aid and Israel’s Advanced Military Technology ..................................................................... 2 Qualitative Military Edge (QME) ................................................................................................... 3 U.S. Bilateral Military Aid to Israel ................................................................................................ 5 The Current 10-Year Security Assistance Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) ................ 6 Foreign Military Financing (FMF) and Arms Sales .................................................................. 8 Cash Flow Financing .......................................................................................................... 9 Early Transfer and Interest Bearing Account ...................................................................... 9 F-35 Joint Strike Fighter ................................................................................................... 10 KC-46A Pegasus ................................................................................................................ 11 Excess Defense Articles .......................................................................................................... 12 Defense Budget Appropriations for U.S.-Israeli Missile Defense Programs ................................ 13 Iron Dome ............................................................................................................................... 13 Iron Dome’s Past Performance ......................................................................................... 14 Co-production and U.S. Funding ...................................................................................... 16 David’s Sling ........................................................................................................................... 17 Overview ........................................................................................................................... 17 Co-production and U.S. Funding ...................................................................................... 18 The Arrow and Arrow II .......................................................................................................... 18 High Altitude Missile Defense System (Arrow III) ................................................................ 19 Emergency U.S. Stockpile in Israel......................................................................................... 21 Defense Budget Appropriations/Authorization for Anti-Tunnel Defense ..................................... 23 Defense Budget Appropriations/Authorization for Countering Unmanned Aerial Systems ......... 24 Aid Restrictions and Possible Violations ....................................................................................... 25 Arms Sales and Use of U.S.-Supplied Equipment .................................................................. 25 Human Rights Vetting (Leahy Law) ....................................................................................... 26 Use of U.S. Funds Within Israel’s Pre-June 1967 Borders ..................................................... 27 Annexation and U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel ............................................................................. 28 Israeli Arms Transfers to Third Parties.................................................................................... 29 Israel and China ................................................................................................................ 29 Other Ongoing Assistance and Cooperative Programs .................................................................. 31 Migration & Refugee Assistance............................................................................................. 31 Loan Guarantees...................................................................................................................... 32 Overview ........................................................................................................................... 32 Loan Guarantees for Economic Recovery ........................................................................ 32 American Schools and Hospitals Abroad Program (ASHA)................................................... 34 U.S.-Israeli Scientific & Business Cooperation ...................................................................... 35 U.S.-Israeli Energy Cooperation (BIRD Energy) ............................................................. 37s Pre-June 1967 Borders- Israeli Arms Transfers to Third Parties
- Israel and China
- Other Ongoing Assistance and Cooperative Programs
- Migration & Refugee Assistance
- Loan Guarantees
- Overview
- Loan Guarantees for Economic Recovery
- American Schools and Hospitals Abroad Program (ASHA)
- U.S.-Israeli Scientific & Business Cooperation
- U.S.-Israeli Energy Cooperation (BIRD Energy)
- U.S.-Israel Center of Excellence in Energy, Engineering and Water Technology
(Energy Center) .............................................................................................................. 37
BIRD Homeland Security (BIRD HLS) ........................................................................... 38
FY2021 Israel Assistance Legislation ........................................................................................... 38
Congressional Research Service
link to page 11 link to page 12 link to page 14 link to page 15 link to page 18 link to page 22 link to page 25 link to page 6 link to page 16 link to page 23 link to page 24 link to page 24 link to page 28 link to page 35 link to page 38 link to page 39 link to page 45 link to page 45 link to page 45 U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel
Figures Figure 1. Phasing Out Off-Shore Procurement (OSP) Under the MOU ......................................... 7 Figure 2. U.S. Military Aid to Israel over Decades ......................................................................... 8 Figure 3. U.S. and Israeli F-35s Fly in Formation ......................................................................... 10 Figure 4. F-35 Helmet Mounted Display ....................................................................................... 11 Figure 5
(Energy Center) - BIRD Homeland Security (BIRD HLS)
- Israel Assistance Legislation in the 116th Congress
Figures
- Figure 1. Phasing Out Off-Shore Procurement (OSP) Under the MOU
- Figure 2. U.S. Military Aid to Israel over Decades
- Figure 3. Iron Dome Launcher
Figure 4. David'. Iron Dome Launcher ...................................................................................................... 14 Figure 6. David’s Sling Launches Stunner InterceptorFigure 5................................................................. 18 Figure 7. Army Officers Inspect WRSA-I ..................................................................................... 21 Tables Table 1. Total U.S. Foreign Aid Obligations to Israel: 1946-2020 .................................................. 2 Table 2. Selected Notified U.S. Foreign Military Sales to Israel .................................................. 12. Army Officers Inspect WRSA-I
Tables
- Table 1. Total U.S. Foreign Aid Obligations to Israel: 1946-2019 and the 2020 Request
- Table 2. Selected Notified U.S. Foreign Military Sales to Israel
- Table 3. U.S. Contributions to the Arrow Program (Arrow, Arrow II, and Arrow III)
- .................. 19 Table 4. Defense Budget Appropriations for U.S.-Israeli Missile Defense: FY2006-
FY2019 - Table 5. U.S.-Israeli Anti-Tunnel Cooperation
- Table 6. Migration and Refugee Assistance Funding Levels for Israel
- Table 7. U.S. Loan Guarantees to Israel: FY2003-FY2019
Table 8. ASHA Program Grants from Israel Account,FY2020 ....................................................................................................................................... 20 Table 5. U.S.-Israeli Anti-Tunnel Cooperation .............................................................................. 24 Table 6. Migration and Refugee Assistance Funding Levels for Israel ......................................... 31 Table 7. U.S. Loan Guarantees to Israel: FY2003-FY2020 .......................................................... 34 Table 8. ASHA Program Grants from Israel Account: FY2000-FY2016 ...................................... 35 Table A-1. U.S. Bilateral Aid to Israel ........................................................................................... 41 Appendixes Appendix. Bilateral Aid to Israel ................................................................................................... 41 Contacts Author Information ........................................................................................................................ 41 Congressional Research Service link to page 7 U.S. Foreign Aid to IsraelFY2000-FY2016
Summary
This report provides an overview of U.S. foreign assistance to Israel. It includes a review of past aid programs, data on annual assistance, and analysis of current issues. For general information on Israel, see Israel: Background and U.S. Relations in Brief, by Jim Zanotti.
Israel is the largest cumulative recipient of U.S. foreign assistance since World War II. To date, the United States has provided Israel $142.3 billion (current, or noninflation-adjusted, dollars) in bilateral assistance and missile defense funding. Almost all U.S. bilateral aid to Israel is in the form of military assistance, although from 1971 to 2007 Israel also received significant economic assistance.
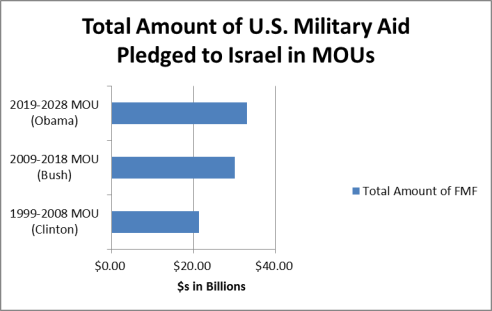
In 2016, the U.S. and Israeli governments signed a new 10-year Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) on military aid, covering FY2019 to FY2028. Under the terms of the MOU, the United States pledges to provide $38 billion in military aid ($33 billion in Foreign Military Financing grants plus $5 billion in missile defense appropriations) to Israel. This MOU replaced a previous $30 billion 10-year agreement, which ran through FY2018.
Israel is the first international operator of the F-35 Joint Strike Fighter, the Department of Defense's fifth-generation stealth aircraft, considered to be the most technologically advanced fighter jet ever made. To date, Israel has purchased 50 F-35s in three separate contracts.
P.L. 116-6, the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2019, provides the following for Israel:
- $3.3 billion in Foreign Military Financing (FMF), of which $815.3 million is for off-shore procurement;
- $5 million in Migration and Refugee Assistance (MRA) for refugee resettlement
- $2 million in a homeland security grant;
- Reauthorization of U.S. loan guarantees to Israel through September 30, 2023; and
- Reauthorization of War Reserve Stock Allies-Israel (WRSA-I) through Sept 30, 2020.
P.L. 115-245, the Department of Defense and Labor, Health and Human Services, and Education Appropriations Act, 2019 and Continuing Appropriations Act, 2019, provides the following for Israel:
- $500 million in missile defense, of which $70 million is for Iron Dome, $187 million for David's Sling, $80 million for Arrow 3, and $163 million for Arrow 2.
For FY2020, the Trump Administration requested $3.3 billion in FMF for Israel and $500 million in missile defense aid to mark the second year of the MOU. The Administration also requested $5 million in MRA humanitarian funding for migrants to Israel.
Background and Recent Trends
Background and Recent Trends The United States and Israel have maintained strong bilateral relations based on a number of factors, including robust domestic U.S. support for Israel and its security; shared strategic goals in the Middle East; a mutual commitment to democratic values; and historical ties dating from U.S. support for the creation of Israel in 1948. U.S. foreign aid has been a major component in cementing and reinforcing these ties. U.S. officials and many lawmakers have long considered Israel to be a vital partner in the region, and U.S. aid packages for Israel have reflected this calculation. While some U.S. citizens have worked to cultivate U.S. support for Israel since its creation in 1948, in the years following the 1973 Yom Kippur War advocates for Israel have created anengaged in organized, broad-based domestic movementefforts to foster bipartisan support in Congress for the bilateral relationship, including for U.S. aid to Israel.
In recent years, however, that strong domestic support for Israel has become more of a subject of debate.1 While both the Republican and Democratic parties have expressed “unequivocal” (Republican party platform 2016) or “ironclad” (Democratic party platform 2020) support for Israel, including aid,2 some Democrats from within the progressive wing of the party have become more vocal about conditioning, repurposing, or even cutting foreign aid to Israel.3 For part of 2020, when Israel considered annexing part of the West Bank, a number of Democratic lawmakers took varying approaches to signaling their opposition to annexation (see below). Some Members warned in general terms that annexation would harm U.S.-Israeli relations, while others were more explicit in cautioning that should Israel go ahead, they might advance legislation that would have either cut aid or prohibited its use or application in annexed territories.
The 2020 Abraham Accords between Israel, the United Arab Emirates (UAE), and Bahrain, which normalized diplomatic relations between Israel and two Gulf Arab monarchies, may portend requests to Congress for a major increase in U.S. foreign aid and military sales to Israel in the years ahead see (“Qualitative Military Edge (QME)”). Although not officially part of Israel’s agreement with the UAE, the United States has proposed selling the UAE, among other things, the F-35 Joint Strike Fighter, the most advanced fighter aircraft ever built. To maintain Israel’s technological superiority in arms over its neighbors, Israel and the United States are working on a package of offsetting sales and foreign aid to Israel. As of October 2020, the Trump Administration was considering an acceleration of the timetable for delivering some of the remaining $26.4 billion in Foreign Military Financing (FMF) grants to Israel (out of a total of $33 billion) pledged in the 2016 Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) to Israel, subject to the approval of Congress. The United States also may approve additional sales of the F-35 to Israel and accelerate the delivery of KC-46A refueling and transport aircraft to Israel.
1 The issue of what constitutes legitimate criticism of U.S. policy toward Israel and what qualifies as the de-legitimization of Israel or even anti-Semitism has received extensive media coverage in recent years. For example, see “How the Battle over Israel and Anti-Semitism is Fracturing American Politics,” New York Times, March 28, 2019. 2 The Republican National Committee’s 2020 platform, unchanged from 2016, is available online here: https://prod-cdn-static.gop.com/docs/Resolution_Platform_2020.pdf. The 2020 Democratic Party Platform is available online at: https://www.demconvention.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/2020-07-31-Democratic-Party-Platform-For-Distribution.pdf.
3 For example, during his campaign to be the 2020 Democratic presidential nominee, Senator Bernie Sanders said in October 2019: “My solution is to say to Israel: ‘You get $3.8 billion every year. If you want military aid, you’re going to have to fundamentally change your relationship to the people of Gaza.’ In fact, I think it is fair to say that some of that should go right now into humanitarian aid. See, “Biden calls Sanders’ Pitch to Leverage Israel Aid ‘Bizarre,’ Associated Press, December 7, 2019.
Congressional Research Service
1
link to page 7 U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel
Table 1. Total U.S. Foreign Aid Obligations to Israel: 1946-2020
debate. Demographic trends have been one element contributing to changing perceptions of U.S.-Israel relations.1 In the United States, younger, religiously-unaffiliated, American Muslim, and liberal U.S. voters appear to hold more critical views of the Israeli government's treatment of Palestinians.2 As a result, American public attitudes toward Israel's government are growing more polarized. In April 2019, the Pew Research Center released survey results indicating that "by nearly two-to-one (61% to 32%), Republicans have a favorable view of Israel's government. By contrast, two-thirds of Democrats view Israel's government unfavorably, while just 26% have a favorable opinion."3
Beyond these trends in public opinion, critics have long expressed a range of dissenting views toward U.S. foreign assistance to Israel. These views span a wide spectrum ranging from broad opposition to U.S. foreign aid globally to objections over Israeli settlement construction in the West Bank or Israel's treatment of the Palestinians. As debate over the U.S.-Israeli relationship has become more complex, it may be more difficult to distinguish between those who seek to withhold or condition assistance to Israel under some circumstances and those who object to U.S. aid for Israel more generally.4
In 2019, Israel is more secure and prosperous than in previous decades. And yet, despite its status as a high income country, military power, and top global weapons exporter, Israel remains largely dependent on the United States for the procurement of certain key high-cost U.S. weapon systems, such as combat aircraft. In order to demonstrate the continued utility of U.S. aid to Israel, proponents of foreign assistance have not only emphasized Israel's defensive, qualitative needs, but also that U.S. aid is mutually beneficial for the United States and Israel. They note that U.S. investments in Israeli defense and non-defense technologies have led to improvements in sectors such as missile defense, energy efficiency, and water supply.5
Table 1. Total U.S. Foreign Aid Obligations to Israel: 1946-2019 and the 2020 Request
current, or non-inflation-adjusted, dollars in millions
|
Fiscal Year |
Military |
Economic |
Missile Defense |
Total |
|
1946-2017 |
94,790.100 |
34,281.000 |
5,705.609 |
134,776.709 |
|
2018 |
3,100.000 |
- |
705.800 |
3,805.800 |
|
2019 |
3,300.000 |
- |
500.000 |
3,800.000 |
|
2020 Request |
3,300.000 |
- |
500.000 |
3,800.000 |
|
Total |
101,190.100 |
34,281.000 |
6,911.410 |
142,382.510 |
current, or non-inflation-adjusted, dollars in millions Fiscal Year Military Economic Missile Defense Total 1946-2018 97,907.700 34,326.000 6,411.409 138,645.109 2019 3,300.000 - 500.000 3,800.000 2020 3,300.000 - 500.000 3,800.000 Total 104,507.700 34,326.000 7,411.409 146,245.109 Sources: U.S. Overseas Loans and Grants (Greenbook), the U.S. State Department, and the Missile Defense Agency.
Notes: The Greenbook figures do not include missile defense funding provided by the Department of Defense. According to USAID Data Services as of July 2019March 2020, in constant 20172018 U.S. dollarsdol ars (inflation-adjusted), total U.S. aid to Israel obligated from 1946-2017 is $228.7 billion.
Qualitative Military Edge (QME)
Overview
2018 is $236 bil ion.
U.S. Aid and Israel’s Advanced Military Technology Almost all current U.S. aid to Israel is in the form of military assistance.64 U.S. military aid has helped transform Israel'’s armed forces into one of the most technologically sophisticated militaries in the world (“Qualitative Military Edge (QME)”)militaries in the world. U.S. military aid for Israel has been designed to maintain Israel's "qualitative military edge" (QME) over neighboring militaries.7 The rationale for QME is that Israel must rely on better equipment and training to compensate for being much smaller in land area and population than its potential adversaries. U.S. military aid also has helped Israel build its domestic defense industry, which now ranks as one of the top global suppliersexporters of arms.85 Israeli defense companies, such as Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI), Rafael, and Elbit Systems export nearly 70% of their products abroad. 6 Israel exports missile defense systems, unmanned aerial vehicles, cybersecurity products, radar, and electronic communications systems to, among others: India,7 Azerbaijan, Vietnam, Thailand, South Korea, Singapore, Philippines, Australia, France, Germany, Italy, Greece, Russia, Brazil, and the United States.98 In addition to a plannedthe U.S. purchase of Iron Dome (see below), the United States has purchased, among other items, the following Israeli defense articles: Trophy active protection systems for M1 Abrams tanks, helmets for F-35 fighter pilots, and an electronic fence along the U.S.-Mexico border.
4 For many years, U.S. economic aid helped subsidize a lackluster Israeli economy, but since the rapid expansion of Israel’s high-tech sector and overall economy in the 1990s (sparked partially by U.S.-Israeli scientific cooperation), Israel has been considered a fully industrialized nation. Consequently, Israel and the United States agreed to gradually phase out economic grant aid to Israel. In FY2008, Israel stopped receiving bilateral Economic Support Fund (ESF) grants. It had been a large-scale recipient of grant ESF assistance since 1971.
5 See, CRS Report R44716, Conventional Arms Transfers to Developing Nations, 2008-2015, by Catherine A. Theohary. Also, according to the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI), from 2015 to 2019, Israel was the 8th largest arms exporter worldwide, accounting for 3% of world deliveries. See, “Trends in International Arms Transfers, 2019,” SIPRI Fact Sheet, March 2020. 6 Sasson Hadad, Tomer Fadlon, and Shmuel Even (editors), “Israel’s Defense Industry and US Security Aid,” INSS, Memorandum No. 202, July 2020.
7 India is the largest buyer of Israeli defense equipment. See, Rina Bassist, “Israel, India Advance on Phalcon AWACS Megadeal,” Al Monitor, September 3, 2020.
8 Israel Ministry of Defense, Defense Export and Defense Co‐Operation Agency (SIBAT), and Jane’s, Navigating the Emerging Markets, Israel, January 10, 2019. Per a 1987 Memorandum of Understanding between the United States and Israel as amended, (Reciprocal Defense Procurement and Acquisition Policy Memorandum of Understanding), Israeli and U.S. defense contractors are able to compete in both countries for contracts on an equal basis. For the text of the MOU, see: https://www.acq.osd.mil/dpap/Docs/mou-israel.pdf.
Congressional Research Service
2
U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel
Qualitative Military Edge (QME) U.S. military aid for Israel has been designed to maintain Israel’s “qualitative military edge” over neighboring militaries.9 The rationale for QME is that Israel must rely on better equipment and training to compensate for being much smaller in land area and population than most of its potential adversaries.10 For decades, successive Administrations, in conjunction with Congress, have taken measures to maintain Israel’s QME in a number of ways. For example:
In practice, U.S. arms sales policy has traditionally allowed Israel first regional
access to U.S. defense technology.11
In cases in which both Israel and an Arab state operate the same U.S. platform,
Israel has first received either a more advanced version of the platform or the ability to customize the U.S. system.12
In cases in which Israel objected to a major defense article sale to an Arab
military (e.g., the 1981 sale of Airborne Early Warning and Control System aircraft or “AWACS” to Saudi Arabia), Congress has, at times, advocated for and legislated conditions on the usage and transfer of such weapons prior to or after a sale.13
The United States has compensated Israel with “offsetting” weapons packages or
military aid when selling other U.S. major defense articles to a Middle Eastern military rival (see textbox below).
Over time, Congress codified informal QME-related practices in a way that encouraged a more deliberate interagency process for each major U.S. arms sale to Middle Eastern governments other than Israel.14 In the 110th Congress, Representative Howard Berman sponsored legislation
9 For more coverage of this issue, see CRS Report R46580, Israel’s Qualitative Military Edge and Possible U.S. Arms Sales to the United Arab Emirates, coordinated by Jeremy M. Sharp and Jim Zanotti.
10 The concept of QME (independent of its application to Israel) dates back to the Cold War. In assessing the balance of power in Europe, U.S. war planners would often stress to lawmakers that, because countries of the Warsaw Pact had a numerical advantage over U.S. and allied forces stationed in Europe, the United States must maintain a “qualitative edge” in defense systems. For example, see, Written Statement of General William O. Gribble, Jr., Hearings on Research, Development, Test, and Evaluation Program for Fiscal Year 1973, Before Subcommittee No. 1 of Committee on Armed Services, House of Representatives, Ninety-Second Congress, Second Session, February 2, 3, 7, 9, 22, 23, 24, March 6, 7, and 8, 1972. The concept was subsequently applied to Israel in relation to its Arab adversaries. In 1981, then-U.S. Secretary of State Alexander Haig testified before Congress, saying, “A central aspect of US policy since the October 1973 war has been to ensure that Israel maintains a qualitative military edge.” Secretary of State Alexander Haig, Statement for the Record submitted in response to Question from Hon. Clarence Long, House Appropriations Subcommittee on Foreign Operations Appropriations, April 28, 1981.
11 For example, Israel acquired the F-15 in 1976, six years before Saudi Arabia. It received the delivery of the F-16 fighter in 1980, three years before Egypt. In 1977, P.L. 95–92 provided that: “In accordance with the historic special relationship between the United States and Israel and previous agreements and continuing understandings, the Congress joins with the President in reaffirming that a policy of restraint in United States arms transfers, including arms sales ceilings, shall not impair Israel's deterrent strength or undermine the military balance in the Middle East.”
12 “The Double Edged Sword of the Qualitative Military Edge,” Israel Policy Forum, April 11, 2016. 13 See Section 131, Certification Concerning AWACS sold to Saudi Arabia, P.L. 99-83, the International Security and Development Cooperation Act of 1985.
14 According to one Senate staffer, prior to 2008, during congressional review of possible U.S. arms sales to the Middle East, QME concerns only were addressed on an ad hoc basis, usually through consultations between the military and committee staff. Some congressional staff felt that assessments for specific arms sales tended to be overly subjective. Since staff frequently raised QME concerns, the attempt to enshrine QME as a statutory requirement stemmed from a desire to rationalize the process, make it more objective, and incorporate it as a regular component of the U.S. arms
Congressional Research Service
3
U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel
(H.R. 5916, Section 201) to “carry out an empirical and qualitative assessment on an ongoing basis of the extent to which Israel possesses a qualitative military edge over military threats.” After becoming Chairman of the House Foreign Affairs Committee, then-Chairman Berman was able to incorporate this language into the Naval Vessel Transfer Act of 2008 (P.L. 110-429). The relevant QME provisions of this law had three primary elements: (1) they defined QME;15 (2) they required an assessment of Israel’s QME every four years; and (3) they amended the Arms Export Control Act (22 U.S.C. §2776) to require a determination, for any export of a U.S. defense article to any country in the Middle East other than Israel, that such a sale would not adversely affect Israel’s QME.
Preserving QME: Offsetting Weapons Packages for Israel
The fol owing specific instances supplement general U.S. efforts to strengthen Israel’s QME, which are documented in a number of sources:16
In 1992, after the United States announced a sale to Saudi Arabia of F-15 fighters, the George H.W. Bush Administration provided Israel with Apache and Blackhawk helicopters, and pre-positioned U.S. defense equipment in Israel for Israeli use with U.S. approval, as various means of preserving Israel’s QME.17
In 2007, after the George W. Bush Administration agreed to sell Saudi Arabia Joint Direct Attack Munitions (JDAMs), the Administration reportedly agreed to sell more advanced JDAMs to Israel as a means of preserving its QME.18
In 2010, the Obama Administration agreed to sell an additional 20 F-35 aircraft to Israel as a means of preserving its QME in response to a sale to Saudi Arabia that included F-15s.19
In 2013, after the Obama Administration agreed to sell the UAE advanced F-16 fighters, then Secretary of Defense Chuck Hagel announced that the United States would provide Israel with KC-135 refueling aircraft, anti-radiation missiles, advanced radar, and the sale of six V-22 Osprey tilt-rotor aircraft.20 At the time, the U.S. proposal marked the first time that the United States had offered to sell tilt-rotor Ospreys to another country. Israel would eventually cancel its planned purchase of the V-22 due to budgetary constraints.
Since the passage of the QME law and its amending of the Arms Export Control Act, the interagency process to assess Israel’s QME has taken place behind closed doors with little fanfare. According to the Defense Security Cooperation Agency’s (DSCA) Security Assistance Manual, QME determinations can be classified.21 After a QME determination has been made
sales review process to Middle Eastern governments. CRS conversation with Senate Foreign Relations Committee staff member, September 24, 2020.
15 Section 201(d)(2) defines QME as “the ability to counter and defeat any credible conventional military threat from any individual state or possible coalition of states or from non-state actors, while sustaining minimal damage and casualties, through the use of superior military means, possessed in sufficient quantity, including weapons, command, control, communication, intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance capabilities that in their technical characteristics are superior in capability to those of such other individual or possible coalition of states or non-state actors.”
16 See, e.g., State Department, Remarks by Andrew J. Shapiro, Assistant Secretary, Bureau of Political-Military Affairs, November 4, 2011; “U.S.-Israel Strategic Cooperation: U.S. Provides Israel a Qualitative Military Advantage,” Jewish Virtual Library.
17 See, Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs, 18 White House Statement on US Military Assistance to Israel, September 26, 1992, VOLUME 13-14: 1992-1994.
18 Dan Williams, “Israel to get ‘smarter’ U.S.-made bombs than Saudis,” Reuters, January 13, 2020. 19 Eli Lake, “In Gates Book, Details of Israel’s Hard Bargaining Over Saudi Arms,” Daily Beast, January 10, 2014. 20 “U.S. Near $10 Billion Arms Deal with Israel, Saudi Arabia, UAE,” Reuters, April 19, 2013. 21 See https://www.samm.dsca.mil/chapter/chapter-5.
Congressional Research Service
4
U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel
regarding a specific proposed sale, DSCA includes a line in the applicable congressional notification reading, “The proposed sale will not alter the basic military balance in the region.”
At times, lawmakers have amended or attempted to amend aspects of the 2008 law. The U.S.-Israel Strategic Partnership Act (P.L. 113-296) amended Section 36 of the AECA to require that the Administration explain, in cases of sales or exports of major U.S. defense equipment to other Middle Eastern states, what is “Israel’s capacity to address the improved capabilities provided by such sale or export.”22 In the 116th Congress, Representative Bradley Schneider sponsored (H.R. 8494), the Guaranteeing Israel's QME Act of 2020, which requires the President to consult with Israeli officials before making a QME determination.23 Another QME-related bill introduced in the 116th Congress is S. 4814, the Secure F-35 Exports Act of 2020. This legislation would, among other things, require a certification by the President before the provision of F-35 aircraft to a Middle Eastern country other than Israel that such sale will not undermine Israel’s QME.
At various times in the past, the U.S. government reportedly has held regular consultations with Israeli officials regarding the potential impact of regional arms sales on QME.24 Some former Obama Administration officials have responded to news of the possible sale of the F-35 to the UAE with criticism of what they perceive as a lack of time for U.S. officials and Congress to properly assess the transaction. Some have written that previous QME determinations encompassed “classified negotiations that got to the heart of Israel’s defense capabilities,”25 and that “the process of military consultations with Israel on a given weapons system typically took several years of extensive defense shuttle diplomacy, completed before formally notifying Congress of the arms sale package.”26
helmets for F-35 fighter pilots, and an electronic fence along the U.S.-Mexico border.
Successive Administrations have routinely affirmed the U.S. commitment to strengthening Israel's QME. However, for years, no official or public U.S. definition of QME existed.10 In order to clarify U.S. policy on preserving Israel's QME, Congress has passed several pieces of legislation addressing the issue. For example, in 2008, Congress passed legislation (P.L. 110-429, the Naval Vessel Transfer Act of 2008) that defined QME as
the ability to counter and defeat any credible conventional military threat from any individual state or possible coalition of states or from non-state actors, while sustaining minimal damage and casualties, through the use of superior military means, possessed in sufficient quantity, including weapons, command, control, communication, intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance capabilities that in their technical characteristics are superior in capability to those of such other individual or possible coalition of states or non-state actors.11
Section 201 of P.L. 110-429 required the President to carry out an "empirical and qualitative assessment on an ongoing basis of the extent to which Israel possesses a qualitative military edge over military threats to Israel." The 2008 law also amended Section 36 of the Arms Export Control Act (AECA) to require certifications for proposed arms sales "to any country in the Middle East other than Israel" to include "a determination that the sale or export of the defense articles or defense services will not adversely affect Israel's qualitative military edge over military threats to Israel." What might constitute a legally defined adverse effect to QME is not clarified in U.S. legislation.
Congress has passed additional legislation addressing Israel's QME. In 2012, Congress passed the United States-Israel Enhanced Security Cooperation Act (P.L. 112-150), which, among other things, reiterated that it is the policy of the United States to "to help the Government of Israel preserve its qualitative military edge amid rapid and uncertain regional political transformation." In 2014, Congress passed The U.S.-Israel Strategic Partnership Act (P.L. 113-296). This act amended Section 36 of the AECA to require that the Administration explain, in cases of sales or exports of major U.S. defense equipment to other Middle Eastern states, what is "Israel's capacity to address the improved capabilities provided by such sale or export."12 The act also requires the Administration to:
- Evaluate "how such sale or export alters the strategic and tactical balance in the region, including relative capabilities; and Israel's capacity to respond to the improved regional capabilities provided by such sale or export."
- Include "an identification of any specific new capacity, capabilities, or training that Israel may require to address the regional or country-specific capabilities provided by such sale or export; and a description of any additional United States security assurances to Israel made, or requested to be made, in connection with, or as a result of, such sale or export."
Finally, P.L. 113-296 amended Section 201(c) of the Naval Vessel Transfer Act of 2008 (22 U.S.C. 2776) by requiring Administration reports on QME every two years rather than (as previously required) every four.13
QME and U.S. Arms Sales to the Gulf
Israeli officials periodically express concern over U.S. sales of sophisticated weaponry, particularly aircraft, airborne radar systems, and precision-guided munitions, to Arab Gulf countries. As the United States has been one of the principal suppliers of defense equipment and training to both Israel and the Arab Gulf states, U.S. policymakers and defense officials have sought to carefully navigate U.S. defense commitments, while following the legal requirement to maintain Israel's QME.
Although in recent times Israel and the Arab Gulf states have coalesced against a commonly perceived Iranian threat, U.S. arms sales to Arab Gulf states still periodically raise Israeli QME concerns. UAE interest in becoming the first Arab state operator of the F-35 Joint Strike Fighter may raise such Israeli QME concerns. The Trump Administration reportedly has agreed to enter into preliminary talks with the UAE on procurement of the F-35.14 In addition to satisfying QME concerns before considering an F-35 sale to the UAE, the United States may also require the UAE to improve its protection of data security due to the sensitive technologies in the F-35's hardware and software.15 To date, no specific decision has been announced to begin preliminary U.S.-UAE talks on the subject. Retired Israeli Defense Force Colonel Shimon Arad has been a vocal critic of selling the F-35 to the UAE, saying: "The release of F-35s to the Gulf states is a fundamental military game-changer that, in combination with the advanced fourth generation fighters and the tens of thousands of sophisticated munitions, will cancel out Israel's QME."16
U.S. Bilateral Military Aid to Israel
U.S. Bilateral Military Aid to Israel Since 1999, overall U.S. assistance to Israel has been outlined in 10-year government-to-government Memoranda of Understanding (MOUs). MOUs are not legally binding agreements like treaties, and thus do not require Senate ratification. Also, Congress may accept or change year-to-year assistance levels for Israel, or provide supplemental appropriations. Nevertheless, past MOUs have significantly influenced the terms of U.S. aid to Israel; Congress has appropriated foreign aid to Israel largely according to the terms of the MOU in place at the time.
22 The Act also requires the Administration to: evaluate “how such sale or export alters the strategic and tactical balance in the region, including relative capabilities; and Israel’s capacity to respond to the improved regional capabilities provided by such sale or export,” and include “an identification of any specific new capacity, capabilities, or training that Israel may require to address the regional or country-specific capabilities provided by such sale or export; and a description of any additional United States security assurances to Israel made, or requested to be made, in connection with, or as a result of, such sale or export.”
23 In the 115th Congress, Representative Schneider sponsored H.R. 2833, Defending Israel’s QME Act of 2017. 24 Barbara Opall-Rome, “Israeli Brass Decry U.S. Arms Sales to Arab States,” Defense News, January 23, 2012. At the time this article was published, the U.S. side of the working group was led by the Under Secretary of Defense for Policy and Assistant Secretary of State for Political-Military Affairs, while the Israeli side was led by the Defense Ministry’s policy chief and the Israel Defense Forces director of planning. 25 Representative Elissa Slotkin, “The Importance of Preserving Israel’s Qualitative Military Edge,” Medium.com, September 14, 2020.
26 Barbara A. Leaf and Dana Stroul, “The F-35 Triangle: America, Israel, the United Arab Emirates,” War on the Rocks, September 15, 2020. See also, Andrew Shapiro and Derek Chollet, “Selling F-35s to the Middle East Was Never Going to Be Easy,” Defense One, September 14, 2020.
Congressional Research Service
5
U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel
Brief History of MOUs on U.S. Aid to Israel
The first 10-year MOU (FY1999-FY2008), agreed to under the Clinton Administration, was known as the In 2007, the Bush Administration and the Israeli government agreed to a second MOU consisting of a $30 |
”28 The Current 10-Year Security Assistance Memorandum of Understanding (MOU)
At a signing ceremony at the State Department on September 14, 2016, representatives of the U.S. and Israeli governments signed a newanother 10-year Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) on military aid covering FY2019 to FY2028. Under the terms of this third MOU, the United States pledges, subject to congressional appropriation, to provide $38 billion in military aid ($33 billion in Foreign Military Financing (FMF) grants, plus $5 billion in defense appropriations for missile defense programs) to Israel. According to the terms of the MOU, "“Both the United States and Israel jointly commit to respect the FMF levels specified in this MOU, and not to seek changes to the FMF levels for the duration of this understanding."19
|
 |
|
Source: CRS. |
The terms of the 2019-2028 MOU differ from previous agreements on issues such as
- ”29
27 See, Joint Statement by President Clinton and Prime Minister Ehud Barak, July 19, 1999. According to the statement, “The United States and Israel will sign a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) which will express their joint intention to restructure U.S. bilateral assistance to Israel. The MOU will state the United States’ intention to sustain its annual military assistance to Israel, and incrementally increase its level by one-third over the next decade to a level of $2.4 billion subject to Congressional consultations and approval. At the same time, the MOU will provide for a gradual phase-out of U.S. economic aid to Israel, over a comparable period, as the Israeli economy grows more robust, less dependent on foreign aid, and more integrated in world markets.”
28 United States-Israel Memorandum of Understanding, Signed by then U.S. Under Secretary of State R. Nicholas Burns and Israeli Ministry of Foreign Affairs Director General Aaron Abramovich, August 16, 2007.
29 Memorandum of Understanding between the United States and Israel, September 14, 2016.
Congressional Research Service
6
link to page 11
U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel
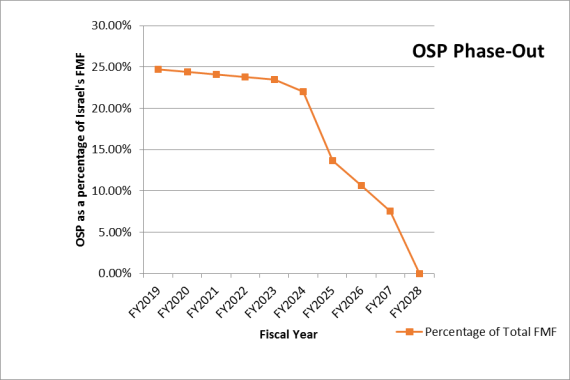
Figure 1. Phasing Out Off-Shore Procurement (OSP) Under the MOU
Source: CRS.
The terms of the 2019-2028 MOU differ from previous agreements on issues such as
Phasing out Off-Shore Procurement (OSP
Phasing out Off-Shore Procurement (OSP). Under the terms of the third MOU, OSP will decrease slowly until FY2024, but will then be phased out more dramatically over the MOU'’s last five years, ending entirely in FY2028 (see Figure 1). The MOU calls on Israel to provide the United States with"“detailed programmatic information related to the use of all U.S. funding, including funds used for OSP."” In response to the planned phase-out of OSP, some Israeli defense contractors may be seeking to merge with U.S. companies or open U.S. subsidiaries in order to continue their eligibility for defense contracts financed through FMF.20 - 30
Missile Defense. Under the terms of the third MOU, the Administration pledges
to request $500 million in annual combined funding for missile defense programs with joint U.S.-Israeli elements—such as Iron Dome, Arrow II and Arrow III, and
David'David’s Sling. Previous MOUs did not include missile defense funding, which has traditionally been appropriated via separate interactions between successive Administrations and Congresses. While the MOU commits both the United States and Israel to a $500 million annual U.S. missile defense contribution, it also stipulates that under exceptional circumstances (major armed conflict involving Israel), both sides may agree on U.S. support above the $500 million annual cap. -
30 “Israeli UAV Firm agrees deal for Unnamed US Company,” Jane’s Defence Weekly, July 18, 2017.
Congressional Research Service
7
U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel
No FMF for Fuel. According to the third MOU, Israel will no longer be
permitted to use a portion of its FMF to purchase fuel (or
"“other consumables")”) from the United States. Under the second MOU, Israel had budgeted an estimated $400 million a year in FMF to purchase jet fuel from the United States.21
Some Israeli officials have argued that the gradual phase-out of OSP will shrink Israel's defense sector and lead to job losses.22 Although as noted above (see Figure 1), Israeli defense planners have several years to adjust to the OSP planned reduction, some Israeli lawmakers have called on the Trump Administration to work with Congress to keep OSP as a provision of appropriations law indefinitely. According to Knesset member Mickey Levy from the centrist Yesh Atid party, "The U.S. administration today is different than the previous one and it is possible to do something on a policy level to change the decision in some way."23 During consideration of the National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2018 (P.L. 115-91), Senator Lindsay Graham proposed an amendment (SA 813), that would have, if it had been adopted, notwithstanding any other provision of law, set the off-shore procurement rate at "not less than" 26.3% from fiscal years 2019 through 2028.
Foreign Military Financing (FMF) and Arms Sales
Israel is the largest recipient of U.S. Foreign Military Financing. For FY2020, the President's request for Israel would encompass approximately 57% of total requested FMF funding worldwide. Annual FMF grants to Israel represent approximately 18% of the overall Israeli defense budget.24 Israel'defense budget.33 Israel’s defense expenditure as a percentage of its Gross Domestic Product (4(5.3% in 20182019) is one of the highest in the world.25
34
Cash Flow Financing
Section 23 of the Arms Export Control Act (22 U.S.C. §2763512763) authorizes the President to finance the "“procurement of defense articles, defense services, and design and construction services by friendly foreign countries and international organizations, on such terms and conditions as he may determine consistent with the requirements of this section."” Successive Administrations have used this authority to permit Israel to finance multiyear purchases through installment payments, rather than having to pay the full amount of such purchases up front.2635 Known as "“cash flow financing," ” this benefit enables Israel to negotiate major arms purchases with U.S. defense suppliers with payments scheduled over a longer time horizon.27
36 Early Transfer and Interest Bearing Account
Since FY1991 (P.L. 101-513), Congress has mandated that Israel receive its FMF aid in a lump sum during the first month of the fiscal year.2837 The FY2019Further Consolidated Appropriations Act, FY2020 ( (P.L. 116-6) 94) states, "“That of the funds appropriated under this heading, not less than $3,300,000,000 shall be available for grants only for Israel which shall be disbursed within 30 days of enactment of this Act."” Once disbursed, Israel'’s military aid is transferred to an interest bearing account with the U.S. Federal Reserve Bank.2938 Israel has used interest collected on its 33 The Israeli Ministry of Defense provides funding figures for its domestic defense budget but excludes some procurement spending and spending on civil defense. The estimate referenced above is based on figures published by Jane’s Defence Budgets, “Israel,” IHS Global Insight, May 15, 2020. Jane’s removes FMF from its Israeli defense budget calculations to reflect how much Israel independently spends on defense.
34 Four other nations spend more on defense as a percentage of GDP: Saudi Arabia, Oman, Algeria, and Kuwait. See Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI), Military expenditure by country as percentage of gross domestic product, 1988-2019, SIPRI Military Expenditure Database, 1949-2019.
35 The United States initially began authorizing installment-style sales to Israel to help it rebuild its military capabilities after the 1973 war with Egypt and Syria. Congress appropriated $2.2 billion for Israel in P.L. 93-199, the Emergency Security Assistance Act of 1973. Section 3 of that act stated that “Foreign military sales credits [loans or grants] extended to Israel out of such funds shall be provided on such terms and conditions as the President may determine and without regard to the provisions of the Foreign Military Sales Act as amended.” At the time, the Foreign Military Sales Act of 1968 (amended in 1971 and the precursor to the Arms Export Control Act of 1976), capped the annual amount of foreign military sales credit that could be extended to a recipient at no more than $250 million per year. Under the authorities contained in P.L. 93-199, President Nixon, in two separate determinations (April & July 1974), allocated the $2.2 billion to Israel as $1.5 billion in grant military aid, the largest U.S. grant aid package ever for Israel at the time. The remaining $700 million was designated as a military loan.
A year and a half later, the Ford Administration reached a new arms sales agreement with Israel providing that, according to the New York Times, “the cost of the new military equipment would be met through the large amount of aid approved by the just-completed session of Congress as well as the aid that will be approved by future Congresses.” See, “U.S. Decides to Sell Some Arms to Israel that it had Blocked in the Past,” New York Times, October 12, 1976. 36 Cash flow financing is defined in Section 25(d) of the Arms Export Control Act and Section 503(a)(3) of the Foreign Assistance Act.
37 When government operations are funded by a continuing appropriations resolution, Congress may at times include provisions in such resolutions that would prevent the early transfer of FMF to Israel (presumably until a final year appropriations bill is passed). For example, see Section 109 of P.L. 113-46, the Continuing Appropriations Act, 2014.
38 According to the Defense Security Cooperation Agency (DSCA), “Some countries may establish an account with the federal reserve bank (FRB), New York, for their FMS [Foreign Military Sales] deposits. An agreement between the FMS purchaser’s defense organization, the purchaser’s central bank, FRB New York and DSCA identifies the terms, conditions, and mechanics of the account’s operation. Countries receiving FMFP funds must maintain their interest bearing account in the FRB.” See, Defense Institute of Security Assistance Management (DISAM), “The Management
Congressional Research Service
9
link to page 16
U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel
Israel has used interest collected on its military aid to pay down its bilateral debt (nonguaranteed) to U.S. government agencies, which, according to the U.S. Department of the Treasury, stood at $148.8 million as of December 2015.30 39 Israel cannot use accrued interest for defense procurement inside Israel.
F-35 Joint Strike Fighter
Israel is the first declared international operator of the F-35 Joint Strike Fighter.40 It has purchased 50 F-35s (called Adirs41) in three separate contracts (see Table 2) using Foreign Military Financing grants. As of September 2020, Israel had received 27 of 50 jets, which they have divided into two squadrons based at Nevatim Air Base in southern Israel.42 From there and without any aerial refueling, Israel’s F-35s could strike targets in Syria, Iraq, Lebanon, Jordan, and most of Egypt, Turkey, and Saudi Arabia.43 To date, Israel reportedly has used its F-35 aircraft to conduct aerial strikes inside Syria.44
The Department of Defense’s F-35 program is an international cooperative program in
Figure 3. U.S. and Israeli F-35s Fly in
which Israel (and Singapore) are considered
Formation
“security cooperation participants” outside of
Joint Exercise Enduring Lightning III (October 2020)
the F-35 cooperative development partnership.45 As a result, Israel is not eligible to assign staff to the F-35 Joint Program Office in Washington and does not receive full F-35 technical briefings.46 The United States government and Lockheed Martin retain exclusive access to the F-35’s software code, which Israel cannot alter itself.
Source: U.S. Air Force
of Security Cooperation (Green Book),” 34th Edition, April 2015.
39 Foreign Credit Reporting System (FCRS), Amounts Due the U.S. Government from Sovereign and Other Foreign Official Obligors as of 12/31/2015, United States Department of the Treasury, Office of International Debt Policy.
40 In September 2008, the Defense Security Cooperation Agency (DSCA) notified Congress of a possible Foreign Military Sale of up to 75 F-35s to Israel in a deal with a possible total value of $15.2 billion. See, Defense Security Cooperation Agency, Transmittal No. 08-83, Israel - F-35 Joint Strike Fighter Aircraft, September 29, 2008.
41 “After F-35 makes Aliyah, it will get new Israeli identity,” Israel Hayom, May 2, 2016. In Hebrew, “aliyah” refers to geographical relocation to Israel. “Adir” is a Hebrew word for “mighty” or “powerful.”
42 Yaakov Lappin, “Israeli Air Force Favouring Additional F-35s,” Jane’s Defence Weekly, September 10, 2020. 43 Gareth Jennings, “Israel Declares F-35 to Be Operational,” Jane’s Defence Weekly, December 6, 2017. 44 “F-35 Stealth Fighter Sees First Combat, in Israeli Operation,” BBC News, May 22, 2018 and “Israel - Air Force,” Jane's World Air Forces, July 5, 2019.
45 See CRS Report RL30563, F-35 Joint Strike Fighter (JSF) Program, by Jeremiah Gertler. 46 “Israel,” Jane's World Air Forces, September 1, 2020.
Congressional Research Service
10
U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel
However, Israel’s involvement in the F-35 program is still extensive, with Israeli
Figure 4. F-35 Helmet Mounted Display
companies making F-35 wing sets (IAI) and
Made by Israeli Manufacturer Elbit Systems
helmets (Elbit Systems). Israel also received significant development access to the F-35 and the ability to customize its planes with Israeli-made C4 (command, control, communications, computers) systems, under the condition that the software coding be done by the United States. In 2018, the Navy awarded Lockheed Martin a $148 million contract for “the procurement of Israel-unique weapons certification, modification kits, and
electronic warfare analysis.”47 Software
Source: Elbit Systems Ltd.
upgrades (called Block 3F+) added to the
Note: The F-35 Helmet Mounted Display is a joint
main computer of Israel’s F-35s does
venture between Elbit Systems and Rockwell Col ins.
reportedly facilitate the “use of Israeli-designed electronic equipment and weaponry” thereby permitting Israel to “employ its own external jamming pod and also allow internal carriage of indigenous air-to-air missiles and guided munitions.”48
In October 2020, the United States and Israel conducted their third Enduring Lightning joint aviation exercise using the F-35. American and Israeli pilots trained together to counter both surface and air adversaries, while supporting units assisted with refueling, radar, and opponent simulations.
KC-46A Pegasus
In March 2020, DSCA notified Congress of a planned sale to Israel of eight KC-46A Boeing “Pegasus” aircraft for an estimated $2.4 billion.49 According to Boeing, the KC-46A Pegasus is a multirole tanker (can carry passengers, fuel, and equipment) that can refuel all U.S. and allied military aircraft. After Japan, Israel is the second country approved by the United States to receive the KC-46A. The Israel Air Force’s current fleet of tankers was originally procured in the 1970s, and it is anticipated that Israel will be able to use the KC-46A to refuel its F-35 fighters.
47 U.S. Department of Defense, U.S. Navy, Contracts For February 2, 2018. 48 Gareth Jennings, “Israel Stands-Up Second F-35 Unit,” Jane's Defence Weekly, January 17, 2020. 49 Defense Security Cooperation Agency, Israel – KC-46A Aerial Refueling Aircraft, Transmittal No 20-12, March 3, 2020.
Congressional Research Service
11
U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel
Table 2. Selected Notified U.S. Foreign Military Sales to Israel50
Amount/Description
Cong. Notice
Primary Contractor(s)
Estimated Cost
75 F-35A Joint Strike Fighter (Lightning
2008
Lockheed Martin
$15.2 billion
II) Aircraft
JP-8 aviation fuel, diesel fuel, and
2013
N/A
$2 bil ion
unleaded gasoline
600 AIM-9X-2 Sidewinder Block II Air-
2014
Raytheon
$544 mil ion
air missiles and associated equipment
14,500 Joint Direct Attack Munitions
2015
Various
$1.879 bil ion
(JDAM) and associated equipment
Equipment to support Excess Defense
2016
Science and Engineering
$300 mil ion
Articles sale of 8 SH-60F Sea Hawk
Services and General
Helicopters
Electric
13 76mm naval guns and technical
2017
DRS North America
$440 mil ion
support
240 Namer armored personal carrier
2019
MTU America
$238 mil ion
power packs and associated equipment
KC-46A aerial refueling aircraft
2020
Boeing Corporation
$2.4 bil ion
JP-8 aviation fuel, diesel fuel, and
2020
N/A
$3 bil ion
unleaded gasoline
international operator of the F-35 Joint Strike Fighter, the Department of Defense's fifth-generation stealth aircraft considered to be the most technologically advanced fighter jet ever made. In September 2008, the Defense Security Cooperation Agency (DSCA) notified Congress of a possible Foreign Military Sale of up to 75 F-35s to Israel in a deal with a possible total value of $15.2 billion.31 Since then, Israel has purchased 50 F-35s in three separate contracts (see Table 2 below) using FMF grants. Israel is installing Israeli-made C4 (command, control, communications, computers) systems in the F-35s it receives, and calls these customized F-35s "Adirs."32
As part of the F-35 deal, the United States agreed to make reciprocal purchases of equipment (known as "offsets") from Israeli defense companies. If Israel elects to purchase all 75 F-35s, it is estimated that its business offsets could be as high as $4 billion. As of 2017, Israeli firms had received more than 1 billion dollars' worth of business from Lockheed Martin to build components for the F-35.33 Israeli defense contractor Elbit Systems has worked with U.S. counterparts to design and supply the Helmet Mounted Display System (HMDS) for F-35 pilots. The United States Army also has awarded a contract to an Elbit subsidiary in the United States to supply helmet mounted displays for U.S. helicopters, such as the Army's CH-47F Chinook and the UH-60L/M/V Black Hawk.34
As mentioned above, the United States has authorized the sale of up to 75 F-35s to Israel, which will have acquired 50 of the aircraft by 2024. Israel has yet to decide whether to use FMF funds to procure an additional 25 F-35s or use U.S. military aid to finance the purchase of an advanced F-15I model. Some Israelis have argued that the F-15I model is cheaper to operate, can carry a heavier weapons payload, and has a wider range than the F-35.35 However, according to one report, U.S. officials may be opposed to Israel's purchase of the F-15 if it would defer Israel's acquisition of the remaining 25 F-35s that it is authorized to purchase.36 To date, Israel has reportedly used both F-35 and F-15 aircraft to conduct aerial strikes inside Syria.37
"Namer" Armored Personnel Carriers
In February 2019, the Defense Security Cooperation Agency (DSCA) notified Congress of a planned foreign military sale to Israel of 270 upgraded engines for the Namer Armored Personnel Carrier (APC) with a total value of $238 million.38 The Namer, which was first produced by Israel in 2008, uses the same armor found on Israel's Merkava IV tanks. It also is equipped with the Trophy active defense system to protect against incoming projectiles. During Operation Protective Edge (July 2014) against Hamas, several Israeli soldiers were killed while riding in an older APC model that was struck by rocket propelled grenade fire. After 2014, Israel increased its production of the Namer.
|
Amount/Description |
Cong. Notice |
Contract |
Delivery |
Primary Contractor(s) |
Estimated Cost |
|
|
75 F-35A Joint Strike Fighter (Lightning II) Aircraft |
|
2010 (19) 2015 (14) 2016 (17) |
16 estimated |
Lockheed Martin |
$15.2 billion |
|
|
6 V-22B Block C Aircraft and associated equipment |
|
Israel evaluating plans |
Bell and Boeing |
$1.13 billion |
||
|
600 AIM-9X-2 Sidewinder Block II Air-air missiles and associated equipment |
|
Raytheon |
$544 million |
|||
|
14,500 Joint Direct Attack Munitions (JDAM) and associated equipment |
|
Various |
5,800 estimated |
Various |
$1.879 billion |
|
|
Equipment to support Excess Defense Articles sale of 8 SH-60F Sea Hawk Helicopters |
|
Science and Engineering Services and General Electric |
$300 million |
|||
|
13 76mm naval guns and technical support |
|
DRS North America |
$440 million |
|||
|
240 Namer armored personal carrier power packs and associated equipment |
|
MTU America |
$238 million |
Sources: Defense Security Cooperation Agency, Stockholm International Peace Research Institute Arms Transfer Database, IHS Jane's.
’s.
Notes: All figures and dates are approximate; blank entries indicate that data is unknown or not applicable.
. Excess Defense Articles
The Excess Defense Articles (EDA) program provides a means by which the United States can advance foreign policy objectives—assisting friendly and allied nations through provision of equipment in excess of the requirements of its own defense forces. This program, managed by DSCA, enables the United States to reduce its inventory of outdated equipment by providing friendly countries with necessary supplies at either reduced rates or no charge.40
51
As a designated "“major non-NATO ally,"41”52 Israel is eligible to receive EDA under Section 516(a) of the Foreign Assistance Act and Section 23(a) of the Arms Export Control Act. According to
50 For open source information on the status of Israeli procurement plans regarding key aircraft platforms such as F-15IA, V-22 Osprey, and KC-46A, see “Israel - Air Force,” Jane’s World Air Forces, July 5, 2019.
51 To access DSCA’s Excess Defense Articles database, see http://www.dsca.mil/programs/eda. 52 On November 4, 1986, President Reagan signed into law P.L. 99-661, the National Defense Authorization Act for FY1987. In Section 1105 of that act, Congress called for greater defense cooperation between the United States and countries that the Secretary of Defense could designate as a “major non-NATO ally” (MNNA). Such cooperation could entail U.S. funding for joint research and development and production of U.S. defense equipment. In February 1987, the United States granted Israel MNNA status along with several other countries (Egypt, Japan, South Korea, and Australia). According to press reports at the time, in the absence of a U.S.-Israeli mutual defense agreement, supporters of Israel had been advocating for Israel to receive “equal treatment” with regard to certain special military benefits (such as the ability to bid on U.S. defense contracts) that NATO allies received from the United States. See, “Israel seeks to obtain the kind of Financial Aid that NATO Members get from U.S. Government,” Wall Street Journal, February 3, 1987. Nearly a decade later, Congress passed additional legislation that further solidified Israel’s MNNA status. In 1996, Section 147 of P.L. 104-164 amended the Foreign Assistance Act of 1961 by requiring the President to
Congressional Research Service
12
U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel
DSCA, from 2010 to 2019, Israel received at least $385 million in EDA deliveries (current value only).53
Defense Budget Appropriations for U.S.-Israeli Missile Defense Programs Congress and successive Administrations have demonstrated strong support for joint U.S.-Israeli missile defense projects designed to thwart a diverse range of threats. Threats include short-range missiles and rockets fired by nonstate actors, such as Hamas and Hezbollah, to mid- and longer-range ballistic missiles in Syria’s and Iran’s arsenals.54 Congress provides regular U.S. funding for Israeli and U.S.-Israeli missile defense programs in defense authorization and appropriations bills. Israel and the United States each contribute financially to several weapons systems and engage in co-development, co-production, and/or technology sharing in connection with them. Since 2001, Israel and the United States have conducted a joint biennial ballistic missile defense exercise, called Juniper Cobra, to work on integrating their weapons, radars, and other systems.55
The following section provides background on Israel’of the Foreign Assistance Act and Section 23(a) of the Arms Export Control Act. According to DSCA, from 2008 to 2018, Israel received $663.6 million in EDA deliveries (current value only).42
Defense Budget Appropriations for U.S.-Israeli Missile Defense Programs
Congress and successive Administrations have demonstrated strong support for joint U.S.-Israeli missile defense projects designed to thwart a diverse range of threats. The range spans from short-range missiles and rockets fired by nonstate actors, such as Hamas and Hezbollah, to mid- and longer-range ballistic missiles in Syria's and Iran's arsenals.43 Congress provides regular U.S. funding for Israeli and U.S.-Israeli missile defense programs in defense authorization and appropriations bills. Israel and the United States each contribute financially to several weapons systems and engage in co-development, co-production, and/or technology sharing in connection with them.
|
Hawk and Patriot Missiles for Israel Before Israel developed its active defense network of missile defense systems (Iron Dome, David's Sling, and Arrow), it relied upon the supply of U.S.-origin Hawk and Patriot missile batteries. In 1962, Israel purchased its first advanced weapons system from the United States (Hawk antiaircraft missiles). At the time, Israeli officials considered the acquisition a milestone in the U.S.-Israeli defense relationship.44 Nearly thirty years later, Israel acquired Patriot missiles from the United States in the context of regional threats such as those from Iraqi Scud missiles. Beginning in 2011, Israel upgraded its Patriot missile to the PAC-3 configuration. In 2014, Israel's Patriot missile batteries shot down two unmanned aircraft launched from the Gaza Strip and also intercepted combat and unmanned aircraft launched from Syria. These 2014 intercepts marked the first time Patriot batteries in Israel had been used in 20 years. Since 2017, Israel has used Patriots to intercept Syrian jet fighters and drones that have penetrated Israeli airspace. |
The following section provides background on Israel's four-layered active defense network: Iron Dome (short range), David'’s Sling (low to mid-range), Arrow II (upper-atmospheric), and Arrow III (exo-atmospheric).
Iron Dome
Iron Dome is a short-range antirocket system (intercept range of 2.5 to 43 miles) developed by Israel'Israel’s Rafael Advanced Defense Systems and originally produced in Israel. Iron Dome's ’s targeting system and radar are designed to fire its Tamir interceptors only at incoming projectiles that pose threats to the area being protected (generally, strategically important sites, including population centers); it is not configured to fire on rockets headed toward unpopulated areas. Israel can move Iron Dome batteries as threats change. Currently, Israel has ten Iron Dome batteries deployed throughout the country, and each battery is designed to defend a 60-square -mile populated area.56 As of January 2020, Iron Dome has carried out more than 2,400 operational interceptions.57
notify Congress 30 days before designating a country as a MNNA. According to the Act, Israel, along with several other countries, “shall be deemed to have been so designated by the President as of the effective date of this section, and the President is not required to notify the Congress of such designation of those countries.” See, 22 U.S.C. §2321j. 53 Excess Defense Articles Database Tool, Defense Security Cooperation Agency. 54 For background on mortar, rocket, and missile threats to Israel, see CRS Report R44017, Iran’s Foreign and Defense Policies, by Kenneth Katzman, CRS Report R41514, Hamas: Background and Issues for Congress, by Jim Zanotti, and “Missiles and Rockets of Hezbollah,” Missile Threat, Center for Strategic and International Studies, June 26, 2018. 55 The United States and Israel also jointly conduct a military exercise known as Juniper Falcon, which is designed to enhance interoperability between both nations’ militaries. In March 2019, the U.S. European Command (EUCOM) deployed a Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD) system to Israel to practice “operational procedures for augmenting Israel's existing air and missile defense architecture.” See, USEUCOM deploys Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD) system to Israel,” United States European Command, March 4, 2019.
56 Each battery has three launchers loaded with up to 20 Tamir interceptors per launcher for a total of 60 interceptors per battery. See, https://www.raytheon.com/capabilities/products/irondome.
57Anna Ahronheim, “100% Success Rate in Trial for Advanced Iron Dome System,” Jerusalem Post, January 13, 2020.
Congressional Research Service
13
U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel
Figure 5. Iron Dome Launcher
Source: Raytheon.
Iron Dome’s Past Performance
populated area.45 Israel also developed a naval version of Iron Dome, which it is installing on its corvettes to protect off-shore natural gas facilities.46
Iron Dome's Performance
Iron Dome was declared operational in early 2011. Its first major test came in November 2012 during a weeklong conflict (termed "“Operation Pillar of Cloud/Defense"” by Israel) between Israel and various Palestinian militant groups, including Hamas. Israeli officials claim that Iron Dome intercepted 85% of the more than 400 rockets fired by Gaza-based militants.47
58
Between 2012 and 2014, Israel upgraded Iron Dome'’s various tracking and firing mechanisms. During Israel'’s 2014 conflict with Hamas and other Palestinian militants, media reports (generally based on Israeli claims) seemed to indicate that Iron Dome had a successful interception rate close to 90%.4859 Five Israeli civilians were killed by rocket fire between July and August 2014.
According to the Israel Defense Forces (IDF) and Jane'’s Defence Weekly, during a two-day conflict in May 2019 with Palestinian militant groups in the Gaza Strip, Israel'’s Iron Dome achieved an 86% successful interception rate against rockets fired at urban areas.4960 In that time period, three Israelis were killed by rocket fire. A commander of the Qassam Brigades, the military wing of Hamas, claimed during the May 2019 conflict that Hamas had "“overcome the so-
58 One assessment concludes that Iron Dome’s initial performance in 2012 was less effective than Israel claims, but subsequent improvements made Iron Dome perform far better. See, “As Missiles Fly, a Look at Israel’s Iron Dome Interceptor,” The Conversation, April 15, 2018. 59 “Israel says Iron Dome scores 90 Percent Rocket Interception Rate,” Reuters, July 10, 2014. 60 “IDF Reports Good Iron Dome Performance,” Jane's Defence Weekly, May 9, 2019.
Congressional Research Service
14
U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel
overcome the so-called Iron Dome by adopting the tactic of firing dozens of rockets in a single burst…. The high intensity of fire and the great destructive ability of the missiles… caused great losses and
Congressional Research Service
15
link to page 24 U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel
destruction to the enemy."50”61 According to an assessment by Uzi Rubin, one of Israel's top missile defense experts, Iron Dome "a former head of the Israel Missile Defense Organization, Iron Dome “faced challenges it never did before, and it faced them quite well… There is no 100% defense, never -– it'’s against the laws of physics…. Even if you manage to hit every incoming missile, there'’s Newton'’s Law - even the debris must come down."51”62 In addition to Iron Dome, Israel also has extensive homeland security policies and alerts designed to protect civilians, such as mobile phone applications that warn of incoming missiles, bomb shelters in neighborhoods, and regulations requiring the construction of safe rooms in homes near the Gaza border.63
homes near the Gaza border.52
 |
|
Source: Raytheon. |
Co-production and U.S. Funding
Co-production and U.S. Funding
To date, the United States has provided $1.5596 billion to Israel for Iron Dome batteries, interceptors, co-production costs, and general maintenance (see Table 4). Because Iron Dome was developed by Israel alone, Israel initially retained proprietary technology rights to it. The United States and Israel have had a decades-long partnership in the development and co-production of other missile defense systems (such as the Arrow). As the United States began financially supporting Israel's ’s development of Iron Dome in FY2011, U.S. interest in ultimately becoming a partner in its co-production grew. Congress then called for Iron Dome technology sharing and co-production with the United States.53
64
In March 2014, the United States and Israeli governments signed a co-production agreement to enable the manufacture of components of the Iron Dome system in the United States, while also providing the U.S. Missile Defense Agency (MDA) with full access to what had been proprietary Iron Dome technology.65 U.S.-based Raytheon is Rafael’s U.S. partner in the co-production of Iron Dome.66
U.S. Army Procurement of Iron Dome
Ongoing U.S. efforts to acquire Iron Dome have come in the context of lawmakers |
In March 2014, the United States and Israeli governments signed a co-production agreement to enable the manufacture of components of the Iron Dome system in the United States, while also providing the U.S. Missile Defense Agency (MDA) with full access to what had been proprietary Iron Dome technology.56 U.S.-based Raytheon is Rafael's U.S. partner in the co-production of Iron Dome.57
After Israel's summer 2014 conflict with Hamas and other Palestinian militant groups, there was high Israeli demand for additional Tamir interceptors, Iron Dome batteries, and the external financing to procure these items.5871 On September 30, 2014, Raytheon received a $149 million contract from Rafael to provide parts for the Tamir interceptor. With U.S. co-production, around 60%-70% of the components of the Tamir interceptor are now manufactured in the United States before final assembly in Israel.5972 Israel also maintains the ability to manufacture Tamir interceptors within Israel.
David's Sling
Overview
In December 2019, Israel agreed to export eight ELM-2084 Multi-Mission Radars (the radar system used by Iron Dome) to the Czech Republic for $125 million. Israel has already exported variants of the radar system to Canada, Singapore, Finland, and India.
David’s Sling
Overview
In August 2008, Israel and the United States officially signed a "“project agreement" to codevelop ” to co-develop the David'’s Sling system.6073 David'’s Sling (aka Magic Wand) is a short/medium-range system designed to counter long-range rockets and slower-flying cruise missiles fired at ranges from 25 miles to 186 miles, such as those possessed by Iran, Syria, and Hezbollah in Lebanon. David's ’s Sling is designed to intercept missiles with ranges and trajectories for which Iron Dome and/or Arrow interceptors are not optimally configured. It has been developed jointly by Rafael Advanced Defense Systems and Raytheon. David'’s Sling uses Raytheon'’s Stunner missile for interception, and each launcher can hold up to 16 missiles. In April 2017, Israel declared David's ’s Sling operational and, according to one analysis, "“two David'’s Sling batteries are sufficient to cover the whole of Israel."61
Israel first used David'”74
66 The FY2014 Emergency Supplemental Appropriations Resolution, P.L. 113-145, exempted $225 million in Iron Dome funding—requested by Israel on an expedited basis during the summer 2014 Israel-Gaza conflict—from the co-production requirements agreed upon in March 2014.
67 In 2018, some Members of Congress advocated for the selection of Iron Dome to protect U.S. troops deployed abroad against threats emanating from Russia and North Korea. See, “Bipartisan House Letter requests Iron Dome Use for US Army,” Jewish Telegraphic Agency, April 24, 2018. 68 “US Army Buys Israel’s Iron Dome for Tactical Missile Defense,” Jewish Policy Center, January 22, 2019. 69 Sydney J. Freedberg Jr., “Army Doubts Iron Dome Can Kill Cruise Missiles,” Breaking Defense, March 4, 2020. 70 Ashley Roque, “Congress Considering Mandating Additional US Army Iron Dome Buy,” Jane’s Defence Weekly, May 7, 2020.
71 See, “Inside The Iron Dome,” Moment Magazine, July 17, 2018. 72 “Inside Iron Dome's Secret Manufacturing Plant,” Globes (Israel Business News), October 7, 2018. 73 This joint agreement is a Research, Development, Test and Evaluation (RDT&E) Framework agreement between the United States and Israel. The joint program to implement the agreement is known as the Short Range Ballistic Missile Defense (SRBMD) David’s Sling Weapon System (DSWS) Project. The Department of Defense/U.S.-Israeli Cooperative Program Office manages the SRBMD/DSWS program, which is equitably funded between the United States and Israel.
74 “IDF officially declares David’s Sling Operational,” Jane’s Defence Weekly, April 3, 2017.
Congressional Research Service
17
link to page 24
U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel
Israel first used David’s Sling in July 2018. At the time, Syrian regime forces were
Figure 6. David’s Sling Launches Stunner
attempting to retake parts of southern Syria as
Interceptor
part of the ongoing conflict there. During the fighting, Asad loyalists fired two SS-21 Tochka or 'Scarab'‘Scarab’ tactical ballistic missiles at rebel forces, but the missiles veered into Israeli territory. David'’s Sling fired two Stunner interceptors, but the final impact point of the Syrian missiles changed mid-flight, and Israel ordered one of the interceptors to self-destruct; the other most likely landed in Syrian territory.75 Chinese media alleged that Asad regime forces recovered the Stunner interceptor intact and handed it over to Russia; the Israeli government has not commented on this report.76
likely landed in Syrian territory.62
|
 |
|
Source: Israel Ministry of Defense. |
Co-production and U.S. Funding
Co-production and U.S. Funding
Since FY2006, the United States has contributed over $1.89 billion to the development of David'’s Sling (seesee Table 4). . In June 2018, the United States and Israel signed a co-production agreement for the
joint manufacture of the Stunner interceptor.
Source: Israel Ministry of Defense.
Some interceptor components may beare built in Tucson, Arizona, by Raytheon.
The Arrow and Arrow II Under a 1986 agreement allowing Israel to participate in the Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI), the United States and Israel have co-developed different versions of the Arrow anti-ballistic missile, and since 1988, Israel and the United States have engaged in joint development.77 The The Arrow and Arrow II
Since 1988, Israel and the United States have been jointly developing the Arrow Anti-Missile System.63 The Arrow is designed to counter short-range ballistic missiles. The United States has funded just under half of the annual costs of the development of the Arrow Weapon System, with Israel supplying the remainder. The total U.S. financial contribution (for all Arrow systems) exceeds
75 See, “Israel, US Complete Successful Advanced David's Sling Missile Tests,” Jerusalem Post, March 20, 2019, and “David’s Sling has Dubious Debut against Syrian Missiles, Jane’s Defence Weekly, July 25, 2018. 76 Tyler Rogoway, “If an Israeli Stunner Missile Really Did Fall Into Russian Hands It Is a Huge Deal,” The Drive, November 13, 2019.
77 Shortly after the start of the Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI) in 1985, the Reagan Administration sought allied political support through various cooperative technology agreements on ballistic missile defense (BMD). A memorandum of understanding was signed with Israel on May 6, 1986, to jointly develop an indigenous Israeli capability to defend against ballistic missiles. Subsequently, a number of additional agreements were signed, including, for example, an April 1989 Memorandum of Agreement (MOA) to develop an Israeli computer facility as part of the Arrow BMD program, a June 1991 agreement to develop a second generation Arrow BMD capability, and a September 2008 agreement to develop a short-range BMD system to defend against very short-range missiles and rockets. Israeli interest in BMD was strengthened by the missile war between Iran and Iraq in the later 1980s, and the experience of being attacked by Scud missiles from Iraq during Operation Desert Storm in 1991.
Congressional Research Service
18
link to page 23 U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel
$3.7 billion (see Table 3). The system became operational in 2000 in Israel and has been tested successfully.
The supplying the remainder. The Arrow II program (officially referred to as the Arrow System Improvement Program or ASIP), a joint effort of Boeing and Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI)IAI, is designed to defeat longer-range ballistic missiles. One Arrow II battery is designed to protect large swaths of Israeli territory. In March 2017, media sources reported the first known use of the Arrow II, when they said that it successfully intercepted a Syrian surface-to-air missile (SAM) that had been fired on an Israeli jet returning to Israel from an operation inside Syria.
In August 2020, nearly 20 years after the first Arrow system became operational, Israel successfully tested the Arrow II system. According to one account of the test, Arrow II “successfully intercepted a Sparrow simulated long-range, surface-to-surface missile, which could one day be fired at Israel by Iran...”78 Table 3. U.S. Contributions to the Arrow Program (Arrow, Arrow II, and Arrow III)
dollars in millions
Fiscal Year
Total
Fiscal Year
Total
1990
52.000
2004
144.803
1991
42.000
2005
155.290
1992
54.400
2006
122.866
1993
57.776
2007
117.494
1994
56.424
2008
118.572
1995
47.400
2009
104.342
1996
59.352
2010
122.342
1997
35.000
2011
125.393
1998
98.874
2012
125.175
1999
46.924
2013
115.500
2000
81.650
2014
119.070
2001
95.214
2015
130.908
2002
131.700
2016
146.069
2003
135.749
2017
272.224
2018
392.300
2019
243.000
2020
214.000
Total
3,763.811
Source:dollars in millions
|
Fiscal Year |
Total |
Fiscal Year |
Total |
|
1990 |
52.000 |
2004 |
144.803 |
|
1991 |
42.000 |
2005 |
155.290 |
|
1992 |
54.400 |
2006 |
122.866 |
|
1993 |
57.776 |
2007 |
117.494 |
|
1994 |
56.424 |
2008 |
118.572 |
|
1995 |
47.400 |
2009 |
104.342 |
|
1996 |
59.352 |
2010 |
122.342 |
|
1997 |
35.000 |
2011 |
125.393 |
|
1998 |
98.874 |
2012 |
125.175 |
|
1999 |
46.924 |
2013 |
115.500 |
|
2000 |
81.650 |
2014 |
119.070 |
|
2001 |
95.214 |
2015 |
130.908 |
|
2002 |
131.700 |
2016 |
146.069 |
|
2003 |
135.749 |
2017 |
272.224 |
|
2018 |
392.300 |
||
|
2019 |
243.000 |
||
|
Total |
3,549.811 |
Source: U.S. Missile Defense Agency.
Under the 1986 agreement allowing Israel to participate in the Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI), the United States and Israel have co-developed different versions of the Arrow anti-ballistic missile. The total U.S. financial contribution exceeds $3.5 billion. The system became operational in 2000 in Israel and has been tested successfully. Since 2001, Israel and the United States have conducted a joint biennial ballistic missile defense exercise, called Juniper Cobra, to work on integrating their weapons, radars, and other systems.64
U.S. Missile Defense Agency. High Altitude Missile Defense System (Arrow III)
Overview
Citing a potential nuclear threat from Iran, Israel has sought a missile interceptor that operates at a higher altitude and greater range than the original Arrow systems. In October 2007, the United States and Israel agreed to establish a committee to evaluate Israel'’s proposed "“Arrow III,"” an upper-tier system designed to intercept medium-range ballistic missiles outside the atmosphere. The Arrow III is a more advanced version—in terms of speed, range and altitude—of the current Arrow II interceptor. In 2008, Israel decided to begin development of the Arrow III and the
78 Anna Ahronheim, “Israel Successfully Carries out Arrow 2 Interception. Test Simulated Shooting Down of Long-Range Missile, Including Possibly from Iran,” Jerusalem Post, August 14, 2020.
Congressional Research Service
19
link to page 24 link to page 24 U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel
United States agreed to co-fund its development despite an initial proposal by Lockheed Martin and the Department of Defense (DOD) urging Israel to purchase the Terminal High-Altitude Area Defense (THAAD) missile defense system instead.
In March 2019, the United States deployed a THAAD missile battery to Israel.
The Arrow III, made (like the Arrow II) by Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI)IAI and Boeing, has been operational since January 2017. In July 2010, the United States and Israel signed a bilateral agreement (The Upper-Tier Interceptor Project Agreement) to extend their cooperation in developing and producing the Arrow III, including an equitable U.S.-Israeli cost share. U.S.-Israeli co-production of Arrow III components is ongoing.6579 A U.S.-based subsidiary of IAI, Stark Aerospace Inc. based in Columbus, Mississippi, is producing canisters for the Arrow III system. Since co-development began in 2008, Congress has appropriated $1.1 billion for Arrow III (seesee Table 4).. In January 2019, the United States and Israel conducted a successful test of Arrow III over the Mediterranean, and in July 2019, Arrow III successfully intercepted targets in a series of tests at the Pacific Spaceport Complex-Alaska (PSCA) in Kodiak, Alaska.
Table 4. Defense Budget Appropriations for U.S.-Israeli Missile Defense:
FY2006-FY2020
current dollars in millions
Arrow III
(High
David’s Sling
Iron
Fiscal Year
Arrow II
Altitude)
(Short-Range)
Dome
Total
FY2006
122.866
—
10.0
—
132.866
FY2007
117.494
—
20.4
—
137.894
FY2008
98.572
20.0
37.0
—
155.572
FY2009
74.342
30.0
72.895
—
177.237
FY2010
72.306
50.036
80.092
—
202.434
FY2011
66.427
58.966
84.722
205.000
415.115
FY2012
58.955
66.220
110.525
70.000a
305.700
FY2013 After
40.800
74.700
137.500
194.000
447.000
Sequestration
FY2014
44.363
74.707
149.712
460.309
729.091
(includes
supp)
FY2015
56.201
74.707
137.934
350.972
619.814
FY2016
56.519
89.550
286.526
55.000
487.595
FY2017
67.331
204.893
266.511
62.000
600.735
FY2018
82.300
310.000
221.500
92.000
705.800
FY2019
163.000
80.000
187.000
70.000
500.000
FY2020
159.000
55.000
191.000
95.000
500.000
Total
1,280.476
1,188.779
1,993.317
1,654.281
6,116.853
a. Table 4. Defense Budget Appropriations for U.S.-Israeli Missile Defense:FY2006-FY2019
current dollars in millions
|
Fiscal Year |
Arrow II |
Arrow III (High Altitude) |
David's Sling (Short-Range) |
Iron Dome |
Total |
|
FY2006 |
122.866 |
— |
10.0 |
— |
132.866 |
|
FY2007 |
117.494 |
— |
20.4 |
— |
137.894 |
|
FY2008 |
98.572 |
20.0 |
37.0 |
— |
155.572 |
|
FY2009 |
74.342 |
30.0 |
72.895 |
— |
177.237 |
|
FY2010 |
72.306 |
50.036 |
80.092 |
— |
202.434 |
|
FY2011 |
66.427 |
58.966 |
84.722 |
205.000 |
415.115 |
|
FY2012 |
58.955 |
66.220 |
110.525 |
|
305.700 |
|
FY2013 After Sequestration |
40.800 |
74.700 |
137.500 |
194.000 |
447.000 |
|
FY2014 |
44.363 |
74.707 |
149.712 |
460.309 (includes supp) |
729.091 |
|
FY2015 |
56.201 |
74.707 |
137.934 |
350.972 |
619.814 |
|
FY2016 |
56.519 |
89.550 |
286.526 |
55.000 |
487.595 |
|
FY2017 |
67.331 |
204.893 |
266.511 |
62.000 |
600.735 |
|
FY2018 |
82.300 |
310.000 |
221.500 |
92.000 |
705.800 |
|
FY2019 |
163.000 |
80.000 |
187.000 |
70.000 |
500.000 |
|
Total |
1,121.476 |
1,133.779 |
1,802.317 |
1,559.281 |
5,616.853 |
a. These funds were not appropriated by Congress but reprogrammed by the Obama Administration from These funds were not appropriated by Congress but reprogrammed by the Obama Administration from
other Department of Defense accounts.
Emergency U.S. Stockpile in Israel
79 The United States and Israel signed the Arrow III co-production agreement in June 2019.
Congressional Research Service
20
U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel
Emergency U.S. Stockpile in Israel In the early 1980s, Israeli leaders sought to expand what they called their "“strategic collaboration"collaboration” with the U.S. military by inviting the United States to stockpile arms and equipment at Israeli bases for American use in wartime.66 In 198980 Beginning in 1984, the United States agreed to establish munitions stockpiles in Israel for use by the United States and, with U.S. permission, by Israel in emergency situations.67
began to stockpile military equipment in Israel, but only “single-use” armaments that could not be used by the Israel Defense Forces.81 In 1989, the George H.W. Bush Administration decided to alter the terms of the stockpile and provide Israel access to it in emergency situations.82 At the time, the United States was attempting to sell Saudi Arabia M1A1 tanks, and U.S. officials sought Israel’s acquiescence to the deal. Section 514 of the Foreign Assistance Act of 1961 (22 U.S.C. §2321h) allows U.S. defense articles stored in war reserve stocks to be transferred to a foreign government through Foreign Military Sales or through grant military assistance, such as FMF. Congress limits the value of assets transferred into War Reserves Stock Allies (WRSA) stockpiles located in foreign countries in any fiscal year through authorizing legislation (see below). The U.S. retains title to the WRSA stocks, and title must be subsequently transferred before the foreign country may use them.
|
 |
|
Source: 405th AFSB exercises War Reserve Stocks for Allies transfer, DVIDS, Defense Visual Information Distribution Service, February 28, 2019. |
The United States European Command (EUCOM) manages the War Reserves Stock
Figure 7. Army Officers Inspect WRSA-I
Allies-Israel (WRSA-I) program. The United States stores missiles, armored vehicles, and artillery ammunition in Israel.6883 According to one Israeli officer, "“Officially, all of this equipment belongs to the US military…. If however, there is a conflict, the IDF [Israel Defense Forces] can ask for permission to use some of the equipment."69”84 According to one expert, "“WRSA-I is a strategic boon to Israel. The process is streamlined: No 60-day congressional notification is required, and there'
there’s no waiting on delivery."70”85 In February 2019, as part of the bilateral military exercise Juniper Falcon 2019, officers from the 405th
Source: 405th AFSB exercises War Reserve Stocks for Allies transfer, DVIDS, Defense Visual Information
Juniper Falcon 2019, officers from the 405th
Distribution Service, February 28, 2019.
Army Field Support Brigade simulated a transfer of munitions from the WRSA-I to Israeli Defense Forces control.
Since 1989, Israel has requested access to the stockpile on multipleat least two occasions, including:
-
80 “U.S. - Israel Strategic Link: Both Sides Take Stock,” New York Times, October 2, 1981. 81 “U.S. Tells Israel it Plans to Sell Saudis 300 Tanks,” New York Times, September 29, 1989. 82 In October 1989, the United States and Israel agreed to pre-position $100 million worth of dual-use defense equipment in Israel.
83 At present, the United States and Israel have a bilateral agreement that governs the storage, maintenance, in-country transit, and other WRSA-related costs. The government of Israel, using both its national funds and FMF, pays for the construction, maintenance and refurbishment costs of WRSA ammunition storage facilities. It also pays for the packaging, crating, handling and transportation of armaments to and from the stockpile. In any future expedited procedure, reserve stocks managed by EUCOM could be transferred to Israel; then, U.S. officials would create an-after-the-fact Foreign Military Sale to account for the transferred equipment.
84 “US may give Israel Iraq Ammo,” Jerusalem Post, February 11, 2010. 85 “Best Friends Don’t Have to Ask,” Politico Magazine, August 14, 2014.
Congressional Research Service
21
link to page 16 U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel
During the summer 2006 war between Israel and Hezbollah, Israel requested that
During the summer 2006 war between Israel and Hezbollah, Israel requested thatthe United States expedite the delivery of precision-guided munitions to Israel. In order to accomplish this, the George W. Bush Administration did not use the emergency authority codified in the Arms Export Control Act (AECA), but rather allowed Israel to access the WRSA-I stockpile. -
In July 2014, during Israeli military operations against Hamas in the Gaza Strip,
the Defense Department permitted Israel to draw from the stockpile, paid with FMF, to replenish 120
71
86
Section 7049(b)(4) of P.L. 116-6, the FY2019 Consolidated Appropriations Act, extended the authorization of WRSA-I through FY2020.7287 Section 1273 of P.L. 115-232, the John S. McCain National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2019, extended the authority for WRSA-I through FY2023.
At times, Congress has passed legislation that has authorized EUCOM to increase the value of materiel stored in Israel. According to DSCA, "“It should be understood that no new procurements are involved in establishing and maintaining these stockpiles. Rather, the defense articles used to establish a stockpile and the annual authorized additions represent defense articles that are already within the stocks of the U.S. armed forces. The stockpile authorizing legislation simply identifies a level of value for which a stockpile may be established or increased."73
”88 Stockpiling Precision-Guided Munitions for Israel
Since 2014, Israel has requested that the United States military increase its own stockpile of precision-guided munitions (PGMs) stored in Israel for possible Israeli emergency use against |
If EUCOM contributed the maximum amount legally permitted in each applicable fiscal year, then the non-inflation adjusted value of materiel stored in Israel would currently stand at $3.4 billion. The following legislation authorized increases in value to the stockpile:
-
FY1990: P.L. 101-167, the Foreign Operations, Export Financing, and Related
Programs Appropriations Act, 1990, provided $165 million for all stockpile programs and expanded their locations to include Korea, Thailand, NATO members, and countries which were then major non-NATO allies (Australia, Japan, Korea, Israel and Egypt). Although the Act did not specify funds for Israel, of the $165 million appropriated, $10 million was for Thailand, $55 million was for South Korea, and $100 million was intended as an initial authorization for Israel.
74 FY1991:89 86 “U.S. Defends Supplying Israel Ammunition during Gaza Conflict,” Reuters, July 31, 2014. 87 The authorization extension states that “Section 12001(d) of the Department of Defense Appropriations Act, 2005 (P.L. 109-108–287; 118 Stat. 1011) is amended by striking ‘2018’ and inserting ‘2019.’” 88 Defense Institute of Security Assistance Management (DISAM), DISAM’s Online Greenbook, Chapter 2, Security Legislation and Policy. 89 Dr. Louis J. Samelson, “Military Assistance Legislation for Fiscal Year 1990,” The DISAM Journal, Winter, 1989/1990. Congressional Research Service 22 U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel FY1991: P.L. 101-513, the Foreign Operations, Export Financing, and Related Programs Appropriations Act for FY1991, authorized additions to defense articles in Israel"“not less than"” $300 million in value for FY1991.-
FY1993: P.L. 102-391, the Foreign Operations, Export Financing, and Related
Programs Appropriations Act for FY1993, authorized additions to defense articles in Israel
"“not less than"” $200 million in value for FY1993. -
FY1994: P.L. 103-87, the Foreign Operations, Export Financing, and Related
Programs Appropriations Act for FY1994, authorized additions to defense articles in Israel up to $200 million in value for FY1994.
- FY1995: P.L. 103-306, the Foreign Operations, Export Financing, and Related Programs Appropriations Act for FY1995, authorized a total addition to defense articles in Israel of $200 million for FYs 1994 and 1995.
-
FY2007-FY2008: Section 13(a)(2)(A)(i) of the Department of State Authorities
Act of 2006 (P.L. 109-472) amended Section 514 of the Foreign Assistance Act of 1961, as amended (P.L. 87-195; 22 U.S.C. §2321h) to authorize additions to defense articles in Israel of up to $200 million in value for each of FY2007 and FY2008.
75 - 90 FY2011-FY2012: P.L. 111-266, the Security Cooperation Act of 2010, authorized additions to defense articles in Israel up to $200 million in value for each of FY2011 and FY2012.
- FY2014-FY2015: P.L. 113-296, the United States-Israel Strategic Partnership Act of 2014, authorized additions to defense articles in Israel up to $200 million in value for each of FY2014 and FY2015.
-
FY2016-FY2017: Section 7034(k)(11)(B) of P.L. 114-113, the FY2016
Consolidated Appropriations Act, authorized additions to defense articles in Israel up to $200 million in value for each of FY2016 and FY2017.
- FY2018-FY2019: Section 7034(l)(7) of P.L. 115-141, the FY2018 Consolidated Appropriations Act, authorized additions to defense articles in Israel up to $200 million in value for each of FY2018 and FY2019.
- FY2019-FY2020: Section 7048(b)(4)(B) of P.L. 116-6, the FY2019 Consolidated Appropriations Act, authorized additions to defense articles in Israel up to $200 million in value for each of FY2019 and FY2020.
Defense Budget Appropriations/Authorization for Anti-Tunnel Defense
In 2016, the Israeli and U.S. governments began collaborating on a new system to detect underground smuggling tunnels and to counter cross-border tunnels used (most prominently by Hamas in the summer 2014 conflict) to infiltrate Israel. Reportedly, this technology uses acoustic or seismic sensors and software to detect the sounds of digging by monitoring vibrations underground.76
90 This increase for each fiscal year is based on legislative language contained in Section 12002 of P.L. 108-287, the Department of Defense Appropriations Act, 2005.
Congressional Research Service
23
link to page 17 link to page 17 U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel
underground.91 This technology may be based on discovery techniques used in the oil and natural gas sector.77
92
Section 1279 of P.L. 114-92, the FY2016 National Defense Authorization Act, authorized the establishment of a U.S.-Israeli anti-tunnel cooperation program.93 This authorization allowed funds from the research, development, test, and evaluation defense-wide account to be used (in combination with Israeli funds) to establish anti-tunnel capabilities that detect, map, and neutralize underground tunnels that threaten the United States or Israel. The authorization requires the Secretary of Defense to report to Congress on, among other things, the sharing of research and development costs between the United States and Israel. Section 1278 of P.L. 115-91, the FY2018 National Defense Authorization Act, extended the authority of the anti-tunnel cooperation program through December 31, 2020. It also required that not less than 50% of U.S. contributions to the program should be used for "research, development, test, and evaluation activities in the United States in connection with such support."
The FY2019 NDAA expanded the scope of the anti-tunnel cooperation program to address the threat posed by the proliferation of unmanned aerial vehicles in the hands of foreign terrorist organizations and other non-state actors. Section 1272 of P.L. 115-232, the John S. McCain National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2019, amended the FY2016 NDAA to include cooperation in establishing "capabilities for countering unmanned aerial systems." It also required a report on identifying specific capability gaps of the United States and Israel with respect to countering unmanned aerial systems before funding may be provided for the program.
|
Fiscal Year |
Appropriation |
|
FY2016 |
40.0 |
|
FY2017 |
42.5 |
|
FY2018 |
47.5 |
|
FY2019 |
47.5 |
|
Total |
177.500 |
Source: Joint Explanatory Statement accompanying Consolidated Appropriations Acts for FY2016-2018.
Table 5. U.S.-Israeli Anti-Tunnel Cooperation
current U.S. dollars in millions
Fiscal Year
Appropriation
FY2016
40.0
FY2017
42.5
FY2018
47.5
FY2019
47.5
FY2020
-
Total
177.500
Source: Joint Explanatory Statement accompanying Consolidated Appropriations Acts for FY2016-2018. For FY2021, Congress is considering providing $47.5 mil ion.
Defense Budget Appropriations/Authorization for Countering Unmanned Aerial Systems As unmanned aerial vehicle technology has proliferated across the Middle East, Israel has sought U.S. assistance in countering various systems used by state and non-state actors alike. In order to counter unmanned drones, States are researching various methods to detect incoming unmanned aircraft (using radio or optical sensors) and then either disabling, destroying, or even seizing them by either jamming their communications, intercepting their flight paths, or hacking their electronic systems.94
Congress first authorized a cooperative U.S.-Israeli Counter Unmanned Aerial Systems (C-UAS) program by expanding the scope of the anti-tunnel cooperation program (see “Defense Budget Appropriations for U.S.-Israeli Missile Defense Programs”). Then, in the FY2020 NDAA (P.L. 116-92), Congress created a separate authority (Section 1278), which authorized the Secretary of Defense to “carry out research, development, test, and evaluation activities, on a joint basis with Israel, to establish capabilities for countering unmanned aerial systems that threaten the United
91 “Israel’s Underground War—Technology and Specialist Troops deployed in face of Subterranean Threat,” Wall Street Journal, March 2, 2016.
92 “Israeli Official bets Advances in Anti-Tunnel Technology will secure Gaza Border,” Washington Post, March 6, 2018.
93 Section 1279 of P.L. 116-92, the FY2020 National Defense Authorization Act, extended the authority of the anti-tunnel cooperation program through December 31, 2024.
94 Ilan Ben Zion, “As Attack Drones Multiply, Israeli Firms Develop Defenses,” Associated Press, September 26, 2019.
Congressional Research Service
24
U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel
States or Israel.” Section 1278 requires a matching contribution from the government of Israel and caps the annual U.S. contribution at $25 million. Congress authorized the program through 2024.
For FY2020, the Joint Explanatory Statement accompanying P.L. 116-93, the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2020, included $13 million under “Combatting Terrorism Technology Support” for the C-UAS program. For FY2021, H.Rept. 116-453 accompanying H.R. 7617, the FY2021 Defense Appropriations bill, would provide $25 million for C-UAS under Combatting Terrorism Technology Support.”
Aid Restrictions and Possible Violations Aid Restrictions and Possible Violations
U.S. aid and arms sales to Israel, like those to other foreign recipients, are subject to U.S. law. Some U.S. citizens and interest groups periodically call upon Congress to ensure that U.S. military assistance to Israel is conditioned on the Israeli government'’s compliance with applicable U.S. laws and policies and with international humanitarian law.
Arms Sales and Use of U.S.-Supplied Equipment78
Equipment95 The 1952 Mutual Defense Assistance Agreement and subsequent arms agreements between Israel and the United States limit Israel'’s use of U.S. military equipment to defensive purposes.7996 The Arms Export Control Act (AECA, 22 U.S.C. §2754) authorizes the sale of U.S. defense articles and services for specific purposes, including "“legitimate self-defense."”97 The AECA (22 U.S.C. §2753) states that recipients may not use such articles "“for purposes other than those for which [they have been] furnished"” without prior presidential consent.8098 The actAct stipulates that sale agreements entered into after November 29, 1999, must grant the U.S. government the right to verify "“credible reports"” that articles have been used for unauthorized purposes. The Foreign Assistance Act
95 See, CRS In Focus IF11197, U.S. Arms Sales and Human Rights: Legislative Basis and Frequently Asked Questions, by Paul K. Kerr and Liana W. Rosen.
96 U.S. State Department, Treaties in Force, Agreement relating to mutual defense assistance, Entered into force July 23, 1952; TIAS 2675.
97 Pursuant to the AECA, when Israel, like other foreign nations, purchases U.S. defense articles and services, it must sign a Letter of Offer and Acceptance (LOA) with the United States government. The LOA lists the items and/or services, estimated costs, and the terms and conditions of sale. Unless otherwise specified, the standard terms and conditions for Israel are consistent with the general terms for all U.S. arms sales abroad. These terms and conditions permit the use of items acquired: for internal security; for legitimate self-defense; for preventing or hindering the proliferation of weapons of mass destruction and of the means of delivering such weapons; to permit the Purchaser to participate in regional or collective arrangements or measures consistent with the Charter of the United Nations, or otherwise to permit the Purchaser to participate in collective measures requested by the United Nations for the purpose of maintaining or restoring international peace security; for the purpose of enabling foreign military forces in less developed countries to construct public works and to engage in other activities helpful to social and economic development; for purposes specified in any Mutual Defense Assistance Agreement between the USG and the Purchaser; or, for purposes specified in any other bilateral or regional defense agreement to which the USG and the Purchaser are both parties. For a sample LOA, see Defense Security Cooperation Agency, Security Assistance Management Manual, available online at: [https://www.samm.dsca.mil/figure/figure-c5f4]
98 Nevertheless, in 22 U.S.C. 2753, the AECA also states that the consent of the President shall not be required for the transfer by a foreign country or international organization of defense articles sold by the United States if the recipient is the government of a member country of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization, the Government of Australia, the Government of Japan, the Government of the Republic of Korea, the Government of Israel, or the Government of New Zealand.
Congressional Research Service
25
U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel
Assistance Act (FAA) of 1961, as amended, also contains general provisions on the use of U.S.-supplied military equipment.99
It is the statutory responsibility of the Departments of State and Defense, pursuant to the AECA, to conduct end-use monitoring (EUM) to ensure that recipients of U.S. defense articles use such items solely for their intended purposes. The AECA also provides authority to the President (through a presidential determination) and Congress (joint resolution) to prohibit the sale or delivery of U.S.-origin defense articles to a recipient country if it has used such articles “for a purpose not authorized” by the AECA or the FAA.100
Questions over the misuse of U.S.-supplied equipment to Israel have arisen in several instances in past decades, including over the sale of tear gas to Israel during the late 1980s,101 the sale of Caterpillar D-9 bulldozers to Israel allegedly used in the destruction of Palestinian homes,102 and Israel's use of U.S.-supplied cluster munitions in Lebanon.103
In March 2020, 64 Representatives wrote a letter to Secretary of State Mike Pompeo posing a series of questions,104 out of concern that Israel may have been using U.S.-origin construction equipment to demolish the homes of Palestinians that Israel has accused of committing terrorism.105 The Members specifically requested “an examination of Israeli compliance with the requirements applied to recipients of U.S.-origin defense articles pursuant to the Arms Export Control Act of 1976 (AECA) as amended [22 U.S.C. 2751, et. seq.]” and “a determination as to whether a report to Congress on this issue is required by section 3(c)(2) of AECA [22 U.S.C. 2753].”
supplied military equipment.81
In the late 1970s and early to mid-1980s, the Carter and Reagan Administrations questioned Israel's use of U.S.-supplied equipment during various military operations in the region. After Israel's 2006 war in Lebanon, the State Department issued a preliminary report to Congress concluding that Israel may have violated the terms of agreements with the United States that restrict Israel's use of U.S.-supplied cluster munitions to certain military targets in non-civilian areas.82
Human Rights Vetting (Leahy Law)83
Human Rights Vetting (Leahy Law)106 Section 620M of the Foreign Assistance Act of 1961 (FAA), as amended, prohibits the furnishing of assistance authorized by the FAA and the AECA to any foreign security force unit where there is credible information that the unit has committed a gross violation of human rights. The State Department and U.S. embassies overseas implement Leahy vetting to determine which foreign security individuals and units are eligible to receive U.S. assistance or training.
In the 115th Congress, Representative Betty In the 116th Congress, Representative |
In February 2016, Senator Leahy and 10 other Members of Congress sent a letter to then-Secretary of State John Kerry asking the State Department to determine whether alleged extrajudicial killings or torture by Israeli military and police (and Egypt separately) should trigger Leahy law restrictions.85 In its response to Congress, the State Department stated that no Israeli individual or unit potentially involved in the letter's alleged incidents had been submitted to receive U.S. assistance.86
Use of U.S. Funds within Israel's Pre-June 1967 Borders
In some instances, U.S. assistance to Israel may be used only in areas subject to the administration of Israel prior to June 1967 (see "Loan Guarantees"). For example, U.S. State Department-provided Migration and Refugee (MRA) assistance (see below), per agreement between the State Department and United Israel Appeal, may only be used for absorption centers, ulpanim (intensive Hebrew-language schools with particular focus on immigrants to Israel), or youth aliyah (relocation to Israel) institutions located within Israel's pre-June 1967 area of control.87 In addition, according to agreements between the U.S. and Israeli governments, programs funded by certain U.S.-Israeli binational foundations, such as the U.S.-Israel Binational Science Foundation (see below), "may not be conducted in geographic areas which came under the administration of the Government of Israel after June 5, 1967, and may not relate to subjects primarily pertinent to such areas."88
Israeli Arms Transfers to Third Parties
Israeli Arms Transfers to Third Parties Per Section §3(a) of the Arms Export Control Act (AECA - 22 U.S. Code §2753) and Section 505(e) of the Foreign Assistance Act (22 U.S. Code §2314), the U.S. government must review and approve any transfer of U.S.-origin equipment from a recipient to a third party that was not previously authorized in the original acquisition.89120 Third Party Transfer (or TPT) is the retransfer of title, physical possession or control of defense articles from the authorized recipient to any person or organization not an employee, officer or agent of that recipient country.90
Although as121
As previously mentioned, Israel is a major global manufacturer of armaments. Yet, it also possesses significant quantities of major U.S.-origin defense equipment stemming from its decades-old security partnership with the United States. At times, third parties have sought to procure U.S. equipment used by Israel, and U.S.-Israel differences over approval of retransfer have has at times caused friction in the U.S.-Israelibilateral relationship. For example, in 2017, Croatia solicited bids for the procurement of fighter aircraft and, a year later, chose to purchase 12 used F-16 Barak fighters from Israel in a deal worth an estimated $500 million, conditioned uponon U.S. TPT approval. In December 2018, the Trump Administration notified Congress that it had approved the sale, but only if all Israeli modifications were removed beforehand. Reportedly, Croatia did not want the F-16s returned to their original condition, and the deal was cancelled despite high level negotiations between Israeli and U.S. officials.91
122 Israel and China
Amidst ongoing global U.S.-Chinese competition in various fields, Israel'’s defense and technology trade with China has at times come under U.S. scrutiny.92123 Since the middle of the last
critical in tone. See, Melissa Weiss, “Scoop: Senators Back Away from Threatening Israel with End of Bipartisan Support,” Jewish Insider, May 10, 2020.
118 Senator Chis Van Hollen, Press Releases, “Van Hollen, Senate Democrats File NDAA Amendment Prohibiting U.S. Funds from Supporting Israeli Annexation of the West Bank,” July 2, 2020. 119 In a floor speech, Senator Van Hollen defended the purpose of the amendment against those who claimed that the Senator would have suspended U.S. missile defense funding to Israel (Iron Dome is not a U.S. defense article). He remarked: “As I explained in my floor statement at the time of its introduction, the amendment would not have reduced U.S. security assistance to Israel by a single penny. It would simply have ensured that no U.S. security assistance could be used for the purpose of unilaterally annexing territory in the West Bank. Furthermore, nothing in this amendment would have prohibited Israel from using U.S.-financed missile defense systems such as Iron Dome to defend against attacks in any territories that could be unilaterally annexed by the Israeli Government.” See, Senate Speeches and Inserts, Page S.4663, Congressional Record, August 3, 2020.
120 See, U.S. State Department, “Third Party Transfer Process and Documentation,” Bureau of Political-Military Affairs, December 17, 2018.
121 See, Defense Institute of Security Cooperation Studies, “The Management of Security Cooperation (Green Book),” Edition 39, January 2019.
122 “Croatia cancels F-16 Deal with Israel due to U.S. Objections,” Axios, January 10, 2019. 123 See, “The Evolving Israel-China Relationship,” RAND Corporation, 2019.
Congressional Research Service
29
U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel
Since the middle of the last decade, Israeli defense exports to China have nearly ceased. Two planned Israeli sales to China drew significant opposition both from successive administrationsAdministrations and from Congress (PHALCON airborne radar systems in 2000 and upgrade of Chinese Harpy Killer drone aircraft in 2004/2005).93124 As a result of U.S. pressure on Israel to cease its long-standing and sometimes clandestine defense relationship with China, Israel created its own arms export control agency, known as the Defense Export Control Agency (DECA). In addition, the United States and Israel signed a 2005 bilateral agreement, known as the "“Declaration of Understanding on Technology Exports,"” whereby both countries pledged to ensure defense export transparency, with the United States pledging not to ban Israel'’s defense deals on commercial grounds to ensure Israeli competitiveness globally.94
125
Though Israeli-Chinese defense ties have essentially ended, China is now Israel’s second largest single-state trading partner (after the United States), and ended, there is still some concern that Israeli technology transfer in the commercial sphere will be used by China to compete with the United States and potentially threaten its national security in various fields, such as cybersecurity, artificial intelligence, and robotics.95126 According to one analyst, "“Since they cannot buy defense equipment from Israel, Chinese companies with links to the country'’s military have looked to civilian technologies instead, particularly those adaptable to military use."96 Currently, Israel does not have an institution akin to the Committee on Foreign Investment in the United States (CFIUS), though some Israelis have considered creating a similar government body to oversee sensitive commercial deals involving foreign companies.
”127 Partly due to U.S. concerns regarding China’s involvement in Israel’s economy, Israel created an advisory panel on foreign investment in Israel in late 2019.128 However, this panel reportedly does not have the authority to review investments in sectors such as high-tech that accounted for most of China’s investments in Israel in the previous decade.129 Apparently, debate continues within Israel’s government about how to balance economic interests with national security concerns.130
Chinese investment in Israel also has raised some concern within the Administration and Congress. Section 1289 of S.1790P.L. 116-92, the National Defense Authorization Act for FY2020, expressesexpressed a sense of the Senate that the United States government should "“urge the Government of Israel to consider the security implications of foreign investment in Israel."” According to one Israeli analysis, President Trump reportedly warned Prime Minister Netanyahu in March 2019 that U.S. security assistance for and cooperation with Israel could be limited if Chinese companies establish a 5G communications network in Israel, in line with similar warnings that the Administration has communicated to other U.S. allies and partners.97131 Additionally, a state-owned Chinese company (the Shanghai International Port Group) has secured the contract to
124 In 2000, Representative Sonny Callahan of Alabama, then Chairman of the Foreign Operations Subcommittee of the House Appropriations Committee, told a hearing on April 6, 2000, that he would block $250 million in FY2001 military assistance to Israel unless Israel cancelled the PHALCON sale to China. Representative Callahan offered an amendment during a June 20 subcommittee markup to withhold $250 million from the $2.88 billion in total economic and military assistance proposed for Israel for FY2001, but the amendment failed by a vote of nine to six. See, “Israel-China Radar Deal Opposed,” Washington Post, April 7, 2000 and “U.S. Congressman: We’ll Block Israeli Aid Unless China Deal Cancelled,” Jerusalem Post, April 7, 2000. 125 “Israel, U.S. Draft Agreement for Openness, Equality in Arms Deals,” Ha’aretz, June 27, 2005. 126 “China Tech Push in Israel Stirs Security Fears,” Wall Street Journal, February 12, 2019. 127 “Israel and China Take a Leap Forward—but to Where?” Mosaic, November 5, 2018. 128 Arie Egozi, “Israelis Create Foreign Investment Overseer; China Targeted,” Breaking Defense, November 13, 2019. 129 Shira Efron, et al., Chinese Investment in Israeli Technology and Infrastructure: Security Implications for Israel and the United States, RAND Corporation, 2020, pp. 24-25.
130 James M. Dorsey, “Israel-China Relations: Staring Into the Abyss of US-Chinese Decoupling,” The Globalist, June 9, 2020; Mercy A. Kuo, “US-China-Israel Relations: Pompeo’s Visit,” The Diplomat, May 27, 2020. 131 Hiddai Segev, Doron Ella, and Assaf Orion, “My Way or the Huawei? The United States-China Race for 5G Dominance,” Institute for National Security Studies Insight No. 1193, July 15, 2019.
Congressional Research Service
30
U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel
owned Chinese company (the Shanghai International Port Group) has secured the contract to operate a new terminal at Haifa'’s seaport for 25 years (beginning in 2021), and another state-owned Chinese company (a subsidiary of China Harbour Engineering Company) is developing Ashdod'Ashdod’s new port. Both Haifa and Ashdod host Israeli naval bases. Due to the Chinese contract for Haifa, the U.S. Navy is reportedly reconsidering its practice of periodically docking at the base there.98
Other Ongoing Assistance and Cooperative Programs
there.132
In spring 2020, after the United States again raised concern over Chinese investment in major Israeli projects, the subsidiary of a Hong Kong-based company lost a bid to build Israel’s largest desalination plant. Shortly before Israel announced the bid decision, Secretary of State Michael Pompeo visited Israel and publicly stated, “We do not want the Chinese Communist Party to have access to Israeli infrastructure, Israeli communication systems, all of the things that put Israeli citizens at risk and in turn put the capacity for America to work alongside Israel on important projects at risk as well.”133 The United States and Israel also are reportedly nearing a deal whereby Israel would pledge not to choose a Chinese technology company to build its 5G next generation mobile network.134
Other Ongoing Assistance and Cooperative Programs
Migration & Refugee Assistance Migration & Refugee Assistance
Since 1973, Israel has received grants from the State Department'’s Migration and Refugee Assistance account (MRA)99135 to assist in the resettlement of migrants to Israel. Funds are paid to the United Israel Appeal, a private philanthropic organization in the United States, which in turn transfers the funds to the Jewish Agency for Israel.100136 Between 1973 and 1991, the United States gave about $460 million for resettling Jewish refugees in Israel. Annual amounts have varied from a low of $125 million to a high of $80 million, based at least partly on the number of Jews leaving the former Soviet Union and other areas for Israel.
Table 6. Migration and Refugee Assistance Funding Levels for Israel
Fiscal Year
Total
FY2000-FY2012
$519.3 mil ion
FY2013
$15 mil ion
FY2014
$15 mil ion
FY2015
$10 mil ion
FY2016
$10 mil ion
FY2017
$7.5 mil ion
FY2018
$7.5 mil ion
132 “U.S. Navy may Stop Docking in Haifa after Chinese Take Over Port,” Jerusalem Post, December 15, 2018. 133 Shirley Zhao and Ivan Levingston, “Li Ka-Shing Hong Kong Group Loses Israel Deal Amid U.S. Push,” Bloomberg, May 26, 2020.
134 “Israel, U.S. Near Deal to Exclude China from Israeli 5G Networks: U.S. Official,” Reuters, August 14, 2020. 135 The MRA account is authorized as part of the State Department’s institutional budget, with funds for the account appropriated through the foreign operations appropriations bill.
136 The Jewish Agency for Israel’s website is available at http://www.jafi.org.il/.
Congressional Research Service
31
U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel
Fiscal Year
Total
FY2019
$5.0 mil ion
FY2020
$5.0 mil ion
FY2021 Request
$5.0 mil ion
Source: U.S. State Department.
Table 6. Migration and Refugee Assistance Funding Levels for Israel
|
FY2000-FY2012 |
$519.3 million total |
|
FY2013 |
$15 million |
|
FY2014 |
$15 million |
|
FY2015 |
$10 million |
|
FY2016 |
$10 million |
|
FY2017 |
$7.5 million |
|
FY2018 |
$7.5 million |
|
FY2019 |
$5.0 million |
|
FY2020 Request |
$5.0 million |
Source: U.S. State Department.
Congress has changed the earmark language since the first refugee resettlement funds were appropriated in 1973. At first, the congressional language said the funds were for "“resettlement in Israel of refugees from the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics and from Communist countries in Eastern Europe."” But starting in 1985, the language was simplified to "“refugees resettling in Israel"Israel” to ensure that Ethiopian Jews would be covered by the funding. Technically, the legislative language designates funds for refugee resettlement, but in Israel little differentiation is made between Jewish "refugees"“refugees” and other Jewish immigrants, and the funds are used to support the absorption of all immigrants.
Loan Guarantees
Overview
Overview
Since 1972, the United States has extended loan guarantees to Israel to assist with housing shortages, Israel'’s absorption of new immigrants from the former Soviet Union and Ethiopia, and its economic recovery following the 2000-2003 recession, which was probably caused in part by the Israeli-Palestinian conflict known as the second intifada. Loan guarantees are a form of indirect U.S. assistance to Israel, since they enable Israel to borrow from commercial sources at lower rates. Congress directs that subsidies be set aside in a U.S. Treasury account in case of a possible Israeli default. These subsidies, which are a percentage of the total loan (based in part on the credit rating of the borrowing country), have come from the U.S. or the Israeli government. Israel has never defaulted on a U.S.-backed loan guarantee.
Loan Guarantees for Economic Recovery
In 2003, then-Prime Minister Ariel Sharon requested an additional $8 billion in loan guarantees to help the Israeli government stimulate Israel’s then-help Israel's ailing economy. The loan guarantee request accompanied a request for an additional $4 billion in military grants to help Israel prepare for possible attacks during an anticipated U.S. war with Iraq. P.L. 108-11, the FY2003 Emergency Wartime Supplemental Appropriations Act, authorized $9 billion in loan guarantees over three years for Israel'’s economic recovery and $1 billion in military grants. P.L. 108-11 stated that the proceeds from the loan guarantees could be used only within Israel'’s pre-June 5, 1967, area of control; that the annual loan guarantees could be reduced by an amount equal to the amount Israel spends on settlements outside of Israel'’s pre-June 1967 area of control; that Israel would pay all fees and subsidies; and that the President would consider Israel'’s economic reforms when determining terms and conditions for the loan guarantees.101
137
137 According to P.L. 108-11, “[Loan] guarantees may be issued under this section only to support activities in the geographic areas which were subject to the administration of the Government of Israel before June 5, 1967: Provided further, That the amount of guarantees that may be issued shall be reduced by an amount equal to the amount extended or estimated to have been extended by the Government of Israel during the period from March 1, 2003, to the date of issue of the guarantee, for activities which the President determines are inconsistent with the objectives and
Congressional Research Service
32
U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel
On November 26, 2003, the Department of State announced that the $3 billion in loan guarantees for FY2003 were reduced by $289.5 million because Israel continued to build settlements in the occupied territories and continued construction of a security barrier separating key Israeli and Palestinian population centers.102138 In FY2005, the U.S. government reduced the amount available for Israel to borrow by an additional $795.8 million. Since then, Israel has not borrowed any funds.
According to the U.S. Department of the Treasury, Israel is legally obligated to use the proceeds of guaranteed loans for refinancing its government debt and also has agreed that proceeds shall not be used for military purposes or to support activities in areas outside its pre-June 5, 1967, areas of control (the West Bank—including East Jerusalem—, the Gaza Strip, and the Golan Heights). However, U.S. officials have noted that since Israel'’s national budget is fungible, proceeds from the issuance of U.S.-guaranteed debt that are used to refinance Israeli government debt free up domestic Israeli funds for other uses.103
139
As of 20192020, Israel has issued $4.1 billion in U.S.-backed bonds.104140 After deducting the amounts mentioned above, Israel might still be authorized to issue up to $3.814 billion in U.S.-backed bonds. However, if the Israeli government sought to issue new U.S.-backed bonds, it is unclear whether the loan guarantees available to Israel might be subject to reduction based on Israel's estimated’s estimated cumulative subsequent expenditures for settlements in the West Bank. Since the original loan guarantee program authorization for Israel in 2003, Congress has extended the program four times.105141 The program is currently authorized through the end of FY2023.
In general, Israel may view U.S. loan guarantees as a "“last resort"” option, which its treasury could use if unguaranteed local and international bond issuances become too expensive. According to one Israeli official in 2012, "“We consider the loan guarantees as preparation for a rainy day.... This is a safety net for war, natural disaster and economic crisis, which allows Israel to maintain economic stability in unstable surroundings."106”142 Israeli officials may believe that although they have not used the loan guarantees in the last 14 years, maintaining the program boosts the country'country’s fiscal standing among international creditors in capital markets.
Table 7. U.S. Loan Guarantees to Israel: FY2003-FY2019
understandings reached between the United States and the Government of Israel regarding the implementation of the loan guarantee program: Provided further, That the President shall submit a report to Congress no later than September 30 of each fiscal year during the pendency of the program specifying the amount calculated under the preceding proviso and that will be deducted from the amount of guarantees authorized to be issued in the next fiscal year.” 138 U.S. State Department, “Boucher cites Concerns over Settlement Building and Security Fence Route,” State Department Press Releases And Documents, November 26, 2003.
139 CRS correspondence with the U.S. Department of the Treasury’s Office of International Affairs, October 2009. 140 This includes $1.6 billion in FY2003; $1.75 billion in FY2004; and $750 million in FY2005. 141 P.L. 108-447, the FY2005 Consolidated Appropriations Act, first extended the authority of the loan guarantees from FY2005 to FY2007. P.L. 109-472, the 2006 Department of State Authorities Act, extended the authority to provide loan guarantees through FY2011. Under that legislation, the loan guarantee program had a stated end of September 30, 2011; however, there was also a “carryover” provision in the statute under which Israel could draw on unused U.S. guarantees until September 30, 2012. In the summer of 2012, Congress passed and the President signed into law P.L. 112-150, the United States-Israel Enhanced Security Cooperation Act of 2012. Section 5(b) of the law extended the loan guarantee authority until September 30, 2015. Section 7034(k)(10) of P.L. 114-113, the FY2016 Consolidated Appropriations Act, further extended the program until September 30, 2019, allowing unused amounts to be carried over into FY2020.
142 “U.S. to Grant Three-year Extension of Loan Guarantees to Israel,” Ha’aretz, January 24, 2012.
Congressional Research Service
33
U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel
Table 7. U.S. Loan Guarantees to Israel: FY2003-FY2020
current dollars in millions
Deductions
Amount
for
Amount
Available for
Settlement
Borrowed by
Israel to
Fiscal Year
Activity
Israel
Borrow
FY2003
289.5
1,600.0
1,110.5
FY2004
—
1,750.0
1,250.0
FY2005
795.8
750.0
1,454.2
FY2006
—
—
3,814.7
FY2007
—
—
3,814.7
FY2008
—
—
3,814.7
FY2009
—
—
3,814.7
FY2010
—
—
3,814.7
FY2011
—
—
3,814.7
FY2012
—
—
3,814.7
FY2013
—
—
3,814.7
FY2014
—
—
3,814.7
FY2015
—
—
3,814.7
FY2016
—
—
3,814.7
FY2017
—
—
3,814.7
FY2018
—
—
3,814.7
FY2019
—
—
3,814.7
FY2020
—
—
3,814.7
current dollars in millions
|
Fiscal Year |
Deductions for Settlement Activity |
Amount Borrowed by Israel |
Amount Available for Israel to Borrow |
|
FY2003 |
289.5 |
1,600.0 |
1,110.5 |
|
FY2004 |
— |
1,750.0 |
1,250.0 |
|
FY2005 |
795.8 |
750.0 |
1,454.2 |
|
FY2006 |
— |
— |
3,814.7 |
|
FY2007 |
— |
— |
3,814.7 |
|
FY2008 |
— |
— |
3,814.7 |
|
FY2009 |
— |
— |
3,814.7 |
|
FY2010 |
— |
— |
3,814.7 |
|
FY2011 |
— |
— |
3,814.7 |
|
FY2012 |
— |
— |
3,814.7 |
|
FY2013 |
— |
— |
3,814.7 |
|
FY2014 |
— |
— |
3,814.7 |
|
FY2015 |
— |
— |
3,814.7 |
|
FY2016 |
— |
— |
3,814.7 |
|
FY2017 |
— |
— |
3,814.7 |
|
FY2018 |
— |
— |
3,814.7 |
|
FY2019 |
— |
— |
3,814.7 |
Source: U.S. Department of the Treasury and U.S. State Department.
Source: U.S. Department of the Treasury and U.S. State Department. Note: For FY2003-FY2005, the U.S. Department of the Treasury authorized Israel to borrow up to $3 billion bil ion per year of the total $9 billionbil ion authorized for the Loan Guarantee program.
American Schools and Hospitals Abroad Program (ASHA)107
143 Through foreign operations appropriations legislation, Congress has funded the ASHA program as part of the overall Development Assistance (DA) appropriation to the United States Agency for International Development (USAID). According to USAID, ASHA is designed to strengthen self-sustaining schools, libraries, and medical centers that best demonstrate American ideals and practices abroad. ASHA has been providing support to institutions in the Middle East since 1957, and a number of universities and hospitals in Israel have been recipients of ASHA grants. In FY2016FY2019 (the most recent year for which data are available), ASHA grant recipients in Israel/West Bank included Shaare Zedek Medical CenterHospital in Jerusalem, St. John Eye Hospital Group,the Feinberg Graduate School of the Weizmann Institute of Science, and the Hadassah Medical OrganizationNazareth Project, Inc. According to USAID, institutions based in Israel have received the most program funding in the Middle East region.
Table 8. ASHA Program Grants from Israel Account,
143 According to USAID, recipients of ASHA grants on behalf of overseas institutions must be private U.S. organizations, headquartered in the United States, and tax-exempt. The U.S. organization must also serve as the founder and/or sponsor of the overseas institution. Schools must be for secondary or higher education and hospital centers must conduct medical education and research outside the United States. Grants are made to U.S. sponsors for the exclusive benefit of institutions abroad. See http://www.usaid.gov/our_work/cross-cutting_programs/asha/.
Congressional Research Service
34
link to page 41 U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel
Table 8. ASHA Program Grants from Israel Account: FY2000-FY2016
Fiscal Year
Amount
FY2000
$2.75 mil ion
FY2001
$2.25 mil ion
FY2002
$2.65 mil ion
FY2003
$3.05 mil ion
FY2004
$3.15 mil ion
FY2005
$2.95 mil ion
FY2006
$3.35 mil ion
FY2007
$2.95 mil ion
FY2008
$3.90 mil ion
FY2009
$3.90 mil ion
FY2010
$3.80 mil ion
FY2011
$4.225 mil ion
FY2012
$3.00 mil ion
FY2013
$3.800 mil ion
FY2014
$3.052 mil ion
FY2015
$3.075 mil ion
FY2016
$3.600 mil ion
FY2017
N/A
FY2018
N/A
FY2019
N/A
Total
$55.452 million
FY2000-FY2016
|
Fiscal Year |
Amount |
|
FY2000 |
$2.75 million |
|
FY2001 |
$2.25 million |
|
FY2002 |
$2.65 million |
|
FY2003 |
$3.05 million |
|
FY2004 |
$3.15 million |
|
FY2005 |
$2.95 million |
|
FY2006 |
$3.35 million |
|
FY2007 |
$2.95 million |
|
FY2008 |
$3.90 million |
|
FY2009 |
$3.90 million |
|
FY2010 |
$3.80 million |
|
FY2011 |
$4.225 million |
|
FY2012 |
$3.00 million |
|
FY2013 |
$3.800 million |
|
FY2014 |
$3.052 million |
|
FY2015 |
$3.075 million |
|
FY2016 |
$3.600 million |
|
Total |
$55.452 million |
Source: USAID.
Source: USAID. U.S.-Israeli Scientific & Business Cooperation
In the early 1970s, Israeli academics and businessmen began looking for ways to expand investment in Israel'’s nascent technology sector. The sector, which would later become the driving force in the country'’s economy, was in need of private capital for research and development at the time. The United States and Israel launched several programs to stimulate Israeli industrial and scientific research, and Congress has on several occasions authorized and appropriated108appropriated144 funds for this purpose to the following organizations:
-
The BIRD Foundation (Israel-U.S. Binational Research & Development
Foundation).
109145 BIRD, which was established in 1977, provides matchmaking 144 With the exception of recent funding for U.S.-Israeli energy cooperation (see “U.S.-Israeli Energy Cooperation” section below), Congress has not appropriated funding for binational foundations since the mid-1980s. At this point, the foundations are able to sustain grant making with interest earned from their respective endowments and fees collected from companies who successfully profited after receiving research support from the foundations. 145 See http://www.birdf.com/default.asp. Congress helped establish BIRD’s endowment with appropriations of $30 million and $15 million in 1977 (P.L. 95-26) and 1985 (P.L. 98-473), respectively. These grants were matched by the Congressional Research Service 35 U.S. Foreign Aid to IsraelBIRD, which was established in 1977, provides matchmakingservices between Israeli and American companies in research and development with the goal of expanding cooperation between U.S. and Israeli private high-tech industries. The mission of the Foundation is"“to stimulate, promote and support joint (nondefense) industrial R&D of mutual benefit to…"” the two countries.110146 Projects are supported in the areas of homeland security, communications, electronics, electro-optics, software, life sciences, and renewable and alternative energy, among others.111147 According to the Foundation,$350$363 million in grants have been awarded toalmosta thousand projects. Awards typically range from $700,000 to $900,000. The award size varies based on total project budget and other considerations. The recipients must provide at least 50% of the total project budget. While support for military projectsareis not a part of the program, several of the completed ventures have yielded products that might be useful in a military setting, including the Aircraft Enhanced Vision System (EVS) camera,"“which is designed to provide day/night improved orientation during taxiing or flying. It allows visual landing in reduced visibility conditions, such as fog, haze, dust, smog etc."” The Foundation also funded the creation of a Through-Wall Location and Sensing System that is portable and"“detects whether people are present behind walls, how many, and where they are situated."112 - ”148
The BSF Foundation (U.S.-Israel Binational Science Foundation).
113149 BSF, which was started in 1972, promotes cooperation in scientific and technological research. Since 2012, BSF has partnered with the National Science Foundation (NSF) to jointly fund collaborative U.S.-Israeli scientific research. In August 2019, Israel'’s Council of Research announced that it would provide $56 million over a five-year period to expand the BSF-NSF program. -
The BARD Foundation (Binational Agriculture and Research and Development
Fund). BARD was created in 1978 and supports U.S.-Israeli cooperation in agricultural research.
114150 In the115th115th Congress, P.L. 115-334,amended the original 1977 authorization of binational agricultural cooperation by adding that BARD should promote research in"“drip irrigation, pesticides, aquaculture, livestock, poultry, disease control, and farm equipment" - ”
In 1995, the United States and Israel established The U.S.-Israel Science and
Technology Foundation (USISTF) to fund and administer projects mandated by the U.S.-Israel Science and Technology Commission (USISTC),
115a bilateral151 a bilateral Israeli government for a total endowment of $90 million. 146 Eitan Ydilevich, “Building U.S.-Israel Economic Partnerships, The BIRD Model,” Washington, DC. June 10, 2010, p. 2. 147 BIRD Foundation, What is BIRD?, available at http://www.birdf.com/Index.asp?CategoryID=22&ArticleID=79. 148 Information from the BIRD Foundation website, http://www.birdf.com. 149 See, http://www.bsf.org.il/Gateway4/. In 1972 and 1984, the United States and Israel contributed a total of $100 million ($50 million each) for BSF’s endowment. The U.S. share ($50 million) first came in 1972 in the form of a $30 million accelerated Israeli repayment of earlier food aid debt to the United States. A second tranche followed in 1984 with $20 million congressional appropriation P.L. 98-473). According to the treaty establishing the Foundation, the Foundation shall use the interest, as well as any funds derived from its activities, for the operations of the Foundation. 150 See http://www.bard-isus.com/. Congress helped establish BARD’s endowment with appropriations of $40 million and $15 million in 1979 (P.L. 95-481) and 1985 (P.L. 98-473), respectively. These grants were matched by the State of Israel for a total endowment of $110 million. In recent years, Congress has provided funds for BARD in annual Agriculture Appropriations legislation at approximately $500,000 a year. 151 The U.S.-Israel Science and Technology Commission (USISTC) was established in 1993 to facilitate cooperative Congressional Research Service 36 U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel entity jointly established by the United States Department of Commerce and the Israel Ministry of Industry, Trade, and Labor in 1994 to foster scientific, technological, and economic cooperation between the two countries.
Since 2007, Congress has repeatedly authorized and appropriated funds for the creation of new U.S.-Israeli cooperative programs in various fields. Most of these new programs fall under the administrative purview of the BIRD Foundation. They include the following:
U.S.-Israeli Energy Cooperation (BIRD Energy)
BIRD Energy is a cooperative program between the U.S. Department of Energy and the Israeli Ministry of Energy designed to further research in renewable energy and energy efficiency. It is nominally part of the BIRD Foundation. Congress authorized the creation of the program in Section 917 of P.L. 110-140, the Renewable Fuels, Consumer Protection, and Energy Efficiency Act of 2007.116152 Although the law did not appropriate any funds for joint research and development, it did establish a grant program to support research, development, and commercialization of renewable energy or energy efficiency. The law also authorized the Secretary of Energy to provide funds for the grant program as needed. Congress authorized the program for seven years from the time of enactment, which was on December 19, 2007. Then, in December 2014, the President signed into law P.L. 113-296, the United States-Israel Strategic Partnership Act of 2014, which reauthorized the U.S.-Israeli Energy Cooperation program for an additional 10 years until September 30, 2024.
Congress and the Administration have provided a total of $1921.7 million for BIRD Energy to date.117153 As of 2019, total combined U.S. and Israeli investment in BIRD Energy for 4041 approved projects stands at $35 million.
stood at $37.69 million. U.S.-Israel Center of Excellence in Energy, Engineering and Water Technology (Energy Center)
In 2018, the U.S. Department of Energy and the Israeli Energy Ministry agreed to establish a new program known as the U.S.-Israel Center of Excellence in Energy, Engineering and Water Technology ("“the Energy Center"”). To date, Congress has appropriated118 $8appropriated154 $12 million for the center, and the Israeli government and private sector partners have matched those funds for initial seed money of $16 million.119 Potential research areas identified by the Energy Center include: energy cybersecurity in critical infrastructure, energy storage, and production and utilization of natural gas. According to the Center, the maximum award for a single consortium is $10 million for a period of five years.120
BIRD Homeland Security (BIRD HLS)
The BIRD Foundation also manages the BIRD Homeland Security Program, a cooperative undertaking between the U.S. Department of Homeland Security (DHS) and the Israel Ministry of Public Security (MOPS) to further joint research of advanced technologies for Homeland Security.121 Currently, DHS's Science and Technology Directorate (S&T) is working together with Israeli counterparts to develop technologies for first responders.122 To date, Congress has provided a total of $7 million in funding for BIRD HLS, of which $4 million was specified in conference report language accompanying FY2018 and FY2019 Homeland Security Appropriation legislation for a "binational cooperative pilot program." The remaining $3 million came in the form of three one-million-dollar Homeland Security Department grants (FY2016-FY2018) for a first responders program.123
Israel Assistance Legislation in the 116th Congress
The following is a select list of bills before Congress concerning U.S. aid to Israel:
S. 1 (H.R. 336) - Strengthening America's Security in the Middle East Act of 2019124 (which passed the Senate in February 2019) would:
- authorize the annual provision of "not less than" $3.3 billion in Foreign Military Financing (FMF) to Israel through FY2028, per the 2016 U.S.-Israel Memorandum of Understanding on Assistance;
- reauthorize both the War Reserves Stock Allies-Israel (WRSA-I) program and Israel's access to $3.8 billion in U.S. loan guarantees through FY2023;
- authorize the President to transfer precision guided munitions from reserve stocks to Israel as necessary for legitimate self-defense; and
- require the President to report to Congress on steps the Administration is taking to include Israel in the list of countries eligible for the 15 C.F.R. 740.20—License Exception Strategic Trade Authorization (STA). Tier 1 of the STA license exception includes 37 countries, who are allowed to receive U.S. high technology and military items without individual export licenses. Israel is currently in Tier 2, which is subject to national security controls.
H.R. 1837 – The United States-Israel Cooperation Enhancement and Regional Security Act (which passed the House in July 2019) would:
- Authorize U.S. FMF for Israel for through FY2024 at the levels set forth for those years in the 2016 U.S.-Israel Memorandum of Understanding on Assistance;
- Extend authorization for WRSA-I and loan guarantees to Israel through FY2025;
- Authorize $55 million in funds for various cooperative programs in the fields of energy, agriculture, water, and homeland security;
- Amend Section 38 of the Arms Export Control Act to authorize the emergency transfer of military equipment to Israel upon a presidential determination that Israel is under an existing or imminent threat of military attack;
- Authorize the transfer from reserve stocks of precision guided munitions to Israel.
S. 1790 – The National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2020 (which passed the Senate in June 2019) would:
- Separately authorize a cooperative program until 2025 to counter unmanned aerial systems apart from the current U.S.-Israel Anti-Tunnel Cooperative Program, not to exceed $25 million annually;
- Authorize $500 million in missile defense funding for Israel.
H.R. 2500 – The National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2020 (which passed the House in July 2019) would:
- Authorize $500 million in missile defense funding for Israel.
H.R. 2740 – Labor, Health and Human Services, Education, Defense, State, Foreign Operations, and Energy and Water Development Appropriations Act, 2020125 (which passed the House in June 2019) would:
- Appropriate $3.3 billion in FMF for Israel in FY2020;
- Appropriate $5 million in MRA grants for refugee resettlement;
- Appropriate $500 million in missile defense funding for Israel.
Author Contact Information
Footnotes
| 1. |
"Changing Demographics: Implications for Israel," Jewish Policy Center, February 28, 2013 and "Israel's Religiously Divided Society," Pew Research Center, March 8, 2016. |
| 2. |
"How Generational Trends could complicate the U.S.-Israeli Relationship," Stratfor, March 27, 2019. |
| 3. |
"U.S. Public Has Favorable View of Israel's People, but is Less Positive Toward Its Government," Pew Research Center, April 24, 2019. |
| 4. |
The issue of what constitutes legitimate criticism of U.S. policy toward Israel and what qualifies as the de-legitimization of Israel or even anti-Semitism has received extensive media coverage in recent years. For example, see "How the Battle over Israel and Anti-Semitism is Fracturing American Politics," New York Times, March 28, 2019. |
| 5. |
Testimony of Howard Kohr, CEO of The American Israel Public Affairs Committee (AIPAC), House Appropriations Committee — Subcommittee on State, Foreign Operations, and Related Programs, March 12, 2019. |
| 6. |
For many years, U.S. economic aid helped subsidize a lackluster Israeli economy, but since the rapid expansion of Israel's high-tech sector and overall economy in the 1990s (sparked partially by U.S.-Israeli scientific cooperation), Israel has been considered a fully industrialized nation. Consequently, Israel and the United States agreed to gradually phase out economic grant aid to Israel. In FY2008, Israel stopped receiving bilateral Economic Support Fund (ESF) grants. It had been a large-scale recipient of grant ESF assistance since 1971. |
| 7. |
The concept of QME (independent of its application to Israel) dates back to the Cold War. In assessing the balance of power in Europe, U.S. war planners would often stress to lawmakers that because countries of the Warsaw Pact had a numerical advantage over U.S. and allied forces stationed in Europe, the United States must maintain a "qualitative edge" in defense systems. For example, see, Written Statement of General William O. Gribble, Jr., Hearings on Research, Development, Test, and Evaluation Program for Fiscal Year 1973, Before Subcommittee No. 1 of Committee on Armed Services, House of Representatives, Ninety-Second Congress, Second Session, February 2, 3, 7, 9, 22, 23, 24, March 6, 7, and 8, 1972. The concept was subsequently applied to Israel in relation to its Arab adversaries. In 1981, then-U.S. Secretary of State Alexander Haig testified before Congress, saying, "A central aspect of US policy since the October 1973 war has been to ensure that Israel maintains a qualitative military edge." Secretary of State Al Haig, Statement for the Record submitted in response to Question from Hon. Clarence Long, House Appropriations Subcommittee on Foreign Operations Appropriations, April 28, 1981. |
| 8. |
See, CRS Report R44716, Conventional Arms Transfers to Developing Nations, 2008-2015, by Catherine A. Theohary. Also, according to the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI), from 2012 to 2016, Israel was the 8th largest arms exporter worldwide, accounting for 3.1% of world deliveries. See, "Trends in International Arms Transfers, 2018," SIPRI Fact Sheet, March 2019. |
| 9. |
Israel Ministry of Defense, Defense Export and Defense Co‐Operation Agency (SIBAT), and Jane's, Navigating the Emerging Markets, Israel, January 10, 2019. Per a 1987 Memorandum of Understanding between the United States and Israel as amended, (Reciprocal Defense Procurement and Acquisition Policy Memorandum of Understanding), Israeli and U.S. defense contractors are able to compete in both countries for contracts on an equal basis. For the text of the MOU, see: https://www.acq.osd.mil/dpap/Docs/mou-israel.pdf. |
| 10. |
William Wunderle and Andre Briere, U.S. Foreign Policy and Israel's Qualitative Military Edge: The Need for a Common Vision, Washington Institute for Near East Policy, Policy Focus #80, January 2008. |
| 11. |
In the 116th Congress, in Section 131 of both House and Senate versions (H.R. 336 and S. 1) of the Strengthening America's Security in the Middle East Act of 2019, the original definition of QME contained in P.L. 110-429 is repeated as a statement of policy, with one addition (denoted in italics): "It is the policy of the United States to ensure that Israel maintains its ability to counter and defeat any credible conventional military, or emerging, threat…" |
| 12. |
Upon signing P.L. 113-296 into law, President Obama issued a signing statement noting: "Sections 11(b) and 12(c)(2) of this bill purport to require me to provide to the Congress certain diplomatic communications and direct the Secretary of State to undertake certain diplomatic initiatives. Consistent with longstanding constitutional practice, my administration will interpret and implement these sections in a manner that does not interfere with my constitutional authority to conduct diplomacy and to protect the confidentiality of diplomatic communications." See Barack Obama: "Statement on Signing the United States-Israel Strategic Partnership Act of 2014," December 19, 2014. Online by Gerhard Peters and John T. Woolley, The American Presidency Project. |
| 13. |
QME reports to Congress are reportedly classified. |
| 14. |
"Trump could let the UAE buy F-35 jets," Defense News, November 4, 2017. |
| 15. |
"To Seal F-35 Deal, UAE Must Agree To Protect Sensitive Information," Aerospace Daily & Defense Report, November 14, 2017. |
| 16. |
"Israeli F-35s: So Good They Spark an Arms Race?" The National Interest, May 8, 2019. A year earlier, the same author wrote: "Israel must retain its regional exclusivity of this platform [F-35] and work to delay the release of fifth- generation fighters to other countries in the region for as long as possible. It appears that it will not be possible to prevent the sale of fifth-generation fighter planes to Arab states forever, but it is certainly possible to delay this development by several years." See, Shimon Arad, "Delaying the Release of Fifth-Generation Fighter Planes to the Arab States," INSS Insight, No. 1029, March 5, 2018. |
| 17. |
See, Joint Statement by President Clinton and Prime Minister Ehud Barak, July 19, 1999. According to the statement, "The United States and Israel will sign a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) which will express their joint intention to restructure U.S. bilateral assistance to Israel. The MOU will state the United States' intention to sustain its annual military assistance to Israel, and incrementally increase its level by one-third over the next decade to a level of $2.4 billion subject to Congressional consultations and approval. At the same time, the MOU will provide for a gradual phase-out of U.S. economic aid to Israel, over a comparable period, as the Israeli economy grows more robust, less dependent on foreign aid, and more integrated in world markets." |
| 18. |
United States-Israel Memorandum of Understanding, Signed by then U.S. Under Secretary of State R. Nicholas Burns and Israeli Ministry of Foreign Affairs Director General Aaron Abramovich, August 16, 2007. |
| 19. |
Memorandum of Understanding between the United States and Israel, September 14, 2016. |
| 20. |
"Israeli UAV Firm agrees deal for Unnamed US Company," Jane's Defence Weekly, July 18, 2017. |
| 21. |
The White House, Office of the Press Secretary, Fact Sheet: Memorandum of Understanding Reached with Israel, September 14, 2016. In the Committee report accompanying H.R. 2839, the Department of State, Foreign Operations, and Related Programs Appropriations Act, 2020, appropriators wrote: "The Committee notes that Israel maintains the flexibility under the MOU to purchase jet fuel from the United States." See, H.Rept. 116-78 - State, Foreign Operations, and Related Programs Appropriations Bill, 2020. |
| 22. |
"Israel-US Aid Accord could Deal Massive Blow to Local Defense Industry, MKs told," Times of Israel, May 22, 2018. |
| 23. |
"Israel Lawmakers hope Trump could ease made-in-USA Rules for Military Aid," Reuters, May 21, 2018. |
| 24. |
The Israeli Ministry of Defense provides funding figures for its domestic defense budget but excludes some procurement spending and spending on civil defense. The estimate referenced above is based on figures published by Jane's Defence Budgets, "Israel," IHS Global Insight, January 30, 2019. |
| 25. |
Only seven other nations spend more on defense as a percentage of GDP: Saudi Arabia, Oman, Algeria, Kuwait, Lebanon, Armenia and Jordan. See Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI), Military expenditure by country as percentage of gross domestic product, 2003-2018, SIPRI Military Expenditure Database, 2019. |
| 26. |
The United States initially began authorizing installment-style sales to Israel to help it rebuild its military capabilities after the 1973 war with Egypt and Syria. Congress appropriated $2.2 billion for Israel in P.L. 93-199, the Emergency Security Assistance Act of 1973. Section 3 of that act stated that "Foreign military sales credits [loans or grants] extended to Israel out of such funds shall be provided on such terms and conditions as the President may determine and without regard to the provisions of the Foreign Military Sales Act as amended." At the time, the Foreign Military Sales Act of 1968 (amended in 1971 and the precursor to the Arms Export Control Act of 1976), capped the annual amount of foreign military sales credit that could be extended to a recipient at no more than $250 million per year. Under the authorities contained in P.L. 93-199, President Nixon, in two separate determinations (April & July 1974), allocated the $2.2 billion to Israel as $1.5 billion in grant military aid, the largest U.S. grant aid package ever for Israel at the time. The remaining $700 million was designated as a military loan. A year and a half later, the Ford Administration reached a new arms sales agreement with Israel providing that, according to the New York Times, "the cost of the new military equipment would be met through the large amount of aid approved by the just-completed session of Congress as well as the aid that will be approved by future Congresses." See, "U.S. Decides to Sell Some Arms to Israel that it had Blocked in the Past," New York Times, October 12, 1976. |
| 27. |
Cash flow financing is defined in Section 25(d) of the Arms Export Control Act and Section 503(a)(3) of the Foreign Assistance Act. |
| 28. |
When government operations are funded by a continuing appropriations resolution, Congress may at times include provisions in such resolutions that would prevent the early transfer of FMF to Israel (presumably until a final year appropriations bill is passed). For example, see Section 109 of P.L. 113-46, the Continuing Appropriations Act, 2014. |
| 29. |
According to the Defense Security Cooperation Agency (DSCA), "Some countries may establish an account with the federal reserve bank (FRB), New York, for their FMS [Foreign Military Sales] deposits. An agreement between the FMS purchaser's defense organization, the purchaser's central bank, FRB New York and DSCA identifies the terms, conditions, and mechanics of the account's operation. Countries receiving FMFP funds must maintain their interest bearing account in the FRB." See, Defense Institute of Security Assistance Management (DISAM), "The Management of Security Cooperation (Green Book)," 34th Edition, April 2015. |
| 30. |
Foreign Credit Reporting System (FCRS), Amounts Due the U.S. Government from Sovereign and Other Foreign Official Obligors as of 12/31/2015, United States Department of the Treasury, Office of International Debt Policy. |
| 31. |
Defense Security Cooperation Agency, Transmittal No. 08-83, Israel - F-35 Joint Strike Fighter Aircraft, September 29, 2008. |
| 32. |
"After F-35 makes Aliyah, it will get new Israeli Identity," Israel Hayom, May 2, 2016. "Adir" is a Hebrew word for "mighty" or "powerful." |
| 33. |
"Israeli F-35 Buy-Back Surpasses $1 Billion," Defense News, February 12, 2017. |
| 34. |
"Elbit to Supply Common Helmet Mounted Displays to the US Army," Israel Defense, May 3, 2019. |
| 35. |
"IAF opens Second F-35 unit. Air force Expected to have 50 'Adir' Fighter Jets by 2024," Jerusalem Post, April 28, 2019. |
| 36. |
"IDF: No decision on Advanced F-15s as yet," Jane's Defence Weekly, November 22, 2018. |
| 37. |
"F-35 Stealth Fighter sees First Combat, in Israeli Operation," BBC News, May 22, 2018 and "Israel - Air Force," Jane's World Air Forces, July 5, 2019. |
| 38. |
Defense Security Cooperation Agency (DSCA), Transmittal No: 19-05, February 12, 2019. |
| 39. |
For open source information on the status of Israeli procurement plans regarding key aircraft platforms such as F-15IA, V-22 Osprey, and KC-46A, see "Israel - Air Force," Jane's World Air Forces, July 5, 2019. |
| 40. |
To access DSCA's Excess Defense Articles database, see http://www.dsca.mil/programs/eda. |
| 41. |
On November 4, 1986, President Reagan signed into law P.L. 99-661, the National Defense Authorization Act for FY1987. In Section 1105 of that act, Congress called for greater defense cooperation between the United States and countries that the Secretary of Defense could designate as a "major non-NATO ally" (MNNA). Such cooperation could entail U.S. funding for joint research and development and production of U.S. defense equipment. In February 1987, the United States granted Israel MNNA status along with several other countries (Egypt, Japan, South Korea, and Australia). According to press reports at the time, in the absence of a U.S.-Israeli mutual defense agreement, supporters of Israel had been advocating for Israel to receive "equal treatment" with regard to certain special military benefits (such as the ability to bid on U.S. defense contracts) that NATO allies received from the United States. See, "Israel seeks to obtain the kind of Financial Aid that NATO Members get from U.S. Government," Wall Street Journal, February 3, 1987. Nearly a decade later, Congress passed additional legislation that further solidified Israel's MNNA status. In 1996, Section 147 of P.L. 104-164 amended the Foreign Assistance Act of 1961 by requiring the President to notify Congress 30 days before designating a country as a MNNA. According to the act, Israel, along with several other countries, "shall be deemed to have been so designated by the President as of the effective date of this section, and the President is not required to notify the Congress of such designation of those countries." See, 22 U.S.C. §2321j. |
| 42. |
Excess Defense Articles Database Tool, Defense Security Cooperation Agency. |
| 43. |
For background on mortar, rocket, and missile threats to Israel, see CRS Report R44017, Iran's Foreign and Defense Policies, by Kenneth Katzman, CRS Report R41514, Hamas: Background and Issues for Congress, by Jim Zanotti, and "Missiles and Rockets of Hezbollah," Missile Threat, Center for Strategic and International Studies, June 26, 2018. |
| 44. |
David Tal, "Symbol Not Substance? Israel's Campaign to Acquire Hawk Missiles, 1960-1962," The International History Review, Vol. 22, No. 2 (Jun., 2000), pp. 304-317. |
| 45. |
Each battery has three launchers loaded with up to 20 Tamir interceptors per launcher for a total of 60 interceptors per battery. See, https://www.raytheon.com/capabilities/products/irondome. |
| 46. |
"With high-tech warships, Navy readies to guard gas fields from Hezbollah, Hamas," Times of Israel, February 5, 2018. |
| 47. |
One assessment concludes that Iron Dome's initial performance in 2012 was less effective than Israel claims, but subsequent improvements made Iron Dome perform far better. See, "As Missiles Fly, a Look at Israel's Iron Dome Interceptor," The Conversation, April 15, 2018. |
| 48. |
"Israel says Iron Dome scores 90 Percent Rocket Interception Rate," Reuters, July 10, 2014. |
| 49. |
"IDF Reports Good Iron Dome Performance," Jane's Defence Weekly, May 9, 2019. |
| 50. |
Open Source Center, "Hamas Military Wing says it 'outsmarted' Israel's Iron Dome during Deadly Gaza Flare-Up," London Al-Araby al-Jadeed (in English), Document ID# IMW2019051085676724, May 7, 2019. |
| 51. |
"Assessing the Damage," Jerusalem Post, May 10, 2019. |
| 52. |
"700 rockets, 240 intercepts, 4 dead Israelis: Is the Iron Dome getting Worse?" Jewish Telegraphic Agency (JTA), May 7, 2019. |
| 53. |
In conference report language accompanying P.L. 112-239, the National Defense Authorization Act for FY2013, conferees agreed: "The Department of Defense needs to obtain appropriate data rights to Iron Dome technology to ensure us the ability to use that data for U.S. defense purposes and to explore potential co-production opportunities. The conferees support this policy and expect the Department to keep the congressional defense committees informed of developments and progress on this issue." |
| 54. |
In 2018, some Members of Congress advocated for the selection of Iron Dome to protect U.S. troops deployed abroad against threats emanating from Russia and North Korea. See, "Bipartisan House Letter requests Iron Dome Use for US Army, Jewish Telegraphic Agency, April 24, 2018. |
| 55. |
"US Army Buys Israel's Iron Dome for Tactical Missile Defense," Jewish Policy Center, January 22, 2019. |
| 56. |
The co-production agreement is formally titled, "'Agreement Between the Department of Defense of the United States of America and the Ministry of Defense of the State of Israel Concerning Iron Dome Defense System Procurement.'' |
| 57. |
The FY2014 Emergency Supplemental Appropriations Resolution, P.L. 113-145, exempted $225 million in Iron Dome funding—requested by Israel on an expedited basis during the summer 2014 Israel-Gaza conflict—from the co-production requirements agreed upon in March 2014. |
| 58. |
See, "Inside The Iron Dome," Moment Magazine, July 17, 2018. |
| 59. |
"Inside Iron Dome's Secret Manufacturing Plant," Globes (Israel Business News), October 7, 2018. |
| 60. |
This joint agreement is a Research, Development, Test and Evaluation (RDT&E) Framework agreement between the United States and Israel. The joint program to implement the agreement is known as the Short Range Ballistic Missile Defense (SRBMD) David's Sling Weapon System (DSWS) Project. The Department of Defense/U.S.-Israeli Cooperative Program Office manages the SRBMD/DSWS program, which is equitably funded between the United States and Israel. |
| 61. |
"IDF officially declares David's Sling Operational," Jane's Defence Weekly, April 3, 2017. |
| 62. |
See, "Israel, US Complete Successful Advanced David's Sling Missile Tests," Jerusalem Post, March 20, 2019, and "David's Sling has Dubious Debut against Syrian Missiles, Jane's Defence Weekly, July 25, 2018. |
| 63. |
Shortly after the start of the Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI) in 1985, the Reagan Administration sought allied political support through various cooperative technology agreements on ballistic missile defense (BMD). A memorandum of understanding was signed with Israel on May 6, 1986, to jointly develop an indigenous Israeli capability to defend against ballistic missiles. Subsequently, a number of additional agreements were signed, including, for example, an April 1989 Memorandum of Agreement (MOA) to develop an Israeli computer facility as part of the Arrow BMD program, a June 1991 agreement to develop a second generation Arrow BMD capability, and a September 2008 agreement to develop a short-range BMD system to defend against very short-range missiles and rockets. Israeli interest in BMD was strengthened by the missile war between Iran and Iraq in the later 1980s, and the experience of being attacked by Scud missiles from Iraq during Operation Desert Storm in 1991. |
| 64. |
The United States and Israel also jointly conduct a military exercise known as Juniper Falcon, which is designed to enhance interoperability between both nations' militaries. In March 2019, the U.S. European Command (EUCOM) deployed a Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD) system to Israel to practice "operational procedures for augmenting Israel's existing air and missile defense architecture." See, USEUCOM deploys Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD) system to Israel," United States European Command, March 4, 2019. |
| 65. |
The United States and Israel signed the Arrow 3 co-production agreement in June 2019. |
| 66. |
"U.S.- Israel Strategic Link: Both Sides Take Stock," New York Times, October 2, 1981. |
| 67. |
In October 1989, the United States and Israel agreed to pre-position $100 million worth of dual-use defense equipment in Israel. |
| 68. |
At present, the United States and Israel have a bilateral agreement that governs the storage, maintenance, in-country transit, and other WRSA-related costs. The government of Israel, using both its national funds and FMF, pays for the construction, maintenance and refurbishment costs of WRSA ammunition storage facilities. It also pays for the packaging, crating, handling and transportation of armaments to and from the stockpile. In any future expedited procedure, reserve stocks managed by EUCOM could be transferred to Israel; then, U.S. officials would create an-after-the-fact Foreign Military Sale to account for the transferred equipment. |
| 69. |
"US may give Israel Iraq Ammo," Jerusalem Post, February 11, 2010. |
| 70. |
"Best Friends Don't Have to Ask," Politico Magazine, August 14, 2014. |
| 71. |
"U.S. Defends Supplying Israel Ammunition during Gaza Conflict," Reuters, July 31, 2014. |
| 72. |
The authorization extension states that "Section 12001(d) of the Department of Defense Appropriations Act, 2005 (P.L. 109-108–287; 118 Stat. 1011) is amended by striking '2018' and inserting '2019.'" |
| 73. |
Defense Institute of Security Assistance Management (DISAM), DISAM's Online Greenbook, Chapter 2, Security Legislation and Policy. |
| 74. |
Dr. Louis J. Samelson, "Military Assistance Legislation for Fiscal Year 1990, The DISAM Journal, Winter, 1989/1990. |
| 75. |
This increase for each fiscal year is based on legislative language contained in Section 12002 of P.L. 108-287, the Department of Defense Appropriations Act, 2005. |
| 76. |
"Israel's Underground War—Technology and Specialist Troops deployed in face of Subterranean Threat," Wall Street Journal, March 2, 2016. |
| 77. |
"Israeli Official bets Advances in Anti-Tunnel Technology will secure Gaza Border," Washington Post, March 6, 2018. |
| 78. |
See, CRS In Focus IF11197, U.S. Arms Sales and Human Rights: Legislative Basis and Frequently Asked Questions, by Paul K. Kerr and Liana W. Rosen. |
| 79. |
U.S. State Department, Treaties in Force, Agreement relating to mutual defense assistance, Entered into force July 23, 1952; TIAS 2675. |
| 80. |
Nevertheless, in 22 U.S.C. 2753, the AECA also states that the consent of the President shall not be required for the transfer by a foreign country or international organization of defense articles sold by the United States if the recipient is the government of a member country of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization, the Government of Australia, the Government of Japan, the Government of the Republic of Korea, the Government of Israel, or the Government of New Zealand. |
| 81. |
For example, see (among other sections), Section 502B, Human Rights (22 U.S.C. 2304), Section 505, Conditions of Eligibility (22 U.S.C. §2314), and Section 511, Considerations in Furnishing Military Assistance (22 U.S.C. §2321d). |
| 82. |
"U.S. Says Israel May Have Violated Agreement on Cluster Bomb Use," Reuters, January 29, 2007. |
| 83. |
For background on the Leahy Law, see CRS Report R43361, "Leahy Law" Human Rights Provisions and Security Assistance: Issue Overview, coordinated by Nina M. Serafino. |
| 84. |
For the latest report on Israel, Golan Heights, West Bank, and Gaza, including information on Israeli military law and detention of Palestinian prisoners (adults and minors), see: https://www.state.gov/reports/2018-country-reports-on-human-rights-practices/israel-golan-heights-west-bank-and-gaza/. |
| 85. |
The letter's text is available at http://www.politico.com/f/?id=00000153-c56c-d662-a75b-cfecc6be0000. |
| 86. |
See the text of then Assistant Secretary of State for Legislative Affairs Julia Frifield's April 18, 2016, response letter to Representative Henry C. Johnson at http://www.politico.com/f/?id=00000154-7c2f-d905-a357-7c7f04750000. |
| 87. |
This stipulation is found in grant agreements between the U.S. State Department's Bureau of Population, Refugees, and Migration (PRM) and United Israel Appeal (clause 8. F. 2 – Use in Territories Subject to the Administration of the State of Israel Prior to June 1967). The FY2013 agreement (S-PRMCO-13-GR-1041 – March 13, 2013) is for $15 million. CRS Correspondence with U.S. State Department, March 2014. |
| 88. |
http://www.bsf.org.il/BSFPublic/DefaultPage1.aspx?PageId=221&innerTextID=221. |
| 89. |
See, U.S. State Department, Third Party Transfer Process and Documentation, Bureau of Political-Military Affairs, December 17, 2018. |
| 90. |
See, Defense Institute of Security Cooperation Studies, "The Management of Security Cooperation (Green Book)," Edition 39, January 2019. |
| 91. |
"Croatia cancels F-16 Deal with Israel due to U.S. Objections," Axios, January 10, 2019. |
| 92. |
See, "The Evolving Israel-China Relationship," RAND Corporation, 2019. |
| 93. |
In 2000, Representative Sonny Callahan of Alabama, then Chairman of the Foreign Operations Subcommittee of the House Appropriations Committee, told a hearing on April 6, 2000, that he would block $250 million in FY2001 military assistance to Israel unless Israel cancelled the PHALCON sale to China. Representative Callahan offered an amendment during a June 20 subcommittee markup to withhold $250 million from the $2.88 billion in total economic and military assistance proposed for Israel for FY2001, but the amendment failed by a vote of nine to six. See, "Israel-China Radar Deal Opposed," Washington Post, April 7, 2000 and "U.S. Congressman: We'll Block Israeli Aid Unless China Deal Cancelled," Jerusalem Post, April 7, 2000. |
| 94. |
"Israel, U.S. Draft Agreement for Openness, Equality in Arms Deals," Ha'aretz, June 27, 2005. |
| 95. |
"China Tech Push in Israel Stirs Security Fears," Wall Street Journal, February 12, 2019. |
| 96. |
"Israel and China Take a Leap Forward—but to Where?" Mosaic, November 5, 2018. |
| 97. |
Hiddai Segev, Doron Ella, and Assaf Orion, "My Way or the Huawei? The United States-China Race for 5G Dominance," Institute for National Security Studies Insight No. 1193, July 15, 2019. |
| 98. |
"U.S. Navy may Stop Docking in Haifa after Chinese Take Over Port," Jerusalem Post, December 15, 2018. |
| 99. |
The MRA account is authorized as part of the State Department's institutional budget, with funds for the account appropriated through the foreign operations appropriations bill. |
| 100. |
|
| 101. |
According to P.L. 108-11, "[Loan] guarantees may be issued under this section only to support activities in the geographic areas which were subject to the administration of the Government of Israel before June 5, 1967: Provided further, That the amount of guarantees that may be issued shall be reduced by an amount equal to the amount extended or estimated to have been extended by the Government of Israel during the period from March 1, 2003, to the date of issue of the guarantee, for activities which the President determines are inconsistent with the objectives and understandings reached between the United States and the Government of Israel regarding the implementation of the loan guarantee program: Provided further, That the President shall submit a report to Congress no later than September 30 of each fiscal year during the pendency of the program specifying the amount calculated under the preceding proviso and that will be deducted from the amount of guarantees authorized to be issued in the next fiscal year." |
| 102. |
U.S. State Department, "Boucher cites Concerns over Settlement Building and Security Fence Route," State Department Press Releases And Documents, November 26, 2003. |
| 103. |
CRS correspondence with the U.S. Department of the Treasury's Office of International Affairs, October 2009. |
| 104. |
This includes $1.6 billion in FY2003; $1.75 billion in FY2004; and $750 million in FY2005. |
| 105. |
P.L. 108-447, the FY2005 Consolidated Appropriations Act, first extended the authority of the loan guarantees from FY2005 to FY2007. P.L. 109-472, the 2006 Department of State Authorities Act, extended the authority to provide loan guarantees through FY2011. Under that legislation, the loan guarantee program had a stated end of September 30, 2011; however, there was also a "carryover" provision in the statute under which Israel could draw on unused U.S. guarantees until September 30, 2012. In the summer of 2012, Congress passed and the President signed into law P.L. 112-150, the United States-Israel Enhanced Security Cooperation Act of 2012. Section 5(b) of the law extended the loan guarantee authority until September 30, 2015. Section 7034(k)(10) of P.L. 114-113, the FY2016 Consolidated Appropriations Act, further extended the program until September 30, 2019, allowing unused amounts to be carried over into FY2020. |
| 106. |
"U.S. to Grant Three-year Extension of Loan Guarantees to Israel," Ha'aretz, January 24, 2012. |
| 107. |
|
| 108. |
With the exception of recent funding for U.S.-Israeli energy cooperation (see "U.S.-Israeli Energy Cooperation" section below), Congress has not appropriated funding for binational foundations since the mid-1980s. At this point, the foundations are able to sustain grant making with interest earned from their respective endowments and fees collected from companies who successfully profited after receiving research support from the foundations. |
| 109. |
See http://www.birdf.com/default.asp. Congress helped establish BIRD's endowment with appropriations of $30 million and $15 million in 1977 and 1985, respectively. These grants were matched by the Israeli government for a total endowment of $90 million. |
| 110. |
Eitan Ydilevich, "Building U.S.-Israel Economic Partnerships, The BIRD Model," Washington, DC. June 10, 2010, p. 2. |
| 111. |
BIRD Foundation, What is BIRD?, available at http://www.birdf.com/Index.asp?CategoryID=22&ArticleID=79. |
| 112. |
Information from the BIRD Foundation website, http://www.birdf.com. |
| 113. |
|
| 114. |
|
| 115. |
The U.S.-Israel Science and Technology Commission (USISTC) was established in 1993 to facilitate cooperative ventures between high tech industries in the two countries. The goal of the program is to "to maximize the contribution of technology to economic growth." While the collaborative work may be somewhat similar to that supported by the BIRD Foundation, "the Science and Technology Commission assists in the commercialization of new technologies with longer lead times to market. These projects involve higher risk and require substantial capital commitments." The ventures are funded and administered by the U.S.-Israel Science and Technology Foundation. The U.S. and Israeli governments each committed $15 million to the effort over three years for a total of $30 million. |
| 116. |
Congress first considered authorizing a program to expand U.S.-Israeli scientific cooperation in the field of renewable energy in legislation entitled, The United States-Israel Energy Cooperation Act (H.R. 1838 – 110th Congress). |
| 117. |
Congress specifies funds for BIRD Energy in conference report language accompanying energy and water appropriations legislation. For FY2019, see P.L. 115-244, the Energy and Water, Legislative Branch, and Military Construction and Veterans Affairs Appropriations Act, 2019 - "Within International Affairs, the agreement includes $2,000,000 for the Israel Binational Industrial Research and Development (BIRD)." |
| 118. |
P.L. 115-141, the FY2018 Consolidated Appropriations Act, provided $4 million for the establishment of a U.S.-Israel Center of Excellence in energy and water technologies. P.L. 115-244, the Energy and Water, Legislative Branch, and Military Construction and Veterans Affairs Appropriations Act, 2019, provided an additional $4 million in funding. |
| 119. |
The U.S.-Israel Strategic Partnership Act (P.L. 113-296) authorized the President to promote cooperative programs with Israel in the fields of energy, water, agriculture, and alternative fuel technologies. P.L. 114-322, the WIIN Act (Water Infrastructure Improvements for the Nation Act), called on the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy to develop a coordinated strategic plan that, among other things, strengthened "research and development cooperation with international partners, such as the State of Israel, in the area of desalination technology." |
| 120. |
U.S. Department of Energy, "DOE, Israel's Ministry of Energy, and Israel Innovation Authority Announce Call for Proposals for the U.S.-Israel Energy Center," April 30, 2019. |
| 121. |
The U.S.-Israel Strategic Partnership Act (P.L. 113-296) authorized the Secretary of Homeland Security, acting through the Director of the Homeland Security Advanced Research Projects Agency and with the concurrence of the Secretary of State, to enter into cooperative research pilot programs with Israel to enhance Israel's capabilities in border, maritime, and aviation security, explosives detection, and emergency services. In 2016, Congress passed P.L. 114-304, the United States-Israel Advanced Research Partnership Act of 2016, a law that permanently authorized the expansion of BIRD HLS to include cybersecurity technologies. |
| 122. |
U.S. Department of Homeland Security, "Snapshot: Israel & U.S.: A Unique Partnership in Science, Technology and Business," January 23, 2018. |
| 123. |
CRS correspondence with BIRD Foundation, July 2019. |
| 124. |
For additional background on S. 1, see CRS Insight IN11014, Strengthening America's Security in the Middle East Act of 2019 (S.1): An Overview, by Jeremy M. Sharp, Jim Zanotti, and Christopher M. Blanchard. |
| 125. |
This bill includes H.R. 2839, the Department of State, Foreign Operations, and Related Programs Appropriations Act, 2020. |