Older Americans Act: Overview and Funding
Changes from July 16, 2018 to November 14, 2018
This page shows textual changes in the document between the two versions indicated in the dates above. Textual matter removed in the later version is indicated with red strikethrough and textual matter added in the later version is indicated with blue.
Older Americans Act: Overview and Funding
Contents
- Introduction
- Older Americans Act: Current Law
- Title I. Declaration of Objectives; Definitions
- Title II. Administration on Aging
- Aging and Disability Resource Centers
- Senior Medicare Patrol Program
- Title III. Grants for State and Community Programs on Aging
- Title IV. Activities for Health, Independence, and Longevity
- Title V. Community Service Senior Opportunities Act
- Title VI. Grants for Services for Native Americans
- Title VII. Vulnerable Elder Rights Protection Activities
FY2018FY2019 Appropriations Overview- OAA Funding History
Figures
Tables
Introduction
The Older Americans Act (OAA) supports a wide range of social services and programs for individuals aged 60 years or older. These include supportive services, congregate nutrition services (i.e., meals served at group sites such as senior centers, community centers, schools, churches, or senior housing complexes), home-delivered nutrition services, family caregiver support, community service employment, the Long-Term Care Ombudsman Program, and services to prevent the abuse, neglect, and exploitation of older persons. Except for Title V, Community Service Employment for Older Americans (CSEOA), all programs are administered by the Administration on Aging (AOA) in the Administration for Community Living (ACL) within the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Title V is administered by the Department of Labor's (DOL's) Employment and Training Administration.
The OAA has been reauthorized and amended numerous times since it was first enacted in 1965. In the 114th Congress, both the House and the Senate considered bipartisan legislation that would reauthorize the OAA for a three-year period. On April 19, 2016, President Barack Obama signed P.L. 114-144 (S. 192), the Older Americans Act Reauthorization Act of 2016. P.L. 114-144 authorizes appropriations for OAA programs for FY2017 to FY2019.1 Prior to enactment of P.L. 114-144, the Older Americans Act Reauthorization of 2016, the last OAA reauthorization occurred in 2006, when the Older Americans Act Amendments of 2006 (P.L. 109-365) was enacted, extending the act's authorizations of appropriations through FY2011. Authorizations of appropriations for most OAA programs expired on September 30, 2011; however, OAA-authorized activities continued to receive funding for FY2012 through FY2016.
The following provides an overview of the Older Americans Act. It briefly describes the act's titles, highlighting selected provisions followed by FY2018FY2019 appropriations and a funding history.
Older Americans Act: Current Law
The OAA statutory language contains seven titles, which are summarized in this section, highlighting selected activities. Funding for most OAA programs is provided in annual HHS appropriations; OAA Title V is part of annual DOL appropriations. The next section provides information on FY2017FY2019 appropriations and the act's funding history.2 Appendix A provides detailed OAA program budget authority for FY2009FY2010 through FY2018FY2019.
Title I. Declaration of Objectives; Definitions
Title I of the OAA sets out broad social policy objectives oriented toward improving the lives of all older Americans, including adequate income in retirement, the best possible physical and mental health, opportunity for employment, and comprehensive long-term care services, among other things. Also, Title I provides definitions for various terms under the act. Title I does not authorize appropriations.
Title II. Administration on Aging
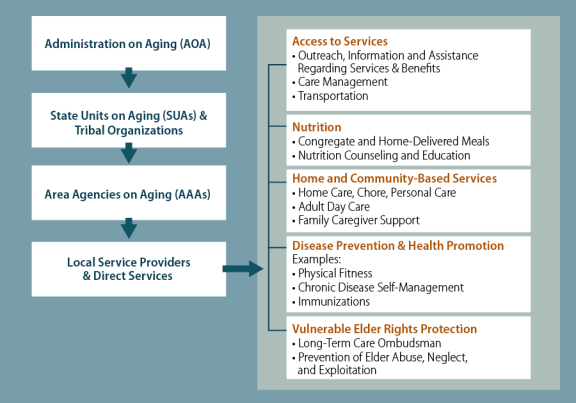
Title II establishes the Administration on Aging (AOA) as the chief federal agency advocating for older persons and sets out the responsibilities of AOA and the Assistant Secretary for Aging. The Assistant Secretary is appointed by the President with the advice and consent of the Senate. Title II also establishes State Units on Aging (SUAs), who serve as the state agency primarily responsible for planning and policy development as well as administration of OAA activities. In addition, the act authorizes the Assistant Secretary to make grants to eligible tribal organizations for social and nutrition services to older Native Americans.
Title II also establishes Area Agencies on Aging (AAAs), which operate within a planning and service area (PSA) designated by the SUA. AAAs serve as local entities who, either directly or through contract with local service providers (LSPs), oversee a comprehensive and coordinated service system for the delivery of social, nutrition, and long-term services and supports to older individuals. AAAs are required to be public or private nonprofit organizations. According to 2015 research on program structure and administrationa 2016 survey of AAAs across the country, the majority of AAAs were public organizations (6255% public versus 3839% private nonprofit, and 5% other).3 Collectively, these 56 SUAs, 629622 AAAs and 246over 250 tribal and Native Hawaiian organizations, and almost 20,000tens of thousands of aging and social service providers in local communities comprise the Aging Network (see Figure 1).4 With respect to the distribution of federal funding, AOA allocates federal funds authorized under OAA statutory funding formulas to SUAs and tribal organizations. SUAs, in turn, award these funds to AAAs based on an intrastate funding formula developed in accordance with AOA guidelines and approved by the Assistant Secretary.
Discretionary funding authorized under Title II goes toward program administration and Aging and Disability Resource Centers (ADRCs), described in greater detail below, as well as other authorized activities that support the Aging Network and Elder Rights activities (see textbox entitled "OAA Title II: Aging Network and Elder Rights Support Activities"). Program administration funding for all Administration for Community Living (ACL) programs, which includes those authorized by the OAA, is funded at $41.1 million in FY2018FY2019.
 |
|
Source: Prepared by the Congressional Research Service. |
Aging and Disability Resource Centers
The aim of Aging and Disability Resource Centers (ADRCs) is to create "one-stop shop" single entry points for information about the range of public and private long-term services and supports (LTSS) available to consumers. ADRCs may provide options counseling regarding public and private LTSS, and provide access to public programs such as Medicaid and Department of Veterans Affairs programs. ADRCs may also provide discharge planning and care transition services to help individuals remain in their own homes after a hospitalization, rehabilitation, or skilled nursing facility visit. There are over 500 ADRC sites nationwide, operating in 50 states, two territories, and the District of Columbia.5 Discretionary funding to ADRCs is $8.1 million in FY2018FY2019.6
Senior Medicare Patrol Program
Also authorized under Titles II and IV (Sections 201, 201, and 411) of the OAA is the Senior Medicare Patrol (SMP) Program, which funds projects that educate older Americans and their families to recognize and report Medicare and Medicaid fraud. Beginning in FY2016, discretionary funding under ACL's budget authority is no longer provided for SMP. Instead, FY2016, FY2017, and FY2018 appropriations language fully fundappropriations language since FY2016 has funded SMP activities under discretionary appropriations from the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) Health Care Fraud and Abuse Control (HCFAC) account. This account distributes funding to various antifraud activities from the Medicare Trust Fund at the joint discretion of the HHS Secretary and Attorney General, and distributes certain discretionary appropriations at the discretion of Congress. Total SMP funding for the program was $17.6 million in FY2015, $18.0 million in FY2016, and $18.0 million in FY2017.7 The Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2018 (P.L. 115-1417 The Department of Defense and Labor, Health and Human Services, and Education Appropriations Act, 2019, and Continuing Appropriations Act, 2019 (P.L. 115-245), instructs the HHS Secretary to provide not less than $17.6 million from HCFAC to SMP in FY2018.8
|
OAA Title II: Aging Network and Elder Rights Support Activities The following OAA programs and activities receive discretionary funding under OAA Title II: Aging Network Support Activities
).Elder Rights Support Activities
Source: Personal communication with G. Steven Hagy, director, ACL Office of Budget and Finance, Note: ACL reported combined program funding for the National Eldercare Locator and civic engagement under National Eldercare Locator and Engagement; however, civic engagement activities are authorized under OAA Title IV, Section 417, and included under Title II activities for simplicity. |
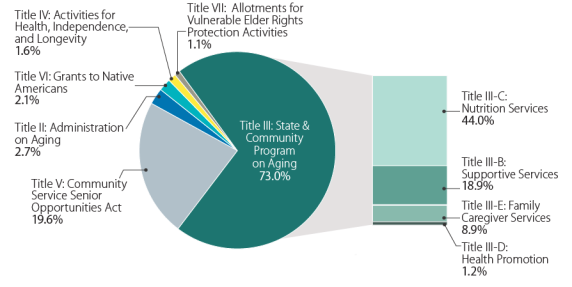
Title III. Grants for State and Community Programs on Aging
Title III authorizes grants to 56 SUAs and 629 AAAs to act as advocates on behalf of, and to coordinate programs for, older persons. Title III accounts for 73.072.9% of the OAA's total FY2018FY2019 funding ($1.487498 billion out of $2.038055 billion). States receive separate allotments of funds based on a statutory funding formula for supportive services and centers, family caregiver support, congregate nutrition, home-delivered nutrition, the nutrition services incentive grant program, and disease prevention and health promotion services.9 The OAA allows states some flexibility to transfer funds among Title III programs. For example, in FY2015, the most recent year for which data are available, states collectively transferred a net total of $97.4 million from congregate nutrition to either supportive services or home-delivered nutrition.10
Title III services are available to all persons aged 60 and older, but are targeted at those with the greatest economic or social need, particularly low-income and minority persons, older individuals with limited English proficiency, and older persons residing in rural areas. Means testing is prohibited. Participants are encouraged to make voluntary contributions for services they receive. States are allowed to implement cost-sharing policies for certain services based on a sliding-scale fee, but older persons must not be denied services due to failure to make cost-sharing payments. State, local, and private funding sources also supplement federal OAA funds for these services.
In FY20162016, the most recent year for which data are available, 11.3 million older persons were served by Title III programs.11 Title III services included the provision of 145.2 million home-delivered meals; 79.2 million congregate meals; 23.7 million rides to medical appointments, grocery stores, and other activities; 40.7 million hours of personal care, homemaker, and chore services; and 10.6 million hours of adult day care/adult day health services in FY20162016.12
Title IV. Activities for Health, Independence, and Longevity
Title IV of the OAA authorizes the Assistant Secretary for Aging to award funds for training, research, and demonstration projects in the field of aging. Over the years, Title IV has supported a wide range of research and demonstration projects, including those related to income, health, housing, retirement, and long-term services and supports, as well as projects on career preparation and continuing education for personnel in the field of aging. Title IV activities receive $3237.0 million in discretionary funding for FY2018FY2019. Funding provided under Title IV goes toward various activities that are designed to support health, independence, and longevity of older individuals (see textbox entitled "OAA Title IV: Activities for Health, Independence, and Longevity").13 FY2018 appropriations language accepted ACL's proposal to consolidate the funding of four Alzheimer's programs into one single program, entitled the Alzheimer's Disease Program. Total funding is $23.5 million for FY2018, of which $8.8 is discretionary budget authority included in this report another $14.7 is mandatory funding from the Prevention and Public Health Fund (PPHF). The four programs to be consolidated are (1) Alzheimer's Disease Initiative – Specialized Supportive Services, (2) the Alzheimer's Disease Initiative – Communications Campaign, (3) Alzheimer's Disease Supportive Services, and (4) the National Alzheimer's Call Center.14
|
OAA Title IV: Activities for Health, Independence, and Longevity The following OAA programs and activities receive discretionary funding under Title IV authorities: Aging Network Support Activities
FY2019 funding is $5.0 million).
The FY2018 explanatory statement Source: Personal communication with G. Steven Hagy, director, ACL Office of Budget and Finance, Note: |
Title V. Community Service Senior Opportunities Act
Title V, Community Service Senior Opportunities Act, also known as Community Service Employment for Older Americans (CSEOA) or the Senior Community Service Employment Program (SCSEP), has as its purpose the promotion of useful part-time opportunities in community service activities for unemployed low-income1516 persons who are 55 years or older and who have poor employment prospects. The Title V program is administered by DOL's Employment and Training Administration; it is the only OAA program not administered by HHS under ACL. For FY2018FY2019, Title V represents 19.65% of OAA discretionary funding ($400.0 million out of $2.038055 billion). DOL allocates Title V funds for grants based on a statutory funding formula to state agencies in all 50 states, the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. territories, and to national organizations. There is a 10% nonfederal match requirement for Title V grant activities.
SCSEP participants are placed in part-time positions working in a variety of community service activities, such as day care centers, senior centers, schools, and hospitals.1617 Participants work part-time and receive on-the-job experience and skills. The program operates on a program year (PY) basis from July 1 through June 30.1718 For PY2016 (ending June 30, 2017), the CSEOA program supported 44,678 job slots, serving 60,002 participants.1819 In FY2017, CSEOA had a cost of $7,339 per participant.1920 Enrollees are paid no less than the highest of the federal minimum wage, the state or local minimum wage, or the prevailing wage paid by the same employer for similar public occupations. In addition to wages, enrollees receive training, physical examinations, personal and job-related counseling, transportation for employment purposes (under certain circumstances), and placement assistance into unsubsidized jobs.
The OAA Reauthorization Act of 2016 made certain changes to SCSEP core performance indicators to more closely align such indicators to those of WIOA. The act required the Secretary of Labor to implement the new indicators by December 31, 2017. DOL published an Interim Final Rule (IFR) on December 1, 2017, and began collecting data.2021 The data on these new indicators will continue to be collected in PY2018 and be used as baseline data to establish targets for future years, subject to continued appropriations.21
Title VI. Grants for Services for Native Americans
Title VI authorizes funds for supportive and nutrition services to older Native Americans. Funds are awarded directly by ACL to Indian tribal organizations, Native Alaskan organizations, and nonprofit groups representing Native Hawaiians. To be eligible for funding, a tribal organization must represent at least 50 Native Americans aged 60 and older. In FY2017, grants were awarded to 270 tribal organizations representing 400 Indian tribes and villages, including one organization serving Native Hawaiian elders.2224 The program provides services such as transportation, home-delivered and congregate nutrition services, information and referral, and a wide range of home care services. Title VI also authorizes caregiver support services to Native American elders. Respite, caregiver training, information and outreach, counseling, and support groups are among the services provided. For FY2018FY2019, these programs receive $42.844.3 million ($3334.2 million for supportive and nutrition services, and $9.610.1 million for Native American family caregivers).
Title VII. Vulnerable Elder Rights Protection Activities
Title VII authorizes the Long-Term Care (LTC) Ombudsman Program as well as Elder Abuse, Neglect, and Exploitation Prevention Programs. For FY2018FY2019, these programs are funded at a total of $21.7 million.2325 The majority of Title VII funding ($16.9 million, or 78%, in FY2018FY2019) is directed at the LTC Ombudsman Program, which investigates and resolves complaints of residents in nursing facilities, board and care facilities, and other adult care homes. In FY2016, ombudsmen handled more than 199,000 resident complaints and provided almost 520,000 consultations to individuals and long-term care facilities.24
FY2018FY2019 Appropriations Overview
The Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2018,(P.L. 115-141)Department of Defense and Labor, Health and Human Services, and Education Appropriations Act, 2019 and Continuing Appropriations Act, 2019 (P.L. 115-245), provided discretionary appropriations for OAA programs, projects, and activities under ACL's Aging and Disability Services Programs budget authority and the Department of Labor budget authority at an estimated total of $2.038055 billion for FY2019, which is $150.217.1 million (8.00.8%) more than FY2017FY2018 levels.2527 Figure 2 shows the distribution of FY2018FY2019 OAA discretionary amounts by title, with program-level detail for Title III State and Community Programs on Aging. Title III programs received the largest proportion of OAA funding, with 73.072.9% of funding appropriated to nutrition, supportive services, family caregivers, and health promotion activities. About one-fifth of OAA funding (19.65%) is allocated to Title V, the CSEOA Program. The remaining funds are allocated to AOA-administered activities under Titles II (2.76%) and IV (1.68%), grants to Native Americans under Title VI (2.12%), and vulnerable elder rights protection activities under Title VII (1.1%).
Several OAA programs saw increases in funding for FY2018FY2019 compared with FY2017FY2018-enacted levels. Title III programs received an additional $30.0 million for the National Family Caregiver Support Program, $34.9 million for supportive services and senior centers, $40.0 million in additional funding for congregate nutrition services, and $19.0 million in additional funding for home-delivered nutrition services. Title VI grants to Native Americans received an additional $4.0 million for supportive and nutrition and caregiver services. Under Title IV, Elder Rights Support Activities received an additional $2.0 million for Elder Justice and Adult Protective Services program activities.
Title V, the CSEOA program, saw no change in funding compared to the FY2017FY2018 level of $400.0 million.
OAA Funding History
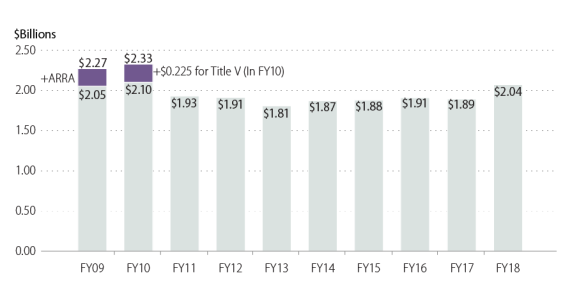
AnnualOverall, annual OAA discretionary funding has declined over the 10-year period from FY2009 to FY2018FY2010 to FY2019 (not adjusted for inflation). Since FY2010, total OAA funding levels have remained below the FY2010 level when discretionary funding was at its highest level (see Figure 3). OAA funding increased from $2.27 billion in FY2009 to $2.328 billion in FY2010. Additional funding was provided in FY2009 under the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act (ARRA; P.L. 111-5amount of $2.328 billion (see Figure 3). For FY2010, a one-time special appropriation fundedprovided additional funding to the CSEOA Program to serve low-income seniors affected by the recession.
Total discretionary funding for OAA programs declined in FY2011 through FY2013, with FY2013 funding of $1.807 billion falling below the FY2007 level of $1.855 (not shown). Most of the 5.5% reduction from FY2012 to FY2013 is attributable to sequestration.2628
For FY2014 through FY2016, total OAA funding increased slightly each year from the FY2013 level, which was the lowest level of OAA funding over the 10-year period. FY2017 saw a slight funding decrease, with total OAA funding at 1.4% less than FY2016; most of the decrease is due to a 7.9% reduction to Title V CSEOA funding in FY2017. ForIn FY2018, total OAA funding increased by $150.2 million, or 8.0%, which is the largest increase in funding over the same 10-year period. For FY2019, total OAA funding increased by $17.1 million, or 0.8%. (Amounts in this discussion are not adjusted for inflation.) For programs and activities funded by OAA title over this time period, see Appendix A.
|
Figure 3. Total Discretionary Funding for Older Americans Act Programs, ($ billions) |
 |
|
Source: Prepared by CRS based on appropriations legislation, committee reports, explanatory statements, and agency operating plans. Amounts are nominal dollars (not adjusted for inflation). Note: |
Appendix A.
Older Americans Act Programs: FY2009-FY2018FY2010-FY2019 Funding
Table A-1 shows the discretionary budget authority history for OAA programs for FY2009FY2010 through FY2018FY2019. Amounts are not adjusted for inflation. The table includes several nonadd lines—in italicized font with funding amounts in parentheses—for specific programs within a larger budget account (i.e., Nutrition Services).
Amounts shown in Table A-1 also account for the following:
- Across-the-board reductions though rescissions and the discretionary spending sequestration in FY2013. These include the following:
- FY2011 amounts reflect the 0.2% across-the-board rescission required by §1119.
- The FY2012 Consolidated Appropriations Act (P.L. 112-74), Division F, §527, applied a 0.189% across-the-board rescission to most Labor-HHS-Education accounts, including OAA accounts.
- FY2013 amounts reflect sequestration pursuant to the Budget Control Act of 2011 (P.L. 112-25) and the American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012 (ATRA; P.L. 112-240) and the across-the-board rescission of 0.2% required by the Consolidated and Further Continuing Appropriations Act, 2013 (P.L. 113-6, §3004), and transfers.
- For FY2011, funding for OAA programs was provided through full-year continuing appropriations. This gave the agency some flexibility in allocating funds across programs for these years. To the extent feasible, CRS determined the amounts in these years for each program based on agency budget documents and operating plans.
- For FY2009, budgetary figures include budget authority from both the FY2009 Omnibus Appropriations Act (P.L. 111-8) and the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act (ARRA, P.L. 111-5). OAA Programs received $220 million in total from ARRA as follows:
- $120 million for OAA Title V, CSEOA,
- $65 million for congregate meals,
- $32 million for home-delivered meals, and
$3 million for Native Americans supportive and nutrition services.
Table A-1. Discretionary Budget Authority for the Older Americans Act (OAA) Programs: FY2009-FY2018
($ in millions)
|
OAA Programs |
FY2009 | FY2010a |
FY2011 |
FY2012 |
FY2013 |
FY2014b |
FY2015 |
FY2016 |
FY2017 |
FY2018 |
FY2019 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Title II: Administration on Aging |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Program administration |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Aging network support activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Senior Medicare Patrol |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Aging and Disability Resource Centers |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Elder rights support activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Title III: Grants for State and Community Programs on Aging |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Supportive services and centers |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Family caregivers |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Disease prevention/health promotion |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Nutrition services |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Congregate meals (nonadd) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Home-delivered meals (nonadd) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Nutrition services incentive grants (nonadd) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Title IV: Activities for Health, Independence, and Longevity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Program Innovations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Elder rights support activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Aging network support activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Alzheimer's Disease Program |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Title V: Community Service Senior Opportunities Act |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Title VI: Grants to Native Americans |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Supportive and nutrition services |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Native American caregivers |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Title VII: Allotments for Vulnerable Elder Rights Protection Activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Long-term care ombudsman program |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Elder abuse prevention |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
TOTAL Older Americans Act Programs |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Source: FY2009 to FY2018FY2019 Labor-Health and Human Services (HHS)-Education Appropriations acts and accompanying report and explanatory statement language available at the CRS appropriations status table; various HHS, Administration on Aging (AOA), Administration for Community Living (ACL), and Department of Labor (DOL) budget documents, including budget justifications (FY2013 and FY2017), and operating plans for FY2010 through FY2013; personal communication with G. Steven Hagy, director, AOA/ACL Office of Budget and Finance, 2011 to 2018, and personal communication with Michael Bernier, HHS Budget Office, 2012.
Notes:
a. FY2010 amounts reflect both appropriations and transferred funds, including the HHS Secretary's transfer of $224,298 from AOA to assist states with AIDS Drug Assistance Programs (ADAP). This was part of $25 million that the Secretary reallocated and transferred in total from various HHS agencies to assist state ADAP programs with wait lists and cost containment.
b. FY2014 numbers reflect appropriated amounts before transfers. Per P.L. 113-76, Division H, Title II §206, the Administration had limited authority to transfer funds among HHS accounts. Under this authority, $3.857 million was transferred out of OAA programs: $3.466 million from the Nutrition Services Incentives Program; $233,000 from ACL Program Administration; $55,000 from Aging network support activities; $52,000 from ADRCs; $29,000 from Elder Rights Support Activities; and $22,000 from Senior Medicare Patrol. (Personal communication with G. Steven Hagy, Director, Office of Budget and Finance, ACL, April 2, 2015).
c. Starting with FY2014, amounts reflect program administration costs for aging and disability services programs administered by ACL, not just aging services programs administered by AOA as in prior years. Prior to FY2014, amounts reflected under program administration included AOA administration of most OAA programs and several programs under non-OAA authorities (e.g., Public Health Service Act [PHSA] and the Medicare Improvements for Patients and Providers Act [MIPPA]).
d. The Omnibus Appropriations Act, 2009 (P.L. 111-8) provided $28.0 million for the Choices for Independence Initiative under Title II Aging network support activities. Choices for Independence was subsequently renamed "Health and Long-Term Care Programs" in the Obama Administration's FY2010 budget request.
e. Several activities that were previously included under Aging network support activities are listed under separate line items starting in FY2011. These activities include the Senior Medicare Patrol Program, ADRCs, and the National Center on Elder Abuse and the National Long-Term Care Ombudsman Resource Center (both under Elder rights support activities). Starting in FY2011, Title II Aging network support activities include only the National Eldercare Locator and the Pension Counseling and Information Program.
fe. Starting in FY2014, Budget documents provide funds for the National Eldercare Locator (authorized under Title II) and Multigenerational Civic Engagement (authorized under Title IV) together under a new "National Eldercare Locator and Engagement" line item. For simplicity, this table includes this funding under Title II Aging network support activities.
gf. Starting in FY2016, Budget documents provide funds for the Resource Center on Women and Retirement Planning (authorized under Title IV) and the Pension Counseling and Information Program (authorized under Title II) together under a new "Pension Counseling and Retirement Information" line item. For simplicity, this table includes this funding under Title II Aging network support activities.
hg. Prior to FY2011, Title II funds to Senior Medicare Patrol and ADRCs were included in the total for Aging network support activities. In addition to discretionary funding, the Senior Medicare Patrol Program receives mandatory Health Care Fraud and Abuse Control (HCFAC) account funds under the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS). In addition to ADRC discretionary funding under Title II, §2405 of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA, P.L. 111-148, as amended) provided mandatory appropriations for ADRCs of $10.0 million for each year from FY2010 to FY2014.
ih. In FY2016, the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2016 (P.L. 114-113), changed the source of discretionary funding for the Senior Medicare Patrol program from that funded under ACL appropriations to CMS HCFAC appropriations. The Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2017 (P.L. 115-31), andthe Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2018 (P.L. 115-141), continued this practice. The FY2016 and FY2017 appropriations laws did not specify a specific amount for these activities. The FY2018 appropriations law requires and the Department of Defense and Labor, Health and Human Services, and Education Appropriations Act, 2019 and Continuing Appropriations Act, 2019 (P.L. 115-245), continued this practice. The FY2016 and FY2017 appropriations laws did not specify a specific amount for these activities. The FY2018 appropriations law required the HHS Secretary to provide not less than $17.621 million from HCFAC for the Senior Medicare Patrol program. The FY2019 appropriations law also required the HHS Secretary to provide not less than $17.621 million from HCFAC for the Senior Medicare Patrol program.
ji. Elder rights support activities include the National Center on Elder Abuse and the National Long-Term Care Ombudsman Resource Center (both authorized under Title II), and Model Approaches to Statewide Legal Assistance and National Legal Assistance and Support Projects (both authorized under Title IV). Prior to FY2011, funding for these programs was included in totals for Aging network support activities and Program Innovations.
kj. Funding for Native American family caregiving is shown in Title VI.
lk. Starting in FY2015, Elder rights support activities also include Elder Justice/Adult Protective Services (APS) funding. For simplicity, this table counts funding for Elder Justice/APS under Title IV elder rights support activities; however, these funds may also be used for activities authorized under OAA Section 751 and the Elder Justice Act (§2042(a) of the Social Security Act).
ml. Title IV Aging network support activities include the National Alzheimer's Call Center; the National Education and Resource Center on Women and Retirement Planning; National Resource Centers on Native Americans; National Minority Aging Organizations and National Technical Assistance Resource Center; Multigenerational Civic Engagement; and Program Performance and Technical Assistance. In AOA budget documents prior to FY2012, funding for these programs was provided under Program Innovations. (In this report, for comparability, the FY2011-FY2013 columns reflect the categorizations in FY2012 and FY2013 appropriations documents.)
nm. Starting in FY2015, Title IV Aging network support activities also includes Holocaust Survivors Assistance.
on. The Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2018 (P.L. 115-141), streamlined ACL's four Alzheimer's disease programs (Alzheimer's Disease Supportive Services, Alzheimer's Disease Initiative—Specialized Supportive Services, Alzheimer's Disease Initiative—Communications, and the National Alzheimer's Call Center previously funded under Aging Network Support Activities) into a single Alzheimer's Disease Program. For FY2018, in addition to $8.8 million in discretionary funds, the Alzheimer's Disease Program also received $14.7 million in mandatory funds from the Prevention and Public Health Fund (PPHF).
po. The FY2010 Title V funding level included $225 million that, according to the DOL, "was intended as a one-time provision related to current economic conditions. The additional funding was provided as a short-term program expansion to support temporary job opportunities for low-income elderly individuals while the nation recovers from the economic downturn." DOL, FY2011 Congressional Budget Justification, Employment and Training Administration, Community Service Employment for Older Americans (CSEOA), p. CSEOA-2.
Appendix B. Older Americans Act: Authorizations of Appropriations
Table B-1 provides authorizations of appropriations under the Older Americans Act, as amended by P.L. 114-144. Authorizations of appropriations are shown by OAA title and program or activity (Titles II through VII). No authorizations of appropriations are under Title I of the act.
Authorizations of appropriations for each fiscal year (FY2017 through FY2019) have been summed to show a total amount for each year (bottom of Table B-1). However, this total amount includes only those OAA authorizations of appropriations with a discrete amount specified in statute, which applies to almost all authorizations of appropriations. The one exception is under OAA Title VII, Subtitle B, Native American Organization and Elder Justice Provisions. OAA Section 751 authorizes to be appropriated "such sums as may be necessary" for Native American elder rights program and grants for state elder justice systems.
Table B-1 shows the authorizations of appropriations by OAA title and program or activity (first column). The second column describes any amendments or changes to statutory language under P.L. 114-144. The last three columns show the authorizations of appropriations amounts for each program or activity for FY2017, FY2018, and FY2019 with a total amount summed below for each fiscal year.
Table B-1. Authorizations of Appropriations for Older Americans Act (OAA) Programs
(as amended by P.L. 114-144)
|
Change to OAA |
Authorizations of Appropriations |
|||
|
For FY2017 |
For FY2018 |
For FY2019 |
||
|
Title II, Administration on Aging (AOA) |
||||
|
Administration, Salaries, and Expenses of AOA |
Amends §216(a) to authorize to be appropriated |
$40,063,000 |
$40,063,000 |
$40,063,000 |
|
Eldercare Locator |
Strikes §216(b) and replaces with §216(b)(1)-(4); in §216(b)(1), relating to the National Eldercare Locator Services, authorizes to be appropriated |
$2,088,758 |
$2,132,440 |
$2,176,121 |
|
Pension Counseling and Information Program |
Strikes §216(c) and replaces with §216(b)(2), relating to Pension Counseling and Information Programs, it authorizes to be appropriated |
$1,904,275 |
$1,944,099 |
$1,983,922 |
|
Elder Rights Support Activities (Title II) |
Adds a new §216(b)(3); it authorizes to be appropriated |
$1,312,904 |
$1,340,361 |
$1,367,817 |
|
Aging and Disability Resource Centers |
Adds a new §216(b)(4); it authorizes to be appropriated |
$6,271,399 |
$6,402,551 |
$6,533,703 |
|
Title III, State and Community Programs on Aging |
||||
|
Supportive Services and Centers |
Amends §303(a) to authorize to be appropriated |
$356,717,276 |
$364,456,847 |
$372,196,069 |
|
Congregate Nutrition Services |
Amends §303(b)(1) to authorize to be appropriated |
$459,937,586 |
$469,916,692 |
$479,895,348 |
|
Home-Delivered Nutrition Services |
Amends §303(b)(2) to authorize to be appropriated |
$232,195,942 |
$237,233,817 |
$242,271,465 |
|
Disease Prevention and Health Promotion |
Amends §303(d) to authorize to be appropriated |
$20,361,334 |
$20,803,107 |
$21,244,860 |
|
Family Caregiver Support |
Amends §303(e) to authorize to be appropriated |
$154,336,482 |
$157,564,066 |
$160,791,658 |
|
Nutrition Services Incentive Program |
Amends §311(e) to authorize to be appropriated |
$164,055,664 |
$167,486,502 |
$170,917,349 |
|
Title IV, Activities for Health, Independence, and Longevity |
||||
|
Aging Network Support Activities |
Amends §411(b) to authorize to be appropriated for aging network support activities |
$6,216,054 |
$6,346,048 |
$6,476,043 |
|
Elder Rights Support Activities (Title IV) |
Amends §411(b) to authorize to be appropriated for elder rights support activities |
$10,856,828 |
$11,083,873 |
$11,310,919 |
|
Title V, Community Service Senior Opportunities Act |
||||
|
Community Service Employment for Older Americans |
Amends §517(a) to authorize to be appropriated |
$445,189,405 |
$454,499,494 |
$463,809,605 |
|
Title VI, Grants for Native Americans |
||||
|
Indian and Native Hawaiian Programs |
Amends §643(1) to authorize to be appropriated |
$31,934,018 |
$32,601,843 |
$33,269,670 |
|
Native American Caregiver Support Program |
Amends §643(2) to authorize to be appropriated |
$7,718,566 |
$7,879,982 |
$8,041,398 |
|
Title VII, Vulnerable Elder Rights Protection Activities |
||||
|
Subtitle A—State Programs |
||||
|
Long-Term Care Ombudsman Program (Chapter 2) |
Amends §702(a) to authorize to be appropriated |
$16,280,630 |
$16,621,101 |
$16,961,573 |
|
Elder Abuse, Neglect, and Exploitation Prevention Program (Chapter 3) and Legal Assistance Development Program (Chapter 4) |
Amends §702(b) to authorize to be appropriated to carry out Chapters 3 and 4 |
$4,891,876 |
$4,994,178 |
$5,096,480 |
|
Subtitle B—Native American Organization and Elder Justice Provisions |
||||
|
Native American Elder Rights Program and Grants for State Elder Justice Systems |
No change to current law; §751(d) authorizes to be appropriated such sums as may be necessary (SSAN) for FY2007 and subsequent fiscal years |
SSAN |
SSAN |
SSAN |
|
Total Authorization of Appropriationsa |
$1,962,331,997 |
$2,003,370,001 |
$2,044,407,000 |
|
Sources: The Older Americans Act, as amended by The Older Americans Act Reauthorization Act of 2016 (P.L. 114-144).
Notes:
a. The "Total Authorization of Appropriations" do not include an amount for OAA §751(d) under Subtitle B, Native American Organizations and Elder Justice Provisions.
Author Contact Information
Acknowledgments
Mariam Ghavalyan, CRS research assistant, provided assistance in updating this report.
Footnotes
| 1. |
For more information on the OAA 2016 reauthorization see CRS Report R44485, Older Americans Act: 2016 Reauthorization. |
|
| 2. |
The funding amounts described in this report are in budget authority. |
|
| 3. |
|
|
| 4. |
|
|
| 5. |
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Administration for Community Living, Administration on Aging, FY2015 Report to Congress: Older Americans Act, January 12, 2017, p. 7, https://www.acl.gov/sites/default/files/about-acl/2017-03/FY15OAAReportCongress_2017-1-24.docx. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Administration for Community Living, Administration on Aging, Aging and Disability Resource Centers in a No Wrong Door System, https://www.acl.gov/sites/default/files/news%202017-03/ADRC_NWD2014.pdf. ADRCs may be located through the Eldercare Locator directory http://www.eldercare.gov. |
|
| 6. |
Beginning in FY2009, Congress provided mandatory funding under the Medicare Improvements for Patients and Providers Act (MIPPA, P.L. 110-275; 42 U.S.C. 1395b-3 note) for Medicare enrollment assistance to Aging Disability Resource Centers (ADRCs), as well as Area Agencies on Aging (AAAs), State Health Insurance and Assistance Programs (SHIPs), and the National Center for Benefits Outreach and Enrollment. ADRCs received $5 million in mandatory funding for |
|
| 7. |
|
|
| 8. |
P.L. 115- |
|
| 9. |
State allotments for Title III programs are listed at HHS, ACL, State and Tribal Funding Allocations, https://www.acl.gov/node/124. |
|
| 10. |
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Administration for Community Living, Administration on Aging, FY2015 Report to Congress: Older Americans Act, pp. 17-18, https://www.acl.gov/sites/default/files/about-acl/2017-03/FY15OAAReportCongress_2017-1-24.docx. |
|
| 11. |
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Administration for Community Living, AGing Integrated Database (AGID), State Program Reports, Data at a Glance, https://agid.acl.gov/DataGlance/SPR/. |
|
| 12. |
Ibid. |
|
| 13. |
Title IV Section 411 also authorizes Falls Prevention activities. Funding for these activities for FY2018 were provided under mandatory funding for the Prevention and Public Health Fund. "Explanatory Statement Submitted by Mr. Frelinghuysen, Chairman of the House Committee on Appropriations, Regarding the House Amendment to the Senate Amendments on H.R. 1625," Congressional Record, vol. 164, no. 50, Book III (March 22, 2018), pp. H2705 and H2748. |
|
| 14. |
The Alzheimer's Disease Initiative Programs are authorized under OAA Section 411 and Section 4002 of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act; funding for these programs is provided from the PPHF. The Alzheimer's Disease Supportive Services Program is authorized under Section 398 of the Public Health Services Act and prior year funding was provided under the Alzheimer's Disease Supportive Services Program line-item appropriation. The National Alzheimer's Call Center is authorized under OAA Section 411 and prior year funding was provided under OAA Title IV Aging Network Support Activities. |
|
| 15. |
The description of Care Corps is based on H.Rept. 115-862, pp. 110-111; H.Rept. 115-952, p. 540.
|
|
|
U.S. Department of Labor, Senior Community Service Employment Program, http://www.doleta.gov/Seniors/. |
||
|
Program Year 2018 allotments were announced in a series of letters and change documents available at U.S. Department of Labor, Training and Employment Guidance Letter No. 17-17, https://wdr.doleta.gov/directives/corr_doc.cfm?docn=8825. Per OAA Section 517(b), CSEOA is forward funded; for example, dollars appropriated in FY2018 (October 1, 2017 to September 30, 2018) are used for PY2018 (July 1, 2018 to June 30, 2019). |
||
|
There are more participants than job slots in a given program year; as participants leave the program, their job slots can be filled by new participants. Personal communication with Bryon Anderson, Senior Advisor, Office of Congressional and Intergovernmental Affairs, U.S. Department of Labor, July 12, 2018. Department of Labor Employment and Training Administration, State Statutory Formula Funding, Community Service Employment for Older Americans, Dollars Tables, PY 2016, https://www.doleta.gov/budget/statfund.cfm. |
||
|
U.S. Department of Labor, Fiscal Year 2019 Congressional Budget Justification, Employment and Training Administration, Community Service Employment for Older Americans, p. CSEOA-13, https://www.dol.gov/sites/dolgov/files/legacy-files/budget/2019/CBJ-2019-V1-05.pdf. |
||
|
Department of Labor, "Senior Community Service Employment Program; Performance Accountability," 82 Federal Register 56869, December 1, 2017. |
||
|
U.S. Department of Labor, Fiscal Year 2019 Congressional Budget Justification, Employment and Training Administration, Community Service Employment for Older Americans, p. CSEOA-13. |
||
|
|
24.
Department of Labor, "Senior Community Service Employment Program; Performance Accountability," 83 Federal Register 36407, July 30, 2018. |
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Administration for Community Living, Fiscal Year |
|
State allocation tables are at ACL, State and Tribal Funding Allocations, https://www.acl.gov/node/124. |
||
|
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Administration for Community Living, Fiscal Year 2019 Justification of Estimates for Appropriations Committees, pp. 123-124. |
||
|
Program Administration funding reflects administration costs for ACL-administered programs authorized under OAA as well as the Developmental Disabilities Assistance and Bill of Rights Act (DD Act), the Help America Vote Act (HAVA), the Assistive Technology (AT) Act, the Rehabilitation Act, the Public Health Services Act (PHSA), the Elder Justice Act (EJA), and the Medicare Improvements for Patients and Providers Act (MIPPA). (U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Administration for Community Living, Fiscal Year 2019 Justification of Estimates for Appropriations Committees, p. 251.) In addition, the Falls Prevention Program and Alzheimer's Disease Program, both authorized under OAA Title IV, receive mandatory funding under the Public Health Prevention Fund (PPHF). The Senior Medicare Patrol Program also receives mandatory HCFAC account funding. These mandatory amounts are not reflected in the estimated OAA total. |
||
|
The Budget Control Act of 2011 (BCA; P.L. 112-25) tasked a Joint Select Committee on Deficit Reduction with developing a deficit reduction plan for Congress and the President to enact by January 15, 2012. The failure of Congress and the President to enact deficit reduction legislation by that date triggered an automatic spending reduction process that included sequestration. This sequestration affected OAA programs through a 5% reduction in nonexempt nondefense discretionary funding in FY2013. In addition, the Consolidated and Further Continuing Appropriations Act, 2013 (P.L. 113-6), which generally funded discretionary HHS and Department of Labor (DOL) programs for FY2013 at their FY2012 levels, also included an across-the-board rescission of 0.2% per Section 3004. |