Federal Funding Gaps: A Brief Overview
Changes from September 13, 2017 to March 26, 2018
This page shows textual changes in the document between the two versions indicated in the dates above. Textual matter removed in the later version is indicated with red strikethrough and textual matter added in the later version is indicated with blue.
Contents
Summary
The Antideficiency Act (31 U.S.C. 1341-1342, 1511-1519) generally bars the obligation of funds in the absence of appropriations. Exceptions are made under the act, including for activities involving "the safety of human life or the protection of property." The interval during the fiscal year when appropriations for a particular project or activity are not enacted into law, either in the form of a regular appropriations act or a continuing resolution (CR), is referred to as a funding gap. Although funding gaps may occur at the start of the fiscal year, they may also occur any time a CR expires and another CR (or the regular appropriations bill) is not enacted immediately thereafter. Multiple funding gaps may occur within a fiscal year.
When a funding gap occurs, federal agencies are generally required to begin a shutdown of the affected projects and activities, which includes the prompt furlough of non-excepted personnel. The general practice of the federal government after the shutdown has ended has been to retroactively pay furloughed employees for the time they missed, as well as employees who were required to come to work.
Although a shutdown may be the result of a funding gap, the two events should be distinguished. This is because a funding gap may result in a total shutdown of all affected projects or activities in some instances but not others. For example, when funding gaps are of a short duration, agencies may not have enough time to complete a shutdown of affected projects and activities before funding is restored. In addition, the Office of Management and Budget has previously indicated that a shutdown of agency operations within the first day of the funding gap may be postponed if a resolution appears to be imminent.
Since FY1977, 1819 funding gaps occurred, ranging in duration from one1 day to 21 full days. These funding gaps are listed in Table 1. About half of these funding gaps were brief (i.e., three days or less in duration). Notably, many of the funding gaps that occurred during this period do not appear to have resulted in a "shutdown." Prior to the issuance of the opinions in 1980 and early 1981 by then -Attorney General Benjamin Civiletti, while agencies tended to curtail some operations in response to a funding gap, they often "continued to operate during periods of expired funding." In addition, some of the funding gaps after the Civiletti opinions did not result in a completion of shutdown operations due to both the funding gap's short duration and an expectation that appropriations would soon be enacted. Some of the funding gaps during this period, however, did have a broader impact on affected government operations, even if only for a matter of hours.
Two of the three most recent funding gaps occurred in FY1996, which amounted to fiveamounting to 5 days and 21 days. The chronology of regular and continuing appropriations enacted during FY1996 is illustrated in Figure 1.
The most recent funding gap occurred during FY2018, when a CR covering all of the regular appropriations bills expired on January 19, 2018. It concluded on January 22, 2018, after lasting two days.The most recent funding gap commenced atAt the beginning of FY2014, on (October 1, 2013), none of the regular appropriations bills had been enacted, so a government-wide funding gap occurred. It concluded on October 17, 2013, after lasting 16 days.
, and concluded on October 17, 2013, for a total of 16 days.
For a general discussion of federal government shutdowns, see CRS Report RL34680, Shutdown of the Federal Government: Causes, Processes, and Effects, coordinated by [author name scrubbed].
Background
The routine activities of most federal agencies are funded annually by one or more of the regular appropriations acts. When action on the regular appropriations acts is delayed, a continuing appropriations act, also sometimes referred to as a continuing resolution or CR, may be used to provide interim budget authority.1
Since FY1952, all of the regular appropriations acts have been enacted by the beginning of the fiscal year in only four instances (FY1977, FY1989, FY1995, and FY1997). No, and CRs were enactednot needed for interim funding in only for three of these fiscal years, but. CRs were enacted for FY1977 to fund certain unauthorized programs whose funding had been dropped from the regular appropriations acts.2 Further, no CRs were enacted for FY1953, even though all but one of the regular appropriations was enacted after the start of the fiscal year.3
The Antideficiency Act (31 U.S.C. 1341-1342, 1511-1519) generally bars the obligation or expenditure of federal funds in the absence of appropriations.4 Exceptions under the act include activities involving "the safety of human life or the protection of property."5 The interval during the fiscal year when appropriations for a particular project or activity are not enacted into law, either in the form of a regular appropriations act or a CR, is referred to as a funding gap.6 Although funding gaps may occur at the start of the fiscal year, they may also occur any time a CR expires and another CR (or the relevant regular appropriations bill) is not enacted immediately thereafter. Multiple funding gaps may occur within a fiscal year.
In 1980 and early 1981, then -Attorney General Benjamin Civiletti issued opinions clarifying the need for the federal government to begin terminating regular activities upon the occurrence of a funding gap.7 As a consequence of these more strict guidelines, when a funding gap occurs, executive agencies begin a shutdown of the affected projects and activities, which includes the prompt furlough of non-excepted personnel. The general practice of the federal government after the shutdown has ended has been to retroactively pay furloughed employees for the time they missed, as well as employees who were required to come to work.8
Under current practice, although a shutdown may be the result of a funding gap, the two events should be distinguished. This is because a funding gap may result in a shutdown of all affected projects or activities in some instances but not in others. For example, when a funding gap is of a short duration, agencies may not have enough time to complete a shutdown of affected projects and activities before funding is restored. In addition, the Office of Management and Budget has previously indicated that a shutdown of agency operations within the first day of a funding gap may be postponed if it appears that an additional CR or regular appropriations act is likely to be enacted that same day.9
To avoid funding gaps, proposals have previously been offered to establish an "automatic continuing resolution" (ACR) that would provide a fallback source of funding authority for activities, at a specified formula or level, in the event that timely enactment of appropriations is disrupted. The funding would become available automatically and remain available as long as needed so that a funding gap would not occur. Although the House and Senate have considered ACR proposals in the past, none has been enacted into law on a permanent basis.
Funding Gaps Since FY1977
As illustrated in Table 1, there have been 1819 funding gaps since FY1977.10 The enactment of a CR on the day after the budget authority in the previous CR expired, which has occurred often, is not counted in this report as involving a funding gap. For example, between FY2000-FY2013 and FY2018, "next-day" CRs were enacted 18 timeson 21 occasions.
Almost all of the funding gaps occurred between FY1977 and FY1995. During this 19-fiscal-year periodperiod of 19 fiscal years, 15 funding gaps occurred.
Multiple funding gaps occurred during a single fiscal year in four instances: (1) three gaps covering a total of 28 days in FY1978, (2) two gaps covering a total of four4 days in FY1983, (3) two gaps covering a total of three3 days in FY1985, and (4) two gaps covering a total of 26 days in FY1996.
Seven of the funding gaps commenced with the beginning of the fiscal year on October 1. The remaining 11 funding gaps occurred at least more than one day after the fiscal year had begun. Ten of the funding gaps ended in October, four ended in November, three ended in December, and one ended in January.
Funding gaps have ranged in duration from one1 to 21 full days. Six of the eight lengthiest funding gaps, lasting between eight8 days and 17 days, occurred between FY1977 and FY1980—before the Civiletti opinions were issued in 1980 and early 1981. After the issuance of these opinions, the duration of funding gaps in general shortened considerably, typically ranging from one day to three days. Of these, most occurred over a weekend.
|
Fiscal Year |
Final Date of Budget Authoritya |
Full Day(s) of |
Date Gap Terminatedc |
|
1977 |
Thursday, 09/30/76 |
10 |
Monday, 10/11/76 |
|
1978 |
Friday, 09/30/77 |
12 |
Thursday, 10/13/77 |
|
Monday, 10/31/77 |
8 |
Wednesday, 11/09/77 |
|
|
Wednesday, 11/30/77 |
8 |
Friday, 12/09/77 |
|
|
1979 |
Saturday, 09/30/78 |
17 |
Wednesday, 10/18/78 |
|
1980 |
Sunday, 09/30/79 |
11 |
Friday, 10/12/79 |
|
1982 |
Friday, 11/20/81 |
2 |
Monday, 11/23/81 |
|
1983 |
Thursday, 09/30/82 |
1 |
Saturday, 10/02/82 |
|
Friday, 12/17/82 |
3 |
Tuesday, 12/21/82 |
|
|
1984 |
Thursday, 11/10/83 |
3 |
Monday, 11/14/83 |
|
1985 |
Sunday, 09/30/84 |
2 |
Wednesday, 10/03/84 |
|
Wednesday, 10/03/84 |
1 |
Friday, 10/05/84 |
|
|
1987 |
Thursday, 10/16/86 |
1 |
Saturday, 10/18/86 |
|
1988 |
Friday, 12/18/87 |
1 |
Sunday, 12/20/87 |
|
1991 |
Friday, 10/05/90 |
3 |
Tuesday, 10/09/90 |
|
1996 |
Monday, 11/13/95 |
5 |
Sunday, 11/19/95 |
|
Friday, 12/15/95 |
21 |
Saturday, 01/06/96 |
|
|
2014 |
Monday, 09/30/13 |
16 |
Thursday, 10/17/13 |
|
2018 |
Friday, 01/19/18 |
2 |
Monday, 1/22/18 |
Source: Compiled by CRS with data from the Legislative Information System of the U.S. Congress.
Notes:
a.
Budget authority expired at the end of the date indicated. For example, for the first FY1996 funding gap, budget authority expired at the end of the day on Monday, November 13, 1995, and the funding gap of five full days commenced on Tuesday, November 14, 1995. The enactment of a CR on the day after the previous CR expired, which has occurred often, is not counted as involving a funding gap.
b.
Full days are counted as beginning after the final day on which budget authority was available and ending the day before the gap terminated. For example, for the first FY1996 funding gap, the full days of the gap were from November 14, 1995, through November 18, 1995, for a total of five full days.
c.
Gap terminated due to the enactment of a continuing resolution or one or more regular appropriations acts.
Notably, many of the funding gaps that occurred since FY1977 do not appear to have resulted in a "shutdown." Prior to the issuance of the Civiletti opinions, while agencies tended to curtail some operations in response to a funding gap, they often "continued to operate during periods of expired funding."11 In addition, some of the funding gaps after the Civiletti opinions did not result in a completion of shutdown operations due to both a funding gap's short duration and an expectation that appropriations would soon be enacted. For example, during the three-day FY1984 funding gap, "no disruption to government services" reportedly occurred, due to both the three-day holiday weekend and the expectation that the President would soon sign into law appropriations passed by the House and Senate during that weekend.12
Some of the funding gaps during this period, however, did have a broader impact on affected government operations, even if only for a matter of hours. For example, in response to the one-day funding gap that occurred on October 4, 1984, a furlough of non-excepted personnel for part of that day was reportedly implemented.13 The three most recent funding gaps, two in FY1996 and one in FY2014, all resulted in a It should be noted that when most of these funding gaps occurred, one or more regular appropriations measures had been enacted, so any effects were not felt government-wide. For example, the three funding gaps in FY1978 were limited to activities funded in the Departments of Labor and Health, Education, and Welfare Appropriations Act. Similarly, 8 of 13 regular appropriations acts had been enacted prior to the three-day funding gap in FY1984.
The most recent funding gaps—two in FY1996, one in FY2014, and one in FY2018—all resulted in a widespread cessation of non-excepted activities and furlough of associated personnel. The legislative history and agency response to these threethe impact of these funding gaps are summarized below.
FY1996
The two FY1996 funding gaps occurred between November 13- and 19, 1995, and December 15, 1995, through January 6, 1996. The chronology of regular and continuing appropriations enacted during that fiscal year is illustrated in Figure 1. In the lead-up to the first funding gap, only three3 out of the 13 regular appropriations acts had been signed into law,14 and budget authority, which had been provided by a CR15 since the start of the fiscal year, expired at the end of the day on November 13. On this same day, President Clinton vetoed a CR16 that would have extended budget authority through December 1, 1995, because of the Medicare premium increases contained within the measure.17 The ensuing funding gap reportedly resulted in the furlough of an estimated 800,000 federal workers.18 After five days, a deal was reached to end the shutdown and extend funding through December 15.19 Agencies that had been zeroed out in pending appropriations bills were funded at a rate of 75% of FY1995 budget authority. All other agencies were funded at the lower of the House- or Senate-passed level of funding contained in the FY1996 full-year appropriations bills. The CR also containedincluded an agreement between President Clinton and Congress regarding future negotiations to lower the budget deficit within seven years.20
During the first FY1996 funding gap and prior to the second one, an additional four regular appropriations measures were enacted, and three others were vetoed.21 The negotiations on the six remaining bills were unsuccessful before the budget authority contained within the CR expired at the end of the day on December 15, 1995.22 Reportedly, about 280,000 executive branch employees were furloughed during the funding gap between December 15, 1995, and January 6, 1996.23 A CR to provide benefits for veterans and welfare recipients and to keep the District of Columbia government operating was passed and signed into law on December 22, 1995.24 The shutdown officially ended on January 6, 1996, when the first of a series of CRs to reopen federal government and provide budget authority through January 26, 1996,25 was enacted.26
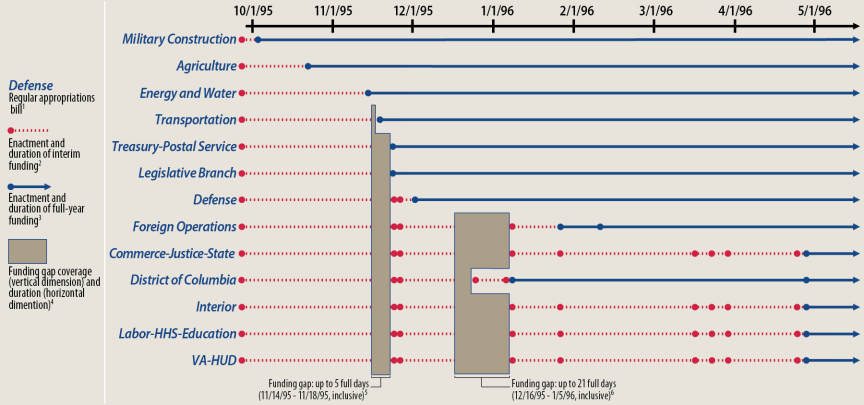 |
|
Source: CRS Report R42647, Continuing Resolutions: Overview of Components and Recent Practices, by [author name scrubbed] and [author name scrubbed], and CRS analysis of public laws available through the Legislative Information System (LIS, lis.gov). Notes: (1) In FY1996, the annual appropriations process anticipated the enactment of 13 "regular appropriations" bills. (2) Interim funding was provided through 13 continuing resolutions (CRs) of varying coverage and duration. For a list of these CRs and their enactment dates, see Table 4 in CRS Report R42647, Continuing Resolutions: Overview of Components and Recent Practices, by [author name scrubbed] and [author name scrubbed]. (3) Full-year funding was provided through eight regular appropriations acts (P.L. 104-32, P.L. 104-37, P.L. 104-46, P.L. 104-50, P.L. 104-52, P.L. 104-53, P.L. 104-61, and P.L. 104-107), two full-year CRs (P.L. 104-92 and P.L. 104-99), and an omnibus appropriations act (P.L. 104-134). For Foreign Operations and District of Columbia, although full-year funding was initially provided in CRs, final action on annual appropriations (P.L. 104-107 and P.L. 104-134) superseded that funding. (4) The "coverage" of the funding gap refers to those regular appropriations bills that had not been enacted during all or some of the days during which the funding gap occurred. The "duration" of the funding gap is calculated here as the number of full days affected by the lapse in funding. Full days are counted as beginning after the final day on which budget authority was available and ending the day before funding resumed. (5) Interim funding was enacted late in the day on November 19, 1995 (P.L. 104-54). As a consequence, in many instances agency operations may not have restarted until the following day. (6) Three interim funding measures included full-year funding for certain activities (P.L. 104-69, P.L. 104-91, and P.L. 104-92). However, this provision of agency- or program-specific, full-year funding is not reflected in the figure, which focuses on the enactment of entire regular appropriations bills. |
FY2014
The most recentDuring the first FY1996 funding gap and prior to the second one, an additional four regular appropriations measures were enacted, and three others were vetoed.21 The negotiations on the six remaining bills were unsuccessful before the budget authority provided in the CR expired at the end of the day on December 15, 1995.22 Reportedly, about 280,000 executive branch employees were furloughed during the funding gap between December 15, 1995, and January 6, 1996.23 A CR to provide benefits for veterans and welfare recipients and to keep the District of Columbia government operating was passed and signed into law on December 22, 1995.24 The shutdown officially ended on January 6, 1996, when the first of a series of CRs to reopen affected agencies and provide budget authority through January 26, 1996,25 was enacted.26
FY2014
This funding gap commenced at the beginning of FY2014 on October 1, 2013. None of the 12 regular appropriations bills for FY2014 was enacted prior to the beginning of the funding gap. In addition, as of the beginning of the fiscal year, an interim CR to provide budget authority for the projects and activities covered by those 12 bills was also not enacted. On September 30, however, an ACR was enacted to cover FY2014 pay and allowances for (1) certain members of the Armed Forces, (2) certain Department of Defense (DOD) civilian personnel, and (3) other specified DOD and Department of Homeland Security contractors (H.R. 3210; P.L. 113-39, 113th Congress).
At the beginning of this 16-day funding gap, more than 800,000 executive branch employees were reportedly furloughed.27 This number was reduced during the course of the funding gap due to the implementation of P.L. 113-39 and other redeterminations of whether certain employees were excepted from furlough.28 Prior to the resolution of the funding gap, congressional action on appropriations was generally limited to a number of narrow CRs to provide funding for certain programs or classes of individuals.29 Of these, only the Department of Defense Survivor Benefits Continuing Appropriations Resolution of 2014 (H.J.Res. 91; P.L. 113-44) was enacted into law.
On October 16, 2013, the Senate passed H.R. 2775, which had been previously passed by the House on September 12, with an amendment. This amendment, in part, provided interim continuing appropriations for the previous year's programs and activities through January 15, 2014. Later that same day, the House agreed to the Senate amendment to H.R. 2775. The CR was signed into law on October 17, 2013 (P.L. 113-46), thus ending the funding gap.
FY2018At the beginning of FY2018, none of the 12 regular appropriations bills had been enacted, so the federal government operated under a series of CRs. The first, P.L. 115-56, provided government-wide funding through December 8, 2017. The second, P.L. 115-90, extended funding through December 22, and the third, P.L. 115-96, extended it through January 19, 2018. In the absence of agreement on legislation that would further extend the period of these CRs, however, a funding gap began with the expiration of P.L. 115-96 at midnight on January 19. A furlough of federal personnel began over the weekend and continued through Monday of the next week, ending with enactment of a fourth CR, P.L. 115-120, on January 22.
Author Contact Information
Acknowledgments
This report is based on awork published in prior CRS Report writtenReports by [author name scrubbed] and updated by [author name scrubbed].
Footnotes
| 1. |
For a discussion of CRs generally, see CRS Report R42647, Continuing Resolutions: Overview of Components and Recent Practices, by [author name scrubbed] |
| 2. |
P.L. 94-473 made continuing appropriations through March 31, 1977. P.L. 95-16 extended the date of the budget authority |
| 3. |
Section 1414 of P.L. 82-547 (66 Stat. 661), which was enacted on July 15, 1952, made regular appropriations retroactively available as of July 1 (the first day of FY1953) and ratified any obligations incurred prior to the law's enactment. |
| 4. |
The Antideficiency Act is discussed in CRS Report RL30795, General Management Laws: A Compendium, by [author name scrubbed] et al. In addition, the Government Accountability Office (GAO) provides information about the act online at http://www.gao.gov/ada/antideficiency.htm. |
| 5. |
See 31 U.S.C. §1342. During a funding gap, personnel and related activities that are determined to be necessary for the "the safety of human life or the protection of property," or fall under other allowable exceptions, are referred to as "excepted." Under Department of Justice guidance (discussed later in this report), agencies may incur obligations ahead of appropriations for these "excepted" purposes. |
| 6. |
In most cases, funding provided in regular appropriations acts is available to be obligated only in a single fiscal year, so that in the event that no subsequent budget authority is provided, agencies may not enter into further obligations. In these instances, budget authority that had previously been enacted and available for obligation for longer periods (e.g., multi-year or "no-year" appropriations) would generally remain available. |
| 7. |
The text of the opinions is included in Appendices IV and VIII to the GAO report Funding Gaps Jeopardize Federal Government Operations, PAD-81-31, March 3, 1981. |
| 8. |
For a discussion of federal government shutdowns, see CRS Report RL34680, Shutdown of the Federal Government: Causes, Processes, and Effects, coordinated by [author name scrubbed]. |
| 9. |
See, for example, Executive Office of the President, Office of Management and Budget (OMB), "Planning for Agency Operations During a Lapse in Government Funding," M-11-13, April 7, 2011, p. 3; and OMB, "Anticipated Enactment of a Continuing Resolution," M-11-14, April 8, 2011. |
| 10. |
FY1977 marked the first full implementation of the congressional budget process established by the Congressional Budget Act of 1974, which moved the beginning of the fiscal year to October 1. |
| 11. |
GAO, Funding Gaps Jeopardize Federal Government Operations, PAD-81-31, March 3, 1981, p. 2. GAO further stated, "Short of telling employees not to show up for work, Federal officials have responded to gaps by cutting or postponing all non-essential obligations—particular personnel actions, travel, and the award of new contracts—in an attempt to continue the operations of programs for which they are responsible." Media reports related to funding gaps prior to FY1982 also suggest that little or no shutdown occurred. See, for example, Congressional Quarterly Almanac, "Continued Funding, 1977," vol. XXXII, pp. 789-790; |
| 12. |
Congressional Quarterly Almanac, "Congress Clears 2nd Continuing Resolution," vol. XXXIX, 1983, pp. 528-531. |
| 13. |
For further information, see Congressional Quarterly Almanac, "Last-Minute Money Bill Was Largest Ever," vol. XXXX pp. 444-447; Robert Pear, "Senate Works Past Deadline on Catchall Government Spending Bill," New York Times, October 4, 1984, p. A29; and Monica Borkowski, "Looking Back; Previous Government Shutdowns," New York Times, November 11, 1995. |
| 14. |
The Military Construction Appropriations Act, H.R. 1817 (P.L. 104-32), was enacted on October 3, 1995. The Agriculture, Rural Development, Food and Drug Administration, and Related Agencies Appropriations Act, H.R. 1976 (P.L. 104-37), was enacted on October 21, 1995. The Energy and Water Development Appropriations Act, H.R. 1905 (P.L. 104-46), was enacted on November 13, 1995. The Legislative Branch Appropriations Act, H.R. 1854 (104th Cong.), was vetoed on October 12, 1995. As of the end of the day on November 13, 1995, the 10 regular appropriations bills that had yet to be enacted were the (1) Department of Transportation and Related Agencies Appropriations Act; (2) Treasury, Postal Service, and General Government Appropriations Act; (3) Legislative Branch Appropriations Act; (4) Department of Defense Appropriations Act; (5) Department of Interior and Related Agencies Appropriations Act; (6) Department of Veterans Affairs and Housing and Urban Development, and Independent Agencies Appropriations Act; (7) Departments of Commerce, Justice, and State, the Judiciary, and Related Agencies Appropriations Act; (8) Foreign Operations, Export Financing, and Related Programs Appropriations Act; (9) Departments of Labor, Health and Human Services, and Education, and Related Agencies Appropriations Act; and (10) District of Columbia Appropriations Act. |
| 15. | |
| 16. |
H.J.Res. 115 (104th Cong.). |
| 17. |
William J. Clinton, "Message to the House of Representatives Returning Without Approval Continuing Resolution Legislation," November 13, 1995, Public Papers of the Presidents of the United States, 1995, Book 2, July 1 to December 31, 1995, p. 1755. See also CQ Today, "Clinton Vetoes Stopgap Bill to Keep Federal Government Open," November 14, 1995. |
| 18. |
For example, see U.S. Congress, House Committee on Government Reform and Oversight, Subcommittee on Civil Service, Government Shutdown I: What's Essential? hearings, 104th Cong., 1st sess., December 6 and 14, 1995 (Washington: GPO, 1997), pp. 6 and 265. |
| 19. |
As provided in 2 CRs: H.J.Res. 123 (P.L. 104-54) and H.J.Res. 122 (P.L. 104-56). |
| 20. |
For a summary of the first FY1996 funding gap and government shutdown, see Congressional Quarterly Almanac, "Overview: Government Shuts Down Twice Due to Lack of Funding," 104th Cong., 1st sess. (1995), vol. LI, pp. 11-3 through 11-6; CQ Weekly, "Special Report—Budget Showdown: Day by Day," November 18, 1995. |
| 21. |
The Department of Transportation and Related Agencies Appropriations Act, H.R. 2002 (P.L. 104-50), was enacted on November 15, 1995. The Treasury, Postal Service, and General Government Appropriations Act, H.R. 2020 (P.L. 104-52), was enacted on November 19, 1995. The Legislative Branch Appropriations Act, H.R. 2492 (P.L. 104-53), was enacted on November 19, 1995. The Department of Defense Appropriations Act, H.R. 2126 (P.L. 104-61), was enacted on December 1, 1995. The Department of Interior and Related Agencies Appropriations Act, H.R. 1977 (104th Cong.), was vetoed on December 18, 1995. The Department of Veterans Affairs and Housing and Urban Development, and Independent Agencies Appropriations Act, H.R. 2099 (104th Cong.), was vetoed on December 18, 1995. The Departments of Commerce, Justice, and State, the Judiciary, and Related Agencies Appropriations Act, H.R. 2076 (104th Cong.), was vetoed on December 19, 1995. |
| 22. |
As of the end of the day on December 15, 1995, the six regular appropriations bills that had yet to be enacted were the (1) Department of Interior and Related Agencies Appropriations Act; (2) Department of Veterans Affairs and Housing and Urban Development, and Independent Agencies Appropriations Act; (3) Departments of Commerce, Justice, State, the Judiciary, and Related Agencies Appropriations Act; (4) Foreign Operations, Export Financing, and Related Programs Appropriations Act; (5) Departments of Labor, Health and Human Services, and Education, and Related Agencies Appropriations Act; and (6) District of Columbia Appropriations Act. |
| 23. |
For further information on the effects of the second FY1996 funding gap, see Dan Moran and Stephen Barr, "When Shutdown Hit Home Ports, GOP Cutters Trimmed Their Sails," Washington Post, January 8, 1996. |
| 24. | |
| 25. |
H.J.Res. 134 (P.L. 104-94). H.R. 1358 (P.L. 104-91) and H.R. 1643 (P.L. 104-92) were also enacted on January 6. These two CRs provided budget authority for some federal government activities until the end of FY1996. |
| 26. |
For a summary of the second FY1996 funding gap and government shutdown, see Congressional Quarterly Almanac, "Overview: Government Shuts down Twice Due to Lack of Funding," 104th Cong., 1st sess. (1995), vol. LI, pp. 11-3 through 11-6; CQ Weekly, "Funding Expires Again in Budget Stalemate," December 23, 1995; CQ Today, "Congress Clears Bills to Reopen Government," January 8, 1996. |
| 27. |
See, for example, Wall Street Journal, "More Than 800,000 Federal Workers Are Furloughed," October 1, 2013. Estimates in this and other media reports were based upon the totals provided by agencies in their contingency plans, which are available at http://www.whitehouse.gov/omb/contingency-plans. These totals do not include legislative or judicial branch employees. |
| 28. |
See, for example, Washington Post, "Pentagon Will Order Almost All Furloughed Civilian Employees Back to Work," October 5, 2013; and Washington Post, "Agencies Increasingly Calling Back Furloughed Workers," October 10, 2013. |
| 29. |
These CRs included H.J.Res. 70, H.J.Res. 71, H.J.Res. 72, H.J.Res. 73, H.J.Res. 75, H.J.Res. 76, H.J.Res. 77, H.J.Res. 79, H.J.Res. 80, H.J.Res. 82, H.J.Res. 83, H.J.Res. 84, H.J.Res. 85, H.J.Res. 89, H.J.Res. 90, H.J.Res. 91, and H.R. 3230. |