Remittances: Background and Issues for the 118th Congress
Changes from December 2, 2019 to May 10, 2023
This page shows textual changes in the document between the two versions indicated in the dates above. Textual matter removed in the later version is indicated with red strikethrough and textual matter added in the later version is indicated with blue.
Remittances: Background and Issues for Congress
Contents
- Introduction
- Background
- Global and U.S. Remittance Flows
- The U.S. Remittance Marketplace
- Money Service Businesses (MSBs)
- Traditional Financial Institutions
- Mobile and Other Emerging Payment Systems
- Regulation of Remittance Providers
- International Standards and Principles
- U.S. Anti-Money Laundering/Combating the Financing of Terrorism (AML/CFT) Efforts
- "Dodd-Frank" Measures
- Issues for Congress
- Regulation of Remittances
- Promoting Remittances as a Development Tool
- Remittances and U.S. Immigration Policy
Figures
Summary
Remittances: Background and Issues for the
May 10, 2023
118th Congress
Martin A. Weiss
This report focuses on remittances, the transfers of money and capital sent by migrants and
Specialist in International
foreign immigrant communities to their home countries. At over $700626 billion, annually,
Trade and Finance
remittances sent home by international migrants to developing countries are larger than official
development assistance (ODA) and more stable than private capital flows to these countries.
The The
Andrew P. Scott
United States is the destination for the most international migrants and is by far the largest source of global remittances. The World Bank estimates there were $56.3 billion in official remittance outflows from the United States in 2014. As remittances have ballooned, according to the
Analyst in Financial
International Monetary Fund and World Bank, the largest global source of remittances, sending
Economics
$72.7 billion in 2021.
As remittances have grown, banks, traditional money transfer companies, and entrepreneurs have
responded to increased demand by increasing the remittance channels available to migrants; these now include mobile, internetInternet, and card-based options.
The dramatic
The rise in the importance of remittances to global capital flows has also led to greater interest from Congress and other policymakers. Key remittance issues for Congress include:
Costs associated with Remittances: In recent Congresses, Members have sought legislative efforts to reduce the cost of remittance services. A number of factors affect the transfer fee charged, including the regulatory and administrative costs, the volume sent, the transfer mechanism, the receiving country’s financial infrastructure, and the level of market competition (in both the sending and receiving country). In addition, the exchange rate used in the transaction can significantly affect the amount actually delivered to the recipient.
Regulation of Remittances. . Members may want to review the regulatory landscape for remittance providers. Effective regulation of remittances can help reduce corruption, enhance transparency, and facilitate a more robust business environment. At the same time, additional regulatory requirements, such as consumer protection requirements included in the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Consumer Protection Act, may raise concerns about the compliance costs for remittance providers and consumers.
Congress may also want to consider whether current federal and state regulation are appropriate for new and emerging payment methods such as mobile and digital payment options, which are starting to capture part of the remittance market. Members may also want to review recent efforts to improve foreign regulatory and supervisory mechanisms. Remittances are often sent to recipients in developing countries with weak regulatory systems, increasing the risk of money laundering and possible financing of terrorism.
Impact on U.S. Development Policy. Remittances represent a substantial percentage of gross domestic product (GDP) in several developing countries. Whether remittances can be leveraged to support U.S. foreign development policy is another issue of concern to some Members of Congress. Some analysts argue that since remittances are private transfers between family members and friends, U.S. efforts should be directed at reducing the transaction costs involved in remittance transactions. Others note the potential beneficial development aspects of remittances, including promoting investment and access to financial services, and encouraging government programs to help stimulate these positive effects.
Remittances and U.S. Immigration Policy. Members may want to consider the interplay of U.S. remittance policy and U.S. immigration policy. A major goal of U.S. policy on remittances is increasing the attractiveness of regulated remittance systems to potential remittance customers, without regard to their legal status. Thus, U.S. Treasury officials allow remittance providers to accept certain foreign-issued means of identification to meet their customer identification requirements. Some Members argue that policies like these could undermine U.S. immigration laws and they advocate restricting remittances to those with legal status under U.S. immigration laws. Others argue that more restrictive identification measures would only push remittance flows toward high-risk, unregulated, and underground channels.
Introduction
This report focuses on remittances, transfers of money and capital sent by migrants and foreign immigrant communities to their home country. Increasing migration is a defining feature of the current global economy. According to the United Nations, the number of international migrants reached an estimated 272 million in 2019.1
Remittances and Cryptocurrency. Cryptocurrencies are a relatively new technology-based payment tool that can facilitate cross-border transactions without the need for banks and centralized intermediaries. To the extent money transmitters, particularly large ones such as PayPal that offer peer-to-peer (P2P) digital options for sending remittances, find ways to facilitate cryptocurrency transactions, the role of cryptocurrencies in remittance markets has the potential to grow. Given this growth, Congress may examine what role cryptocurrencies will play in remittance markets in the future, and consider whether the existing financial regulatory framework is sufficiently authorized to manage the risks of using cryptocurrency in light of other more traditional financial services, such as banking or money transmitters.
Congressional Research Service
link to page 4 link to page 5 link to page 6 link to page 7 link to page 8 link to page 8 link to page 9 link to page 9 link to page 10 link to page 11 link to page 11 link to page 12 link to page 13 link to page 15 link to page 5 link to page 5 link to page 6 link to page 8 link to page 12 link to page 13 link to page 13 link to page 17 Remittances: Background and Issues for Congress
Contents
Overview of the Global and U.S. Remittance Market ..................................................................... 1
Key Institutions in the Domestic Market .................................................................................. 2
Money Service Businesses (MSBs) .................................................................................... 3 Traditional Depository Institutions ..................................................................................... 4
U.S. Remittance Flows .............................................................................................................. 5
Regulation of Remittances .............................................................................................................. 5
U.S. Anti-Money Laundering/Combating the Financing of Terrorism Efforts ................... 6 Federal Consumer Protection Provisions ............................................................................ 6 ACH and FedGlobal Services ............................................................................................. 7
International Standards and Principles ...................................................................................... 8
Issues for Congress .......................................................................................................................... 8
Costs Associated with Remittances ........................................................................................... 9 Regulatory Issues and De-Risking .......................................................................................... 10 Remittances and Cryptocurrencies .......................................................................................... 12
Figures Figure 1. Remittances, Foreign Direct Investment, and Official Development Assistance
Flows to Low- and Middle-Income Countries ............................................................................. 2
Figure 2. Overview of Remittance Channels................................................................................... 3 Figure 3. Estimated Remittances from the United States (2021) .................................................... 5 Figure 4. Global Cost of Sending $200 ........................................................................................... 9 Figure 5. Total Average Cost of Sending Remittances by Traditional and Digital Money
Transfer Operators (MTOs) ........................................................................................................ 10
Contacts Author Information ........................................................................................................................ 14
Congressional Research Service
Remittances: Background and Issues for Congress
Overview of the Global and U.S. Remittance Market Remittances are a prominent type of cross-border financial transfer.1 Often these payments are made between migrant families. The United States has more immigrants than any other country in the world: immigrants account for 14.1the world, 44.7 million in 2017.2 Immigrants account for 13.6% of the U.S. population, triple the share in 1970 (4.7%).3
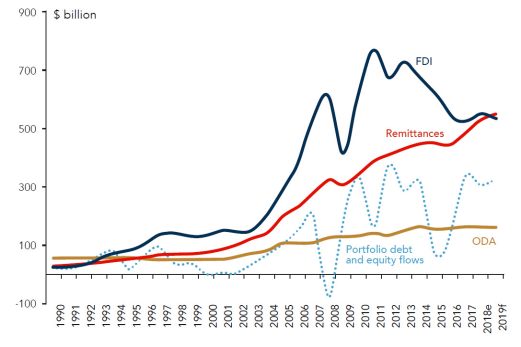
As migrants have become more integrated into the global economy, their involvement in the economic activities of their home countries has also increased. In 2019, worldwide remittance flows are estimated to exceed $707 billion. Of that amount, low- and middle-income countries are estimated to receive about $550 billion, nearly three times the amount of official development assistance (ODA).4 Only foreign direct investment (FDI) is a comparable source of foreign capital for the world's developing countries than remittances.5
% of the U.S. population and are the largest global source of remittances.2
Remittance transactions typically involve a sender from one country, a recipient in another country, financial intermediaries in both countries, and a payment system used by the intermediaries. The financial institutions involved in the $540 billion remittances market can be banks or credit unions,3 but they are often money transmitters, such as MoneyGram, Western Union, or PayPal.
Remittances have increased steadily over the past three decades and are the largest source of external finance for low- and middle-income countries (Figure 1), exceeding foreign direct investment (FDI), portfolio investment, and official development assistance (ODA).4 In 2022, remittances to low- and middle-income countries are estimated at $626 billion, an increase from $597 billion in 2021 levels and up from about $75 billion in 1990. The World Bank notes that in 2022, India was the largest remittance-receiving country ($100 billion), followed by Mexico ($60 billion), China ($51 billion) and the Philippines ($38 billion).
The World Bank had expected the combined impact of travel bans and the Coronavirus Disease 2019-related global economic downturn to have a much larger negative impact on remittance flows; however, recent research found that an impact of the pandemic’s border closures shifted remittances from informal to formal channels.5
Official remittance figures do not include informal remittance flows (discussed in the next section). Estimates of informal remittance flows vary greatly, from between 50% and 250% of total remittance flows.6 The dramatic rise in the importance of remittances to global capital flows has also led to greater interest from Congress and other policymakers. Members may want to review the regulatory landscape for remittance providers. Effective regulation of remittances can help reduce corruption, enhance transparency, and facilitate a more robust business environment. At the same time, additional regulatory requirements, such as consumer protection requirements included in the Dodd-Frank Wall Street has led Congress and other policymakers to take a greater interest in these flows and how they are covered under U.S. and state regulation. For example, P.L. 111-203, the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, provided federal consumer protections on remittance transactions. Remittances are also subject to federal regulation to prevent money laundering and terrorist financing.
This report provides general background on remittances, analyzes global and U.S. remittance flows, examines the remittance marketplace and the regulatory regime for sending remittances from the United States, and discusses key issues for Congress.
Background
Remittances are cross-border migrant financial transfers. The primary source for international remittances data is the International Monetary Fund (IMF), which compiles statistics submitted by its member countries. Using IMF statistics, the World Bank publishes migration and remittances data on its website.6
Remittances are defined as the sum of three entries in the IMF's annual Balance of Payments Statistics Yearbook: workers' remittances; compensation of employees; and migrants' transfers.7
- Workers' remittances are defined by the IMF as transfers (cash or in kind) by migrants who are both employed and considered resident in another country. If the migrants live in the host country for one year or longer, they are considered residents, regardless of their immigration status.
- Compensation of employees includes wages, salaries, and other benefits of border, seasonal, and other nonresident workers (such as local staff of embassies) away from their home country for less than a year.
- Migrants' transfers are the net worth of migrants' assets that are transfers from one country to another at the time of migration (for a period of at least one year), such as in the case of temporary workers.
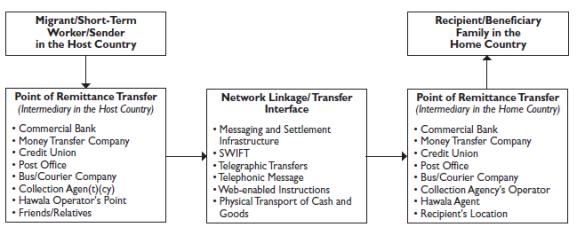
A remittance transaction typically involves a sender, a recipient, intermediaries in both countries, and a payment system used by the intermediaries (Figure 1).8 Remittances can be sent through informal or formal channels. Informal channels have been labeled by various terms, including ", or new regulation on digital remittances may raise concerns about the compliance costs for remittance providers and consumers. Congress may also want to consider whether current federal and state regulation are
1 The term “remittance” can be used in a few different contexts. Generally, a remittance is money sent somewhere to pay for something. This report discusses a type of remittance that consists of cross-border payments, where money is sent by someone in a country to someone outside that country.
2 Miriam Jordan and Robert Gebeloff, “Amid Slowdown, Immigration Is Driving U.S. Population Growth,” New York Times, February 5, 2022. : World Bank, Migration and Development Brief 37, Figure 1.1b, November 2022, https://www.knomad.org/sites/default/files/publication-doc/migration_and_development_brief_37_nov_2022.pdf.
3 World Bank, “Low- and Middle-Income Countries Received $540 billion in 2020, $8 Billion Less Than in 2019,” May 12, 2021, at https://www.worldbank.org/en/news/press-release/2021/05/12/defying-predictions-remittance-flows-remain-strong-during-covid-19-crisis.
4 For 2021, low- and middle-income countries include those with a gross national income per capita below $12,695, https://blogs.worldbank.org/opendata/new-world-bank-country-classifications-income-level-2021-2022.
5 5 Kangni Kpodar et al., “Defying the Odds: Remittances During the COVID-19 Pandemic,” International Monetary Fund Working Paper 21/186, July 2021, https://www.imf.org/-/media/Files/Publications/WP/2021/English/wpiea2021186-print-pdf.ashx.
6 Ibid.
Congressional Research Service
1
link to page 6
Remittances: Background and Issues for Congress
appropriate for new and emerging payment methods such as mobile and digital payment options. Members may also want to review recent efforts to improve foreign regulatory and supervisory mechanisms. Remittances are often sent to recipients in developing countries with weak regulatory systems, increasing the risk of money laundering and possible financing of terrorism.
Figure 1. Remittances, Foreign Direct Investment, and Official Development
Assistance Flows to Low- and Middle-Income Countries
Source: World Bank, Migration and Development Brief 37, Figure 1.1b, November 2022, https://www.knomad.org/sites/default/files/publication-doc/migration_and_development_brief_37_nov_2022.pdf. Note: (e): estimated; (f): forecast; (FDI): Foreign Direct Investment; (ODA): Official Development Assistance.
Key Institutions in the Domestic Market Migrants/customers can send remittances through informal or formal channels (Figure 2).7 Analysts have labeled the informal channels with various terms, including “alternative remittance systems," "” “underground banks,"” and "“informal value transfer systems." The ” These services are less expensive than formal banking or money-transfer arrangements and can reach countries where there is no formal banking sector, in some cases even arranging for hand delivery of the cash. The most well-known is hawalamost well-known is hawala (hawala means "transfer"“transfer” in Arabic), which originated in India and has been in use in South Asia and the Middle East for several hundred years.9 These services are less expensive than formal banking or money transfer arrangements, can provide anonymity for all parties involved, and can reach countries where there is no formal banking sector, in some cases even arranging for hand delivery of the cash. While most use these systems for legitimate purposes, their lack of documentation and their anonymity and informality may make them attractive for money laundering, terrorist financing, or other illegal purposes.
Formal channels involve intermediaries that are officially licensed to operate money transfer businesses. These consist of banks; nonbank financial institutions, such as credit unions, savings and loan institutions, and post offices;8 While most remittance customers use these arrangements for legitimate purposes, these systems’ lack of documentation and their anonymity and informality can make them attractive for money laundering, terrorist financing, or other illegal purposes.
7 International Transactions in Remittances: Guide for Compilers and Users. Washington, DC: International Monetary Fund, 2009, at https://www.imf.org/external/np/sta/bop/2008/rcg/pdf/guide.pdf.
8 Often regionally based, alternative remittance systems date back hundreds of years and were originally used to finance trade in regions where traveling with gold or other forms of payment was not safe. These systems go by various names including Hue (Vietnam), Fei-Ch’ien (China) Phei Kwan (Thailand) Hundi (South Asia), or Hui Kuan (Hong Kong).
Congressional Research Service
2
Remittances: Background and Issues for Congress
Formal channels involve intermediaries that are officially licensed to operate money-transfer businesses. These formal channels consist of banks, nonbank financial institutions (including post offices), and money service businesses such as Western Union or MoneyGram. Increased use of technology in developing countries has also facilitated the use of mobile-phone-based and other electronic payment methods.
The price of sending a remittance can vary significantly. A number of factors affect the transfer fee charged, including the regulatory and administrative costs, the volume sent, the transfer mechanism, the receiving country's financial infrastructure, and the level of market competition (in both the sending and receiving country). In addition, the exchange rate used in the transaction can significantly affect the amount actually delivered to the recipient.
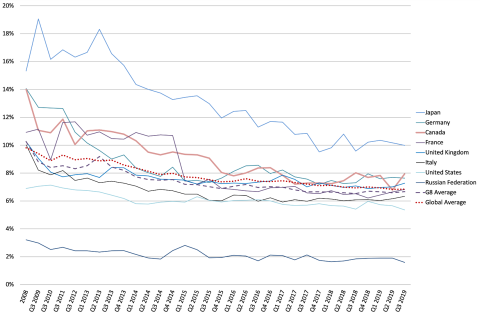
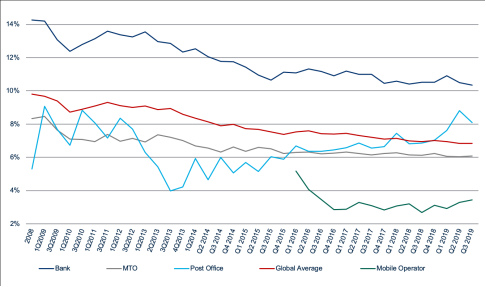
For the most part, the cost of sending remittances has declined slightly in recent years, but substantial progress would be needed to meet the G8 target of 5% of total cost set in 2009. According to World Bank analysis, the global average remittance cost has declined from 9.81% of the total transaction in 2008 to 6.84% during the third quarter of 2019.10 Among the major economies, the United States is among the least costly from which to send money (Figure 2). For the first quarter of 2016, the average cost to send a remittance from the United States was 6.04% of the transaction.11 The World Bank also tracks the cost of sending remittances from the main remittance providers. Recent data show that banks continue to be the most expensive providers, followed by post offices. Mobile Operators and Money Transfer Operators (MTOs) such as Western Union and Moneygram are the cheapest (Figure 3).
|
 |
|
Source: Remittance Prices Worldwide, the World Bank |
|
 |
|
Source: Remittance Prices Worldwide, the World Bank |
Global and U.S. Remittance Flows
Remittances have increased steadily over the past three decades and are the largest source of external finance for many countries (Figure 4). In 1990, remittances to low- and middle-income countries totaled about $75 billion and are expected to reach $551 billion in 2019. Official remittance figures do not include informal remittance flows, which may account for an additional 35% to 75% of total remittance flows.12 In 2019, India was the largest remittance-receiving country ($82.2 billion), followed by China ($70.3 billion), and Mexico ($38.7 billion). Figure 4 shows the geographical distribution of remittances since 2000.
In Billions of U.S. Dollars |
 |
|
Source: World Bank, World Development Indicators |
The emergence of large Indian, Chinese, and Philippine diaspora populations led to the explosive growth of remittances over the past 15 years. Between 2000 and 2014, remittances to developing countries in East Asia and Pacific increased by 370%, growing from $17 billion in 2000 to $79 billion in 2014. In South Asia, remittances increased by 571% over that time, growing from $17 billion in 2000 to $116 billion in 2014. Despite accounting for a much smaller amount of global remittances, flows to Sub-Saharan Africa increased by 608% from 2000 ($5 billion) to 2014 ($34 billion).
The IMF, World Bank, and the U.S. government do not compile and publish remittance flows from the United States (or other countries) to individual countries or regions. However, since 2010, the World Bank has estimated bilateral remittance flows between its member countries.13 Table 1 presents the World Bank's estimates for the largest recipients of remittances from the United States from 2010 to 2018 and Table 2 presents the ten largest remittance corridors in 2018. The United States is the largest sending jurisdiction, accounting for 23.27% of all remittances sent in 2018 and originating remittances in seven of the ten largest corridors.
|
2010 |
2011 |
2012 |
2013 |
2014 |
2015 |
2016 |
2017 |
2018 |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Mexico |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||
|
China |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||
|
India |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||
|
Philippines |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||
|
Vietnam |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||
|
Guatemala |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||
|
Nigeria |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||
|
El Salvador |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||
|
Dominican Republic |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||
|
Honduras |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Source: World Bank, Bilateral Remittances Matrices, various years
|
Receiving Country |
Remittance Estimate ($ billions) |
|
|
United States |
Mexico |
34.7 |
|
United Arab Emirates |
India |
18.53 |
|
Hong Kong |
China |
16.34 |
|
United States |
China |
14.25 |
|
United States |
India |
12.74 |
|
Saudi Arabia |
India |
11.67 |
|
United States |
Philippines |
11.43 |
|
United States |
Guatemala |
8.49 |
|
United States |
Vietnam |
8.33 |
|
United States |
Nigeria |
7.27 |
Source: World Bank, 2018 Bilateral Remittance Matrix
The U.S. Remittance Marketplace
Money Service Businesses (MSBs)
Currently, the U.S. foreign remittance market is dominated by MSBs, a category of nonbank financial institutions that generally own proprietary, so-called "closed-loop" payment systems and operate largely outside of conventional banks.14 The capacities of MSBs include issuing money orders and traveler's checks, transmitting money, cashing checks, exchanging currency, dealing currency, and storing value.15 MSBs cover a broad variety of enterprises ranging from small and simple operations to large firms. MSBs include the U.S. Postal Service, because it issues money orders. Western Union and MoneyGram are the two largest money transmission companies and their agents are often located in a wide variety of other businesses, including supermarkets, check cashing agents, gas stations, liquor stores, convenience stores, and currency exchange offices. The main reason foreign remittance customers use MSBs is that they are often "unbanked"; that is, they do not have an account with a depository financial institution. In addition, money transmission services may be an ancillary service: the foreign remittance customer may be able to cash a paycheck, send money to family in his home country, and shop for groceries at the same location.
Traditional Financial Institutions
Remittance transactions are not a service traditionally provided by banks. International money transfer services provided by banks are expensive, and have thus been marketed primarily to corporate clients who send larger amounts than a typical migrant remitter. According to the Federal Reserve, the median amount of a consumer-initiated wire transfer processed by financial institutions is about $6,500 in domestic and foreign transfers, much larger than most remittance transactions, which are typically a few hundred dollars.16 Another constraint for bank provision of remittances is the underdeveloped financial systems in many of the largest remittance-receiving countries. Since many recipients lack a bank account, they prefer to collect remittance money in cash. International wire transfer, however, is only an option when both the sender and receiver have access to deposit accounts at depository institutions. Unlike the "closed loop" payment system used by MSBs, banks and credit unions generally use "open loop" payment systems such as wire-transfer systems and correspondent banking channels. Because they act through retail store locations such as grocery stores, MSBs often have more extensive distribution networks in their countries of operation than traditional financial institutions do.
As consumer demand for remittances has grown over the past two decades, banks and credit unions have shown a greater interest in directly providing remittance services to consumers. Remittance services can be a way to bring low-income migrants into the financial mainstream and introduce them to other financial products and services, such as interest-bearing savings accounts, checking accounts for paying bills (a replacement for money orders), free and secure check cashing services, and small dollar loans, among other services. Credit union participation has also been encouraged by the development of the World Council of Credit Unions' International Remittance Network, a credit union network for international money transfers.
To generate more remittances business, since 1998, U.S. depository institutions have had the option of transmitting remittance transfers through the Automated Clearing House (ACH) system. The ACH system clears and settles batched electronic transfers for participating depository institutions. Since financial transfers are batched together and sent on a fixed schedule, banks can charge a lower price than for traditional international wire transfers, which are sent individually. The originating institution combines the payment instructions from its various customers and sends them in a batch to an ACH operator—the U.S. Federal Reserve Bank's FedGlobal Payments Service or the Clearing House's Electronic Payments Network—for processing. In addition to being used for remittances, international ACH transfers are used for various small recurring cross-border payments, such as social security and other benefit payments; business transactions, such as vendor payments; and consumer transactions, such as bill payments and remittance transfers.
Since 2001, the U.S. Federal Reserve has provided so-called "account-to-receiver" FedGlobal services that allow funds from accounts at a U.S. depository financial institution to be sent to unbanked receivers for retrieval at either a bank location or a trusted, third-party provider. As of 2013, FedGlobal services are available to Europe, Mexico, Panama, and Latin America, covering 35 countries in total.17
Participation in the remittance market by banks and credit unions, while growing, is still limited. The U.S. Federal Reserve does not collect precise statistics on remittance transfers, but reports that in 2014, the two U.S. ACH operators handled 18.3 billion ACH transactions, of which 54.6 million (or 0.3%) were initiated by a business or a consumer, but not by the U.S. government.18
Mobile and Other Emerging Payment Systems
In addition to remittance services provided by MSBs and traditional financial institutions, there has been a proliferation of new companies using new technologies to provide remittances in recent years. Such new options include computer and mobile-based payments;19 pre-paid cards, which can be cashed at an ATM or spent at retail stores;20 directed transfer options in which the sender transmits funds directly to payments on behalf of the recipient;21 and money transfers through social media.22 A study conducted in July 2013 by the World Bank's Consultative Group to Assist the Poor (CGAP) found that there are 41 so-called "branchless" remittance providers in 2013, up from 10 in 2010.23 CGAP also found that traditional remittance providers are introducing flat fees and transparent foreign exchange rates in response to the increased competition.
Regulation of Remittance Providers
At the international level, international standards and principles governing remittances have been set by the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) and the Bank for International Settlements (BIS). In the United States, the operations of U.S. banks and credit unions are closely regulated and supervised at both the state and federal level. Foreign bank branches and agencies are also governed by a combination of state and federal statutes, the provisions of which include licensing requirements and permissible activities. The primary focus of federal regulation is on anti-money laundering (AML) and combating the financing of terrorism (CFT). Individual state regulators, on the other hand, regulate the operations of federally chartered banks and MSBs. Since October 2013, the U.S. Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) has enforced various consumer protection measures included by Congress in the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Consumer Protection Act (Dodd-Frank).
Notes: Not all transactions sent through these channels are remittances.
Money Service Businesses (MSBs)
The U.S. foreign remittance market is dominated by MSBs, a category of nonbank financial institutions that generally own proprietary, so-called “closed-loop” payment systems, and operate largely outside of conventional banks.9 A reason remittance customers may use MSBs is that the customers are often “unbanked”; that is, they do not have an account with a depository financial institution. MSBs issue money orders and traveler’s checks, transmit money, cash checks, exchange currency, and store value.10 MSBs cover a broad variety of enterprises ranging from small and simple operations to large firms. MSBs typically are private enterprises.11
Money Transmitters One of the more common types of MSBs in the United States is called a money transmitter. Americans use money transmitters to pay bills, purchase items online, or send funds to family members and friends domestically and abroad. Although some prominent companies, such as Western Union, MoneyGram, and PayPal, belong to this group of financial institutions, thousands of money transmitters in the United States operate in the background of financial services. Traditional money transmitters like Western Union and MoneyGram are often located in a wide
9 For example, a remittance-sender goes to a Western Union (a type of money service business called a money transmitter) agent in Chicago to send money to her uncle in Brazil, who collects the funds from one of the more than 10,000 Western Union agents in Brazil. Since there are Western Union agents on both ends of the transaction, the transaction occurs outside the conventional banking system.
10 Stored value is funds or monetary value represented in digital electronic format and stored or capable of storage on electronic media in such a way as to be retrievable and transferable electronically, such as a prepaid Visa gift card.
11 Within the context of remittances, the U.S. Postal Service also acts as an MSB, because it issues money orders.
Congressional Research Service
3
Remittances: Background and Issues for Congress
variety of other businesses, including supermarkets, check cashing agents, gas stations, liquor stores, convenience stores, and currency exchange offices. Hence, money transmission services may be an ancillary service: the remittance customer may be able to cash a paycheck, send money to family in their home country, and shop for groceries at the same location. Alternatively, many peer-to-peer (P2P) platforms, such as PayPal and Venmo, operate through mobile apps and web browsers, and so are not ancillary to another business sharing a physical location. While remittances traditionally have been channeled through brick-and-mortar MSBs, the advent of mobile apps and cryptocurrencies has facilitated a new channel for remittance flows.
Traditional Depository Institutions
Small amount remittance transactions are not a service banks and credit unions traditionally provide. More often, those institutions transfer fewer remittances with larger, average dollar value than money-services businesses.12 International money-transfer services provided by banks are marketed primarily to corporate clients who send larger amounts than a typical migrant remitter. One constraint for bank provision of remittances is the underdeveloped financial systems in many of the largest remittance-receiving countries. Since many recipients lack a bank account, they may prefer to collect remittance money in cash. International wire transfer, however, is only an option when both the sender and receiver have access to deposit accounts at depository institutions. Unlike the “closed loop” payment system used by MSBs, banks and credit unions generally use “open loop” payment systems, such as wire-transfer systems and correspondent banking channels. Because MSBs often act through retail store locations such as grocery stores, they tend to have more extensive distribution networks in their countries of operation than traditional depositories do.
As consumer demand for remittances has grown over the past two decades, banks and credit unions have shown a greater interest in providing remittance services directly to consumers. Remittance services can be a way to bring low-income migrants into the financial mainstream and introduce them to other financial products and services, such as interest-bearing savings accounts, checking accounts for paying bills, free and secure check cashing services, and small-dollar loans, among other services. Further, a credit union network for international money transfers called the World Council of Credit Unions’ International Remittance Network has facilitated credit union participation.
U.S. depository institutions have the option of using the Automated Clearing House (ACH) payments system, which can batch and process financial transfers at a lower price than traditional international wire transfers. (The Federal Reserve is one of two ACH payment system operators—this is discussed in more detail in the Regulation of Remittances section below.) Participation in the remittance market by banks and credit unions, while growing, is still limited. The Federal Reserve does not collect precise statistics on remittance transfers, but the latest available data from the Federal Reserve suggest that in 2018, the two U.S. ACH operators handled a total of 22.9 billion ACH transactions, of which 83.8 million (less than 1%) were international ACH transactions.13
12 Consumer Financial Protection Bureau, Remittance Rule Assessment Report, pp. 63-64, October 2018, at https://s3.amazonaws.com/files.consumerfinance.gov/f/documents/bcfp_remittance-rule-assessment_report.pdf.
13 Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, Report to the Congress on the Use of the ACH System and Other Payment Mechanisms for Remittance Transfers to Foreign Countries, May 2019, at https://www.federalreserve.gov/publications/2019-may-ach-report-other-payment-mechanisms.htm.
Congressional Research Service
4
Remittances: Background and Issues for Congress
U.S. Remittance Flows The primary source for international remittances data is the International Monetary Fund (IMF), which compiles statistics submitted by its member countries. Using IMF statistics, the World Bank publishes migration and remittances data on a dedicated website.14
The IMF, World Bank, and the U.S. government do not compile and publish remittance flows from the United States (or other countries) to individual countries or regions. The World Bank estimates bilateral remittance flows between its member countries based on migration figures and historical trends.15 Figure 3 presents the World Bank’s most recent estimates for the largest recipients of remittances from the United States. The United States is consistently the largest sending jurisdiction, accounting for 26% of all remittances sent in 2021. Mexico is by far the largest recipient of remittances from the United States.
Figure 3. Estimated Remittances from the United States (2021)
Source: World Bank Bilateral Remittance Database.
Regulation of Remittances As stated above, remittances can be made through different types of financial institutions, and these institutions are subject to different regulatory frameworks. In the United States, the operations of banks and credit unions are closely regulated and supervised at both the state and federal level. Foreign bank branches and agencies operating in the United States are also governed by a combination of state and federal statutes, the provisions of which include licensing requirements and permissible activities. State regulators also oversee other types of financial
14 https://www.knomad.org/data/remittances. 15 The World Bank’s bilateral remittances matrices are available at https://www.knomad.org/data/remittances. The World Bank uses two datasets to construct the Bilateral Remittance Matrix. The first is UN Population Division estimates of migrant stock by country of origin and destination, also used by this tool. The second dataset is remittance inflows data, constructed as the sum of three components in the IMF’s Balance of Payments Statistics: (i) compensation of employees, (ii) workers’ remittances, and (iii) migrants’ transfers. A country’s total remittance inflows in a given year are allocated to its emigrant stocks, adjusting for the migrant sending and receiving countries’ per capita income.
Congressional Research Service
5
Remittances: Background and Issues for Congress
companies like MSBs.16 Regulatory efforts at the state level focus primarily on licensing and consumer protection. Currently, 49 states have legal frameworks for MSBs.17
Though the various financial institutions are subject to different frameworks, the primary focus of federal remittance regulation is generally on anti-money laundering (AML) and combating the financing of terrorism (CFT). In addition, the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) promulgates certain consumer protection rules implementing provisions set forth in Section 1073 of the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act (Dodd-Frank, P.L. 111-203), which have included cross-border payments regulations.18 Additionally, the Federal Reserve operates a major payments network over which banks can process remittances. These efforts are discussed in the following sections.
U.S. Anti-Money Laundering/Combating the Financing of Terrorism Efforts
In the United States, remittance providers (including banks and MSBs), are required to take certain steps to identify, assess, design, and implement controls to comply with their obligations under the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA, P.L. 91-508). The BSA is the primary AML law in the United States.19 Congress has amended the BSA a number of times, most notably by Title III of the USA PATRIOT Act (P.L. 107-56) in 2001, which expanded the BSA framework beyond AML to also fight terrorist financing. The BSA requires financial institutions to maintain appropriate records and file reports that can be used in criminal, tax, or regulatory investigations or proceedings. The Treasury Department’s Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) administers the BSA.20 With limited exceptions, MSBs are subject to the full range of BSA regulatory controls, including requirements for maintaining financial records, conducting customer identification procedures, in particular for larger transfers, and filing reports for large or suspicious transactions.21
Remittances to certain foreign countries may also be subject to sanctions under various federal statutes administered by the Treasury Department’s Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC). The U.S. government restricts remittances to countries, individuals, or companies that are subject to U.S. sanctions and embargoes.
Federal Consumer Protection Provisions
Section 1073 of the Dodd-Frank Act amended the Electronic Fund Transfer Act (EFTA, P.L. 95-630) to create a consumer protection regime for remittance transfers sent by consumers in the
16 For more on the regulation of MSBs, see CRS Report R46486, Telegraphs, Steamships, and Virtual Currency: An Analysis of Money Transmitter Regulation, by Andrew P. Scott.
17 According to the CSBS, Montana is the sole state without an MSB legal framework. For more, see CSBS, “Chapter Four: Overview of Money Services Business,” 2019, p. 4, at https://www.csbs.org/system/files/2020-08/Chapter%204%20-%20MSB%20Final%20FINAL.pdf.
18 For example, see Remittances: Access, Transparency, and Market Efficiency: A Progress Report, hearing, House Committee on Financial Services, Subcommittee on Domestic and International Monetary Policy, Trade, and Technology, 110th Congress, May 17, 2007; and Remittances: Regulation and Disclosure in a New Economic Environment, hearing, House Committee on Financial Services, Subcommittee on Financial Institutions and Consumer Credit, 111th Congress, June 3, 2009.
19 Office of the Comptroller of the Currency, “Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) & Related Regulations,” accessed January 15, 2020, at https://www.occ.treas.gov/topics/supervision-and-examination/bsa/bsa-related-regulations/index-bsa-and-related-regulations.html.
20 For more on FinCEN, see https://www.fincen.gov/resources/statutes-regulations/fincens-mandate-congress. 21 U.S. Department of the Treasury, Report to Congress in Accordance with Section 359 of the USA PATRIOT Act, November 2002, p. 8, at https://www.fincen.gov/sites/default/files/shared/hawalarptfinal11222002.pdf.
Congressional Research Service
6
Remittances: Background and Issues for Congress
United States to individuals and businesses abroad. In 2012 and 2013, the CFPB implemented Section 1073 through its Remittance Transfer Rule.
The rule requires companies that offer remittances to provide consistent, reliable disclosure of the price of a transfer, the amount of currency to be delivered to the recipient, and the date of availability prior to the consumer making any payment. The rule also aims to increase consumer protections by requiring remittance providers to investigate disputes and remedy errors related to the transaction, and to provide disclosures that explain the impact fees and taxes will have on the transfer amount.22
In May 2020, the CFPB issued a final rulemaking to amend the Remittance Transfer Rule to impose requirements on entities that send international money transfers, or remittance transfers, on behalf of consumers.23 Under the rule, remittance transfer providers generally must disclose the exact exchange rate, the amount of certain fees, and the amount expected to be delivered to the recipient (accounting for fees and exchange rate). The final rule also increases the threshold that determines whether an entity makes remittance transfers covered under the rule: entities making 500 or fewer transfers annually in the current and prior calendar years would not be subject to the rule. According to the CFPB, the rulemaking impacts over 400 banks and almost 250 credit unions that send a relatively small number of remittances—less than 0.06% of all remittances.
ACH and FedGlobal Services
U.S. depository institutions have the option of transmitting remittances through the ACH system. The ACH system clears and settles batched electronic transfers for participating depository institutions. Since financial transfers are batched together and sent on a fixed schedule, banks can charge a lower price than for traditional international wire transfers, which are sent individually. The originating institution combines the payment instructions from its various customers and sends them in a batch to an ACH operator—the Federal Reserve’s FedGlobal Payments Service or the Clearing House’s Electronic Payments Network—for processing. In addition to remittances, international ACH transfers are used for various small, recurring, cross-border payments, such as Social Security and other benefit payments; business transactions, such as vendor payments; and consumer transactions, such as bill payments and remittance transfers.
Since 2001, the Federal Reserve has provided so-called “account-to-receiver” FedGlobal services that allow funds from accounts at a U.S. depository financial institution to be sent to unbanked receivers for retrieval at either a bank location or a trusted, third-party provider. FedGlobal services are available to several countries in Europe and Latin America.24
22 Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB), “Electronic Fund Transfers (Regulation E),” 78 Federal Register 30661, 2013.
23 CFPB, “Consumer Financial Protection Bureau Issues Final Remittance Rule,” May 11, 2020, at https://www.consumerfinance.gov/about-us/newsroom/cfpb-issues-final-remittance-rule/.
24 The European service includes Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, and the United Kingdom. The Latin American service includes Argentina, Brazil, Columbia, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Peru, and Uruguay. The Latin American service, which only involves account-to-receiver ACH transfers, is in addition to the account-to-account service for Mexico.
Congressional Research Service
7
Remittances: Background and Issues for Congress
International Standards and Principles International Standards and Principles
Global standards for remittances have emerged over the past decade, largely due to concerns raised about unregulated money transfer services and their use in planning the September 11, 2001, terrorist attacks. International efforts have been negotiated at the FATFFinancial Action Task Force, an inter-governmental body comprising 34 countries and two regional organizations, including the United States, and two regional organizations, that develops and promotes policies and standards to combat money laundering and terrorist financing.2425 FATF was established in 1989 by the G-7 countries to implement the Vienna Convention Against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances, the first international agreement to criminalize money laundering. ItFATF is housed at the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) in Paris.
The , France.
FATF sets minimum standards and makes recommendations for its member countries. Each country must implement the recommendations according to its particular laws and constitutional frameworks. In 2001, FATF issued nine special recommendations to counter terrorist financing. For example, FATF Special Recommendation VI required FATF member countries to regulate all MSBs. In 2012, FATF substantively revised its recommendations and Special Recommendation VI became FATF Recommendation 14 on Money or Value Transfer Services.2526 Several other recommendations are relevant for remittance providers, including recommendation 10recommendations 10 and 16 on wire transfers, recommendation 11 on record keeping, recommendation 16 on wire transfers, recommendation 18 on internal controls and foreign branches and subsidiaries, and recommendation 20 on suspicious transaction reporting.26
27
International efforts have also focused on improving the operational aspects of remittance transfers. In 2007, the BIS and the World Bank jointly issued General Principles for International Remittance Services, to "“help to achieve the public policy objectives of having safe and efficient international remittance services, which require the markets for the services to be contestable, transparent, accessible and sound."27”28 General Principle 3 states that "“Remittance services should be supported by a sound, predictable, nondiscriminatory and proportionate legal and regulatory framework in relevant jurisdictions,"” and affirms the FATF recommendations, advocating that remittance providers comply with all relevant FATF recommendations. FATF maintains a mutual evaluation system and provides oversight of nonmember countries'’ AML/CFT regimes.
Issues for Congress Key issues that Congress may consider regarding remittances include:
25 Members of FATF are Argentina, Australia, Austria, Belgium, Brazil, Canada, China, Denmark, the European Commission, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, the Gulf Cooperation Council, Hong Kong, Iceland, India, Ireland, Italy, Japan, Korea, the Netherlands, Luxembourg, Mexico, New Zealand, Norway, Portugal, Russia, Singapore, South Africa, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey, the United Kingdom, and the United States. On February 24, 2023, Russia was suspended from FATF. See CRS Report RS21904, The Financial Action Task Force: An Overview, by James K. Jackson.
26 The Financial Action Task Force, The FATF Recommendations: International Standards on Combating Money Laundering and the Financing of Terrorism and Proliferation, February 2012.
27 Ibid. 28 Bank for International Settlements and the World Bank, General Principles for International Remittance Services, January 2007.
Congressional Research Service
8
Remittances: Background and Issues for Congress
Costs Associated with Remittances In recent Congresses, Members have sought legislative efforts to reduce the cost of remittance services. A number of factors affect the transfer fee charged, including the regulatory and administrative costs, the volume sent, the transfer mechanism, the receiving country’s financial infrastructure, and the level of market competition (in both the sending and receiving country). In addition, the exchange rate used in the transaction can significantly affect the amount actually delivered to the recipient.
In 2009, the G8 set a target, later adopted by the G20, to reduce the average cost of a $200 international remittance from 10% of the remittance amount to 5% within five years. The target was dubbed the “5x5 Objective.” The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, adopted in September 2015, included a target to reduce to less than 3% the transaction costs of migrant remittances and eliminate remittance corridors with costs higher than 5%.29
According to the World Bank, the global average cost for sending $200 in remittances was 6.30% in Q3 2022 (Figure 4); the global average for digital remittances was recorded at 5.21%, while the global average for non-digital remittances was 6.82%. According to the World Bank, “A digital remittance must be sent via a payment instrument in an online or self-assisted manner, and received into a transaction account, i.e. bank account, transaction account maintained at a non-bank deposit taking institution (say a post office), mobile money or e-money account.”30
Figure 4. Global Cost of Sending $200
Source: World Bank Remittance Prices Worldwide Quarterly, September 2022.
Notes: SDGs: United Nation’s Sustainable Development Goals.
29 Gloria M. Grandolini, “Getting SmaRT about Reducing Remittances Costs,” World Bank, June 16, 2015, https://blogs.worldbank.org/voices/getting-smart-about-reducing-remittances-costs. Historically, the World Bank has used the cost of sending $200 as the baseline for its remittance cost data. Supplemental statistics for higher transaction amounts ($500) show that the cost is lower as a percentage of the total than the cost of $200, but follows the same overall trend.
30 World Bank Remittance Prices Worldwide Quarterly, September 2022.
Congressional Research Service
9
Remittances: Background and Issues for Congress
The 2021 G20 Rome Leaders Declaration called for the monitoring of National Remittance Plans, the gathering of more granular data, and continuing facilitation of the flow of remittances and reduction of average remittance transfer costs.31 Among the major economies, the United States is among the least costly from which to send money.32
The World Bank also tracks the cost of sending remittances from the main remittance service providers. Recent data show that banks continue to be the most expensive providers, followed by post offices. The data show a substantial cost difference between traditional MTOs (Money Transfer Operators, such as Western Union and Moneygram) and digital mobile operators and MTOs such as Transferwise (Wise), Remitly, WorldRemit, InstaReM and Xoom. In Q3 2022, the World Bank’s International MTO Index recorded a decrease to 5.93% from the previous value of 6.17% in Q2 2022. The cost of digital remittances, on the other hand, has increased in recent years. In Q3 2022, the World Bank’s digital-only MTO Index was recorded at 4.38% (Figure 5).
Figure 5. Total Average Cost of Sending Remittances by Traditional and Digital
Money Transfer Operators (MTOs)
Source: World Bank Remittance Prices Worldwide Quarterly, September 2022. Notes: SDG: United Nation’s Sustainable Development Goals.
Regulatory Issues and De-Risking Some industry observers assert that the current regulatory framework is generally effective and comprised of proportional regulation of remittances and reduces corruption, enhances transparency, and facilitates a more robust business environment. However, other observers raise AML/CFT regimes.
U.S. Anti-Money Laundering/Combating the Financing of Terrorism (AML/CFT) Efforts
In the United States, remittance providers, both banks and MSBs, are required to identify, assess, and take steps to design and implement controls in compliance with their obligations under the U.S. Bank Secrecy Act (BSA). The BSA has been amended a number of times, most notably by Title III of the USA PATRIOT Act in 2001. Among other things, Title III expanded the BSA framework beyond AML to also fight terrorist financing. The main purpose of the BSA is to require financial institutions to maintain appropriate records and file reports that can be used in criminal, tax, or regulatory investigations or proceedings. The Treasury Department's Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) administers the BSA on behalf of Treasury. With limited exceptions, MSBs are subject to the full range of BSA regulatory controls.
Remittance providers must maintain financial records and conduct customer identification procedures for certain transactions. All MSBs must obtain and verify customer identity as well as record beneficiary information for transfers of more than $3,000. They must file Currency Transaction Reports (CTRs), for customer transactions of $10,000 or more in a day, and Suspicious Activities Reports (SARs) for dubious transactions of generally more than $2,000, that the remittance provider "knows, suspects, or has reason to suspect involves funds from illegal activity or is designed to conceal their origin, is designed to evade BSA obligations, or has no apparent business or law purpose."28
Remittances to certain foreign countries may also be subject to sanctions under various federal statutes administered by the Treasury Department's Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC). The U.S. government only restricts remittances on countries, individuals, or companies that are subject to U.S. sanctions and embargoes. Furthermore, the Treasury Department does not have the authority to direct any financial institution to open or maintain a particular account or relationship. The decision to maintain any financial relationship is made by each financial institution itself, while complying with U.S. laws.
Regulatory efforts at the state level focus primarily on consumer protection. Separate from banking regulation and registration, most states have laws requiring that money transmitters be licensed by the state banking agency. Some of these states (usually those with significant immigrant populations) have specific licensing requirements for transmitters sending money to foreign countries. Of the 50 states, only a few states do not require state licenses for MSBs.
"Dodd-Frank" Measures
In response to concerns from U.S. immigrant communities raised during the 110th and 111th Congresses over inadequate disclosure of remittance fees and insufficient consumer protection for remittance transactions, Congress created new consumer protections as part of the Dodd Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act (Dodd Frank).29 The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) released on April 30, 2013, a final rule implementing the Dodd-Frank remittance provisions. The effective date of the Final Rule is October 28, 2013.
Under the new law (Section 1073 of Dodd-Frank), a remittance transfer provider must provide consistent, reliable disclosure of the price of a transfer, the amount of currency to be delivered to the recipient, and the date of availability prior to the consumer making any payment. The new requirements also increase consumer protections by requiring remittance providers to investigate disputes and remedy errors related to the transaction.
During the rulemaking process, remittance providers raised concerns about the feasibility of disclosing third-party fees and taxes, which are often unknown prior to the transaction's taking place, and the "error-resolution" provisions, given remittance providers' risk of loss and fraud due to remittance customers' providing incorrect information. To address industry concerns, the CFPB's Final Rule provides greater flexibility for remittance providers on the disclosure of third-party fees and taxes and exempts remittance providers from error remedy procedures due to errors made by the remittance customer, such as providing an incorrect account number for the recipient.30
While the new protections may decrease the cost of remittances over the long run by improving transparency and potentially increasing competition, short-run cost increases may be significant. The increased cost to remittance providers for maintaining up-to-date information on exchange and tax rates of receiving countries and fees charged by third parties may likely be passed on to their customers. The error remedy requirement may also expose remittance transfer providers to potential litigation resulting from fraudulent transactions.31 At the same time, costs for remittance transactions may increase since bank fee income is capped elsewhere.32
Issues for Congress
Key issues on remittances that Members of Congress may want to consider include the following:
Regulation of Remittances
Members may wish to explore the current federal and state regulatory regime for remittance providers and customers. Effective and proportional regulation of remittances can reduce corruption, enhance transparency, and facilitate a more robust business environment. Some observers, however, raise concerns about the costs for remittance providers (and subsequently consumers) of navigating the patchwork of banking and anti-money laundering regulation.33 According to the Federal Reserve:
[R]eports suggest that large depository institutions may be reducing or restricting correspondent banking relationships, which in turn may limit the ability of smaller depository institutions to provide remittance transfer services. Reports also suggest that depository institutions may be terminating the accounts of some nonbank payment providers that offer financial services to consumers, such as money services businesses. Without accounts at depository institutions, some nonbank payment providers may be unable to access the financial system and therefore may be unable to continue providing services, including remittance transfer services.34
Regarding licensing and supervision of remittance providers, recent reform proposals include assigning a single national regulator with responsibility for regulating the entire money transmission business or, at a minimum, increasing coordination and harmonization of state and federal rules on MSBs.35 There have been recent congressional efforts in this direction. For example, in the 111th Congress, Representative Spencer Bachus introduced H.R. 4331, The Money Services Business Compliance Facilitation Act of 2009, which would have established an office of MSB compliance in the U.S. Department of the Treasury, charged with ensuring that state and federal regulators coordinate standards for MSB licensing and registration.
Other legislation has been introduced and passed that aims to facilitate remittances services by making it easier for MSBs to comply with federal and state regulations. The Money Remittances Improvement Act of 2014 (, and ask whether these costs are unnecessarily high, resulting in an undue reduction in the provision of legitimate remittances.33
31 G20 Rome Leaders Declaration, https://www.g20.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/G20-ROME-LEADERS-DECLARATION.pdf.
32 World Bank Remittance Prices Worldwide Quarterly, September 2022. 33 See CRS Report R46486, Telegraphs, Steamships, and Virtual Currency: An Analysis of Money Transmitter
Congressional Research Service
10
Remittances: Background and Issues for Congress
In the past decade, legislation has sought to improve the efficiency of remittance regulation. The Money Remittances Improvement Act of 2014 (P.L. 113-156)P.L. 113-156), signed into law on August 8, 2014, allows federal regulators, including FinCEN and the IRS, to rely on examinations conducted by state financial supervisory agencies if (1) the category is required to comply with federal requirements, or (2) the state supervisory agency examines the category for compliance with federal requirements. According to Treasury, this legislation "should allow for better allocation of state and federal resources, better targeting of higher risk MSBs, and improved AML/CFT compliance across the [financial] industry."36
Others propose that U.S. policymakers should prioritizeTo date, state supervisory regimes for MBS are varied, and the framework for examining these institutions is likely less robust than, say, the existing supervisory regime for banking organizations.
Other proposals focus on prioritizing access to remittance services for communities with specific needs. This may mean more money for technical assistance to boost the capacity of poorly regulated jurisdictions; oneregulated foreign jurisdictions. One such example iswould be Somalia. In this case, the U.S. Treasury Department could help integrate Somali American MSBs into an ACH payment system; help improve training of MSBs to improve monitoring of their agents; and/or help Somalia regulate its payment systems.37
Members of Congress may wish to34
Congress may examine the impact of the current regulatory regime on the development of emerging payments systems for sending remittances, such as mobile, card, or internet-based modelsother systems like cryptocurrency. Some observers arguehave argued that current federal and state money transmission laws may be inappropriate for new and emerging payments systems.3835 Remittance payments already touch multiple regulatory agencies, and as mobile remittances services increase, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) and the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) will likely play an increasing role. Mobile carriers and other alternative providers are less familiar than MSBs with U.S. and international banking laws, and the lack of U.S. guidance or framework for mobile payments creates coverage, liability, and AML/CFT concerns that Congress may move to explore.39
Members may also pay special attention to the implementation of the "Dodd-Frank" consumer protections following their October 2013 implementation. On one hand, some argue that the new protections will drive down the cost of remitting by requiring greater transparency of fees associated with money transfers. Others argue that the costs of new systems and increased liability for transaction problems will raise costs and deter MSBs and financial institutions from providing remittance services.40
Promoting Remittances as a Development Tool
Members of Congress may consider whether U.S. government efforts on remittances should extend to influencing how they are spent. There are multiple viewpoints on the extent to which the U.S. government should promote remittances as a development tool. Many U.S. development aid officials, for example, are interested in understanding the economic impact of remittances on both the sending and receiving communities and in developing policies to help channel remittances to their most productive use. Others argue that the remittances are foremost an anti-poverty tool, and that policymakers should be cautious about placing too much emphasis on remittances as a development tool or even confusing remittances with foreign aid. Importantly, remittances are a private transaction, and thus any official policy efforts, they argue, should be narrowly focused on reducing the cost of remittance transactions and creating additional opportunities for labor migration.41
Remittances and U.S. Immigration Policy
Members may consider the interplay of U.S. remittance policy efforts and U.S. immigration policy. Some Members of Congress, however, have raised concerns that current customer identification policies, which do not require a remittance customer to provide documentation of legal U.S. immigration status, could undermine efforts to enforce U.S. immigration laws. In light of this concern, in the 114th Congress Senator David Vitter introduced, S. 79, Remittance Status Verification Act of 2015, which would require remittance providers to impose a 7% fine on any sender of remittances that is unable to provide documentation of their legal status under U.S. immigration laws. Other efforts to restrict the ability of migrants to send remittances have been passed at the state level. In 2009, Oklahoma became the first U.S. state to tax remittances.42 The Oklahoma remittance tax imposes a five-dollar minimum fee on a consumer making a wire transfer from a nondepository financial institution. For transactions of $500 or more, an additional 1% of the amount being sent is also charged. A consumer with tax liability to Oklahoma may claim a credit on their income tax return for the fees paid. Several states have considered measures nearly identical to the Oklahoma tax model including Georgia, Iowa, Kansas, Nebraska, Tennessee, Mississippi, and Texas.43
Some analysts argue, however, that restricting remittances through taxes or additional customer identification rules would not deter migration to the United States and would only drive remittances underground to informal methods of money transfer.44 In addition to increased AML/CFT risk related to informal money transfer systems, shifting remittance flows to informal channels may impede policy efforts to use remittances as a means to promote access to financial services.
Author Contact Information
Footnotes
| 1. |
United Nations, International Migrant Stock Dataset, September 17, 2019. |
| 2. |
Radford, Jynnah, Pew Research Center, Key Findings about U.S. Immigrants, June 17, 2019. |
| 3. |
Ibid. |
| 4. |
Dilip Ratha, Supriyo De, Sonia Plaza, Kirsten Schuettler, William Shaw, Hanspeter Wyss, Soonhwa Yi, "Migration and Remittances – Recent Developments and Outlook" Migration and Development Brief, World Bank, April 26, 2016. |
| 5. |
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) can be defined as cross-border investment by a resident entity in one economy with the objective of obtaining a lasting interest in an enterprise resident in another economy. |
| 6. | |
| 7. |
The IMF's Balance of Payments Yearbook includes annual aggregate and detailed time series for balance of payments and international investment position for countries. |
| 8. |
International Transactions in Remittances: Guide for Compilers and Users. Washington, DC: International Monetary Fund, 2009. |
| 9. |
Often regionally based, alternative remittance systems date back hundreds of years and were originally used to finance trade in regions where traveling with gold or other forms of payment was not safe. These systems go by various names including Hue (Vietnam), Fei-Ch'ien (China) Phei Kwan (Thailand) Hundi (South Asia), or Hui Kuan (Hong Kong). |
| 10. |
World Bank, Remittances Prices Worldwide Issue n. 31, September 2019. |
| 11. |
Ibid. |
| 12. |
Freund, Caroline and Spatafora, Nikola, "Remittances: Transaction Costs, Determinants and Informal Flows," World Bank Policy Research Working Paper 3704, 2005. |
| 13. |
The World Bank's bilateral remittances matrices are available at: http://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/migrationremittancesdiasporaissues/brief/migration-remittances-data. The World Bank uses two datasets to construct the Bilateral Remittance Matrix. The first is UN Population Division estimates of migrant stock by country of origin and destination, also used by this tool. The second dataset is remittance inflows data, constructed as the sum of three components in the IMF's Balance of Payments Statistics: (i) compensation of employees, (ii) workers' remittances, and (iii) migrants' transfers. A country's total remittance inflows in a given year are allocated to its emigrant stocks, adjusting for the migrant sending and receiving countries' per capita income. |
| 14. |
For example, a remittance-sender goes to a Western Union agent in Chicago to send money to her uncle in Brazil, who collects the funds from one of the more than 10,000 Western Union agents in Brazil. Since there are Western Union agents on both ends of the transaction, the transaction occurs outside the conventional banking system. |
| 15. |
Stored value is funds or monetary value represented in digital electronic format and stored or capable of storage on electronic media in such a way as to be retrievable and transferable electronically, such as a prepaid Visa gift card. |
| 16. |
Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, Report to the Congress on the Use of the ACH System and Other Payment Mechanisms for Remittance Transfers to Foreign Countries, May 2015. |
| 17. |
The European service includes Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, and United Kingdom. The Latin American service includes Argentina, Brazil, Columbia, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Peru, and Uruguay. The Latin American service, which only involves account-to-receiver ACH transfers, is in addition to the account-to-account service for Mexico. |
| 18. |
Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, Report to the Congress on the Use of the ACH System and Other Payment Mechanisms for Remittance Transfers to Foreign Countries, April 2013. |
| 19. |
Examples include Xoom (Global), Globe GCASH (Philippines) and Safaricom M-PESA (Kenya and Tanzania). |
| 20. |
Examples include iRemit Visa (Asia) and mPower Yap Card (Global). |
| 21. |
Examples include Regalo Pay (Central and South America) and WillStream (Africa). |
| 22. |
Examples include Azimo and Fastacash, which allow transfer between Facebook users. |
| 23. |
World Bank Consultative Group on the Poor (CGAP), CGAP Landscape Study on International Remittances through Branchless Banking, February 2012. |
| 24. |
Members of FATF are Argentina, Australia, Austria, Belgium, Brazil, Canada, China, Denmark, the European Commission, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, the Gulf Cooperation Council, Hong Kong, Iceland, India, Ireland, Italy, Japan, Korea, the Netherlands, Luxembourg, Mexico, New Zealand, Norway, Portugal, Russia, Singapore, South Africa, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey, the United Kingdom, and the United States. See CRS Report RS21904, The Financial Action Task Force: An Overview, by James K. Jackson. |
| 25. |
The Financial Action Task Force, The FATF Recommendations: International Standards on Combating Money Laundering and the Financing of Terrorism and Proliferation, February 2012. |
| 26. |
Ibid. |
| 27. |
Bank for International Settlements and the World Bank, General Principles for International Remittance Services, January 2007. |
| 28. |
Treasury/FinCEN Report to Congress in Accordance with Section 359 of the USA PATRIOT Act, Department of the Treasury, November 2002. |
| 29. |
For example, see: Remittances: Access, Transparency, and Market Efficiency: A Progress Report: Hearing before the House Committee on Financial Services, Subcommittee on Domestic and International Monetary Policy, Trade, and Technology., 110th Congress, May 17, 2007; and Remittances: Regulation and Disclosure in a New Economic Environment, Hearing before the House Committee on Financial Services, Subcommittee on Financial Institutions and Consumer Credit, 111th Congress, June 3, 2009. |
| 30. |
Habib, Azba, "A Summary of the Final Remittance Transfer Rule (Section 1073)," Retail Payments Risk Forum, May 2013. |
| 31. |
World Bank, Migration and Development Brief No. 19, November 20, 2012. |
| 32. |
For example, see CRS Report R41913, Regulation of Debit Interchange Fees, by Darryl E. Getter and CRS Report R42744, U.S. Implementation of the Basel Capital Regulatory Framework, by Darryl E. Getter. |
| 33. |
Clay Lowery and Vijaya Ramachandran, Unintended Consequences of Anti-Money Laundering Policies for Poor Countries, Center for Global Development, Washington, DC, 2015. |
| 34. |
Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, Report to the Congress on the Use of the ACH System and Other Payment Mechanisms for Remittance Transfers to Foreign Countries, May 2015. |
| 35. |
Watterson, Collin, "More Flies with Honey: Encouraging Formal Channel to Combat Money Laundering," Texas Law Review, Vol. 91, 2013. |
| 36. |
Daniel L. Glaser, Treasury's Work to Support Money Transmitters, U.S. Department of the Treasury, Treasury Notes, Washington, DC, August 10, 2014. |
| 37. |
Orozco, Manuel and Julia Yansura, "Keeping the Lifeline Open: Remittances and Markets in Somalia," Oxfam America, African Development Solutions, and the Inter-American Dialogue, July 2013. |
| 38. |
Tu, Kevin, "Regulating the New Cashless World," Alabama Law Review, Vol. 65, Issue 1, 2013. |
| 39. |
Mark E. Budnitz, The Legal Framework of Mobile Payments: Gaps, ambiguities, and overlap, Pew Charitable Trust, Washington, DC, February 10, 2016. |
| 40. |
Witkowski, Rachel, "How CPFB's Remittance Rule Will Reshape Global Money Transfers," American Banker, May 20, 2013. |
| 41. |
Rosser, Ezra. "Immigrant Remittances," Connecticut Law Review, Vol. 41, No. 1, November 2008. See also, Feibelman, Adam, "The Very Uneasy Case Against Remittances: An Ex Ante Perspective," North Carolina Law Review, Vol. 88, 2010. |
| 42. |
Cipriano, Meredith, "Comments: The Illegal Immigrant Tax: Evaluating State Remittance Taxes under the Dormant Commerce Clause and the Equal Protection Clause," University of Baltimore Law Review, vol. 43, no. 2 (Spring 2014). |
| 43. |
Cuevas-Mohr, Hugo. 2016. "The Taxing of Remittances in the US." IMTC |
| 44. |
Mohaptra, Sanket, "Taxing Remittances is not a good idea," World Bank, December 18, 2012. |