Background
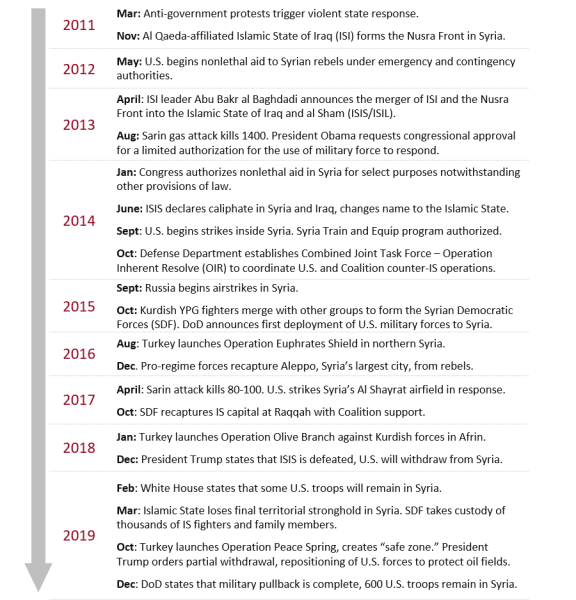
In March 2011, antigovernment protests broke out in Syria, which has been ruled by the Asad family for more than four decades. The protests spread, violence escalated (primarily but not exclusively by Syrian government forces), and numerous political and armed opposition groups emerged. In August 2011, President Barack Obama called on Syrian President Bashar al Asad to step down. Over time, the rising death toll from the conflict, and the use of chemical weapons by the Asad government, intensified pressure for the United States and others to assist the opposition. In 2013, Congress debated lethal and nonlethal assistance to vetted Syrian opposition groups, and authorized the latter. Congress also debated, but did not authorize, the use of force in response to an August 2013 chemical weapons attack.
In 2014, the Obama Administration requested authority and funding from Congress to provide lethal support to vetted Syrians for select purposes. The original request sought authority to support vetted Syrians in "defending the Syrian people from attacks by the Syrian regime," but the subsequent advance of the Islamic State organization from Syria across Iraq refocused executive and legislative deliberations onto counterterrorism. Congress authorized a Department of Defense-led train and equip program to combat terrorist groups active in Syria, defend the United States and its partners from Syria-based terrorist threats, and "promote the conditions for a negotiated settlement to end the conflict in Syria."
In September 2014, the United States began air strikes in Syria, with the stated goal of preventing the Islamic State from using Syria as a base for its operations in neighboring Iraq. In October 2014, the Defense Department established Combined Joint Task Force-Operation Inherent Resolve (CJTF-OIR) to "formalize ongoing military actions against the rising threat posed by ISIS in Iraq and Syria." CJTF-OIR came to encompass more than 70 countries, and has bolstered the efforts of local Syrian partner forces against the Islamic State. The United States also gradually increased the number of U.S. personnel in Syria from 50 in late 2015 to roughly 2,000 by late 2017.
President Trump in early 2018 called for an expedited withdrawal of U.S. forces from Syria,1 but senior Administration officials later stated that U.S. personnel would remain in Syria to ensure the enduring defeat of the Islamic State. Then-National Security Advisor John Bolton also stated that U.S. forces would remain in Syria until the withdrawal of Iranian-led forces.2 In December 2018, President Trump ordered the withdrawal of all U.S. forces from Syria, contributing to the subsequent decision by Defense Secretary James Mattis to resign, and drawing criticism from several Members of Congress. In early 2019, the White House announced that several hundred U.S. troops would remain in Syria.
As the Islamic State and armed opposition groups have relinquished territorial control over most of Syria since 2015, the Syrian government and its foreign partners have made significant military and territorial gains. The U.S. intelligence community's 2018 Worldwide Threat Assessment stated in February 2018 that the conflict had by that point "decisively shifted in the Syrian regime's favor, enabling Russia and Iran to further entrench themselves inside the country."3 Coalition and U.S. gains against the Islamic State came largely through the assistance of Syrian Kurdish partner forces, but neighboring Turkey's concerns about those Kurdish forces emerged as a persistent challenge for U.S. policymakers. In 2019, Turkey launched a cross border military operation attempting to expel Syrian Kurdish U.S. partner forces from areas adjacent to the Turkish border. In conjunction with the operation, President Trump ordered the withdrawal of some U.S. forces from Syria and the repositioning of others in areas of eastern Syria once held by the Islamic State group.
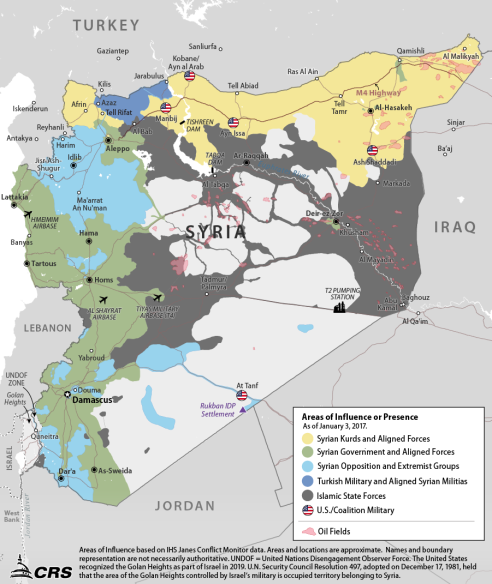
Territorial gains by the Syrian government have pushed remaining opposition forces (including Al Qaeda affiliates) into a progressively shrinking geographic space that is also occupied by roughly 3 million Syrian civilians. (Figure 3 and Figure 4 show how territory held by Syrian opposition forces was significantly reduced between 2017 and 2020.) The remaining opposition-held areas of Idlib province in northwestern Syria have faced intensified and ongoing Syrian government attacks since 2019.
The U.N. has sponsored peace talks in Geneva since 2012, but it appears unlikely that the parties will reach a political settlement that would result in a transition away from Asad. With many armed opposition groups weakened, defeated, or geographically isolated, military pressure on the Syrian government to make concessions to the opposition has been reduced. U.S. officials have stated that the United States will not fund reconstruction in Asad-held areas unless a political solution is reached in accordance with U.N. Security Council Resolution 2254.
 |
|
Sources: CRS using data from U.S. State Department; Esri; CIA, The World Factbook; and the United Nations. Note: On March 25, 2019, President Trump recognized the Golan Heights as part of the state of Israel. |
 |
|
Note: For more information, see CRS In Focus IF11080, Syria Conflict Overview: 2011-2018, by Carla E. Humud. |
Issues for Congress
Prior to the 2019 Turkish military incursion and U.S. withdrawal decisions, the 116th Congress had been considering the Administration's FY2020 requests for defense and foreign aid appropriations, which presumed continued counterterrorism, train and equip, and humanitarian operations in Syria. Members debated legislative proposals that would have extended and amended related authorities and made additional funding available to continue U.S. efforts, including stabilization programs. Following President Trump's withdrawal and redeployment decisions, Congress enacted revisions to the underlying authority for U.S. military train and equip efforts in Syria and appropriated additional funds to continue related operations.
During 2020, Congress may further consider what, if any, revised defense and foreign assistance needs may be appropriate in connection with revised U.S. plans and any forthcoming changes to U.S. military deployments in Syria or in neighboring Iraq. Similarly, Members may consider how, if at all, Congress should increase, decrease, or reallocate defense, humanitarian, and stabilization resources for FY2021 and what, if any, new or revised oversight mechanisms ought to be employed.
Specific issues for congressional consideration could include the following.
U.S. military operations and authorities
U.S. forces have operated inside Syria since 2015 pursuant to the 2001 and 2002 Authorizations for Use of Military Force (AUMF),4 despite ongoing debate about the applicability of these authorizations to current operations in Syria.5 In December 2018, President Trump declared the Islamic State "defeated," raising questions about the authorities underlying a continued U.S. military presence in Syria. Defense and State Department officials continue to highlight the ongoing threat posed by the Islamic State, including to the U.S. homeland.6 Islamic State attacks continue in areas of eastern Syria, and oversight reporting suggests that Administration officials believe the group could resurge if military pressure on its remnants lessens.7 Nevertheless, some observers have argued that some U.S. military outposts in Syria (such as the U.S. garrison at At Tanf) appear primarily designed to stem the flow of Iranian-backed militias into Syria.8
Future of U.S.-SDF Partnership
Following the October 2019 Turkish incursion into northern Syria, the U.S.-backed Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) sought protection from the Asad government. U.S. Special Representative for Syria Engagement and the Special Envoy to the Global Coalition to Defeat ISIS Ambassador James Jeffrey stated that the SDF and the Asad government reached "an agreement in some areas to coordinate."9 In December 2019, senior U.S. military officials acknowledged "dialogue" between the SDF and the Syrian military, but testified that U.S. forces continue to conduct combined operations with the SDF.10 U.S. officials have not publicly elaborated on the scale of coordination and/or dialogue between the Syrian military and the SDF, or on how this may impact U.S. interactions with, or funding for, the group.
|
Who are the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF)? Since 2014, U.S. armed forces have partnered with a Kurdish militia known as the People's Protection Units (YPG) to counter the Islamic State in Syria. In 2015, the YPG joined with other Syrian groups to form the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF), comprising the SDF's leading component. Turkey considers the YPG to be the Syrian branch of the PKK (Kurdistan Workers' Party), a U.S.-designated terror group that has waged a decades-long insurgency in Turkey. Ankara has strongly objected to U.S. cooperation with the SDF. U.S. officials have acknowledged YPG-PKK ties, but generally consider the two groups distinct.11 The Syrian Arab Coalition. Roughly 50 percent of the SDF is composed of ethnic Arab forces, according to U.S. officials;12 this component sometimes is referred to as the Syrian Arab Coalition (SAC). In 2018, the U.S. military assessed that the SAC probably is unable to conduct counter-IS operations on its own without the support of the SDF's primary component, the YPG.13 In 2020, the Defense Intelligence Agency (DIA) described the SAC as "a patchwork of Arab tribal militias, military councils, and former opposition groups recruited by the YPG initially as a 'symbolic' move to help attract western support and training."14 |
Security of U.S. Forces in Syria
Syrian government forces, with the support of Russia, have expanded their operations and presence in some areas of eastern Syria evacuated by U.S., Coalition, and SDF forces in 2019. The expanded presence of Syrian government forces in these areas may increase the potential for interactions between remaining U.S. personnel and Syrian or Russian forces, with uncertain implications for force protection and potential conflict. The Syrian government continues to refer to U.S. forces as occupiers and has warned that "resistance" forces might target U.S. personnel.15 Syrian officials have specifically called for the United States to end what they describe as the "illegal" presence of U.S. forces at Syrian oilfields.16 The Defense Department has stated that U.S. forces in Syria maintain "the inherent right to self-defense against any threat, includ[ing] while securing the oil fields."17 President Trump has stated that, "we may have to fight for the oil. It's okay. Maybe somebody else wants the oil, in which case they have a hell of a fight."18 Vice President Pence has stated that U.S. troops in troops in Syria will "secure the oil fields so that they don't fall into the hands of either ISIS or Iran or the Syrian regime."19 In February 2020, pro-regime forces manning a checkpoint in Qamishli opened fire on Coalition forces conducting a patrol; no Coalition injuries were reported.20
In early 2020, media reports highlighted increasingly frequent "standoffs" between U.S. and Russian personnel along highways in northeast Syria.21 U.S. officials have described these incidents as occurring along a road that is shared by U.S., Russian, and Syrian forces operating in adjacent areas of the northeast, particularly around Qamishli.22 Ambassador Jeffrey has stated that, on a limited number of occasions, Russian personnel have "tried to come deep into the area where [the United States] and the SDF are patrolling, well inside the basic lines that we have sketched, not right along the borders. Those are the ones that worry me."23 CJTF-OIR has reported that "although established de-confliction procedures exist, both Russia and the United States have limited options for enforcement if a party violates protocols, which could lead to increased risk to force protection and the potential for unintended escalation or miscalculation."24
Syria Provisions in FY2020 Defense and Foreign Operations Legislation
FY2020 National Defense Authorization Act (P.L. 116-92)
The FY2020 NDAA (P.L. 116-92) extends the Syria Train and Equip program's authority until the end of 2020, and modifies the program's purposes. Changes under Section 1222 of the act include
- specifying the program's beneficiaries to include "appropriately vetted Syrian groups and individuals," striking previous language referencing Syrian opposition forces;25
- amending the program objectives to include securing territory formerly controlled by the Islamic State and supporting the temporary detention and repatriation of IS detainees;
- eliminating some of the details previously reported to congressional committees (such as the concept of operations, timelines, and types of training, equipment, stipends, sustainment, construction, and supplies to be required), while preserving broader reporting requirements on the goals and objectives of authorized assistance, and on the number and role of U.S. military personnel involved;
- removing the previously existing requirement for the Defense Department to use prior approval reprogramming procedures to obligate funds for the Syria T&E program and substituting a more frequent prior notification system (requiring reports no later than 15 days before the expenditure of each 10 percent increment of FY2019 and FY2020 funds);
- adding new reporting requirements on (1) the relationship between program recipients and civilian governance authorities; (2) U.S. stabilization activities in IS-liberated areas; and (3) IS detainees held by vetted Syrian groups; and
- restricting the provision of U.S. weapons to small arms.
Section 1224 of the act requires the president to identify or designate a senior-level coordinator responsible for the long-term disposition of IS members currently in SDF custody. The congressionally mandated Syria Study Group highlighted the lack of such a coordinator in its September 2019 final report.
The Syria Civilian Protection Act of 2019
The FY2020 NDAA also incorporates the Caesar Syria Civilian Protection Act of 2019 (Title LXXIV). Section 7411 of the act requires the Secretary of the Treasury to make a determination within 180 days of enactment on whether the Central Bank of Syria is a financial institution of primary money laundering concern. If so, the Secretary would be required to impose one or more of the special measures described in Section 5318A(b) of title 31, United States Code, with respect to the Central Bank of Syria.
Section 7412 directs the President to impose sanctions on any foreign person who the President determines is knowingly providing significant financial, material, or technological support to the government of Syria or to a foreign person operating in a military capacity inside Syria on behalf of the governments of Syria, Russia, or Iran. It also makes eligible for sanctions foreign persons who knowingly sell or provide (1) goods, services, technology, or information that significantly facilitates the maintenance or expansion of the government of Syria's domestic production of natural gas, petroleum, or petroleum products; (2) aircraft or spare aircraft parts that are used for military purposes in Syria in areas controlled by the Syrian government or associated forces;( 3) significant construction or engineering services to the government of Syria.
Section 7413 requires the President to determine the areas of Syria controlled by the governments of Syria, Iran, and Russia, and to submit a strategy to deter foreign persons from entering into contracts related to reconstruction in those areas. The bill includes several suspension and waiver authorities for the President, including for nongovernmental organizations providing humanitarian assistance. Its provisions would expire five years after the date of enactment.
Further Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2020 (P.L. 116-94)
The FY2020 State and Foreign Operations Appropriation Act (Division G of the Further Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2020, P.L. 116-94) contains several Syria-related provisions:
- Section 7033(c) makes ESF funds available notwithstanding any other provision of law for assistance for ethnic and religious minorities in Iraq and Syria.
- Section 7035(a) makes NADR funds available for the Counterterrorism Partnerships Fund (CTPF) for programs in areas liberated from the Islamic State.
- Section 7041(i) makes not less than $40 million in ESF, INCLE, and PKO funds appropriated by this act available, notwithstanding any other provision of law, for nonlethal stabilization assistance for Syria—of which, not less than $7 million shall be made available for emergency medical and rescue response, and chemical weapons use investigations. These funds may not be used for activities that support Iran or Iranian proxies, or that further the strategic objectives of Russia. They also may not be used in areas of Syria controlled by the Asad government or associated forces.
- Section 7065(a) states that not less than $200 million of funds appropriated under ESF, INCLE, NADR, PKO, and FMF shall be made available for the Relief and Recovery Fund for assistance for areas liberated or at risk from, or under the control of, the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria, other terrorist organizations, or violent extremist organizations, including for stabilization assistance for vulnerable ethnic and religious minority communities affected by conflict.
- This section also states that, of the funds made available for the Relief and Recovery Fund, not less than $10 million shall be made available for programs to promote accountability for genocide, crimes against humanity, and war crimes, including in Iraq and Syria.
- Title V of the bill, known as the Global Fragility Act of 2019, establishes a new fund titled the Prevention and Stabilization Fund, and authorizes $200 million to be appropriated to the fund for each of the fiscal years 2020 through 2024. These funds are authorized be used to support stabilization of conflict affected areas, and to provide assistance to areas liberated from the Islamic State or other terrorist organizations—as well as to support vulnerable ethnic and religious minority communities affected by conflict. This new fund will replace the Relief and Recovery Fund designation applied in recent appropriations acts.
Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2020 (P.L. 116-93)
The Department of Defense Appropriations Act, 2020 (Division A of the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2020, P.L. 116-93 ) makes $1.195 billion in the Counter ISIS Train and Equip Fund (CTEF) available to counter the Islamic State globally, including to provide training, equipment, logistics support, infrastructure repair, and sustainment to countries or irregular forces engaged in counter-IS activities. No specific amount is designated for Syria in the act, but the accompanying explanatory statement allocates $200 million for Syria programs, $100 million less than the Administration's request. Section 9019 states that no funds made available by the act may be used for the "introduction of United States armed or military forces into hostilities in Syria, into situations in Syria where imminent involvement in hostilities is clearly indicated by the circumstances, or into Syrian territory, airspace, or waters while equipped for combat."
Syria-Related Legislation in the 116th Congress
Special Immigrant Status for U.S. Partner Forces26
The October 2019 Turkish military incursion into northern Syria targeted Syrian Kurdish forces that had worked closely with the United States to secure the territorial defeat of ISIS. The same month, three bills were introduced that would each establish a special immigrant visa (SIV) program for certain Syrians27 who had worked with U.S. military forces or the U.S. government. These programs would provide a new avenue under the U.S. immigration system for eligible individuals to be considered for admission to the United States. Upon admission, these individuals would become U.S. lawful permanent residents. Although the particular criteria in the three proposed SIV programs differ, all three would require applicants to obtain a favorable recommendation regarding their work with the U.S. government and be determined to be admissible to United States, which requires clearance of background checks and security screening, among other screening. All three programs would be subject to annual numerical limits, which would apply to the principal applicants but not to their accompanying spouses or children.
Syrian Allies Protection Act (S. 2625). Introduced by Senator Warner, the bill would authorize the Secretary of Homeland Security to provide special immigrant status to a Syrian national who had worked directly with U.S. military forces as a translator or in another role deemed "vital to the success of the United States military mission in Syria," as determined by the Secretary of Defense, for a period of at least six months between September 2014 and October 2019. Applicants would need to obtain a written recommendation from a general or flag officer. The SIV program would be capped at 250 principal applicants per fiscal year.
Syrian Partner Protection Act (H.R. 4873). Introduced by Representative Crow, the bill would authorize the Secretary of Homeland Security to provide special immigrant status to a Syrian national or stateless person habitually residing in Syria who worked for or with the U.S. government in Syria "as an interpreter, translator, intelligence analyst, or in another sensitive and trusted capacity" for an aggregate period of not less than one year after January 2014. The individual's "service to United States efforts against the Islamic State" would need to be documented in a positive recommendation or evaluation. The SIV program, which would be temporary, would be capped at 4,000 principal applicants per year for five fiscal years.
Promoting American National Security and Preventing the Resurgence of ISIS Act of 2019 (S. 2641). Section 203 of S. 2641, as reported by the Senate Foreign Relations Committee, would authorize the Secretary of Homeland Security to provide special immigrant status to a Syrian or stateless Kurd habitually residing in Syria who is or was employed by or on behalf of the U.S. government "in a role that was vital to the success of the United States' Counter ISIS mission in Syria," as determined by the Secretary of State in consultation with the Secretary of Defense. The individual must have been so employed for a period of at least one year after January 2014 and must obtain a favorable written recommendation from a senior supervisor. In addition, the applicant must have experienced or must be "experiencing an ongoing serious threat as a consequence of the alien's employment by the United States Government." The SIV program would be capped at 400 principal applicants per fiscal year.
The Syrian SIV programs proposed by these bills are generally modeled on the existing temporary SIV programs for Iraqis and Afghans who have worked for or on behalf of the U.S. government, although there are some key differences. For example, under both the Iraqi and Afghan SIV programs, the recommendation or evaluation (attesting to valuable service) that an applicant is required to submit must be accompanied by approval from the appropriate Chief of Mission. The Syrian SIV bills would not require applicants to obtain Chief of Mission approval, although S. 2641 would require an applicant's recommendation to be approved by a senior foreign service officer designated by the Secretary of State. S. 2641 is also the only one of the three bills to require an applicant to show that he or she has experienced or is experiencing a serious threat as a result of employment by the U.S. government; this is a requirement under both the Iraqi and Afghan SIV programs. In addition, all three Syrian SIV bills include provisions that do not have counterparts under the Iraqi and Afghan programs that would provide for the protection or relocation of applicants who are in imminent danger or whose lives or safety are at risk.
No Assistance for Assad Act (H.R. 1706)
Introduced in March 2019 by Representative Engel, the bill would state that it is the policy of the United States that U.S. foreign assistance made available for reconstruction or stabilization in Syria should only be used in a democratic Syria or in areas of Syria not controlled by the Asad government or aligned forces. Reconstruction and stabilization aid appropriated or otherwise available from FY2020 through FY2024 could not be provided "directly or indirectly" to areas under Syrian government control—as determined by the Secretary of State—unless the President certifies to Congress that the government of Syria has met a number of conditions. These include ceasing air strikes against civilians, releasing all political prisoners, allowing regular access to humanitarian assistance, fulfilling obligations under the Chemical Weapons Convention, permitting the safe and voluntary return of displaced persons, taking steps to establishing meaningful accountability for perpetrators of war crimes, and halting the development and deployment of ballistic and cruise missiles. The House passed an earlier version of the bill during the 115th Congress.
By noting restrictions on U.S. aid provided "directly or indirectly," the bill also would limit U.S. funds that could flow into Syria via multilateral institutions and international organizations, including the United Nations, the International Monetary Fund, and the World Bank. The bill would permit exceptions to the above restrictions on aid to government-held areas for humanitarian projects, "projects to be administered by local organizations that reflect the aims, needs, and priorities of local communities," and projects that meet basic human needs including drought relief; assistance to refugees, IDPs, and conflict victims; the distribution of food and medicine; and the provision of health services.
Military Developments
Turkish Incursion into Northern Syria
On October 9, 2019, Turkey's military (and allied Syrian opposition groups) entered northeastern Syria in a military operation targeting Kurdish People's Protection Unit (YPG) forces. Known as Operation Peace Spring (OPS), the Turkish operation followed a call between President Trump and Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdogan. After the phone call, President Trump ordered a pullback of U.S. forces from the area of the anticipated Turkish incursion. (28 Special Forces Green Berets located along Turkey's initial "axis of advance" were withdrawn prior to the Turkish operation.)28 This drew accusations among many, including some Members of Congress, that the Administration had offered a tacit "green light," to the Turkish operation, a charge strongly denied by Administration officials who described the U.S. decision to withdraw forces as a matter of personnel safety.29 President Trump said in a statement, "The United States does not endorse this attack and has made it clear to Turkey that this operation is a bad idea."30
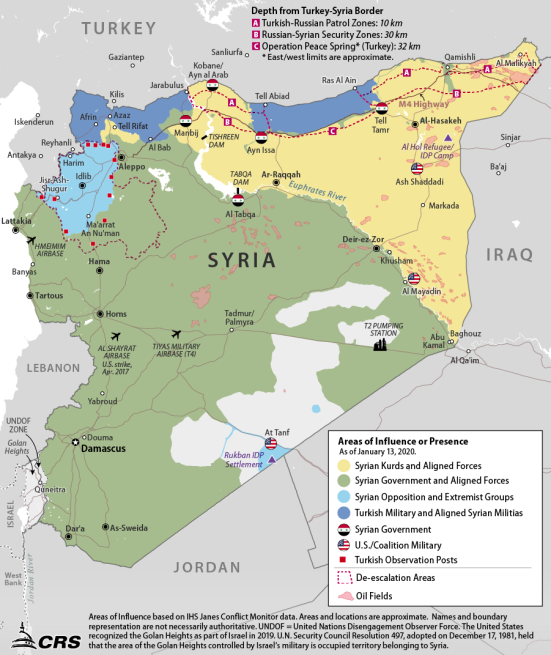
A subsequent U.S.-brokered ceasefire in mid-October allowed for the withdrawal of SDF forces from the Turkish zone of incursion, roughly corresponding to the area between the towns of Tell Abiad and Ras al Ayn (see Figure 5). It also created a Turkish "safe zone" stretching between the two towns, extending to a depth of 32km inside Syria. Separately, Turkey and Russia negotiated security zones east and west of the OPS area, from which SDF forces were also expected to withdraw (to a depth of 30km from the border). These latter areas are being patrolled by a mix of Turkish, Russian, and Syrian forces.
|
As of January 13, 2020 |
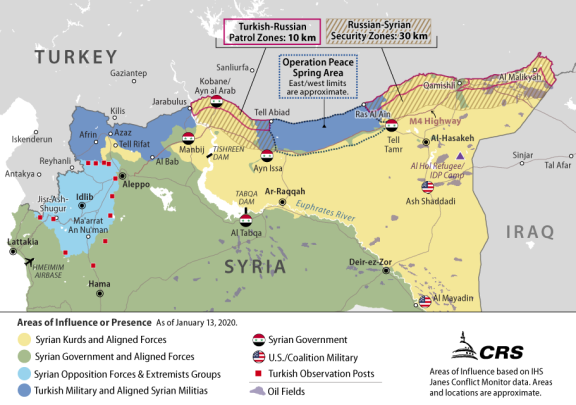 |
|
Source: CRS, using areas of influence data from IHS Conflict Monitor. Note: This map does not depict precisely or comprehensively all U.S. bases or operating locations in Syria. |
According to U.S. military sources, the Turkish operation "set in motion a series of actions that affected the Operation Inherent Resolve (OIR) mission against the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS); the U.S. relationship with the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF), the United States' most reliable partner in Syria; and the control of territory in northeastern Syria."31 Similarly, Ambassador Jeffrey testified that the Turkish incursion was launched despite U.S. objections, "undermining the D-ISIS campaign, risking endangering and displacing civilians, destroying critical civilian infrastructure, and threatening the security of the area. Turkey's military actions have precipitated a humanitarian crisis and set conditions for possible war crimes."32
Ultimate Turkish and YPG objectives regarding the areas in question remain unclear. Since late October, Turkish-led fighters have periodically skirmished against YPG or Syrian government forces in places outside the areas under nominal Turkish control.33 Turkish officials also have blamed Kurdish forces for car bomb and land mine attacks in Turkish-held areas, some of which have caused civilian casualties.34
As a result of the Turkish operation, SDF operations against the Islamic State were temporarily paused, as was U.S. training for the SDF in areas affected by the Turkish incursion.35 U.S. forces withdrew from outposts in northern Syria (including Manbij and Ayn Issa); Syrian and Russian forces moved in "to fill the void created by departing U.S. forces."36 The State Department also moved its Syria Transition Assistance Team personnel inside Syria (START-Forward) out of the country. In the same period, the SDF redoubled its dialogue with the Asad government and reached an agreement to coordinate in some areas. As of December 2019, U.S. military officials testified that, "[ ... ] we continue combined operations with the Syrian Democratic Forces in order to complete the enduring defeat of ISIS and prevent their reemergence."37
Islamic State: Ongoing Threats
In March 2019, the Islamic State lost its final territorial stronghold in Syria, as a result of Coalition operations in partnership with the SDF. Since then, U.S. military officials have warned that the group is defeated but not eliminated, and that it continues to pose a significant threat to local and regional stability. A U.S. airstrike in October 2019 killed IS leader Abu Bakr al Baghdadi in Syria's northwest province of Idlib. Abu Ibrahim al-Hashemi al-Qurayshi was named as Baghdadi's successor; little is publicly known about him. CENTCOM Commander Gen. Kenneth McKenzie stated that while Baghdadi's death may cause a slight disruption to the Islamic State's activities, "ISIS is first and last an ideology, so we are under no illusions that it's going to go away just because we killed Baghdadi."38
President Trump's announcement in October 2019 that all U.S. forces would withdraw from northern Syria, triggered warnings about the potential for an IS resurgence. In January 2020, U.S. officials estimated that the Islamic State retained about 14,000-18,000 IS fighters active between Syria and Iraq—similar to estimates provided in mid-2019.39
The October 2019 OIG Inspector General Report on Operation Inherent Resolve stated that, "With SDF and Coalition operations against ISIS in Syria diminished, U.S. military, intelligence, and diplomatic agencies warned that ISIS was likely to exploit the reduction in counterterrorism pressure to reconstitute its operations in Syria."40 According to the report, the Defense Intelligence Agency (DIA) assessed that a reduction in counterterrorism pressure "will provide the group with time and space to expand its ability to conduct transnational attacks targeting the West."41 The withdrawal announcement has since been modified to allow for the continued deployment of roughly 600 U.S. forces to Syria.
Prior to the Turkish incursion, U.S. and Coalition forces had been training and equipping the SDF and other partner forces to enable them to hold territory and conduct counterinsurgency operations against the Islamic State in northeast Syria. CJTF-OIR reported that as of the end of fourth quarter of FY2019, the SDF remained in need of additional personnel, training, and equipment to conduct counterinsurgency operations against the Islamic State. As noted above, in December 2019, Congress modified existing authorities for train and equip activities in Syria and appropriated an additional $200 million for related Syria programs.
Islamic State Detainees
The capture of the final Islamic State stronghold in Syria in March 2019 led to the surrender of thousands of IS fighters, as well as their spouses and children. Since then, the SDF has retained custody of roughly 10,000 IS militants (including approximately 2,000 foreign fighters) at several makeshift prisons in northern Syria. Wives and children of IS fighters (some of whom also may be radicalized) are held at separate IDP camps. The largest of these is Al Hol, which houses about 66,000 individuals, 96% of whom are women or children.42 Media reports suggest that the Islamic State continues to operate and recruit within the camp.43
The SDF has stated that it is unable to assume long-term responsibility for IS detainees and their families, and the United States has urged countries to repatriate their citizens. To date, many countries have been reluctant to do so, citing concerns about their inability to prosecute or successfully monitor individuals who may have been radicalized. Some countries also have stripped IS fighters and/or family members of their citizenship.
The security of facilities housing IS fighters and family members continues to be a significant concern. The Islamic State has urged its followers to free IS detainees, and U.S. military assessments have noted that the SDF is unable to provide more than "minimal security" at Al Hol.44 At the same time, humanitarian conditions within detention facilities such as Al Hol are dire. According to the Kurdish Red Crescent, at least 517 people, mostly children, died inside the Al Hol camp in 2019, due to malnutrition, inadequate healthcare for newborns, and hypothermia.45
Idlib: The Final Opposition Stronghold
Armed Syrian opposition groups first captured Idlib province in 2015, and as of 2020 roughly half the province remains under opposition control (see Figure 3). An estimated 3 million people reside in Idlib; including several thousand Al Qaeda-linked fighters.46 In 2019, the Syrian government escalated military operations in Idlib; in 2020 these operations reportedly have been bolstered by Russian, Iranian, and Hezbollah forces.47
The ongoing military offensive in Idlib has generated what U.N. officials have described as a "humanitarian catastrophe,"48 with over half a million people having fled their homes between 1 December 2019 and 2 February 2020 as a result of ongoing hostilities.49 An estimated 400,000 people previously had been displaced from southern Idlib and northern Hama between April and August 2019.50 The U.N. has estimated that 80 percent of those recently displaced are women and children.51
Al Qaeda in Idlib
U.S. officials in 2017 described Idlib as "the largest Al Qaeda safe haven since 9/11,"52 and Administration officials continue to describe the province as "a major terrorist concern."53 U.S. initiatives in Idlib aimed at countering violent extremism (CVE) were halted in May 2018 as part of a broader withdrawal of U.S. assistance to northwest Syria.54 In January 2019, the Al Qaeda-linked group Haya't Tahrir al Sham (HTS) seized large areas of Idlib province from rival armed groups. In early 2019, the U.S. intelligence community also highlighted another Al Qaeda-linked group in Syria known as Hurras al Din ("Guardians of Religion", HD). While HTS and HD have occasionally clashed in Idlib, some analysts have assessed that the two groups "serve different functions that equally serve al-Qa`ida's established objectives: one [HD] appeals to hardened jihadis with an uncompromising doctrine focused on jihad beyond Syria and one [HTS] appeals to those focused on the Syrian war."55
In February 2019, the two groups signed an accord pledging broader cooperation.56 In June and August of 2019, CENTCOM announced two U.S. strikes against "al-Qaida in Syria (AQ-S) leadership" in Aleppo and Idlib provinces, respectively.57 The second strike
targeted AQ-S leaders responsible for attacks threatening U.S. citizens, our partners, and innocent civilians. [ ... ] Northwest Syria remains a safe haven where AQ-S leaders actively coordinate terrorist activities throughout the region and in the West.58
In September 2019, the U.S. government named Hurras al Din as a Specially Designated Global Terrorist entity pursuant to Executive Order 13224, as amended by Executive Order 13886.
Al Qaeda-Islamic State Links in Idlib
In October 2019, Islamic State leader Abu Bakr al Baghdadi was killed in a U.S. strike in the village of Barisha in northern Idlib province. Baghdadi appears to have sought protection from the AQ-affiliated Hurras al Din—dominant in that area of Idlib—despite the fact that other senior IS and AQ leaders have been rivals and their forces have, at times, been adversaries.59 Prior to the Islamic State's territorial defeat in March 2019, some IS members had requested safe passage to Idlib from SDF and coalition forces in exchange for the return of captured SDF personnel.60
Political Negotiations
The Geneva Process
Since 2012, the Syrian government and opposition have participated in U.N.-brokered negotiations under the framework of the Geneva Communiqué. Endorsed by both the United States and Russia, the Geneva Communiqué calls for the establishment of a transitional governing body with full executive powers. According to the document, such a government "could include members of the present government and the opposition and other groups and shall be formed on the basis of mutual consent."61 The document does not discuss the future of Asad.
Subsequent negotiations have made little progress, as both sides have adopted differing interpretations of the agreement. The opposition has said that any transitional government must exclude Asad.62 The Syrian government maintains that Asad was reelected (by referendum) in 2014, and notes that the Geneva Communiqué does not explicitly require him to step down. In the Syrian government's view, a transitional government can be achieved by simply expanding the existing government to include members of the opposition. Asad continues to state that a comprehensive solution to the current conflict must begin by "striking at terrorism" (which his government defines broadly to include most opposition groups) and by ending external interference in Syria.63
As part of the Geneva Process, U.N. Security Council Resolution (UNSCR) 2254, adopted in 2015, endorsed a "road map" for a political settlement in Syria, including the drafting of a new constitution and the administration of U.N.-supervised elections. U.S. officials continue to stress that a political solution to the conflict must be based on the principles of UNSCR 2254.
While the United States continues to call for a political settlement to the conflict, the U.S. intelligence community since 2018 has assessed that Asad is "unlikely to negotiate himself from power"64 or make meaningful concession to the opposition:
The regime's momentum, combined with continued support from Russia and Iran, almost certainly has given Syrian President Bashar al-Asad little incentive to make anything more than token concessions to the opposition or to adhere to UN resolutions on constitutional changes that Asad perceives would hurt his regime.65
In October 2019, Ambassador Jeffrey testified that the United States continues to support U.N.-led political negotiations in Geneva pursuant to UNSCR 2254.66 State Department officials have identified three points of leverage that the United States and its foreign partners could use to encourage the Asad regime to accept a political settlement: the withholding of reconstruction assistance, barring Syria's re-entry into the Arab League, and refusing to restore diplomatic relations with Damascus.67
The United States has repeatedly expressed its view that Geneva should be the sole forum for a political settlement to the Syria conflict, possibly reflecting concern regarding the Russia-led Astana Process (see below). However, the United States supported efforts by the U.N. Special Envoy for Syria to stand up a Syrian Constitutional Committee, an initiative originally stemming from the Russian-led Sochi conference in January 2018 (see below).68 In December 2018, Norwegian diplomat Geir Pederson succeeded Staffan de Mistura as U.N. Special Envoy for Syria. In September 2019, Pederson announced the successful formation of the Syrian Constitutional Committee. Pederson stated that the committee would be facilitated by the United Nations in Geneva (see "Constitutional Committee," below).69
The Astana Process
Since January 2017, peace talks hosted by Russia, Iran, and Turkey have convened in the Kazakh capital of Astana. These talks were the forum through which three "de-escalation areas" were established—two of which have since been retaken by Syrian military forces. The United States is not a party to the Astana talks but has attended as an observer delegation.
Russia has played a leading role in the Astana process, which some have described as an alternate track to the Geneva process. The United States has strongly opposed the prospect of Astana superseding Geneva. Following the release of the Joint Statement by President Trump and Russian President Putin on November 11, 2017 (in which the two presidents confirmed that a political solution to the conflict must be forged through the Geneva process pursuant to UNSCR 2254), U.S. officials stated that
We have started to see signs that the Russians and the regime wanted to draw the political process away from Geneva to a format that might be easier for the regime to manipulate. Today makes clear and the [Joint Statement] makes clear that 2254 and Geneva remains the exclusive platform for the political process.70
In January 2018, Russia hosted a "Syrian People's Congress" in Sochi, in which participants agreed to form a constitutional committee comprising delegates from the Syrian government and the opposition "for drafting of a constitutional reform," in accordance with UNSCR 2254.71 The conference was boycotted by most Syrian opposition groups and included mainly delegates friendly to the Asad government.72 The statement noted that final agreement regarding the mandate, rules of procedure, and selection criteria for delegates would be reached under the framework of the Geneva process.
Constitutional Committee. The committee, whose formation took nearly two years, consists of 150 delegates—50 each representing the Syrian government and the Syrian opposition, as well as a "middle third" list comprising 50 Syrian-national delegates selected by the U.N. from among the country's legal experts, civil society members, political independents, and tribal leaders. The committee includes a limited number of Kurds but does not include representatives from the YPG, the SDF or the SDF's political wing—the Syrian Democratic Council, SDC—which administer large areas of northern Syria.73 The committee met for the first time in Geneva in October 2019, where it formed a smaller 45-member Constitution-drafting group. The current Syrian constitution was approved in a February 2012 referendum, replacing the constitution that had been in place since 1973.
Humanitarian Situation
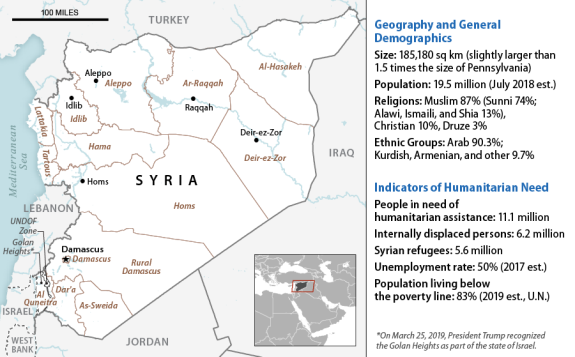
As of early 2020, more than 11.1 million people in Syria are in need of humanitarian assistance, 6.2 million Syrians are internally displaced, and an additional 5.6 million Syrians are registered with the U.N. High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) as refugees in nearby countries.74 The U.N. Secretary-General regularly reports to the Security Council on humanitarian issues and challenges in and related to Syria pursuant to Resolutions 2139 (2014), 2165 (2014), 2191 (2014), 2258 (2015), 2332 (2016), 2393 (2017), 2401 (2018), and 2449 (2018).75
Cross-Border Aid Endangered
The Syrian government has long opposed the provision of humanitarian assistance across Syria's border and across internal lines of conflict outside of channels under Syrian government control. Successive U.N. Security Council resolutions have nevertheless authorized the provision of such assistance. UNSCR 2449 authorized cross-border and cross-line humanitarian assistance until January 10, 2020. Russia and China abstained in the December 2018 vote that approved the resolution, and the Russian representative argued at the time that "new realities ... demand that [the mandate] be rejiggered with the ultimate goal of being gradually but inevitably removed."76
On December 20, 2019, Russia and China vetoed a U.N. Security Council resolution that would have renewed the authorization enabling U.N. agencies to deliver aid into Syria from two points in Turkey and one in Iraq for another 12 months. U.N. officials warned that without cross-border operations, "we would see an immediate end of aid supporting millions of civilians."77 On January 10, the Security Council approved Resolution 2504, re-authorizing cross border aid into Syria via two of the four existing border crossings—Bab al Salam and Bab al Hawa, both in Turkey—for a period of six months (rather than one year). The continued use of border crossings at Ramtha (Jordan) and Al Yarubiyah (Iraq) was not authorized.78
U.S. Humanitarian Funding
The United States is the largest donor of humanitarian assistance to the Syria crisis, drawing from existing funding from global humanitarian accounts and some reprogrammed funding.79 As of December 2019, total U.S. humanitarian assistance for the Syria crisis since 2011 had reached nearly $10.5 billion.80 These funds have gone towards meeting humanitarian needs inside Syria, as well as towards support for communities in Lebanon, Jordan, Turkey, Iraq, and Egypt that host Syrian refugees.81
International Humanitarian Funding
Multilateral humanitarian assistance in response to the Syria crisis includes both the Regional Refugee and Resilience Plan (3RP) and the Humanitarian Response Plan (HRP). The 3RP is designed to address the impact of the conflict on Syria's neighbors, and encompasses the Lebanon Crisis Response Plan, the Jordan Response Plan, and country chapters in Turkey, Iraq, and Egypt. It includes a refugee/humanitarian response coordinated by UNHCR and a "resilience" response (stabilization-based development assistance) led by the U.N. Development Program (UNDP).82
In parallel to the 3RP, the HRP for Syria is designed to address the crisis inside the country through a focus on humanitarian assistance, civilian protection, and increasing resilience and livelihood opportunities, in part by improving access to basic services. This includes the reconstruction of damaged infrastructure (water, sewage, electricity) as well as the restoration of medical and education facilities and infrastructure for the production of inputs for sectors such as agriculture.83
The 2019 3RP appeal sought $5.5 billion and the HRP for Syria sought $3.3 billion, on par with previous years. The 2020 requirements have not yet been finalized.
U.S. Policy
Since 2011, U.S. policy toward the unrest and conflict in Syria has attempted to pursue parallel interests and manage interconnected challenges, with varying degrees of success. Among the objectives identified by successive Administrations and by many Members in successive sessions of Congress have been
- supporting Syrian-led efforts to demand representative, accountable, and effective governance;
- seeking a negotiated settlement that includes a transition in Syria away from the leadership of Bashar al Asad and his supporters;
- limiting or preventing the use of military force by state and nonstate actors against civilian populations;
- mitigating transnational threats posed by Syria-based Islamist extremist groups;
- meeting the humanitarian needs of internally and externally displaced Syrians;
- preventing the presence and needs of Syrian refugees from destabilizing neighboring countries;
- limiting the negative effects of other third party interventions on regional and international balances of power; and
- responding to and preventing the use of chemical weapons.
As Syria's conflict has changed over time from civil unrest to nationwide military conflict involving multiple internal and external actors to the apparent resurgence of the Asad government, the policies, approaches, and priorities of the United States and others also have changed. The United States and its Syrian and regional partners have not succeeded in inducing or compelling Syrian President Bashar al Asad to leave office or secured a fundamental reorientation of Syria's political system as part of a negotiated settlement process. The United States continues to advocate for an inclusive negotiated solution, but has largely acquiesced to Asad's resumption of political and security control. Forceful interventions in Syria by Russia, Iran, Turkey, the United States, and Israel have created a fundamentally different set of calculations for policymakers to consider relative to those that prevailed prior to the conflict.
|
Syria Study Group Findings and Recommendations In September 2019, the congressionally mandated Syria Study Group (SSG) released its final report and recommendations. The group's principal findings were as follows (direct quotations):
The group's principal recommendations were as follows:
|
Trump Administration Statements on Syria Policy
Since 2018, U.S. policy in Syria has sought three primary goals: the enduring defeat of the Islamic State, a political settlement to the Syria conflict pursuant to UNSCR 2254, and the withdrawal of Iranian-backed forces.84 The October 2019 Turkish military incursion into northern Syria and subsequent withdrawal and/or repositioning of the bulk of U.S. forces in the country raised questions about whether U.S. policy in Syria had (or would) shift. In late October 2019, Ambassador Jeffrey confirmed that previously articulated U.S. goals for Syria remained U.S. policy.85 When asked whether the enduring defeat of the Islamic State could be accomplished without ground forces, Jeffrey stated, "We need ground forces. They do not necessarily have to be American."86
In December 2019, Defense Secretary Mark Esper stated that, "The United States strategy in the Middle East seeks to ensure the region is not a safe haven for terrorists, is not dominated by any power hostile to the United States and contributes to a stable global energy market."87 Esper added that the overarching U.S. goal with regard to Syria is to support a U.N.-sponsored political settlement to the conflict that addresses those three objectives, clarifying that the hostile power in the Syria context is Iran.
Administration officials have stated that the United States continues to work with the SDF, despite the group's decision following the Turkish incursion to coordinate in some areas with the Asad government. Joint Chiefs of Staff Chairman Gen. Mark Milley stated, "[ ... ] we're still working with [the SDF] in the eastern portion of northeast Syria, and then they are working with the Russian and Syrian regime in—in other parts of Syria."88 In response to questioning from Members of Congress, U.S. military leaders in December 2019 confirmed that U.S. policy in Syria remains to work "by with and through" local partners. When asked about what conditions would need to be in place for U.S. forces to withdraw from Syria, Esper stated, "[ ... ] when we could consider redeploying if you will would be when we feel confident that local security and police forces are capable of handling any type of resurgence [ ... ] of ISIS."89
U.S. Assistance to Vetted Syrian Groups
U.S. Military Operations; Train, Advise, Assist, and Equip Efforts
U.S. Military Presence in Syria
Since 2015, U.S. forces have operated in Syria in support of the counter-IS campaign. The Special Operations Joint Task Force, Operation Inherent Resolve (SOJTF-OIR) led by Brigadier General Patrick B. Roberson has been "the primary advise, assist and accompany force in Syria, working closely with the SDF."90 SOJTF-OIR has reported to the Combined Joint Task Force-Operation Inherent Resolve (CJTF-OIR), which leads the international coalition to defeat the Islamic State in Iraq and Syria.91 In September 2018, Lieutenant General Paul LaCamera assumed command of CJTF-OIR. U.S. forces have operated in northern and eastern Syria in partnership with the SDF and in southeast Syria in partnership with the Maghawir al Thawra militia near the At Tanf garrison adjacent to the tri-border area shared by Syria, Jordan, and Iraq (Figure 3).
Military Authorities
U.S. strike operations against the Islamic State and Al Qaeda-affiliated targets in Syria are conducted pursuant to the 2001 Authorization for Use of Military Force (AUMF). U.S. forces have operated in Syria for train and equip program purposes as well as to advise and assist U.S. partner forces, whether or not those specific partner forces were trained and/or armed under the train and equip program. Such "advise and assist" activities may have been conducted pursuant to the authorities outlined by train and equip program provisions or pursuant to other defense authorities defined in law or asserted by the executive branch. This includes military operations against IS targets conducted pursuant to the 2001 AUMF. U.S. operations in Syria also are supported in part by the 2014 request of the Iraqi government to the U.N. Security Council for military support to address the threat of terrorism emanating from Syria. It remains to be seen whether the Iraqi government may seek to amend or rescind that request in light of some Iraqis' efforts to expel foreign military forces from Iraq.
U.S. Repositions Forces in 2019
Following an October 6 call between President Trump and Turkish President Erdogan, the White House announced that Turkey would "soon be moving forward with its long-planned operation into Northern Syria," and that U.S. forces would "no longer be in the immediate area."92 A total of 28 Special Forces Green Berets located along Turkey's initial "axis of advance" subsequently withdrew from the border area.93 On October 9, Turkey launched Operation Peace Spring into northern Syria. On October 14, Defense Secretary Esper announced that, at the President's direction, the United States would withdraw the approximately 1,000 remaining U.S. troops in northeast Syria. Esper stated that, "Due to Turkey's irresponsible actions, the risk to U.S. forces in northeast Syria has reached an unacceptable level. We are also at risk of being engulfed in a broader conflict."94 In an October 19 briefing, Esper reinforced that "all forces" except those at At Tanf garrison in southeast Syria would be withdrawn "within weeks."95
On October 21, Secretary Esper stated that U.S. troops located next to oil fields in northeast Syria "are not in the present phase of withdrawal. The present phase of withdrawal from northeast Syria involves those troops up along the border." Esper added that the focus for troops remaining in Syria would be to "deny access, specifically revenue, to ISIS and any other groups that may want to seek that revenue to enable their own malign activities."96On October 21, President Trump stated, "We've secured the oil [ ... ] We want to keep the oil. And we'll work out something with the Kurds so they have some money, they have some cash flow."97
Military officials stated on November 7, "I would be cautious with saying that 'the mission [is] to secure the oil fields.' The mission is the defeat of ISIS. The securing of the oil fields is a subordinate task to that mission, and—and the purpose of that task is to deny ISIS the—the revenues from that oil infrastructure."98 On November 13, President Trump stated, "We're keeping the oil. We have the oil. The oil is secure. We left troops behind, only for the oil."99 On December 11, Defense Secretary Esper clarified, "We are there to ensure the enduring defeat of ISIS. So, a sub task of that, as we've directed to our commander on the ground, is to deny ISIS access to that oil, because whoever controls that oil controls a resource that allows them to buy weapons, equipment, fighters, to provide for their communities, etc."100
On December 5, Secretary Esper stated in an interview with Reuters that the U.S. military withdrawal from Syria was complete.101 Esper stated that approximately 600 U.S. troops would remain in Syria. A DOD Inspector General report on Operation Inherent Resolve covering the period October-December 2019 stated that U.S. forces in northern Syria had been reduced from approximately 1,000 to 500. An additional 100 U.S. troops would remain at the At Tanf garrison in the tri-border area of southeast Syria.
|
2015 |
Oct: White House announces that less than 50 U.S. Special Operations Forces will deploy to Syria to support operations against the Islamic State.102 |
|
2016 |
Dec: Force Management Level (FML) for U.S. personnel in Syria increased to allow the deployment of up to 500 individuals. |
|
2017 |
Dec: DOD states that approximately 2,000 U.S. personnel are operating in Syria.103 |
|
2018 |
Jan: Secretary of State Tillerson states that "the United States will maintain a military presence in Syria focused on ensuring that ISIS cannot re-emerge."104 Mar: President Trump states that U.S. troops will leave Syria "very soon."105 Nov: Special Representative for Syria Engagement James Jeffrey states that, "U.S. troops will stay on in Syria we say until the enduring defeat of ISIS."106 Dec: President Trump announces U.S. forces will be returning from Syria "now."107 |
|
2019 |
Feb: White House states U.S. will leave some forces in Syria, seeks troop contributions from allies to offset planned U.S. withdrawal. 6 Oct: President Trump directs withdrawal of U.S. troops from areas of northern Syria in advance of Turkish military incursion; 28 U.S. Special Forces withdraw.108 14 Oct: President Trump directs the full withdrawal of the roughly 1,000 remaining U.S. troops in northern Syria.109 21 Oct: Secretary Esper states that U.S. troops located near Syrian oil fields will remain to deny the Islamic State or "other groups" access to oil revenue.110 5 Dec. Secretary Esper states that the pullback of U.S. forces in Syria complete; roughly 600 U.S. troops to remain inside the country.111 |
Syria Train and Equip Program
Overview
In 2014, Congress created a new authority for the Department of Defense (DOD) to train and equip select Syrians in the FY2015 National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA, Section 1209 of P.L. 113-291, as amended). This authority, as amended by subsequent legislation, enables DOD "to provide assistance, including training, equipment, supplies, stipends, construction of training and associated facilities, and sustainment, to appropriately vetted elements of the Syrian opposition and other appropriately vetted Syrian groups and individuals." Such assistance activities are authorized for select purposes, including supporting U.S. efforts to combat the Islamic State and other terrorist organizations in Syria and promoting the conditions for a negotiated settlement to Syria's civil war.
Congress has not appropriated funds specifically for the Syria train and equip program since the program's inception. Rather, through 2019, Congress required the Department of Defense to reprogram funds from global counterterrorism assistance accounts to operations and maintenance accounts to support program activities, with each reprogramming subject to the prior approval of the four congressional defense committees. Amendments to the train and equip authority included in the FY2020 NDAA changed this procedure and shifted the requirement to prior notification of each ten percent increment of available funds. (Table 2 provides information about program funding and related requests.)
|
FY2015 Approved Transfers |
FY2016 Approved Transfers |
FY2017 Defense Appropriation |
FY2018 Request |
FY2019 Defense Appropriation |
FY2020 Defense Appropriation |
FY2021 Request |
|||||
|
225,000 |
116,453 |
220,000 (CTEF) |
500,000 (CTEF) |
252,000 (CTEF) |
200,000 (CTEF) |
200,000 (CTEF) |
|||||
|
220,500 (CTPF FY15/16) |
300,000 (CTPF FY16/17) |
||||||||||
|
279,500 (CTPF FY15/16) |
— |
||||||||||
|
-157,408 (CTPF FY15/16) |
— |
||||||||||
|
Net Total |
567,592 |
416,453 |
220,000 |
500,000 |
252,000 |
200,000 |
200,000 |
||||
|
Combined Net Total |
2,356,045 |
||||||||||
Source: Executive branch appropriations requests and reprogramming notifications.
Notes: Counterterrorism Partnerships Fund (CTPF). Counter-Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS) Train and Equip Fund (CTEF). The authority for the Syria Train and Equip Program requires the Department of Defense to submit prior approval notices to transfer funds into various service and department-wide Operations and Maintenance accounts for program activities. Funds listed were approved for transfer by the required congressional defense and appropriations committees during the fiscal years noted.
FY2021 Defense Funding Request
The Administration's FY2021 defense funding request seeks $200 million in CTEF funds for the Syria Train and Equip Program, to "develop and sustain a force of 10,000 personnel to secure, defend, and stabilize territory previously controlled by ISIS."112 This represents a shift from the FY2020 request, which envisioned a vetted Syrian opposition (VSO) force of 61,000.113 The FY21 request notes that the Defense Department adjusted its planning in light of the additional drawdown of U.S. forces in Syria.
The request calls for continued support to the following groups operating in eastern Syria:
Finish Forces, (commando and counterterrorism units) which conduct raids and clearance operations against Islamic State cells in urban areas.
Internal Security Forces, which provide civil protection and security via checkpoints and city patrols.
Provincial Internal Security Forces (PRISF), which provide wide area security (including perimeter security operations for uninhabited areas to limit IS freedom of movement). The PRISF also provide security at facilities for Islamic State detainees.
The request also calls for continued support to a group in southeastern Syria, Jaysh Maghawir ath Thawra (MaT). MaT operates out of the At Tanf garrison in the Syria-Iraq-Jordan tri-border area. In addition, the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF), "through its military councils and oil protection force, remains a committed partner eligible for military assistance as it continues to counter ISIS."
Roughly a quarter of the request would provide logistical support, supplies, and services to VSOs, including $15 million for basic life support services (subsistence, latrines, power generation) at detention facility sites operated by local partner forces in Syria.
U.S. Nonlethal and Stabilization Assistance
The Administration's FY2020 foreign assistance budget request reflected the Trump Administration's intent to end U.S. nonlethal assistance for the Syrian opposition, and to shift funding responsibility for stabilization projects to coalition partners. From 2012 through 2018, the United States provided nonlethal assistance to some Syrian opposition groups for specific, congressionally approved purposes. The United States also has funded stabilization efforts in areas of northeastern Syria liberated from Islamic State control. Possibly reflecting a recognition that the Syria conflict has "decisively shifted in the Syrian regime's favor,"114 the FY2020 request sought no Syria-specific funding. However, Congress appropriated funds for Syria programs and directed specific amounts for stabilization and other priorities (see below).
Background
Since 2012, the United States has provided a range of nonlethal assistance to Syrian opposition and civil society groups. At the start of the Syria conflict, U.S. ability to provide aid to the Syrian opposition was limited by restrictions stemming from an existing body of U.S. bilateral sanctions against Syria, as well as Syria's status as a state sponsor of terrorism. President Obama invoked emergency and contingency authorities under the Foreign Assistance Act to enable initial deliveries. To enable the expanded delivery of aid to Syrian opposition groups, the executive branch requested and Congress granted specific authorities to provide nonlethal foreign assistance in Syria for certain purposes notwithstanding other provisions of law. Over time, Congress expanded and amended these authorities to focus on areas of congressional priority and to put into place oversight and reporting requirements.115
Nonlethal and Stabilization Aid to Syria: 2017-2020
Since FY2012, successive Administrations and Congresses have taken evolving approaches to requests and appropriations of funds for assistance and stabilization programs in Syria. Funding for both types of projects has been drawn from a mix of regular and OCO funds from multiple accounts—largely ESF—with the Administration required to notify Congress of its intent to use these funds for assistance and stabilization efforts in Syria.
FY2017 Funds. In January 2017, the Obama Administration notified Congress that it intended to spend $230 million in FY2017 ESF-OCO funds (originally appropriated under the Further Continuing and Security Assistance Appropriations Act, 2017, P.L. 114-254) to support stabilization in areas liberated from the Islamic State in Syria. In August and September 2018, the Trump Administration notified Congress of plans to reprogram those funds and instead rely on contributions from foreign partners—reflecting a broader assessment by the Administration that the United States was bearing more than its share of costs in regards to Syria stabilization. The Administration's FY2020 budget request stated that $422 million in OCO funds were obligated for Syria in FY2017.
FY2018 Funds. The Administration did not obligate or expend FY2018 foreign operations funds for nonlethal assistance and stabilization in Syria. The FY2018 appropriations act (P.L. 115-141) designated $500 million in FY2018 funds from various foreign assistance accounts for a "Relief and Recovery Fund" (RRF) for areas liberated or at risk from the Islamic State and other terrorist organizations. The accompanying explanatory statement stated that funds were appropriated, among other purposes, "for non-lethal assistance programs to address the needs of civilians affected by conflict in Syria in a manner consistent with the prior fiscal year," but neither the act nor the statement allocated a specific amount for Syria. FY2018 RRF funds were available for Syria stabilization, but as of September 2019, FY2018 monies had only been notified for Syria-related atrocity crime accountability programs as directed by the act.
FY2019 Funds. The FY2019 Consolidated Appropriations Act (P.L. 116-6) stated that, of the funds appropriated under the ESF, INCLE, and PKO accounts, no less than $40 million should be made available for nonlethal stabilization assistance for Syria, of which not less than $7 million should be made available for emergency medical and rescue response, and chemical weapons use investigations. Notably, the act stated only that nonlethal assistance is to be provided for stabilization purposes. This was a significant departure from the FY2018 Consolidated Appropriations Act (P.L. 115-141), which authorized the use of appropriated funds for 14 listed purposes, including establishing inclusive local governance, bolstering the viability of the Syrian opposition, developing civil society and independent media, and countering extremism. In late 2019, $4.5 million in FY2019 ESF-OCO funds allocated to the RRF were obligated to support the Syrian Civil Defense (also known as the White Helmets).
FY2020. The Administration's FY2020 State and Foreign Operations request for Syria sought no ESDF or NADR funding for Syria-specific programs, in contrast to the FY2019 request which sought $130 million and $44.5 million for Syria programs in the two accounts, respectively. Similar to the FY2019 Consolidated Appropriations Act, the FY2020 Further Consolidated Appropriations Act (P.L. 116-94) makes not less than $40 million available for nonlethal stabilization in Syria, and specifies that no less than $7 million shall be used for emergency medical and rescue response, and chemical weapons use investigations.
In October 2019, the White House announced that it was releasing $50 million in stabilization assistance for Syria.116 The funds are intended to support human rights and civil society groups, as well as ethnic and religious minorities affected by the conflict. It will support the removal of explosive remnants of war, and documentation and accountability efforts for human rights abuses. It is not clear which account or fiscal year these funds will be drawn from.
FY2021 Request. The Administration's FY2021 State and Foreign Operations request seeks no funds for Syria-specific programs. The request would allocate $135 million to the Relief and Recovery Fund, to support efforts in places including Syria. The request also seeks $5.9 billion for the new International Humanitarian Assistance account (IHA) to address humanitarian needs in crisis areas including Syria.
Uncertain Future for Syria START Programs
To monitor and implement U.S. assistance programs, several regionally based teams were established. A Syria Transition Assistance and Response Team (START) operated from Turkey and coordinated U.S. humanitarian and foreign assistance to northern Syria, including assistance to opposition-held areas. In Jordan, the Southern Syria Assistance Platform (SSAP) monitored and coordinated comparable U.S. humanitarian and foreign assistance to southern and eastern Syria, including assistance to opposition-held areas. The Trump Administration also deployed a small team of U.S. civilian assistance officials from the Department of State and USAID (known as START Forward) inside areas of northern Syria where DOD-trained and/or equipped local forces were in control.
These programs have undergone significant changes since 2018. Some START programs were amended and/or ended in 2018 in line with the Administration's plans to focus on stabilizing former IS-held areas to the east. Cross-border SSAP programs reportedly were halted in mid-2018, after Syrian military forces regained control of southwestern Syria.117 In late 2018, the announced withdrawal of U.S. forces was preceded by the withdrawal of U.S. civilian personnel from northern Syria. In 2019, the Administration announced that some U.S. forces would remain in Syria, and START Forward personnel redeployed to the country in July.118 In October 2019, following the Turkish military incursion into northern Syria, START Forward personnel were again withdrawn from Syria, although most Department of State and USAID assistance activities continued outside of the Turkish incursion zone.119
To date, stabilization programming for areas of northeast Syria liberated from IS control has comprised four primary lines of effort: (1) demining, (2) promotion of local governance and civil society, (3) rehabilitation of basic infrastructure, and (4) promotion of economic growth and development. The ability of the United States and U.S. partners to pursue these efforts in areas under SDF and/or Syrian government control may now be limited.
Outlook & Challenges
The victory of pro-Asad forces in the broader conflict appears likely, and, from a U.S. perspective, that may further complicate several unresolved issues, including
- the stabilization and governance of areas recaptured from the Islamic State;
- the resolution of security threats posed by extremist groups in northwest Syria;
- the return and reintegration of internally and externally displaced Syrians;
- the reconstruction of conflict-damaged areas;
- the management of Syria-based threats to Syria's neighbors; and
- the terms of a post-conflict political order in Syria.
In light of current trends and conditions related to these issues, Administration officials and Members of Congress may reexamine appropriate terms and conditions for U.S. investment, force deployment, and the nature of relationships with U.S. partners in and around Syria. Looking forward, challenges for U.S. policy in Syria may include
Consolidating Gains against the Islamic State
U.S. efforts to prevent the resurgence of the Islamic State have focused on stabilization programming in IS-liberated areas as well as ongoing support to local partner forces. The Trump Administration in 2019 sought to shift financial responsibility for stabilization programs (which have included activities such as restoring electricity to liberated areas) to coalition partners, while also redeploying U.S. military personnel within and out of Syria. The State Department has reported that stabilization activities via the START (Turkey-based), SSAP (Jordan-based), and START-Forward platforms continue, albeit "almost exclusively with Coalition contributions."120 To the extent that it relies on contributions by coalition partners, the future of stabilization programming in Syria appears uncertain.
As noted above, the Trump Administration did not seek funds for Syria stabilization in its FY2020 budget request, but Congress appropriated funds for this purpose. The Further Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2020 states that not less than $40 million shall be made available for nonlethal stabilization assistance for Syria. The act also makes additional funds available for IS-liberated areas, including via the Relief and Recovery Fund and the Prevention and Stabilization Fund. These funds could be used for stabilization activities in Syria, but are not specifically designated as such.
The Administration has come under some scrutiny for failing to obligate funds appropriated by Congress for Syria stabilization. The Syria Study Group report, issued in September 2019, recommended that the Administration obligate unspent funds in the Relief and Recovery Fund designated for areas liberated from the Islamic State (Congress has not appropriated these funds on a country-specific basis, but has used explanatory statement language to authorize their use in specific countries).
U.S. support to local partner forces has been another key element in the U.S. effort to securing the enduring defeat of the Islamic State and consolidating coalition gains. While the Administration in 2019 reduced its troop presence in Syria from roughly 1,000 to 600 forces, senior U.S. military leaders have emphasized their view that a continued U.S. military presence in Syria is vital to preventing the re-emergence of the Islamic State. In December 2019, Joint Chief of Staff Chairman Gen. Milley stated, "If we withdraw all our capabilities and support to the indigenous governments and we don't continue to operate by, with, and through them, then I believe that the conditions will be set for [an Islamic State] resurgence."121 Milley assessed that, in his view, the SDF does not have "the independent capability" to prevent an Islamic State resurgence in the absence of U.S. support. Moreover, ongoing political debate in Iraq concerning the future of U.S. and other foreign forces in that country may affect related U.S. and coalition operations in Syria during 2020.
Preserving Relationships with Partner Forces
Numerous Members of Congress have expressed concern about what they describe as the abandonment of U.S. Kurdish allies in Syria. In October 2019, Senator Menendez stated
It was the Kurds who were largely our ground forces. It's the Kurds that lost about 11 to 13,000 of their people. It's the Kurds that were detaining over 10,000 ISIS fighters and families for us [ ... ] when you betray the person who you—the entity who you were fighting on the battlefield with and you basically leave them when you're finished using them and say, you know, you're on your own, it's a hell of a way to send a global message that, in fact, don't fight for the United States because when they're finished with you they'll let you die on the battlefield.
President Trump has defended his decision, stating, "We never agreed to protect the Kurds for the rest of their lives [ ... ] Where's an agreement that said we have to stay in the Middle East for the rest of humanity, for the rest of civilization, to protect the Kurds?"122 Defense Secretary Esper also stated, "The handshake with the Kurds, with the SDF in particular, was a handshake that we would ensure that we would defeat ISIS. It was not a handshake that said yes, we would also help you establish an autonomous Kurdish state. It was also not a handshake that said yes, we would fight Turkey for you."123 At the same time, U.S. military officials have stated that "allies and partners, both nation states but also indigenous partners like the SDF, are important to fulfill our national security objectives."124 Some have noted that the U.S. raid that killed Islamic State leader Abu Bakr al Baghdadi was reportedly made possible by information provided by an informant run by Kurdish intelligence officers.125
It is unclear whether or how changes in U.S. posture in Syria during 2019 will durably reshape the U.S. relationship with Syrian Kurds. Military officials in late 2019 stated that joint U.S.-SDF operations against the Islamic State had resumed, and Congress has appropriated funds for the continued training and equipping of partner forces in Syria including the SDF. However, the perceived uncertainty regarding U.S. policy in Syria and the future of the U.S. military presence may prompt U.S. partner forces, including Kurds, to seek support elsewhere—including from U.S. adversaries.
In early 2019, CJTF-OIR assessed that it was possible the SDF would splinter into separate security force factions, depending in part on their negotiations with the Syrian government. CJTF-OIR reported that the SDF "seeks to maintain semi-autonomous control of northeastern Syria, either by controlling the territory with support from Coalition forces or by striking a deal favorable to the constituent parts of the SDF with the Syrian regime and Russia."126 It is possible that as part of such an arrangement, the Syrian government and/or Russia could insist on limitations being placed on U.S. operations, with uncertain but potentially negative effects on U.S. operations against the Islamic State.
Countering Iran
U.S. military assessments continue to highlight the risks posed by foreign states operating in Syria, particularly Iran. In late 2019, CENTCOM reported that Iran continued to maintain a presence inside Syria in support of the Asad government and Iran's own strategic objectives.127 CJTF-OIR reported to the DOD OIG that Iran's goals in Syria include "retaining access to Hezbollah in Lebanon, maintaining the ability to strike Israel from Syrian territory, maintaining a military presence and military influence in Syria, and recouping investment through securing economic and security contracts in Syria."128
Some Members of Congress have raised concerns about Iranian drones conducting overflight operations of U.S. bases in Syria and Iraq, which Joint Chiefs of Staff Chairman Milley has described as "a very serious threat."129 On at least two occasions in 2017, the U.S. Air Force shot down armed Iranian UAVs that had advanced towards coalition forces in Syria with "hostile intent."130 Pro-Iranian militias operating in Syria, such as Kata'ib Hezbollah (KH), also may pose a threat to U.S. forces. In December 2019, the United States launched retaliatory airstrikes on two KH facilities in eastern Syria (and three KH facilities in Iraq) following a KH rocket attack in northern Iraq that killed a U.S. contractor. U.S. personnel in Syria may be vulnerable to additional attacks by Iran-backed forces, particularly following the January 2020 U.S. airstrike that killed Iranian Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps-Qods Force (IRGC-QF) Commander Qassem Soleimani.
Addressing Humanitarian Challenges in Extremist-Held Areas
The international response to the humanitarian crisis in Idlib reflects a broader debate regarding humanitarian assistance and counterterrorism, and how donors should balance the needs of civilians against the risks that extremist groups could inadvertently benefit from, divert, or influence the distribution of humanitarian assistance.131 Areas of Idlib province are the most significant zone remaining outside of government control in western Syria, and the civilian population has been described as caught between various extremist groups operating in the area (some affiliated with Al Qaeda), and Syrian military forces which seek to bring the province under central government control. Nevertheless, the presence of extremist groups in Idlib has complicated the provision of humanitarian assistance to the province, out of concern that aid could fall into the hands of Al Qaeda affiliated groups.132
Assisting Displaced Syrians
Conflict in Syria has taken the lives of hundreds of thousands of people and has displaced millions within the country and beyond its borders. As the intensity of conflict has declined in some areas of the country, displaced Syrians have faced difficult choices about whether or how to return to their home areas amid uncertainty about security, potential political persecution, crime, economic conditions, lost or missing documentation, and prospects for recovery. In 2018, the Asad government passed legislation enabling the state to designate land anywhere in the country for redevelopment and displace its current residents—a measure which could alter the demographics of formerly opposition-held areas and complicate the return of refugees and displaced persons.133 Humanitarian advocates and practitioners continue to raise concerns about the security and protection of returnees and displaced individuals in light of conditions in many areas of the country and questions about the Syrian government's approach to political reconciliation.134
In addition, mechanisms and mandates that have provided for the delivery of humanitarian assistance across the Syrian border without the consent of the Syrian government are facing increasingly forceful opposition by Russia and China at the U.N. Security Council. These states argue that the situation on the ground has changed, making it possible for aid to transit through official checkpoints, and that cross border aid mechanisms should be evaluated and adjusted in light of these developments.135 In January 2020, the Security Council renewed a more limited mandate for cross-border delivery of humanitarian assistance for six months instead of twelve. The United States remains the leading donor for international humanitarian efforts related to Syria, and U.S. policymakers may face a series of decisions about whether or how to continue or adapt U.S. support in light of changing conditions and administrative and logistical constraints.
Preventing Involuntary Refugee Returns
Despite the various impediments to the safe and voluntary return of refugees to Syria, neighboring states that have hosted thousands of Syrian refugees since the beginning of the crisis in 2011are increasingly calling for refugees to return home. In Lebanon, which hosts the largest number of Syrian refugees per capita (Syrian refugees are estimated to comprise up to a quarter of the population) political leaders have stated that the return of refugees should not be contingent on a political solution to the Syrian conflict.136
In a September 2019 address to the U.N. General Assembly, Lebanese President Aoun argued that the conditions for the "safe and dignified return" of refugees to Syria have been met, stating, "per international reports, the security situation on most of the Syrian territories has become stable, the military confrontations have become confined to the Idlib region, and the Syrian State has officially declared, time and again, that it welcomes the return of its displaced citizens."137 Aoun stated that more than 250,000 displaced persons had returned to Syria, and accused some states of trying to hinder refugee return by "sowing fear among the displaced."138 In some cases, the return of refugees to Syria has been facilitated by the Lebanese Armed Forces (LAF).139 It is unclear whether all refugees departed Lebanon voluntarily.140 UNHCR has continued to assess that conditions are not right for the large-scale return of refugees to Syria.
Turkey, which hosts the largest number of Syrian refugees overall, has proposed using international funds to resettle a portion of its refugee population in territory it currently occupies in northern Syria.141 In November 2019, President Erdogan presented the U.N. Secretary General with a plan for "new settlement areas for the return of Syrian refugees."142 The plan, which was reviewed by some media organizations, reportedly would require more than $26 billion in foreign assistance.143 Some observers have questioned whether the plan would alter the demographics of northern Syria by moving (primarily) Sunni Arab refugees into areas formerly administered by Kurdish forces.144 U.N. Secretary General Antonio Guterres "stressed the basic principles relating to the voluntary, safe and dignified of return of refugees," but stated that UNHCR would form a team to study the Turkish proposal.145 In late 2019, human rights organizations stated that it is "likely" that hundreds of Syrian refugees had been detained and returned to Syria.146 In a December 2019 hearing, Secretary of Defense Mark Esper also stated that Turkey was beginning to return refugees to northern Syria.147
Managing Reconstruction Aid
In 2017, U.N. Special Envoy for Syria Staffan de Mistura estimated that Syria's reconstruction will cost at least $250 billion, and a group of U.N.-convened experts estimated in August 2018 that the cost of conflict damage (including lost economic opportunity during the conflict) could exceed $388 billion.148 The Trump Administration has stated its intent not to contribute to the reconstruction of Asad-controlled Syria absent fundamental political change and to use U.S. diplomatic influence to discourage other international assistance to Asad-controlled Syria. Congress also has acted to restrict the availability of U.S. funds for assistance projects in Asad-controlled areas.149
In the absence of U.S. engagement, other actors such as Russia or China could conceivably provide additional assistance for reconstruction purposes, but may be unlikely to mobilize sufficient resources or adequately coordinate investments with other members of the international community to meet Syria's considerable needs. Predatory conditional assistance could also further indebt the Syrian government to these or other international actors and might strengthen strategic ties between Syria and third parties in ways inimical to U.S. interests. A lack of reconstruction, particularly of critical infrastructure, could delay the country's recovery and exacerbate the legacy effects of the conflict on the Syrian population, with negative implications for the country's security and stability.
Supporting a Political Settlement to the Conflict
Since 2011, the United States has pursued a policy of seeking fundamental political change in Syria, initially reflected in U.S. calls for President Asad to step aside. The Trump Administration has stated that it seeks behavior change rather than regime change in Syria. However, the Administration still calls for a political settlement to the Syria conflict based on UNSCR 2254, which requires the drafting of a new constitution and the holding of U.N.-supervised elections.
Asad's reelection in self-administered 2014 elections and his subsequent reconsolidation of security control in much of western Syria may limit the likelihood of substantive political change in line with U.S. preferences. U.N.-led negotiations over a settlement of the conflict remain open-ended, but appear unlikely to result in the meaningful incorporation of opposition figures or priorities into new governing arrangements in the short term. Alternative negotiations backed by Asad's Russian and Iranian supporters have their own logic and momentum, and place Syria's opposition groups in a political predicament. Congress and the Administration may reexamine what remaining points of leverage the United States can exercise or whether new points of leverage could be developed that might better ensure a minimally acceptable political outcome. Members of Congress and Administration officials may differ among themselves over what such an outcome might entail. Perceptions among Syrian opposition supporters of U.S. abandonment or acquiescence to an Asad victory may also have long-term diplomatic and security consequences for the United States and its partners.