Introduction
FY2019 is the fourth year in a row that Congress has enacted a special provision to allow for the issuance of H-2B visas beyond the annual statutory cap of 66,000 in response to high levels of demand for the visa. For FY2016, Congress exempted certain H-2B workers from the statutory cap. For the three past fiscal years, Congress has authorized the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) to make additional H-2B visas available subject to certain conditions. For FY2017 and FY2018, DHS used this authority to make an additional 15,000 H-2B visas available each year. For FY2019, DHS is making an additional 30,000 H-2B visas available.
H-2B Nonagricultural Worker Visa
The Immigration and Nationality Act (INA) of 1952, as amended,1 enumerates categories of aliens,2 known as nonimmigrants, who are admitted to the United States for a temporary period of time and a specific purpose. Nonimmigrant visa categories are identified by letters and numbers, based on the sections of the INA that established them. Among the major nonimmigrant visa categories is the "H" category for temporary workers. Included in this category is the H-2B visa for temporary nonagricultural workers.3
The H-2B program allows for the temporary admission of foreign workers to the United States to perform nonagricultural labor or services of a temporary nature if unemployed U.S. workers are not available. H-2B workers perform a wide variety of jobs. Top H-2B occupations in recent years have included landscape laborer, groundskeeper, forest worker, housekeeper, and amusement park worker. By regulation, participation in the H-2B program is limited to designated countries, and DHS publishes a list of eligible countries each year.4
Bringing workers into the United States under the H-2B program is a multiagency process involving the U.S. Department of Labor (DOL), DHS, and the Department of State (DOS). The program itself is administered by DHS's U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) and DOL's Employment and Training Administration (ETA). DOL's Wage and Hour Division (WHD) also has certain concurrent enforcement responsibilities. The H-2B program currently operates under regulations issued by DHS in 2008 on H-2B requirements, DHS and DOL jointly in 2015 on H-2B employment, and DHS and DOL jointly in 2015 on H-2B wages.5
For work to qualify as temporary under the H-2B visa, the employer's need for the duties to be performed by the worker must "end in the near, definable future" and must be a one-time occurrence, a seasonal need, a peak load need, or an intermittent need.6 The employer's need for workers generally must be for a period of one year or less, but in the case of a one-time occurrence, can be for up to three years.
In order to bring H-2B workers into the United States, an employer must first receive labor certification from DOL. An interim final rule on H-2B employment that was issued jointly by DHS and DOL in April 2015 establishes a new registration requirement as a preliminary step in the labor certification process; once it is implemented, prospective H-2B employers would demonstrate their temporary need to DOL through this registration process before submitting a labor certification application. (As of the date of this report, however, DOL continues to make determinations about temporary need during the processing of labor certification applications.)7
At the same time that the employer submits the labor certification application to DOL, the employer must submit a job order to the state workforce agency (SWA) serving the area of intended employment. The job order is used to recruit U.S. workers. The employer also must conduct its own recruitment.
In order to grant labor certification to an employer, DOL must determine that (1) there are not sufficient U.S. workers who are qualified and available to perform the work, and (2) the employment of foreign workers will not adversely affect the wages and working conditions of U.S. workers who are similarly employed. To prevent an adverse effect on U.S. workers, H-2B employers must offer and provide required wages and benefits to H-2B workers and workers in "corresponding employment."8 H-2B employers must pay their workers the highest of the prevailing wage rate or the federal, state, or local minimum wage. They must provide a "three-fourths guarantee"; that is, they must guarantee to offer workers employment for at least three-fourths of the contract period.9 H-2B employers also must pay worker visa fees and certain worker transportation costs. H-2B employers are not required to provide health insurance coverage.10
After receiving labor certification, a prospective H-2B employer can submit an application, known as a petition, to DHS to bring in foreign workers. If the foreign workers are already in the United States, the employer can request a change of status to H-2B status on the petition. In the typical case, however, the workers are abroad. If the petition is approved, they can visit a U.S. embassy or consulate to apply for H-2B nonimmigrant visas from DOS. If the visa applications are approved, the workers are issued visas that they can use to apply for admission to the United States at a port of entry. H-2B workers can be accompanied by eligible spouses and children, who are issued H-4 visas.
An alien's total period of stay as an H-2B worker may not exceed three consecutive years. An H-2B alien who has spent three years in the United States may not seek an extension of stay or be readmitted to the United States as an H-2B worker until he or she has been outside the country for at least three months.
The INA grants enforcement authority with respect to the H-2B program to DHS, but allows for the delegation of that authority to DOL.11 DHS has delegated that authority to DOL, and now DOL's WHD has responsibility for enforcing compliance with the conditions of an H‐2B petition and temporary labor certification.
Seafood Industry Staggered Entry Provision
As part of the labor certification process, prospective H-2B employers must accurately indicate the starting and ending dates of their period of need for H-2B workers. According to the supplementary information to the 2015 DHS-DOL interim final rule on H-2B employment: "An application with an accurate date of need will be more likely to attract qualified U.S. workers to fill those open positions, especially when the employer conducts recruitment closer to the actual date of need."12 If within a season an employer has more than one date of need for workers to perform the same job, the employer must file a separate labor certification application for each date of need. The employer is not allowed to stagger the entry of H-2B workers based on one date of need.
There is an exception to this prohibition on the staggered entry of H-2B workers, however, that applies to employers in the seafood industry. First enacted as part of the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2014,13 and subsequently incorporated into the 2015 DHS-DOL interim final rule on H-2B employment,14 this provision permits an employer with an approved H-2B petition to bring in the H-2B workers under that petition any time during the 120 days beginning on the employer's starting date of need. In order to bring in the workers between day 90 and day 120, though, the employer must conduct additional U.S. worker recruitment. This provision has been reenacted in DOL appropriations acts for each year from FY2015 through FY2019.15
Numerical Limitations
The H-2B program is subject to an annual statutory numerical limit. Under the INA, as amended by the Immigration Act of 1990, the total number of aliens who may be issued H-2B visas or otherwise provided with H-2B nonimmigrant status in any fiscal year may not exceed 66,000.16 Also, since FY2006 there has been a cap of 33,000 on the number of aliens subject to H-2B numerical limits who may enter the United States on an H-2B visa or be granted H-2B status during the first six months of a fiscal year.17 This INA amendment, enacted as part of the REAL ID Act of 2005, effectively divided the annual H-2B cap of 66,000 into two semiannual caps of 33,000, respectively covering work in the first and second halves of the fiscal year.18
Certain categories of H-2B workers are exempt from the cap, including the following:
- current H-2B workers seeking an extension of stay, change of employer, or change in the terms of employment;
- H-2B workers previously counted toward the cap in the same fiscal year;
- fish roe processors, fish roe technicians, and/or supervisors of fish roe processing;19 and
- H-2B workers performing labor in the U.S. territories of the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI) and/or Guam until December 31, 2029.
As noted, spouses and children who are accompanying H-2B workers are issued H-4 visas and, as such, are not counted against the H-2B cap.
Special H-2B Cap-Related Provisions
Legislation has been regularly introduced in Congress concerning the H-2B cap.20 Several measures have been enacted since 2005 to provide for the issuance of H-2B visas, or the granting of H-2B status, beyond the statutory cap. The enacted provisions have been of two main types.
Returning Worker Exemption
The INA was amended during the 109th Congress to add a provision establishing a temporary exemption from the H-2B statutory cap for certain H-2B returning workers. The provision, initially in effect for FY2005 and FY2006, exempted from the cap H-2B returning workers who had been counted against the cap in any one of the three prior fiscal years.21 This H-2B returning worker provision was subsequently extended for FY2007,22 and expired at the end of that fiscal year.23 An H-2B returning worker exemption of the same type was reinstated for FY2016. It provided that an H-2B returning worker who had been counted against the statutory cap in FY2013, FY2014, or FY2015 would not be counted again in FY2016.24 Multiple bills were introduced in the 115th Congress to enact temporary or permanent H-2B returning worker exemptions from the statutory cap.25 At least one H-2B returning worker bill has been introduced in the 116th Congress as of the date of this report.26
Provision Authorizing Additional H-2B Visas
For FY2017 and FY2018, a different type of H-2B cap-related provision was enacted by the 115th Congress. For each of these years, provisions in year-end omnibus appropriations laws authorized DHS to make additional H-2B visas available beyond the statutory cap after consultation with DOL and "upon the determination that the needs of American businesses cannot be satisfied" with available U.S. workers. Under these provisions, the number of additional aliens who could receive H-2B visas each year was limited to "not more than the highest number of H–2B nonimmigrants who participated in the H–2B returning worker program in any fiscal year in which returning workers were exempt from such numerical limitation."27
The FY2019 Consolidated Appropriations Act includes a provision of the same type for FY2019. Using the same language as the FY2017 and FY2018 provisions, the FY2019 provision authorizes DHS, after consultation with DOL and "upon the determination that the needs of American businesses cannot be satisfied" with available U.S. workers, to make additional H-2B visas available for FY2019 up to a maximum of "the highest number of H–2B nonimmigrants who participated in the H–2B returning worker program in any fiscal year in which returning workers were exempt from such numerical limitation."28 As discussed below, the DHS-DOL rule implementing this provision limits the additional visas to H-2B returning workers.
FY2017 Provision
In July 2017, DHS and DOL jointly published a final rule to implement the FY2017 provision.29 The rule temporarily amended DHS regulations on the H-2B visa to state that for FY2017, DHS "has authorized up to an additional 15,000 aliens who may receive H–2B nonimmigrant visas."30 In the supplementary information to the rule, DHS explained that the statutory provision applied only to H-2B workers entering the United States on visas and not to aliens in the United States who were seeking a change of status to H-2B status.31
The statutory definition of the maximum authorized number (i.e., "the highest number of H–2B nonimmigrants who participated in the H–2B returning worker program in any fiscal year") can be interpreted in different ways, as DHS acknowledged in the supplementary information to the rule. However, the agency determined that 64,716 was the most appropriate maximum number of additional H-2B visas authorized under the special FY2017 provision, this being "the number of beneficiaries covered by H–2B returning worker petitions that were approved for FY 2007."32
The supplementary information to the rule included the following explanation for limiting the FY2017 numerical increase to 15,000:
Most recently, in FY 2016, 18,090 returning workers were approved for H–2B petitions, despite Congress having reauthorized the returning worker program with more than three-quarters of the fiscal year remaining. Of those 18,090 workers authorized for admission, 13,382 were admitted into the United States or otherwise acquired H–2B status.... [T]he Secretary, in consideration of the statute's reference to returning workers, determined that it would be appropriate to use these recent figures as a basis for the maximum numerical limitation under section 543. This rule therefore authorizes up to 15,000 additional H–2B visas (rounded up from 13,382) for FY 2017.33
In addition, in implementing the statutory provision, DHS decided to limit eligibility for the additional H-2B workers to certain U.S. businesses. Under the FY2017 rule, the prospective H-2B employer must submit to DHS, along with the H-2B petition, a new attestation form
evidencing that without the ability to employ all of the H–2B workers requested on the petition ... its business is likely to suffer irreparable harm (that is, permanent and severe financial loss).34
FY2018 Provision
In May 2018, DHS and DOL jointly published a final rule to implement the FY2018 H-2B cap-related provision.35 The FY2018 rule, which is similar to the FY2017 rule, temporarily amended DHS H-2B regulations to state that for FY2018, DHS had authorized the issuance of up to 15,000 additional H–2B visas.36 In supplementary information to the FY2018 rule, DHS explained its decision to authorize up to 15,000 additional visas despite the fact that all 15,000 additional visas authorized in FY2017 were not used.
Out of a maximum of 15,000 supplemental H–2B visas for FY 2017, a total of 12,294 beneficiaries were approved for H–2B classification.... [T]he Secretary has determined that it is appropriate to authorize 15,000 additional visas again, as employers will have a longer period in which to submit their petitions due to the earlier publication date of this rule, thereby allowing for the possibility of more petitions being filed this fiscal year than in FY 2017.37
The FY2018 rule also included the same language as the FY2017 rule requiring an employer petitioning for supplemental visas to submit an attestation along with the H-2B petition evidencing that without the ability to employ all the requested H–2B workers the employer's business would likely suffer irreparable harm.
FY2019 Provision
In May 2019, DHS and DOL jointly published a final rule to implement the FY2019 provision.38 The FY2019 rule temporarily amends DHS H-2B regulations to state that for FY2019, DHS has authorized the issuance of up to 30,000 additional H–2B visas. As it did in the supplementary information to the FY2017 and FY2018 rules, DHS clarifies in the supplementary information to the FY2019 rule that the FY2019 provision only authorizes DHS to increase the number of H-2B visas; it does not cover individuals in the United States who change to H-2B status. As a result, DHS states that the supplemental cap is limited to workers who obtain visas abroad and then seek admission to the United States.39
The supplementary information to the FY2019 rule, consistent with the supplementary information to the FY2017 and FY2018 rules, indicates that the most appropriate maximum number of additional H-2B visas authorized under the statutory provision is 64,716.40 DHS explains its decision to allow 30,000 supplemental visas as follows:
In setting the number of additional H–2B visas to be made available during FY 2019, DHS considered this number [i.e., 64,716], overall indications of increased need, and the time remaining in FY 2019, and determined that it would be appropriate to limit the supplemental cap to approximately half of the highest number for returning workers, or up to 30,000.41
Like its FY2017 and FY2018 predecessors, the FY2019 rule requires an employer petitioning for supplemental visas to submit an attestation along with the H-2B petition evidencing that without the ability to employ all the requested H–2B workers the employer's business would likely suffer irreparable harm.
In addition, the FY2019 rule imposes a limitation not applicable under the FY2017 and FY2018 rules. Under the FY2019 rule, an employer may request supplemental visas only for H-2B workers "who have been issued an H–2B visa or otherwise granted H–2B status in Fiscal Years 2016, 2017, or 2018."42 DHS offers the following rationale for limiting the additional visas to H-2B returning workers:
Such workers (i.e., those who recently participated in the H–2B program) have previously obtained H– 2B visas and therefore been vetted by DOS, would have departed the United States after their authorized period of stay as generally required by the terms of their nonimmigrant admission, and therefore may obtain their new visas through DOS and begin work more expeditiously.43
The supplementary information to the rule highlights the importance, in particular, of returning workers' proven "willingness to return home after they have completed their temporary labor or services or their period of authorized stay."44 It states:
The returning workers condition therefore provides a basis to believe that H–2B workers under this cap increase will likely return home again after another temporary stay in the United States. That same basis does not exist for non-returning workers, not all of whom have a track record of returning home. Although the returning worker requirement limits the flexibility of employers, the requirement provides an important safeguard, which DHS deems paramount.45
Implementation of H-2B Numerical Limits
USCIS is responsible for implementing numerical limits on temporary worker visas (including the H-2B visa), which it does at the petition receipt stage. Under DHS regulations:
When calculating the numerical limitations ... USCIS will make numbers available to petitions in the order in which the petitions are filed. USCIS will make projections of the number of petitions necessary to achieve the numerical limit of approvals, taking into account historical data related to approvals, denials, revocations, and other relevant factors. USCIS will monitor the number of petitions (including the number of beneficiaries requested when necessary) received and will notify the public of the date that USCIS has received the necessary number of petitions (the "final receipt date").... If the final receipt date is any of the first five business days on which petitions subject to the applicable numerical limit may be received (i.e., if the numerical limit is reached on any one of the first five business days that filings can be made), USCIS will randomly apply all of the numbers among the petitions received on any of those five business days.46
In one recent fiscal year, the final receipt date announced by USCIS ended up being too early. For FY2015, USCIS announced on April 2, 2015, that March 26, 2015, was the final receipt date for new H-2B petitions. The agency had accepted about 3,900 H-2B petitions for FY2015 through March 26, 2015, which it believed was sufficient to reach the annual 66,000 cap. In early June 2015, however, USCIS announced that it would reopen the H-2B cap for the second half of FY2015 and accept additional petitions for new H-2B workers. It offered the following public explanation:
USCIS continues to work in collaboration with DOS to monitor the issuance of H-2B visas and has determined that as of June 5, 2015, DOS received fewer than the expected number of requests for H-2B visas. A recent analysis of DOS H-2B visa issuance and USCIS petition data reveals that the number of actual H-2B visas issued by DOS is substantially less than the number of H-2B beneficiaries seeking consular notification listed on cap-subject H-2B petitions approved by USCIS. In light of this new information, USCIS has determined that there are still available H-2B visa numbers remaining for the second half of the FY15 cap.47
Following a brief reopening, USCIS announced that June 11, 2015, was the final receipt date for new H-2B worker petitions for FY2015.
FY2018
Until FY2018, the final receipt date for H-2B petitions had never fallen within the first five days of filing and, thus, the random selection process (lottery) described in the regulatory provision in the preceding section had never been required.48 As described below, that changed with petition filings by employers seeking to hire H-2B workers for the second half of FY2018, which began on April 1, 2018. DOL was also impacted by the high level of employer demand for H-2B workers for the second half of FY2018 since an employer must receive labor certification from DOL before filing an H-2B petition.
DOL Labor Certification Applications
In accordance with H-2B regulations, January 1, 2018, was the first date that employers could submit H-2B temporary labor certifications to DOL requesting a work start date of April 1, 2018. On January 1, 2018, DOL received about 4,498 applications requesting an April 1, 2018, start date; those applications covered 81,008 workers. In response, DOL announced a process change. It indicated in a Federal Register notice that it would not begin releasing certified H–2B applications, which employers need in order to petition USCIS for H-2B workers (see "H-2B Nonagricultural Worker Visa"), until February 20, 2018, and on that date, it would issue such certified applications in order of receipt.49 DOL offered the following explanation for adopting this procedure:
This process change will allow employers who filed promptly on January 1, 2018, sufficient time to meet regulatory requirements, including the recruitment and hiring of qualified and available U.S. workers, thus preserving the sequential order of filing that took place on January 1, 2018, to the extent possible.50
DHS Petitions
On March 1, 2018, USCIS announced that in the first five business days of accepting H-2B petitions for the second half of FY2018, it had received petitions requesting about 47,000 H-2B workers subject to the statutory cap. It further reported that it had conducted a lottery on February 28, 2018, to randomly select a sufficient number of these petitions to meet the statutory cap.51
As discussed, on May 31, 2018, USCIS published a final rule authorizing the issuance of up to 15,000 additional H–2B visas for FY2018. In the first five business days of accepting petitions under this supplemental cap, USCIS received petitions for more beneficiaries than the number of H-2B visas available. As a result, it conducted a second FY2018 H-2B lottery on June 7, 2018, to randomly select a sufficient number of petitions to meet the supplemental cap.52
FY2019
Employer demand for H-2B visas and associated temporary labor certifications for the second half of FY2019 reached new heights.
DOL Labor Certification Applications
January 1, 2019, was the first day that employers could file H-2B labor certification applications for the second half of FY2019. On January 2, 2019, DOL announced that due to high demand its iCERT online application filing system had "experienced a system disruption" on January 1, 2019, that prevented some employers from submitting their H-2B certification applications: "Within the first five minutes of opening the semi-annual H-2B certification process on January 1, 2019, the U.S. Department of Labor iCERT system had an unprecedented demand for H-2B certifications with more than 97,800 workers requested in pending applications for the 33,000 available visas."53 When the system re-opened on January 7, 2019, it "handled the submission of approximately 4,749 H-2B applications covering more than 87,900 workers positions for an April 1, 2019, start date of work within the first one hour of operation."54 This experience led DOL to announce additional process changes for FY2020, as described below.
DHS Petitions
On February 19, 2019, the first day of accepting H-2B petitions for the second half of FY2019, USCIS announced that it had received petitions for more H-2B workers than there were remaining H-2B numbers under the FY2019 cap. On February 21, 2019, USCIS conducted a lottery to randomly select a sufficient number of petitions to meet the cap.
FY2020
In February 2019, in light of its experience with H-2B submissions in January 2019 and the unanticipated "burdens" placed on "its electronic filing system, network infrastructure, and staff resources," DOL announced new H-2B temporary labor certification application processing changes for FY2020.55 It indicated that beginning with H-2B certification applications for the first half of FY2020, it would randomly order and assign for processing all applications submitted within designated groups. The first group would consist of applications requesting the earliest start date of work (e.g., October 1, 2019, for the first half of FY2020) and filed during the first three calendar days of the filing period (which begins on July 3, 2019, for the first half of FY2020). DOL maintains that this new process "balances employers' interest in utilizing the H-2B program with OFLC's [DOL's Office of Foreign Labor Certification's] interest in ensuring that access to its filing system is equitable and occurs with no user disruption."56 DOL is seeking comments on these changes and plans for the new procedures to take effect on July 3, 2019.
Numbers Granted H-2B Status
In any year, most, but not all, foreign nationals who obtain H-2B status acquire that status through admission to the United States on H-2B visas. Those who obtain H-2B status but are not issued visas include H-2B workers who are admitted to the United States without visas (mostly Canadians) and individuals who change to H-2B status while in the United States. USCIS data are available on the latter group. These data show that between FY2009 and FY2017, the number of individuals who were approved for a change of status to H-2B status ranged from about 110 (in FY2017) to about 470 (in FY2010).57
H-2B Visa Issuances
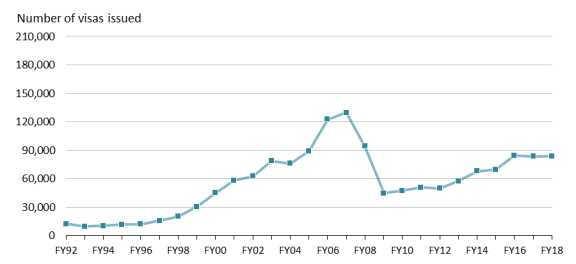
Figure 1 provides data on H-2B visa issuances from FY1992 through FY2018. These data offer one way to measure the growth of the H-2B program over the years. As explained above, the visa application and issuance process occurs after DOL has granted labor certification and DHS has approved the visa petition.
 |
|
Source: CRS presentation of data from U.S. Department of State, Bureau of Consular Affairs. |
As illustrated in Figure 1, the number of H-2B visas issued generally increased from FY1992 until FY2007, when H-2B visa issuances reached a highpoint of 129,547 (see the Appendix for yearly visa issuance data). H-2B visa issuances fell after FY2007 with the start of the economic recession, but, as shown in Figure 1, they have generally been increasing since FY2009.
In FY2005-FY2007 and FY2016-FY2018, as discussed, temporary provisions established exceptions to the statutory annual cap of 66,000. In some other years in which visa issuances surpassed 66,000, it seems reasonable to assume that the H-2B cap was exceeded given the magnitude of the numbers.58
Conclusion
With employer demand for H-2B visas exceeding supply, H-2B admissions and the statutory cap are once again receiving attention from policymakers. While previous Congresses considered broad immigration reform bills that included proposals for new temporary worker programs to address any perceived shortfalls in the supply of foreign workers, any legislative efforts to address the numerical limitations on nonagricultural guest workers in the near term seem likely to be focused on the existing H-2B program.
Appendix. H-2B Visa Issuances
|
Fiscal Year |
H-2B Visas Issued |
|
1992 |
12,552 |
|
1993 |
9,691 |
|
1994 |
10,400 |
|
1995 |
11,737 |
|
1996 |
12,200 |
|
1997 |
15,706 |
|
1998 |
20,192 |
|
1999 |
30,642 |
|
2000 |
45,037 |
|
2001 |
58,215 |
|
2002 |
62,591 |
|
2003 |
78,955 |
|
2004 |
76,169 |
|
2005 |
89,135 |
|
2006 |
122,541 |
|
2007 |
129,547 |
|
2008 |
94,304 |
|
2009 |
44,847 |
|
2010 |
47,403 |
|
2011 |
50,826 |
|
2012 |
50,009 |
|
2013 |
57,600 |
|
2014 |
68,102 |
|
2015 |
69,684 |
|
2016 |
84,627 |
|
2017 |
83,600 |
|
2018 |
83,774 |
Source: CRS presentation of data from U.S. Department of State, Bureau of Consular Affairs.