DWSRF Program Overview
The quality of water delivered by public water systems has been regulated at the federal level since enactment of the 1974 Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA). Since then, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has issued regulations for more than 90 contaminants, and all states (except Wyoming) have assumed primary responsibility for administering the federal drinking water program and overseeing public water system compliance. Congress last broadly amended the law in 1996 (P.L. 104-182) in response to criticism that the statute had too little flexibility, too many unfunded mandates, and an arduous but unfocused regulatory schedule.
Among the key provisions, the 1996 amendments authorized a Drinking Water State Revolving Fund (DWSRF) program to help public water systems finance improvements needed to comply with federal drinking water regulations and to address the most serious risks to human health.1 The law authorizes EPA to make grants to states each year to capitalize a state revolving loan fund. Each state must match 20% of its annual capitalization grant. States are authorized to use DWSRF funds to provide financial assistance (primarily subsidized loans) to eligible public water systems for expenditures that EPA has determined, through guidance, will facilitate SDWA compliance or significantly further the act's health protection objectives.2 More specifically, the law directs each state to develop an intended use plan each year indicating how the allotted funds will be used and requires states to give funding priority to projects that
- address the most serious human health risks,
- are necessary to ensure compliance, and
- assist systems most in need on a per-household basis according to state affordability criteria.3
The federal grants and state match—combined with funds from loan repayments, leveraged bonds, and other sources—are intended to generate an ongoing source of water infrastructure funding over time. The DWSRF program is patterned after the Clean Water Act State Revolving Fund (CWSRF) program that Congress authorized in 1987 for financing municipal wastewater treatment projects.4
Projects eligible for DWSRF assistance include installation and replacement of treatment facilities, distribution systems, and certain storage facilities. Projects to replace aging infrastructure are eligible if they are needed to maintain compliance or to further health protection goals. Projects to consolidate water supplies and enhance water system security may also be eligible. DWSRF funds may be used for preconstruction activities. They may not be used to pay for operation and maintenance activities or for projects needed primarily to accommodate growth.
Public water systems eligible to receive DWSRF assistance include roughly 50,000 community water systems (whether publicly or privately owned) and 17,500 not-for-profit noncommunity water systems.5 States generally may not provide DWSRF assistance to systems that lack the capacity to ensure compliance with the act or are in significant noncompliance with SDWA requirements unless these systems meet certain conditions to return to compliance. Systems owned by federal agencies are not eligible. Although the law authorizes assistance to privately owned community water systems, some states have laws or policies that preclude privately owned utilities from receiving DWSRF assistance.
DWSRF Allotments and Set-Asides
The law directs EPA to allot DWSRF funds among the states based on the results of the most recent quadrennial needs survey (discussed under "Drinking Water Infrastructure Needs"), except that each state (including the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico and the District of Columbia)6 must receive at least 1% of available funds.7 SDWA authorizes EPA and the states to reserve portions of the available funds for specified purposes.
EPA Reserves
Before distributing funds among the states, EPA reserves 2% of the appropriated amounts for grants to Indian tribes and Alaska Native villages for water infrastructure projects.8 For FY2017, Congress authorized EPA to set aside as much as $20.0 million for these grants. The law also directs EPA to allot grants to the Virgin Islands, the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands, American Samoa, and Guam, using not more than 0.33% of the funds available for grants to the states. Congress has regularly increased this amount to 1.5% in appropriations acts.9
The SDWA further directs EPA to set aside from the annual DWSRF appropriation $2.0 million to pay for monitoring of unregulated contaminants in small and medium systems.10 EPA may reserve up to $30.0 million annually to reimburse states for operator training and certification costs if separate funding is not provided under Section 1419 of the SDWA. EPA reserved the full amount for several years but reserved none after FY2003, as state training programs had matured. To provide technical assistance to small systems, EPA may reserve up to 2% with a $15.0 million cap. However, Congress has appropriated funding for this activity under Section 1442(e), and EPA has not set aside DWSRF funds for this purpose.11
State Set-Asides and Requirements
The SDWA also includes several set-asides and directives that apply to the states. These provisions offer states flexibility in tailoring their individual DWSRF programs to address state priorities. They also demonstrate the emphasis that the 1996 amendments placed on enhancing compliance, especially among smaller systems. The act requires states to make available at least 15% of their annual allotment for loan assistance to systems that serve 10,000 or fewer persons to the extent that the funds can be obligated to eligible projects.
The act also allows states to use up to 30% of their DWSRF capitalization grants to provide additional assistance, such as forgiveness of loan principal or negative interest rate loans, to help disadvantaged communities (as determined by the state).12 Through appropriations acts, Congress has frequently required states to provide additional subsidization.
Among other optional set-aside provisions, SDWA Section 1452(g) authorizes states to reserve a portion of their annual capitalization grants to cover the costs of administering the DWSRF program. Congress increased the amount states may use for administration purposes in the Water Infrastructure Improvements for the Nation Act (WIIN Act; P.L. 114-322), enacted on December 16, 2016.13
States may use an additional portion to help pay the costs of other SDWA mandates. Specifically, states may set aside as much as 10% for a combination of the following:
- Public water system supervision programs (Section 1443(a)),
- Technical assistance through source water protection programs,
- State capacity development strategies (Section 1420(c)), and
- Operator certification programs (Section 1419).
In the WIIN Act, Congress removed the requirement that, in order to use DWSRF funds for the above four purposes, states were to match expenditures with an equal amount of state funds. Section 1452(g) further authorizes states to use an additional 2% of funds to provide technical assistance to systems that serve 10,000 or fewer persons.
States also have the option of using as much as 15% for a combination of the following:
- Loans for the acquisition of land or conservation easements,
- Loans to implement voluntary source water protection measures,
- Technical and financial assistance to water systems as part of a capacity development strategy, and
- Expenditures from the fund for wellhead protection programs.14
Expenditures may not exceed 10% for any one of these activities. Other SDWA provisions separately authorized funds to be appropriated for several of these activities (e.g., wellhead protection provisions, Section 1428). Congress has generally not provided separate appropriations for these activities, leaving states the option to use DWSRF resources for such activities.
To further promote public water system compliance, the 1996 amendments added capacity development and operator certification requirements. Section 1420 required states to establish capacity development programs that include (1) legal authority or other means to ensure that new systems have the technical, financial, and managerial capacity to meet SDWA requirements and (2) a strategy to assist existing systems that are experiencing difficulties in coming into compliance.15 States were also required to adopt programs for training and certifying operators of community and non-transient non-community water systems.
Congress designed the DWSRF program to give states implementation flexibility. Additionally, Congress provided states flexibility in setting priorities between the DWSRF and CWSRF programs to accommodate the divergent drinking water and wastewater needs and priorities among the states. Section 302(a) of the 1996 SDWA amendments authorized states to transfer as much as 33% of the annual DWSRF allotment to the CWSRF or an equivalent amount from the CWSRF to the DWSRF. The act authorized these transfers through FY2001. In 2000, EPA recommended that Congress continue to authorize transfers between the SRF programs to give states flexibility to address their most pressing water infrastructure needs. Several annual appropriations acts had authorized states to continue to transfer as much as 33% of funds between the two programs, and in P.L. 109-54, Congress made this authority permanent.16
DWSRF Program Appropriations
In the 1996 SDWA amendments, Congress directed EPA to establish the DWSRF program and authorized program appropriations at a level of $599.0 million for FY1994 and $1.0 billion annually for each of FY1995 through FY2003, for a total appropriations authority of $9.6 billion. Although the authorization of appropriations expired in 2003, the program authority has no expiration date, and Congress has continued to provide annual appropriations for the program. Table 1 presents annual appropriations for the program since it began.
From FY2000 through FY2009, annual appropriations for the DWSRF program ranged from $820 million to $850 million. For FY2009, Congress appropriated $829.0 million for the program through regular appropriations. The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 (P.L. 111-5) provided another $2.0 billion for water infrastructure projects, delivered through the DWSRF program, for a total of some $2.83 billion in appropriations for this program for FY2009.17 For FY2010, in P.L. 111-88, Congress appropriated $1.39 billion for the DWSRF. For FY2011, the President requested $1.29 billion, and after several continuing resolutions, P.L. 112-10 funded the program at $965.0 million ($963.1 million after applying an across-the-board rescission of 0.2%).
For FY2012, the President requested $999.0 million, and Congress appropriated $919.4 million in P.L. 112-74 ($917.9 million after applying an across-the-board rescission of 0.16%). In this act, Congress applied Davis-Bacon prevailing wage requirements to DWSRF program funding for FY2012 and all future years.
For FY2013, the President requested $850.0 million for the DWSRF program. The Consolidated and Further Continuing Appropriations Act, 2013 (P.L. 113-6), provided full-year continuing appropriations for Interior, EPA, and related agencies through September 30, 2013. After taking into account sequestration and a 0.2% rescission pursuant to P.L. 113-6, EPA allocated $861.3 million for the program for FY2013.18 Additional SRF funds were appropriated for FY2013 in the Disaster Relief Appropriations Act, 2013 (P.L. 113-2), including $95.0 million ($100.0 million before sequestration) for the DWSRF program and $475.0 million ($500.0 million before sequestration) for the CWSRF program. These funds were targeted for drinking water and wastewater infrastructure projects in areas of New Jersey and New York affected by Hurricane Sandy.
For FY2014, the President requested $817.0 million, and EPA received $906.9 million. The President reduced the request to $757.0 million for FY2015, but Congress again appropriated $906.9 million in P.L. 113-235. For FY2016, the President requested $1.18 billion for the DWSRF program, and Congress appropriated $863.2 million (P.L. 114-113).
For FY2017, the Obama Administration requested $1.02 billion for the DWSRF program. The Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2017 (P.L. 115-31, Division G, Title II), included $863.23 million for DWSRF capitalization grants for FY2017. P.L. 114-254 included another $100 million in DWSRF funds to provide assistance to Flint, MI, to address lead in the water system.
For FY2018, President Trump requested $863.0 million, while Congress provided $1,163.2 million in P.L. 115-141.19 As in recent appropriations acts, Congress required each state to use 20% of its FY2018 capitalization grant "to provide additional subsidy to eligible recipients in the form of forgiveness of principal, negative interest loans, or grants (or any combination of these)." For FY2019, the Administration has requested $863.23 million.
From 1997 through June 2017, cumulative appropriations for the DWSRF program reached $20.03 billion. Adjusted for set-asides and transfers between the clean water and drinking water SRFs, cumulative net federal contributions totaled $19.17 billion. When combined with the 20% state match ($3.71 billion), bond proceeds, loan principal repayments, and other funds, the total DWSRF investment through June 2017 had reached $36.96 billion, and the program had provided more than $35.38 billion in assistance. Over the same period, more than 14,090 projects had received assistance, and 9,836 had been completed.20
In contrast to direct grants for construction projects—which would not create an ongoing funding source—the revolving fund program was designed to provide seed money to states in the form of capitalization grants to help generate a sustainable source of funding in each state over time.
Table 1. Drinking Water State Revolving Fund Program Funding, FY1997-FY2018
(in millions of dollars, nominal and adjusted for inflation 2017 dollars)
|
Fiscal Year |
Authorizations |
Appropriations |
|
|
Nominal |
Adjusted for Inflation |
||
|
1997 |
$1,000.0 |
$1,275.0 |
$1,850.8 |
|
1998 |
$1,000.0 |
$725.0 |
$1,039.6 |
|
1999 |
$1,000.0 |
$775.0 |
$1,097.4 |
|
2000 |
$1,000.0 |
$820.0 |
$1,137.4 |
|
2001 |
$1,000.0 |
$823.2 |
$1,115.2 |
|
2002 |
$1,000.0 |
$850.0 |
$1,133.2 |
|
2003 |
$1,000.0 |
$844.5 |
$1,104.7 |
|
2004 |
— |
$845.0 |
$1,078.6 |
|
2005 |
— |
$843.2 |
$1,043.6 |
|
2006 |
— |
$837.5 |
$1003.9 |
|
2007 |
— |
$837.5 |
$977.3 |
|
2008 |
— |
$829.0 |
$947.7 |
|
2009 |
— |
$829.0 |
$936.8 |
|
2009/ARRA |
— |
$2,000.0 |
$2,260.2 |
|
2010 |
— |
$1,387.0 |
$1,553.8 |
|
2011 |
— |
$963.1 |
$1,057.4 |
|
2012 |
— |
$917.9 |
$989.7 |
|
2013 |
— |
$956.3a |
$1,013.9 |
|
2014 |
— |
$906.9 |
$994.4 |
|
2015 |
— |
$906.9 |
$933.1 |
|
2016 |
— |
$863.2 |
$878.0 |
|
2017 |
— |
$963.2b |
$963.2 |
|
2018 |
— |
$1,163.2 |
$1,145.3 |
|
Total |
$22,161.6c |
$26,205.6 |
|
Sources: Prepared by CRS using the most current information available from House, Senate, or conference committee reports accompanying the annual appropriations bills that fund EPA and Administration budget documents, including the President's annual budget requests as presented by the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) and EPA's accompanying annual congressional budget justifications. "ARRA" refers to the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 (P.L. 111-5). Inflation-adjusted values are based on OMB, Budget of the United States Government Fiscal Year 2019, Historical Tables, Table 5.4—Discretionary Budget Authority by Agency 1976-2023, and Table 10.1—Gross Domestic Product and Deflators Used in the Historical Tables—1940-2023, https://www.whitehouse.gov/omb/historical-tables/.
a. FY2013 post-sequestration enacted amounts are as presented in EPA's FY2013 Operating Plan. This amount reflects the baseline appropriation level of $861.3 million ($908.7 million pre-sequestration and pre-rescission) plus $95.0 million ($100.0 million pre-sequestration) for the DWSRF program in the Disaster Relief Appropriations Act, 2013 (P.L. 113-2), for projects in New Jersey and New York to address damage from Hurricane Sandy.
b. The Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2017 (P.L. 115-31), included $863.23 million for the DWSRF program. The Continuing and Security Assistance Appropriations Act, 2017 (P.L. 114-254), included an additional $100 million in DWSRF funding to assist Flint, MI, as authorized in the WIIN Act (P.L. 114-322).
c. Funds available to states are reduced by amounts that EPA sets aside from the annual appropriation. For FY2017, EPA reserved $20.0 million for American Indian and Alaska Native water system grants (SDWA §1452(i)) and $2.0 million to reimburse small systems for unregulated contaminants (§1452(o)).
Drinking Water Infrastructure Needs
To determine how to allot DWSRF funds among the states, SDWA directs EPA to assess the capital improvement needs of eligible public water systems every four years.21 Concurrently, and in consultation with the Indian Health Service and Indian tribes, EPA must assess needs for drinking water treatment facilities to serve Indian tribes and Alaska Native villages.22 EPA is required to distribute the DWSRF funds among the states based on the results of the most recent needs survey. Eligible systems include approximately 50,000 community water systems (publicly or privately owned) and 17,500 not-for-profit non-transient, non-community water systems.
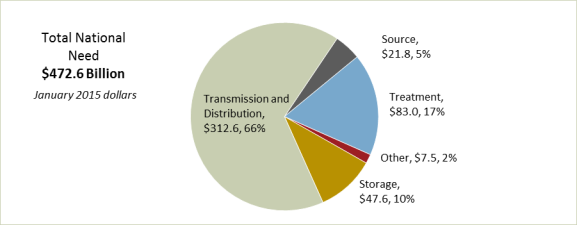
In March 2018, EPA issued the 2015 Drinking Water Needs Survey and Assessment, which presents estimated needs for DWSRF-eligible infrastructure projects for the period 2015-2034.23 This survey indicates that public water systems need to invest $472.6 billion on infrastructure improvements over 20 years ($19.2 billion annually) to achieve compliance with SDWA drinking water regulations and "to continue to provide safe drinking water to the public."24 EPA reports that this amount represents an increase of 10% in the estimated total national need compared to the 2011 survey estimate of $384.2 billion ($428.6 billion in 2015 dollars)—with water transmission and distribution projects comprising the largest increase in needs.
The 2015 needs survey presents the 20-year needs estimates for DWSRF-eligible projects by category: transmission and distribution, treatment, source, storage, and other. As Figure 1 indicates, the largest needs category—installation and rehabilitation of transmission and distribution systems—accounts for $312.6 billion (66.2%) of total 20-year needs. EPA reports that community water systems have an estimated total of 2.2 million miles of transmission lines and distribution mains.25 Water treatment needs constituted the next largest category, accounting for $83.0 billion (17.6%) of total needs, while water storage accounts for $47.6 billion (10.1%), and source—projects needed to obtain safe water supplies, including rehabilitation and installation of wells—accounts for $21.8 billion (4.6%) of total 20-year needs. The 2015 assessment did not specifically breakout needs related to water system security improvements. In the 2011 survey, EPA estimated a 20-year need of $235.9 million for security-related projects. For that assessment, EPA concluded that security-related needs may be far greater, because many water systems incorporate these costs into the costs of broader construction projects rather than report them separately.
The needs survey also breaks down the 20-year needs estimates according to system size and ownership. The 20-year drinking water infrastructure need for states totaled $463.6 billion. Within that total, the reported needs among community water systems and not-for-profit non-community water systems (e.g., schools with their own water wells) broke out as follows:
- Large community water systems (serving more than 100,000 people): $174.4 billion (36% of the total 20-year need);
- Medium systems (serving from 3,301 to 100,000 people): $210.6 billion (43.6%);
- Small systems (serving 3,300 or fewer people): $64.5 billion (17.4%); and
- Not-for-profit non-community systems: $5.1 billion (3%).
In addition, the American Indian and Alaska Native village water system needs totaled $3.8 billion. The 20-year needs reported by American Samoa, Guam, the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands, and the U.S. Virgin Islands totaled $669.7 million. EPA estimated that an additional $4.9 million would be needed for systems to comply with proposed and recently promulgated regulations.
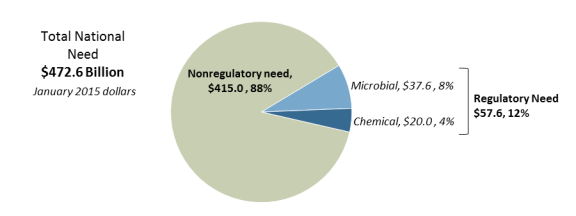
EPA reports that all the infrastructure projects in the needs assessment would promote the health objectives of the act. Within the total needs reported, $57.6 billion (12.2%) is directly attributable to regulatory costs, while $415.0 billion (87.8%) represents non-regulatory costs (e.g., replacing old distribution lines).26 (See Figure 2.) Most regulatory funding needs typically involve the upgrade, replacement, or installation of treatment technologies. Most non-regulatory funding needs typically involve installing, upgrading, or replacing transmission and distribution infrastructure to allow a system to continue to deliver safe drinking water. Although these system problems often do not cause a violation of a specific drinking water standard, projects to correct infrastructure problems may be eligible for DWSRF funding if needed to address public health risks.
EPA noted that the total needs estimate may be conservative for several reasons: (1) systems are required to meet stringent documentation criteria when identifying needs; (2) many systems had not fully evaluated their security needs at the time of the assessment; (3) capital improvement plans often cover fewer than 10 years, while the survey tries to capture 20-year estimates; and (4) the survey is limited to eligible needs, thus excluding water infrastructure projects related to dams, raw water reservoirs, fire protection, operation and maintenance, and future growth.
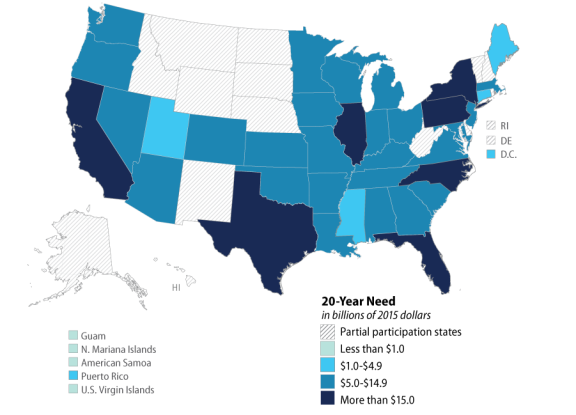
EPA also presents drinking water infrastructure needs by state, as shown in Figure 3. As noted, the act provides that, regardless of needs survey results, each state, the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, and the District of Columbia is to receive at least 1% of available funds.27
Lead Service Lines
Among other assessments of drinking water infrastructure needs, a 2012 study prepared by the American Water Works Association (AWWA) projected that restoring and expanding water systems to keep up with population growth would require a nationwide investment of at least $1 trillion over the next 25 years.28 Additionally, the authors of a 2012 AWWA-sponsored analysis of lead service line occurrence estimated that there may be 6.1 million lead service lines nationwide. The AWWA notes that, while progress has been made, removal of these lines could represent an additional $30.0 billion in infrastructure funding needs.29
In conducting the needs assessment, some public water systems included needs estimates for replacing lead service lines, although EPA has not specifically asked water systems to report the number of lead service lines in their systems. Lacking project-specific data, the needs assessment model assumes that the cost to replace a lead service line is $3,777. Using that figure, EPA provides the following partial estimate:
Based on data from large and medium systems in the 2015 Assessment and from small systems in the 2007 Assessment, water systems identified needs for replacement of approximately 1.4 million lead service lines over the 20-year period of January 2015 through December 2034. The estimated total cost of replacing these lead service lines is $4.2 billion in 2015 dollars.30
The survey notes several factors that might affect this estimate. For example, water systems that have lead service lines but control lead in drinking water through corrosion control may not report a need to replace lead service lines.31
Drinking Water Infrastructure Funding Issues
Overall, federal spending on drinking water infrastructure represents a small portion of total spending across federal, state, and local governments. The Congressional Budget Office reported that, in 2014, the federal share of total public spending on water and wastewater utilities was 4%, while state and local government expenditures accounted for 94% of all public spending on this infrastructure.32
In addition to infrastructure needs, other SDWA mandates are eligible for DWSRF funding, thus increasing competition for these resources. The DWSRF program includes competing objectives, and, thus, this competition is perhaps unavoidable. On the one hand, the fundamental purpose of the program is to capitalize revolving funds in the states in order to generate a sustainable source of funding for drinking water projects. On the other hand, Congress authorized multiple set-asides to fund other drinking water program priorities and requirements, such as system compliance-capacity assurance, operator certification, wellhead protection, and small system technical assistance. Overall, states may use as much as 31% of their grants for the set-asides and another 30% to provide additional loan subsidies to disadvantaged communities.
While these options offer states flexibility to tailor their programs to meet their particular needs, using funds for these activities could significantly erode the corpus of state funds and slow the rate at which they become capitalized. A concern for states is that, to the degree that Congress relies on the DWSRF to fund other SDWA requirements—rather than providing separate appropriations—the potential of the DWSRF program is diminished. Moreover, in recent appropriations acts, Congress has added several policy directives not present in the SDWA that may also affect the states' ability to grow or maintain their SRFs. These added provisions include specified additional subsidization requirements for disadvantaged systems, Davis-Bacon prevailing wage requirements, and Buy American (iron and steel) provisions.33 In FY2010 and subsequent appropriations acts, Congress has mandated that states use a certain portion (usually 20%) of their federal capitalization grants to provide additional subsidies to borrowers. EPA notes:
This change allowed states to aid communities most in need and incentivize particular types of projects. Because this subsidy comes from the federal dollars, continued federal support is needed to maintain this benefit and continue growing the fund.34
A chronic issue concerns the need for communities to address drinking water infrastructure requirements outside the scope of the DWSRF program. Communities must typically address several categories of infrastructure requirements that are unrelated to SDWA compliance or public health and, thus, ineligible for DWSRF assistance.35 These categories include future growth, ongoing rehabilitation, and operation and maintenance of systems. EPA has reported that outdated and deteriorated drinking water infrastructure poses a fundamental long-term threat to drinking water safety and that, in many communities, basic infrastructure costs can far exceed SDWA compliance costs. As reported in EPA's most recent drinking water needs assessment, roughly 12% of the 20-year estimated need is directly related to compliance with SDWA regulations.
A fundamental question has concerned the long-term federal role in water infrastructure financing. A subset of questions concerns how deficit reduction efforts might affect federal involvement—for example, how deficit reduction objectives might impact proposals to develop a small system grant program or sustainable funding source, such as a water infrastructure trust fund. Other persistent water infrastructure issues include the gap between funding and estimated needs, the growing cost of complying with SDWA standards (particularly for small communities), the ability of small or disadvantaged communities to afford DWSRF financing, and the broader need for cities to maintain, upgrade, and expand infrastructure unrelated to SDWA compliance.
Congressional Actions
In the face of large needs, competition for limited federal resources, and debate over the federal role in funding water infrastructure, EPA, states, and communities and utilities have increasingly focused on alternative management and financing strategies to address costs and promote greater financial self-reliance among water systems. Strategies include establishing public-private partnerships, improving asset management, and adopting full-cost pricing for water services. Such approaches are intended to improve the financial and managerial sustainability of water systems. However, they may be limited in their ability to fully meet needs, particularly among poorer communities, small water systems that may lack economies of scale, or communities with declining populations.36 Consequently, interest in exploring new infrastructure financing options (such as an infrastructure bank) and expanding federal assistance has persisted.
Water Infrastructure Finance and Innovation Act (WIFIA)
Deficit reduction pressures are not new to DWSRF appropriations considerations, but statutory spending caps in the Budget Control Act of 2011, as amended by the American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012, placed added constraints on appropriators. The 113th Congress considered various water infrastructure funding options. As discussed below, one such approach was enacted.
The Water Resources Reform and Development Act of 2014 (P.L. 113-121, H.R. 3080) included in Title V, Subtitle C, the Water Infrastructure Finance and Innovation Act of 2014 (WIFIA). In WIFIA, Congress authorized a pilot loan guarantee program to test the ability of innovative financing tools to promote increased development of, and private investment in, water infrastructure projects—while reducing costs to the federal government. The five-year pilot program is intended to complement—not replace—the SRF programs.
Eligible projects include SRF-eligible projects and a wide range of water resource development projects that generally have costs of at least $20.0 million. Such large projects face difficulty securing significant funding through the SRF programs. Moreover, unlike the SRF programs, WIFIA is not focused on regulatory compliance and, therefore, may be more available for other large-scale water infrastructure projects. For projects serving areas with a population of 25,000 or fewer individuals, eligible projects must have a total cost of at least $5.0 million. Projects financed under this program are subject to Davis-Bacon prevailing wage requirements. Also, WIFIA funds may be used only if all the iron and steel used in a project are produced in the United States (unless this requirement would increase project costs by more than 25%).
WIFIA authorized to be appropriated to the Secretary of the Interior and the EPA Administrator $20.0 million each for FY2015 and $25.0 million each for FY2016, with amounts increasing annually to $50.0 million each for FY2019.37
WIFIA Appropriations
For each of FY2015 and FY2016, Congress appropriated $2.2 million for EPA to hire staff and develop the WIFIA program, but no project funds were provided. In the President's FY2016 budget request, EPA noted that it faced a complex task in standing up a new federal loan program.38 For FY2017, the President requested $20.0 million for EPA to provide WIFIA financing for large drinking water and wastewater infrastructure projects (including administrative costs). The budget request stated that the program goal was to "accelerate investment in our nation's water and wastewater infrastructure by providing supplemental credit assistance to credit worthy nationally and regional significant water projects."39 EPA estimated, "Of the total requested, $15 million in credit subsidy translates into a potential loan capacity of nearly $1 billion to eligible entities for infrastructure projects with the initial loans taking place in FY2017."
In the Continuing and Security Assistance Appropriations Act of 2017 (P.L. 114-254), Congress provided $20.0 million for EPA to begin providing loan guarantees for infrastructure projects under WIFIA. Also, Congress provided for WIFIA $10 million in the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2017 (P.L. 115-31),40 for a total of $30.0 million for the program for FY2017. For FY2018, the President requested $20.0 million for WIFIA, and Congress provided $63 million in the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2018 (P.L. 115-141)—$8 million of which is for administrative costs.41
114th Congress
The detection of elevated lead levels in drinking water in Flint, MI, and elsewhere heightened attention to the state of the nation's drinking water infrastructure and the challenges many communities face in addressing their infrastructure needs. The 114th Congress focused attention on funding levels for and implementation of the DWSRF program as well as EPA efforts to implement WIFIA. Further, numerous bills were introduced to establish new water infrastructure funding sources through grants, a trust fund, and other means and to revise the tax code to promote private sector investment in water infrastructure.
An array of proposals were introduced to provide infrastructure funding assistance to Flint to address lead contamination of drinking water associated with old pipes and corrosion problems and, more broadly, to increase water infrastructure funding for communities nationwide.
As in previous Congresses, legislation was offered to amend the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 to provide that the volume cap for private activity bonds (PABs) would not apply to bonds for drinking water or wastewater facilities. These tax-exempt bonds provide a financing tool to stimulate private sector investment in public projects. However, federal law imposes state bond caps, limiting the ability of state and local governments to use PABs to finance drinking water and wastewater infrastructure projects.42
Water Infrastructure Improvements for the Nation (WIIN) Act
Senate-passed S. 2848, the Water Resources Development Act (WRDA) of 2016, included a number of SDWA and CWA infrastructure provisions and incorporated various bills introduced in response to the Flint water crisis. The House-passed WRDA bill, H.R. 5303, excluded such EPA provisions and proposed to authorize the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers to provide water infrastructure assistance to certain communities in states subject to presidential emergency declarations as a result of lead or other contaminants in the water system. In lieu of convening a formal conference on these bills, Congress incorporated various provisions of S. 2848 and H.R. 5303—along with other water resource provisions—into S. 612, which became the Water Infrastructure Improvements for the Nation (WIIN) Act.43
Enacted on December 16, 2016, the WIIN Act (P.L. 114-322) included an array of water resources, drought, and drinking water provisions. Title II of this wide-ranging water resources law comprises the Water and Waste Act of 2016. Title II, Subtitle B, authorized $100 million in DWSRF funding and other emergency assistance to help Flint address lead in the water system. In P.L. 114-254, Congress appropriated the funding authorized in the WIIN Act to assist Flint.
Title II, Subtitle A, of the WIIN Act made several revisions to the DWSRF program, including requiring that funds made available from a state DWSRF during FY2017 may not be used for water system projects unless all iron and steel products to be used in the project are produced in the United States. (Certain waivers of the requirement are specified.) The act further amended SDWA to direct EPA to establish two new drinking water infrastructure grant programs: New SDWA Section 1459A authorizes grants to provide compliance assistance to small or disadvantaged public water systems, and new Section 1459B authorizes grants for lead reduction projects, including lead service line replacement. For each grant program, Congress authorized to be appropriated $60 million per year for FY2017-FY2021.44 The act did not reauthorize appropriations for the DWSRF program.
The WIIN Act, Section 2107, rewrote SDWA Section 1464 to require EPA to establish a voluntary program for testing for lead in drinking water at schools and child care programs under the jurisdiction of local education agencies. States or local education agencies may apply to EPA for grants to cover testing costs. Appropriations for this grant program are authorized at $20 million per year for FY2017-FY2021. (Funding for the three new grant programs is discussed below.)
DWSRF and Related Bills and Appropriations in the 115th Congress
The 115th Congress continues efforts to address drinking water infrastructure management and investment challenges. Members have introduced bills to increase federal investment in water infrastructure and to promote improved water system asset management and SDWA compliance capacity. Budget constraints, debate over debt reduction, and debate over the federal role in funding municipal infrastructure continue to be significant factors in the deliberations.
As noted above, President Obama had requested $1.02 billion for the DWSRF program for FY2017. In the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2017 (P.L. 115-31, Division G, Title II), Congress appropriated $863.23 million for DWSRF capitalization grants.45 P.L. 114-254 included an additional $100 million in DWSRF funding to provide assistance to Flint to address lead in the public water system.
For FY2018, President Trump requested $863.0 million for the DWSRF program, while Congress provided $1,163.2 million. The appropriated amount represents an increase of $300 million above the FY2017 level (excluding $100 million provided to assist Flint). Although funding was not requested, Congress also appropriated funds for the three new grant programs authorized in the WIIN Act.46 For FY2019, the Administration has requested $863.23 million for the DWSRF program.
DWSRF and related drinking water infrastructure bills pending in the 115th Congress are identified below.
Reported:
- H.R. 3387 (H.Rept. 115-380), the Drinking Water System Improvement Act of 2017, would amend the DWSRF program and SDWA more broadly. It would authorize $8 billion to be appropriated for DWSRF capitalization grants over five years. It would specify that DWSRF funds could be used for replacing or rehabilitating aging treatment, storage, or distribution facilities; extend through FY2022 the requirement that projects receiving DRSRF assistance use American iron and steel; apply Davis-Bacon prevailing wage requirements to projects receiving DWSRF assistance (currently required through appropriations acts); and increase the portion of the capitalization grant that a state may use to provide additional subsidization to disadvantaged communities from 30% to 35% and conditionally require at least 6% to be used for this purpose. H.R. 3387 would require needs surveys to include assessments of costs to replace lead service lines, renew states' authority to use DWSRF funds to assess source water protection areas, require large systems to consider cost and effectiveness of relevant processes and materials to receive DWSRF assistance through FY2022, and direct EPA to develop and provide to states best practices for administering their DWSRFs. Among other provisions, H.R. 3387 would (1) expand water system reporting to consumers, (2) promote partnerships and authorize assessment of consolidation options for struggling systems, (3) authorize $750 million over five years for states and tribes to oversee water systems and enforce SDWA regulations, (4) expand unregulated contaminant monitoring and increase related funding, (5) encourage systems to develop asset management plans, (6) require systems serving more than 3,300 persons to assess risks and resiliency to malevolent acts and natural hazards and authorize $175 million over five years for a drinking water infrastructure risk and resiliency grant program, (7) direct EPA to develop a strategic plan to improve accuracy and availability of compliance monitoring data, and (8) authorize $25 million for grants for local educational agencies to replace school drinking water fountains and monitor for lead. The bill would also amend the Emergency Planning and Community Right-To-Know Act to require prompt notification of hazardous substances releases to the state agency and any community water systems with affected source waters. On July 27, 2017, the Committee on Energy and Commerce held a markup session and ordered H.R. 3387, as amended, to be reported favorably. The committee filed a written report on November 11, 2017.
- S. 2800 (S.Rept. 115-294), America's Water Infrastructure Act of 2018, a broad water infrastructure and water resources bill, includes various EPA- and SRF-related provisions, primarily in Title V. The bill would make permanent the requirement to use U.S.-produced iron and steel in all projects receiving DWSRF assistance and authorize states to use a portion of their DWSRF funds to implement source water protection plans. S. 2800 would amend WIFIA to authorize special terms for loan assistance provided to state DWSRF and CWSRF finance authorities (see related bills, H.R. 4902/S. 2364, SRF WIN, described below). On May 22, 2018, the Senate Environment and Public Works Committee ordered S. 2800, as amended in the nature of a substitute, to be reported favorably. On July 10, 2018, the committee filed a written report on S. 2800. Available on the committee's website is the text of an amendment in the nature of a substitute to H.R. 8 (Water Resources Development Act of 2018), which includes various changes from S. 2800 as reported.47 (For further information, see CRS Report R45212, Water Resources Development Act of 2018 and America's Water Infrastructure Act of 2018: An Overview, by [author name scrubbed] and [author name scrubbed].)
Introduced:
- H.R. 904, the Buy American Improvement Act of 2017, would standardize and expand Buy American requirements across federal agencies and programs and make permanent requirements to use U.S.-manufactured iron and steel for projects receiving DWSRF assistance.
- H.R. 939, the Buy America for Drinking Water Extension Act of 2017, would expand and make permanent the SDWA provision that required, for FY2017, the use of U.S.-manufactured iron and steel in projects receiving DWSRF assistance.
- H.R. 1068, the Safe Drinking Water Act Amendments of 2017, is a broad SDWA reauthorization bill, and Title IV includes numerous amendments to the DWSRF program. Among other revisions, the bill would (1) add Davis-Bacon prevailing wage requirements, (2) make permanent the Buy American iron and steel requirement for projects receiving DWSRF assistance (which SDWA applied to FY2017 funding), (3) direct states to give funding priority to projects that improve the ability of water systems to protect health and comply with SDWA affordably and to give greater weight to applications that describe measures to improve the management and financial stability of the water system, (4) conditionally require states to use at least 6% of their capitalization grants to provide additional subsidization to disadvantaged communities, (5) incorporate in the statute a governor's authority to transfer as much as 33% of the annual DWSRF or CWSRF capitalization grant to the other fund,48 (6) increase the amount reserved for insular areas from 0.33% to 1.5%, (7) authorize DWSRF program appropriations at a level of $21.17 billion over five years, (8) authorize EPA to use unobligated funds to make grants to states with water systems disproportionately affected by new regulations to assist those systems, and (9) require EPA to use information from states to develop best practices for DWSRF program administration. Further, the bill would expand eligible uses of funds to include replacement or rehabilitation of aging water systems or for producing or capturing sustainable energy. H.R. 1068 would increase the authorized funding level under SDWA Section 1459B for lead reduction projects (including lead service line replacement) from $60 million annually to $100 million annually for FY2018-FY2022. It would create grant programs for replacing school lead service lines and water fountains that contain lead. (Bills with related lead provisions include H.R. 3387; H.R. 2479, Title II; H.R. 4908; H.R. 4907; and S. 1401.) H.R. 1068 would also authorize grant programs for increasing the resiliency or adaptability of water systems and for developing real-time contaminant monitoring technologies. It would also establish deadlines for EPA to issue a revised Lead and Copper Rule49 and new regulations for perchlorate, perfluorinated compounds, and microcystin toxin.
- H.R. 1071—the Assistance, Quality, and Affordability Act of 2017—would amend and reauthorize the DWSRF program, paralleling DWSRF provisions in H.R. 1068, Title IV (above), among other purposes. H.R. 1071 would authorize to be appropriated for the DWSRF program a total of $21.17 billion over five years. It would also place greater program emphasis on assisting disadvantaged communities, revise the list of eligible activities, and require states to give funding priority to projects needed to make compliance affordable. The bill would also increase the level of funding authorized to be appropriated under Section 1459B(d) for lead reduction projects. (See also H.R. 2479, Title II.)
- H.R. 1647, the Water Infrastructure Trust Fund Act of 2017, would direct the Secretary of the Treasury to establish a voluntary product labeling system informing consumers that the manufacturer, producer, or other stakeholder is participating in the Water Infrastructure Investment Trust Fund and contributing to clean water. The Secretary would provide a label for a fee of 3 cents per unit. Funds would be made available only when the CWSRF appropriation is not less than the average of the preceding five fiscal years. Funds made available for a fiscal year would be split equally between the DWSRF and CWSRF programs. (This parallels H.R. 4468 from the 114th Congress.)
- H.R. 1653, the Drinking Water Affordability Act, would (1) extend DWSRF loan amortization periods to 30 years after project completion for public water systems generally and to 40 years for disadvantaged communities, (2) increase the portion of DWSRF funds states may use to provide additional subsidization to disadvantaged communities from 30% to 35%, (3) reauthorize state authority to use DWSRF funds for source water assessment and protection activities, (4) direct EPA to exempt water systems from a federal cross-cutting requirement50 if the Administrator determined that the state had an equivalent requirement, (5) require EPA to review best practices for streamlining the DWSRF loan process and fund administration and to report to Congress, and (6) direct the Government Accountability Office (GAO) to study and report on the cost-effective and economically feasible rehabilitation or replacement of drinking water infrastructure to meet SDWA goals and an assessment of barriers that preclude use of materials and technologies identified in the study.
- H.R. 3009/S. 3358, the Sustainable Water Infrastructure Investment Act of 2017/2018, would amend the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 to provide that the volume cap for private activity bonds shall not apply to bonds for drinking water and sewage facilities. (See also identical bills, H.R. 3912 and S. 1229.)
- H.R. 4902/S. 2364, the Securing Required Funding for Water Infrastructure Now Act (SRF WIN), would add a new section to WIFIA authorizing EPA to provide financial assistance (e.g., secured loans) to SRF programs to support eligible wastewater and drinking water projects. Although state SRF financing authorities are currently eligible to receive WIFIA assistance, the SRF WIN bills would authorize EPA to provide secured loans at subsidized interest rates for eligible states. These states would include those that received less than 2% of the SRF funds in the most recent year or states in which the President declared a major disaster between 2017 and the enactment date. (These loans would be limited to wastewater or drinking water infrastructure damaged by the major disaster.) Funding for the subsidized loans would be capped. Unlike other WIFIA assistance, the federal assistance under this section would be able to support 100% of project costs, and application fees would be waived. The bills would authorize appropriations of $200 million for each fiscal year between FY2019 and FY2023. However, no funding would be available if the SRF program or the WIFIA appropriation (excluding this new section) were less than the amount provided in FY2018.
- H.R. 5609, the Water Affordability, Transparency, Equity, and Reliability Act of 2018, would (1) establish a trust fund with funds going to EPA to support CWA and SDWA SRFs and activities and to the U.S. Department of Agriculture for household water well systems; (2) direct EPA to report on water affordability nationwide, discriminatory practices of water and sewer service providers, and water system regionalization; (3) authorize use of DWSRF funds to purchase privately owned community water systems from willing or unwilling sellers; (4) require states to use at least 50% of their capitalization grants to provide additional subsidization to disadvantaged communities; (5) authorize a grant program for repairing or replacing school drinking water coolers to ensure they are lead free; (6) require states to permit recipients of SRF assistance to enter into project labor agreements under the National Labor Relations Act; and (7) make permanent the SDWA requirement to use American iron and steel for projects receiving DWSRF assistance. (See also H.R. 1673.)
- H.R. 6653, the Innovative Materials for America's Growth and Infrastructure Newly Expanded Act of 2018, is a broad infrastructure bill to encourage research and use of innovative materials in transportation and water infrastructure systems. It would direct the Secretary of Transportation to innovative material innovation hubs. Section 8 would direct EPA to establish a water infrastructure innovation grant program for the design and installation of drinking water and wastewater systems that use innovative materials to reduce total costs and extend the service life of installed structures. It would authorize to be appropriated for this program $65 million for each of FY2019 through FY2023.
- S. 181 would require GAO to (1) publish a report identifying all federal public works and infrastructure programs and whether a domestic content preference requirement (e.g., iron, steel, and manufactured products) applied and (2) include a list of programs for which a listed preference requirement does not apply. Generally, once GAO issued the report, no federal funds or credit assistance could be made available under a program that lacks a domestic content preference for infrastructure projects unless all iron, steel, manufactured goods, and commodity construction materials used were produced in the United States.
- S. 880, the Made in America Water Infrastructure Act, would expand and make permanent the SDWA provision requiring use of U.S.-manufactured iron and steel in projects receiving DWSRF assistance. The bill would apply American iron and steel requirements to maintenance projects (in addition to construction, alteration, and repair projects).
- S. 1137, the Clean Safe Reliable Water Infrastructure Act, includes a sense of Congress that appropriations for the DWSRF and CWSRF should be robust. The bill would increase DWSRF set-aside authority for state implementation of source water protection plans and would apply 40 U.S.C. Chapter 11 (the Brooks Act) to negotiation of DWSRF-assisted contracts for communities serving more than 10,000 individuals. The bill would also authorize EPA's WaterSense Program51 and authorize to be appropriated a total of $18 billion over five years for combined sewer overflow projects grants under CWA Section 221. (See also S. 2800.)
- S. 2727 would direct EPA to establish a discretionary grant program for drinking water and wastewater infrastructure projects, including projects eligible under the CWSRF and DWSRF programs.
- S. 3121 would amend DWSRF and CWSRF provisions to require states to ensure, to the maximum extent practicable, that each procurement transaction for a project receiving SRF assistance is conducted in a manner that provides maximum open and free competition and that water systems consider use of all suitable materials for each solicitation of a procurement offer for a project. The bill would make similar revisions to WIFIA.