U.S.-Israel Relations
Key Concerns
Strong relations between the United States and Israel have reinforced bilateral cooperation in many areas. Matters of particular significance include the following:
- Concerns about Iran and Iranian allies, including the 2015 international nuclear agreement and growing tension and conflict involving Iran and its allies (including Hezbollah) at Israel's northern border with Syria and Lebanon.
- Israeli-Palestinian issues, including President Trump's recognition of Jerusalem as Israel's capital and relocation of the U.S. embassy in Israel there.
- Israeli domestic political issues, including criminal cases pending against Prime Minister Netanyahu.
For background information and analysis on these and other topics, including aid, arms sales, and missile defense cooperation, see CRS Report RL33476, Israel: Background and U.S. Relations, by [author name scrubbed]; CRS Report RL33222, U.S. Foreign Aid to Israel, by [author name scrubbed]; and CRS Report R44281, Israel and the Boycott, Divestment, and Sanctions (BDS) Movement, coordinated by [author name scrubbed].
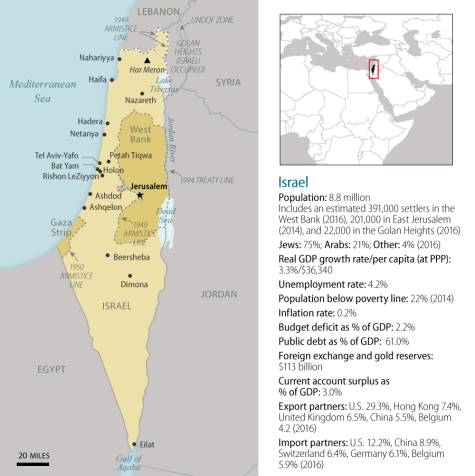 |
|
Notes: According to the Department of State: (1) The West Bank is Israeli occupied with current status subject to the 1995 Israeli-Palestinian Interim Agreement; permanent status to be determined through further negotiation. (2) The status of the Gaza Strip is a final status issue to be resolved through negotiations. (3) The United States recognized Jerusalem as Israel's capital in 2017 without taking a position on the specific boundaries of Israeli sovereignty. (4) Boundary representation is not necessarily authoritative. See https://www.state.gov/p/nea/ci/is/. Sources: Graphic created by CRS. Map boundaries and information generated by [author name scrubbed] using Department of State Boundaries (2011); Esri (2013); the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency GeoNames Database (2015); DeLorme (2014). Fact information from CIA, The World Factbook; Economist Intelligence Unit; IMF World Outlook Database; Israel Central Bureau of Statistics. All numbers are estimates and as of 2017 unless specified. |
Addressing Threats
Israel relies on a number of strengths, along with discreet coordination with Arab states, to manage potential threats to its security and existence.
Military Superiority and Homeland Security Measures
Israel maintains conventional military superiority relative to its neighbors and the Palestinians. Shifts in regional order and evolving asymmetric threats have led Israel to update its efforts to project military strength, deter attack, and defend its population and borders. Israel appears to have reduced some unconventional threats via missile defense systems, reported cyber defense and warfare capabilities, and heightened security measures vis-à-vis Palestinians.
Israel has a robust homeland security system featuring sophisticated early warning practices and thorough border and airport security controls; most of the country's buildings have reinforced rooms or shelters engineered to withstand explosions. Israel has also proposed and partially constructed a national border fence network of steel barricades (accompanied at various points by watch towers, patrol roads, intelligence centers, and military brigades) designed to minimize militant infiltration, illegal immigration, and smuggling from Egypt, Syria, Lebanon, Jordan, and the Gaza Strip.1
Undeclared Nuclear Weapons Capability
Israel is not a party to the Nuclear Nonproliferation Treaty (NPT) and maintains a policy of "nuclear opacity" or amimut. A 2017 report estimated that Israel possesses a nuclear arsenal of around 80-85 warheads.2 The United States has countenanced Israel's nuclear ambiguity since 1969, when Israeli Prime Minister Golda Meir and U.S. President Richard Nixon reportedly reached an accord whereby both sides agreed never to acknowledge Israel's nuclear arsenal in public.3 Israel might have nuclear weapons deployable via aircraft, submarine, and ground-based missiles.4 No other Middle Eastern country is generally thought to possess nuclear weapons.
U.S. Cooperation
Israeli officials closely consult with U.S. counterparts in an effort to influence U.S. decisionmaking on key regional issues. Israel's leaders and supporters routinely make the case to U.S. officials that Israel's security and the broader stability of the region remain critically important for U.S. interests. They also argue that Israel has multifaceted worth as a U.S. ally and that the Israeli and American peoples share core values.5 The United States and Israel do not have a mutual defense treaty or agreement that provides formal U.S. security guarantees.6
Iran and the Region
Iran remains of primary concern to Israeli officials largely because of (1) Iran's antipathy toward Israel, (2) Iran's broad regional influence, and (3) the possibility that Iran will be free of nuclear program constraints in the future. As mentioned above, in recent years Israel and Arab Gulf states have discreetly cultivated closer relations with one another in efforts to counter Iran.
Iranian Nuclear Agreement and the U.S. Withdrawal
Prime Minister Netanyahu has sought to influence U.S. decisions on the international agreement on Iran's nuclear program (known as the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action, or JCPOA). He argued against the JCPOA when it was negotiated in 2015, and welcomed President Trump's May 2018 withdrawal of the United States from the JCPOA and accompanying reimposition of U.S. sanctions on Iran's oil and central bank transactions. In a September 2017 speech before the U.N. General Assembly, Netanyahu had called on the signatories of the JCPOA to "fix it or nix it."7 Then, a few days before President Trump's May announcement, Netanyahu presented information that Israeli intelligence operatives apparently seized in early 2018 from an Iranian archive. Netanyahu used the information, which purportedly describes past work by Iran on a nuclear weapons program, to express concerns about Iran's credibility and its potential to parlay existing know-how into nuclear-weapons breakthroughs after the JCPOA expires.8
Although concern about Iran and its nuclear program is widespread among Israelis, their views on the JCPOA vary. Netanyahu and his supporters in government have routinely complained that the JCPOA fails to address matters not directly connected to Iran's nuclear program, such as Iran's development of ballistic missiles and its sponsorship of terrorist groups.9 Media reports suggest that a number of current and former Israeli officials have favored preserving the JCPOA because of the limits it placed on Iranian nuclear activities for some time or these officials' doubts about achieving international consensus for anything stricter.10
Commentators speculate on the possibility that Israel might act militarily against Iranian nuclear facilities if Iran resumes certain activities currently stopped under the JCPOA.11 According to one analyst, one group of Israeli officials have preferred to keep the nuclear deal in place while focusing on pressing challenges in Syria, while another group (including Netanyahu) have favored seizing the opportunity to make common cause with the Trump Administration to pressure Iran economically and militarily.12 However, shortly after Netanyahu publicly presented the Iranian nuclear archive, he said in an interview that he was not seeking a military confrontation with Iran.13
Iran in Syria: Cross-Border Attacks with Israel14
A "shadow war" has developed between Israel and Iran over Iran's presence in Syria. In the early years of the Syria conflict, Israel primarily employed airstrikes to prevent Iranian weapons shipments destined for Hezbollah in Lebanon. Since 2017, with the government of Bashar al Asad increasingly in control of large portions of Syria's territory, Israeli leaders have expressed intentions to prevent Iran from constructing and operating bases or advanced weapons manufacturing facilities in Syria. The focus of Israeli military operations in Syria has expanded in line with an increasing number of Iran-related concerns there. Further exacerbating Israeli sensitivities, Iran-backed forces (particularly Hezbollah) have moved closer to the Israeli-occupied Golan Heights since late 2017 via actions against Syrian opposition groups.
On February 10, 2018, Iranian personnel based at Tiyas air base in central Syria apparently sent an armed drone into Israeli airspace. A senior Israeli military source was quoted as saying, "This is the first time we saw Iran do something against Israel—not by proxy. This opened a new period."15
In May 2018, Prime Minister Netanyahu asserted that Iran had transferred advanced weaponry to Syria (weaponized drones, ground-to-ground missiles, anti-aircraft batteries) in recent months. He stated that Israel was "determined to block Iran's aggression" and that "we do not want escalation, but we are prepared for any scenario."16
Since the February 10 incident, Israel has reportedly struck Iranian targets on multiple occasions. The resulting exchanges of fire (including the downing of an Israeli F-16 during the February incident) and subsequent official statements from Israel, Iran, Syria, and Russia have highlighted the possibility that limited Israeli strikes to enforce "redlines" against Iran-backed forces could expand into wider conflict, particularly in cases of miscalculation by one or both sides.
On May 10, according to the Israeli military, Iran's Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps-Quds Force fired rockets at Israeli military positions in the Golan Heights, as retaliation against earlier Israeli strikes against Iranian targets in Syria.17 This triggered Israeli strikes in Syria on a larger scale than any Israeli operations there since the 1973 Yom Kippur War.18 Reportedly, Israel has since conducted some additional airstrikes in Syria, and on two separate occasions in July its military claimed that it shot down a Syrian drone and a fighter jet over the Golan Heights using Patriot missiles.19
Russia20
Russia's advanced air defense systems in Syria could affect Israeli operations.21 To date, Russia does not appear to have acted militarily to thwart Israeli airstrikes against Iranian or Syrian targets. However, Russian officials' statements in response to Israeli actions in Syria since February have fueled speculation about Russia's position vis-à-vis Israel and Iran,22 given that Russia's military presence in Syria is protected by Iran-backed ground forces.
Reportedly, Israeli officials continue to consult with Russian officials about deconflicting Israeli military operations in Syria and ways to limit Iran's presence there.23 In May 2018, Russian Foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov called for the withdrawal of all non-Syrian forces from the southern border area "on a reciprocal basis."24 However, as of July, Hezbollah reportedly has been helping lead an offensive against rebels in southern Syria.25 In a press conference following his July 16 summit with President Trump, Russian President Vladimir Putin stated a desire to have the situation between Israel and Syria in the Golan Heights return to what it had been before Syria's civil war.26
Hezbollah in Lebanon
Hezbollah has challenged Israel's security near the Lebanese border for decades—with the antagonism at times contained near the border, and at times escalating into broader conflict.27 Speculation persists about the potential for wider conflict and its regional implications.28 In recent years, Israeli officials have sought to draw attention to Hezbollah's weapons buildup—including reported upgrades to the range, precision, and power of its projectiles—and its alleged use of Lebanese civilian areas as strongholds.29 Previously during Syria's civil war, Israel reportedly provided various means of support to rebel groups in the vicinity of the Syria-Israel border in order to prevent Hezbollah or other Iran-linked groups from controlling the area.30
Increased conflict between Israel and Iran over Iran's presence in Syria raises questions about the potential for Hezbollah's Lebanon-based forces to open another front against Israel. In April 2018, Hezbollah leader Hassan Nasrallah said that an Israeli strike on Iranian targets at Tiyas air base was a "pivotal incident in the history of the region that can't be ignored" and a "historic mistake." Earlier that same day, Hezbollah's deputy leader Naim Qassem said that Hezbollah would not open a front against Israel from Lebanon, but that it was ready for "surprises."31 One May analysis expressed doubt that either Israel or Iran would seek to expand the scope of their emerging conflict in Syria to Lebanon.32 However, the same analysis and some others speculated that if Israel-Iran conflict in Syria worsens and Iran feels cornered, it could look to gain leverage over Israel by having Hezbollah launch attacks from Lebanon.33
Israeli-Palestinian Issues
Peace Process and International Involvement
The prospects for an Israeli-Palestinian peace process are complicated by many factors. Since President Trump took office, he and officials from his Administration have expressed interest in brokering a final-status Israeli-Palestinian agreement. Many of their statements and policies, however, have raised questions about the timing and viability of any new U.S.-backed diplomatic initiative.34 As discussed below (see "Jerusalem: U.S. Stance and Embassy Move"), the change in U.S. policy on Jerusalem in December 2017 has complicated the U.S. role. Israeli leaders generally celebrated the change, but PLO Chairman Abbas strongly objected.35 Many other countries opposed President Trump's statements on Jerusalem. This opposition was reflected in December action at the United Nations.36
Citing alleged U.S. bias favoring Israel, Palestinian leaders have broken off high-level political contacts with the United States and have sought support from other international actors and organizations to improve their negotiating position with Israel.37 However, the PA continues security coordination with Israel.38 Tensions over Jerusalem appear to have influenced Administration decisions to reduce or delay certain types of aid to the Palestinians,39 and have made prospects for restarting Israeli-Palestinian talks in 2018 less certain.40
Reports suggest that the Administration is preparing a detailed document on the peace process that it may share in an attempt to overcome obstacles to progress.41 At the end of a June 2018 trip to meet with various Middle Eastern leaders, senior White House advisor Jared Kushner (the President's son-in-law) said that the Administration's plan was almost done. Kushner also said, "If President Abbas is willing to come back to the table, we are ready to engage; if he is not, we will likely air the plan publicly."42 Some former U.S. officials have cautioned against presenting a plan given current Palestinian opposition.43 In May, Abbas characterized the possible removal of core issues of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict—namely, Jerusalem's status and Palestinian refugee claims—from the negotiating table as "an American slap."44
The Administration seeks support from some Arab states, including Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, Jordan, and Egypt, for the anticipated U.S. initiative. While these Arab states have criticized the U.S. stance on Jerusalem,45 there are also signs that the shared goal of countering Iranian influence in the region is leading some of them to interact more overtly with Israeli counterparts and to dissuade the Palestinians from abandoning U.S.-backed diplomacy.46 The 2002 Arab Peace Initiative remains a key reference point for Arab positions on issues of Israeli-Palestinian dispute.47
Speculation surrounds the particulars of the possible Trump Administration proposal. Dating back to unconfirmed reports from late 2017, some observers anticipate that a proposal could favor Israeli positions that call for limited Palestinian sovereignty, maintaining most West Bank settlements, locating a Palestinian capital on the outer fringes of Jerusalem, and dismissing refugee claims to a right of return.48 Palestinian officials have complained that the United States is trying to undermine Abbas and dictate a solution.49 In June, Abbas's spokesperson accused the Administration and Israel of seeking to separate Gaza from the West Bank under the guise of humanitarian aid.50
|
Gaza's Complicated Security, Political, and Humanitarian Situation Israel faces a threat from the Gaza Strip (via Hamas and other militant groups).51 Although Palestinian militants maintain rocket and mortar arsenals, the threat from projectiles has reportedly been diminished by Israel's Iron Dome defense system.52 Tunnels that Palestinian militants used somewhat effectively in a 2014 conflict with Israel have been largely neutralized by systematic Israeli efforts, with some financial and technological assistance from the United States.53 Under President Abdel Fattah al Sisi, Egyptian military efforts have significantly reduced smuggling over land into Gaza. In 2018, protests and violence along security fences dividing Gaza from Israel have attracted international attention. Israel's use of live fire and the death of more than 120 Palestinians in the spring (including several deaths on May 14, the day that the U.S. embassy opened in Jerusalem) led the U.N. Human Rights Council to call in May for an "independent, international commission of inquiry" to produce a report.54 A June U.N. General Assembly resolution condemned both Israeli actions against Palestinian civilians and the firing of rockets from Gaza against Israeli civilians.55 Subsequently, some Israel-Gaza violence has ensued over Palestinians' use of incendiary kites or balloons to set fires in southern Israel and a sniper's killing of an Israeli soldier in July, fueling speculation about possible escalation.56 U.S. and PA funding reductions have added to questions about humanitarian assistance for Gaza's population, who remain largely dependent on external donor funding and face chronic economic difficulties and shortages of electricity and safe drinking water.57 Since 2007, as part of a larger regime of Israeli-Egyptian control over access to and from Gaza, Israel has limited the shipment of building materials into Gaza because of concerns that Hamas might divert materials for reconstruction toward military infrastructure. The possibility that humanitarian crisis could destabilize Gaza has prompted discussions among U.S., Israeli, and Arab leaders aimed at improving living conditions and reducing spillover threats.58 These discussions have sparked public debate about how closely humanitarian concerns should be linked with political outcomes involving Israel, Hamas, and the PA, or with an anticipated U.S. diplomatic initiative.59 |
Jerusalem: U.S. Stance and Embassy Move
In December 2017, President Trump recognized Jerusalem as Israel's capital and pledged to move the U.S. embassy from Tel Aviv to Jerusalem. These actions represented a departure from the decades-long U.S. executive branch practice of not recognizing Israeli sovereignty over Jerusalem or any part of it.60 The President pointed to the Jerusalem Embassy Act of 1995 (P.L. 104-45) as a significant factor in the policy change. The western part of Jerusalem that Israel has controlled since 1948 has served as the official seat of its government since shortly after its founding as a state. Israel officially considers Jerusalem (including the eastern part it unilaterally annexed after the 1967 Arab-Israeli war, while also expanding the city's municipal boundaries) to be its capital.61
In his December remarks, President Trump stated that he was not taking a position on "specific boundaries of the Israeli sovereignty in Jerusalem," and would continue to consider the city's final status to be subject to Israeli-Palestinian negotiations.62 However, he did not explicitly mention Palestinian aspirations regarding Jerusalem; Palestinians envisage East Jerusalem as the capital of their future state. In a February 2018 interview, the President said that he would support specific boundaries as agreed upon by both sides.63 He also has called on all parties to maintain the "status quo" arrangement at Jerusalem's holy sites.64
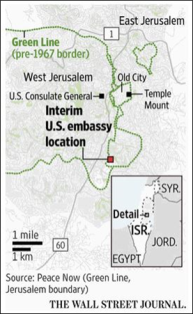 |
|
Source: Peace Now via the Wall Street Journal. |
On February 23, the State Department spokesperson issued the following press statement announcing that the embassy would open in May 2018, to coincide with Israel's 70th anniversary:
The Embassy will initially be located in the Arnona neighborhood, in a modern building that now houses consular operations of U.S. Consulate General Jerusalem. Those consular operations, including American citizen and visa services, will continue at the Arnona facility without interruption, as part of the Embassy. Consulate General Jerusalem will continue to operate as an independent mission with an unchanged mandate, from its historic Agron Road location. Initially, the interim Embassy in Arnona will contain office space for the Ambassador and a small staff. By the end of next year, we intend to open a new Embassy Jerusalem annex on the Arnona compound that will provide the Ambassador and his team with expanded interim office space. In parallel, we have started the search for a site for our permanent Embassy to Israel, the planning and construction of which will be a longer-term undertaking.
The embassy opened on May 14 at the Arnona facility amid criticism from several international actors and violence on the same day at the Gaza-Israel frontier. According to the State Department spokesperson, the site is located "partly in West Jerusalem and partly in what's considered no man's land," as it lies "between the 1949 armistice lines" in a zone that was demilitarized between 1949 and 1967.65 The White House stated that it cost $400,000 to modify the facility to function as an embassy.66 The ambassador's official residence is to transition to Jerusalem at a later date.67
Congress could consider a number of legislative and oversight options with regard to the plans mentioned above to expand the embassy at the Arnona site, and later to plan and construct a permanent embassy. These options could focus on funding, timeframe and logistics, progress reports, and security for embassy facilities and staff. A State Department official said in February that a new embassy building would take 7 to 10 years to construct, and a former official estimated that building a new embassy in Jerusalem may cost about $500 million.68
Domestic Israeli Developments
Corruption Allegations Involving Netanyahu
The Israeli police recommended in February 2018 that Attorney General Avichai Mandelblit indict Prime Minister Netanyahu for bribery, fraud, and breach of trust.69 Mandelblit may decide in 2019 whether to press charges.70 In response to the police recommendations, Netanyahu—who has consistently denied the allegations—said that the recommendations "will end with nothing" and that he will stay in office to pursue Israel's well-being.71 However, they could potentially threaten Netanyahu's position as prime minister.
The recommendations cover two specific cases.72 Later in February, developments in ongoing investigations appeared to implicate Netanyahu or his close associates in additional instances of alleged corruption.73 In June 2018, Netanyahu's wife Sara was indicted, along with a former staffer from Netanyahu's office, for the fraudulent use of state funds.74
Legally, Netanyahu could continue in office if indicted, but he could face public pressure to resign, and his coalition partners could face public pressure to withdraw their support for the government. Israel's previous prime minister, Ehud Olmert, announced his decision to resign in July 2008 amid corruption-related allegations, two months before the police recommended charges against him.75
Major Domestic Issues
The Knesset has recently passed some notable legislation. In July 2018, it passed a Basic Law defining Israel as the national homeland of the Jewish people.76 Also in July, the Knesset voted to withhold funds from the Palestinian Authority to "penalize it for paying stipends to Palestinian prisoners in Israel, their families and the families of Palestinians killed or wounded in confrontations with Israelis."77 Another bill passed in July permits single women to be surrogate parents, but does not extend the same permission to single men or same-sex couples.78
Additionally, controversial legislation has passed to apply some aspects of Israeli law to settlements in the West Bank,79 and is pending to limit the Supreme Court's power of judicial review over legislation.80 Several of the government's opponents and critics have voiced warnings that these and other initiatives may stifle dissent or undermine the independence of key Israeli institutions such as the media, the judiciary, and the military.
Early elections could happen (legally, elections are required in the second half of 2019) if the governing coalition splits over the cases against Prime Minister Netanyahu or some other issue. If early elections take place, Netanyahu (if he runs) could face challenges from figures on the right of the political spectrum (including Education Minister Naftali Bennett and Defense Minister Avigdor Lieberman), or nearer the center or left (former finance minister Yair Lapid, Labor Party leader Avi Gabbay, and retired generals Gabi Ashkenazi and Benny Gantz). Reportedly, Netanyahu may call for elections before the attorney general decides on whether to bring criminal charges against him, in hopes of claiming a popular mandate to continue in office even if he is indicted.81