Introduction
Apprenticeship is a workforce development strategy that trains a worker for a specific occupation using a structured combination of paid on-the-job training and related instruction. Increased costs for higher education and possible mismatches between worker skills and employer needs have led to increased congressional interest in alternative workforce development strategies such as apprenticeship.
Compared to some other developed nations, utilization of apprenticeship in the United States is relatively low.1 Some commentators have interpreted the relative dearth of apprenticeship programs in the United States as an opportunity for large-scale expansion.2 Others have suggested that other nations' labor market institutions and employers are more accommodating to apprenticeship models and prospects for domestic growth may be limited.3
Historically, the primary federal mechanism in the United States for supporting apprenticeships has been registering individual programs that comply with federally directed standards ("registered apprenticeships"). Registration is carried out by the Department of Labor (DOL) or a DOL-approved state agency. In recent years, DOL has supported expanded use of apprenticeship through a series of competitive grants to states and other intermediaries.
This report discusses federal efforts related to apprenticeship. It begins by describing the long-established federal role in certifying apprenticeships programs through the registered apprenticeship system. It then discusses more recent federal efforts to support apprenticeship expansion. The appendix of the report discusses federal funding streams that focus on other human capital development strategies but can support apprenticeship in certain circumstances.
Registered Apprenticeship
The National Apprenticeship Act of 19374 directs DOL to "formulate and promote the furtherance of labor standards necessary to safeguard the welfare of apprentices." DOL has carried out these provisions by developing a system in which DOL or a DOL-recognized state apprenticeship agency registers individual programs as meeting federal and/or state standards. Registration agencies also issue certificates of completion to apprentices who complete a registered program.
The National Apprenticeship Act is relatively concise, and the Registered Apprenticeship system has been established and developed predominantly through regulations and non-regulatory guidance.5 The agency within DOL that carries out the National Apprenticeship Act is the Office of Apprenticeship; the office's chief official is the administrator.
Registration of an apprenticeship program does not entitle an apprenticeship sponsor (typically an employer, although it can also be a labor union, industry group. or other eligible entity) to direct financial support from the federal government. Registration can make it easier for an apprenticeship program to operate within the eligibility rules of some federal programs and systems. For example, registered apprenticeship programs are approvable for GI Bill support, and are automatically eligible training providers for federal workforce funds.6 It is very likely, however, that at least some federally registered programs do not receive any federal funds.7
In the federal context, "apprenticeship" has been typically synonymous with registered apprenticeship programs. Programs that may have a strategy or format similar to apprenticeship but are not registered are not typically considered apprenticeships by the federal government, though they may be considered on-the-job training under federal education and workforce programs. Unless specified otherwise, when this report refers to apprenticeship, it is referring to registered apprenticeship.
|
Related Instruction Component of Registered Apprenticeship While on-the-job training is the most visible component of apprenticeship, registered apprenticeship programs are also required to have a "related instruction" component. Regulations define related instruction as "an organized and systematic form of instruction designed to provide the apprentice with the knowledge of the theoretical and technical subjects related to the apprentice's occupation." While there is no required amount of related instruction, regulations recommend at least 144 hours per year.8 Related instruction can be provided by a postsecondary institution such as a community college, directly by the apprenticeship sponsor, or through another provider. It can be provided in a classroom setting or through other means, such as self-study. Related instruction may lead to a degree or other credential, but it is not required to do so. It is often provided at no cost to the apprentice, but there is no requirement to that effect.9 |
Registration Agencies
Registered apprenticeships are programs that have been certified by a qualified registration agency as being in compliance with applicable standards. DOL's Office of Apprenticeship may register programs. A state may also elect to establish a state apprenticeship agency (SAA) that can register apprenticeship programs in the state.
If a state elects to establish an SAA, the SAA must be approved by the federal DOL using a process established in regulations.10 The state must submit an application to DOL that specifies the applicable agency and describes its standards, criteria, and requirements for registration. Once approved by DOL, an SAA's recognition is effective for five years, during which DOL will monitor the state agency. After five years, DOL may notify the SAA that it is in conformity with regulations and renew its recognition for an additional five years. If the SAA is not in conformity, DOL will notify the state of its nonconformity and provide technical assistance. After the nonconformities are corrected, DOL will renew recognition for another five years.
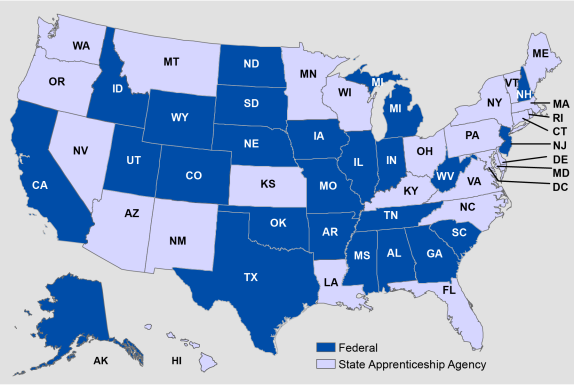
Currently, 25 states operate an SAA and 25 states register programs through DOL (see Figure 1). The District of Columbia and Guam operate SAAs. Apprenticeship programs in Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands are registered through DOL.
|
Figure 1. Entity Responsible for Registering Apprenticeship Programs in Each State |
 |
|
Source: Map created by CRS GIS Analyst Jim Uzel based on data from U.S. Department of Labor, Office of Apprenticeship, https://doleta.gov/OA/contactlist.cfm. |
Pre-apprenticeship Programs
Pre-apprenticeship programs are educational programs designed to prepare individuals for a registered apprenticeship program. Pre-apprenticeship programs can provide instruction in general education (e.g., mathematics) or vocational fields. DOL does not register or regulate pre-apprenticeship programs, though it has issued guidance on the characteristics of a quality pre-apprenticeship program.11 Among other attributes, DOL specified that a quality pre-apprenticeship program should have facilitated entry into a registered apprenticeship program.
Registration Criteria and Process
To register an apprenticeship program, the apprenticeship sponsor must submit an application to the applicable registration body (either DOL or an SAA).12 The application must include a description of the program and how it complies with standards established in regulation.
Apprenticeship sponsors have several options for assistance in developing their programs and corresponding registration applications. Sponsors can seek assistance directly from the registration agencies or from an intermediary such as an industry group.
|
Why Register an Apprenticeship Program? Because many apprenticeship sponsors receive no direct financial benefit from the federal government, it may be reasonable to ask why a sponsor would choose to register a program. There are several potential benefits:
|
Qualified Occupations
Not all occupations can be taught through an apprenticeship. Regulations specify that an occupation for which a worker can be trained through an apprenticeship must
- involve skills that are customarily learned in a practical way through a structured, systematic program of on-the-job supervised learning;
- be clearly identified and commonly recognized throughout an industry;
- involve the progressive attainment of manual, mechanical, or technical skills and knowledge which, in accordance with the industry standard for the occupation, would require the completion of at least 2,000 hours of on-the-job learning to attain; and
- require related instruction to supplement the on-the-job learning.13
DOL maintains a list of more than 1,300 apprenticeable occupations.14 Sponsors who wish to establish an apprenticeship in a new occupation should contact DOL or the applicable SAA for an apprenticeability determination.
Program Frameworks and Standards of Apprenticeship
Sponsors have a number of options in designing an apprenticeship program. Regulations establish three general frameworks for a program:15
- Time-based approach measures skill attainment through completion of a specified number of hours of on-the-job training (at least 2,000), as specified by the work process schedule (see below).
- Competency-based approach measures skill attainment through the apprentice's demonstration of specified skills and knowledge, verified by the sponsor. A competency-based program must still address how on-the-job training is incorporated into the program.
- Hybrid approach measures an apprentice's skill attainment through a combination of a specified minimum number of on-the-job hours and verified demonstration of competencies.
Each registered apprenticeship program must have a written plan specifying the terms and conditions of the apprenticeship ("program standards"). Among other required content, the plan must include a work process schedule, which outlines the major competencies of the occupation and how a combination of on-the-job training and/or related instruction will lead to the worker demonstrating proficiency in those competencies.
Regulations specify a number of components that the apprenticeship sponsors' standards must address. Standards relate to program design, apprentice protections, and rules related to administration and recordkeeping. Some key standards include the following:
- Outline of the work processes in which the apprentice will receive supervised experience and training and the approximate amount of time spent on each process.
- Description of the related instruction the apprentice will receive in a classroom or alternative setting. A minimum of 144 hours of related instruction per year is recommended.
- Schedule of progressively increasing wages for the apprentice. The entry wage may not be less than the federal minimum wage, or a higher wage level if required by another federal law, state law, or collective bargaining agreement.
- Assurance of adequate and safe equipment and facilities and safety training for apprentices.
- Definition of probationary period for apprentices in the program. The probationary period cannot exceed 25% of the length of the program or one year, whichever is shorter.
- Contact information for the appropriate authority to receive, process, and make disposition of complaints.
Additional standards relate to administrative matters such as the construction of apprenticeship agreements, credit for previous experience, compliance with Equal Employment Opportunity provisions, and records maintenance.16
Program Approval and Registration Process
If the registration agency finds that the program conforms to standards in regulation, the program is granted provisional approval for one year. At the conclusion of the provisional year, the registration agency reviews the program for quality and conformity with regulations. After the review, the registration agency may make the program's registration permanent; continue provisional approval through the first training cycle; or, if the program is not in compliance, recommend the program for deregistration.17
Oversight, Program Performance, and Deregistration
Once a program is permanently registered, the registration agency must review the program no less than once every five years to ensure that it remains in compliance with the required standards. Regulations specify that factors in evaluation must include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Quality assurance assessments. These reviews determine that programs are providing on-the-job training, related instruction, wage increases, and meeting other requirements consistent with registration standards.
- Equal Employment Opportunity (EEO) Compliance Reviews. The registration agency may review company records or interview employees or hiring officials to ensure compliance with EEO requirements.18
- Completion rates. To evaluate completion rates, the registration agency compares a program's rate to the national average. Apprenticeships that are cancelled during the probationary period do not have an adverse effect on the program's completion rate.
In cases where a program sponsor has completion rates below the national average, the registration agency will provide technical assistance. In cases of persistently low completion rates, the program may be subject to deregistration.
Deregistration Process
A registration agency may undertake deregistration proceedings if a program fails to comply with the required standards of apprenticeship or demonstrates "persistent and significant failure to perform successfully."19 Regulations define a program that fails to perform as one that
- consistently fails to register at least one apprentice,
- shows a pattern of poor quality assessments by the registration agency over a period of several years,
- demonstrates an ongoing pattern of very low completion rates over a period of several years, or
- shows no indication of improvement in the areas identified by the registration agency during a review process as requiring corrective action.
If a program is not performing in accordance with standards or requirements, the registration agency must notify the sponsor in writing of the shortcomings and the remedies required. Following this notice, the registration agency must "assist the sponsor in every reasonable way to achieve conformity." If the program does not demonstrate the required corrections in the allotted period of time, the registration agency notifies the sponsor of deregistration proceedings.20 The sponsor may request a hearing with an administrative law judge. If the sponsor does not request a hearing, the recommendation for deregistration and all supporting documents are submitted to the administrator of the Office of Apprenticeship. The administrator makes the final decision regarding deregistration.
Role of Intermediaries in the Registration Process
While a sponsor has the option of designing an apprenticeship program independently and then registering the program directly with the applicable registration agency, many sponsors work with an intermediary in the development and registration of a program. Intermediaries can include public agencies, private nonprofits, labor organizations (unions), or industry groups.
Intermediaries can assist employers with the construction of a program that will meet the required standards. Intermediaries can facilitate connections with providers of related instruction or help sponsors develop their own instructional programs. Intermediaries can also assist sponsors with applying to a registration agency.
In some cases, an intermediary can develop a program, register it, and then partner with individual employers to carry out the actual apprenticeships. This approach allows individual employers to participate in an apprenticeship program without the burden of developing and registering it.21 For example, the American Hotel and Lodging Association (AHLA) developed and registered an apprenticeship program for the occupation of lodging manager. Individual employers that wish to use the program complete an employer acceptance agreement, committing to the work processes and other standards developed by the AHLA.22 Individual hotels are then responsible for recruiting apprentices and carrying out the program, using AHLA's standards.
United Services Military Apprenticeship Program (USMAP)
In some circumstances, members of the Armed Forces may complete a registered apprenticeship program while serving on active duty. Typically, USMAP participants may complete at least some apprenticeship requirements through their normal military duties.
Military apprenticeships are registered with DOL using an application process that is similar to the process used by civilian employers. Members of the Armed Forces who complete a USMAP apprenticeship receive a certificate of completion from DOL, which can serve as a nationally recognized indicator of proficiency in an occupation to civilian employers.
USMAP participants must pursue an apprenticeship that is related to their military occupational specialty (MOS), though there may be several apprenticeship options within a single MOS. For example, an utilitiesman in the Navy (an occupation responsible for working with plumbing, heating, steam, fuel, and other systems) may pursue an apprenticeship in six different occupations.23
Registered Apprenticeship Participation Data
Table 1 presents participation in registered apprenticeships from FY2013 through FY2017. The "National Total" column includes all registered apprenticeship programs. The "Military Apprenticeship Program" column is members of the Armed Forces in the USMAP; these participants are included in the national totals.
The table includes counts of active, new, and completer apprentices. Readers should not use the data in the table to calculate annual completion percentages. The multiyear nature of most programs means that most new apprentices would not complete a program until a subsequent fiscal year. Further, new apprentices who discontinue a program within the probationary period may be included in Table 1 but would not be counted in the eventual calculation of the completion rate.
|
National Total |
U.S. Military Apprenticeship Program |
|||||
|
Fiscal Year |
Active Apprentices |
New Apprentices |
Total Completers |
Active Apprentices |
New Apprentices |
Total Completers |
|
2013 |
375,425 |
164,746 |
52,542 |
87,675 |
51,001 |
8,194 |
|
2014 |
410,375 |
170,544 |
44,417 |
95,452 |
54,430 |
9,834 |
|
2015 |
447,929 |
197,535 |
52,717 |
95,770 |
55,445 |
11,511 |
|
2016 |
505,371 |
206,020 |
49,354 |
95,001 |
54,756 |
11,104 |
|
2017 |
533,607 |
191,563 |
64,021 |
89,301 |
48,715 |
12,063 |
Source: Department of Labor, "Registered Apprenticeship National Results," https://doleta.gov/oa/data_statistics.cfm.
Notes: U.S. Military Apprenticeship Program participants are included in totals.
While total participation is available for registered apprenticeships nationwide, some data are limited to programs that are registered with DOL (not state apprenticeship agencies). Table 2 is limited to federally registered apprentices and presents industries with the most apprentices in FY2017. About 68% of active apprentices were in the construction industry. The data in the table exclude apprentices in the USMAP and apprenticeships registered by state approving agencies.
Table 2. Active Apprentices in Registered Programs by Industry for FY2017
Data are limited to nonmilitary apprentices in federally registered programs
|
Industry |
Active Apprentices |
Share |
|
Construction |
175,195 |
67.9% |
|
Public Administration |
23,004 |
8.9% |
|
Manufacturing |
17,559 |
6.8% |
|
Transportation |
15,895 |
6.2% |
|
Utilities |
9,019 |
3.5% |
|
Health Care and Social Assistance |
2,549 |
1.0% |
|
Othera |
14,698 |
5.7% |
|
Total |
257,306 |
100.0% |
Source: Department of Labor, Registered Apprenticeship National Results Fiscal Year 2016, https://doleta.gov/oa/data_statistics.cfm.
Notes: Table excludes apprentices in United Services Military Apprenticeship Program and apprentices in states with state approving agencies.
a. Total of industries with less than 1.0% of total apprentices.
Recent Federal Activity
While registered apprenticeship has historically been a primarily private sector initiative with federal oversight, there have been several efforts in recent years to expand the federal role and support apprenticeship more directly. These efforts have included competitive grants that supported varied approaches to expanding apprenticeship and a 2017 Executive Order that proposed modifying the registration process and directed federal departments to increase promotion of apprenticeship.
Competitive Grant Programs
In recent years, the federal government has supplemented its registration and technical support efforts with competitive grants supported by multiple funding streams.
Grants Supported by Appropriated Funds
In each of the past three fiscal years, Congress has appropriated funds to DOL "to expand opportunities relating to apprenticeship programs registered under the National Apprenticeship Act ... through grants, cooperative agreements, contracts, and other arrangements." Appropriations were $90 million in FY2016, $95 million in FY2017, and $145 million in FY2018.
Examples of the efforts competitive grants funded through these appropriations have supported include the following:24
- State Expansion Grants. These grants to state agencies were awarded in November 2016 and were designed to help state agencies develop and implement strategies to support the expansion of apprenticeship as a workforce development strategy. The grants were supported by funds appropriated in the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2016 (P.L. 114-113). There were 37 successful grantees, and grants totaled $50.5 million.25
- National Industry and National Equity Partner Grants. These grants were awarded to nongoverment organizations in September 2016 to engage in efforts to expand apprenticeship in certain industries and among certain underrepresented populations. The grants were supported by funds appropriated in the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2016 (P.L. 114-113). There were 14 grantees, and grants totaled $20.4 million.26
Grants Supported by H-1B Training Funds
When sponsoring high-skill immigrants under H-1B visas, employers pay a fee that is subsequently allocated to DOL to support training programs.27 The department has some flexibility in choosing the exact activities that are supported by these funds. Statute specifies that the funding must support training in "high growth industries and economic sectors."28 In recent years, appropriations laws have further specified that the funds must be used for grants intended to support training in occupations and industries for which employers are using H-1B visas to hire foreign workers.29
DOL has used this funding stream to support a variety of grants. In 2015, it used $175 million of the H-1B training funds for "American Apprenticeship Initiative Grants." These grants were awarded to partnerships of public and private entities to create new apprenticeship programs and expand existing programs.30
The Trump Administration expressed interest in using these funds to support apprenticeship-oriented activities in a 2017 Executive Order. As of this writing, however, the Administration had not solicited any apprenticeship-related grants supported by this funding stream.
2017 Executive Order
In June 2017, President Trump issued Executive Order (EO) 13801.31 The EO emphasized the promotion of apprenticeship as an employer-driven workforce development strategy that may come at a lower cost than traditional higher education.
The EO directed the Secretary of Labor to "consider proposing regulations" that "reflect an assessment of whether" to modify the registration process to increase the role of nongovernment entities. The EO specified that the current approving agencies may retain their current role in finalizing the registration of apprenticeship programs, but programs that have been recognized by a qualified third party may qualify for "expedited and streamlined" registration.
The EO encouraged specified federal agencies to promote apprenticeship as a workforce development strategy. The EO directed the Secretary of Labor to establish a task force on apprenticeship to identify strategies and proposals to promote apprenticeship and submit a report to the President.32
The EO specifies that DOL shall use funding to promote apprenticeships, "subject to available appropriations and consistent with applicable law." The only specific funding stream mentioned in the EO is the aforementioned funding DOL receives each year from H-1B immigration visa fees. It is unclear if or how other funding streams will support the objectives of the EO.
2016 Department of Commerce Report
In November 2016, the Department of Commerce issued an agency-commissioned report that discussed apprenticeship from a business perspective and provided detailed case studies of 13 existing programs.33 The case studies included firms in health care, information technology, and several industrial fields. The study acknowledged that firms included may not be representative of all firms that have started or considered apprenticeship programs. Still, the report may offer some useful "on the ground" perspectives on how employers develop and implement apprenticeship programs.
Several themes emerged throughout the report:
- Employer investments in apprentices are substantial. The report found that "Not considering start-up costs, the most expensive program in our sample of firms cost $250,000 per apprentice; the least less than $25,000."34 The variation was at least partially attributable to differences in program lengths: the longest program was four years, and the shortest was one year. All companies reported that the major cost for their program was apprentice wages. Other costs included program start-up, tuition and materials for related instruction, staff time, and overhead.35
- Companies in the sample were generally satisfied with the results of their programs. The report found that "the companies in our sample were unanimous in their support of apprenticeships." It also noted that the "poaching" of apprentices by other employers was not a major issue for apprenticeship sponsors. The report further noted that some firms reduced the cost risks of poaching by developing their apprenticeship programs in consortia with similar employers.36
- At least some programs were very competitive. Not all programs in the study described the number of applicants relative to the number of apprentices, but the programs that did were selective, with sponsors selecting approximately 10% to 15% of applicants for an apprenticeship.37
Appendix. Federal Funding Streams that May Directly Support Apprenticeship
In addition to the activities at the Department of Labor's Office of Apprenticeship, there are other federal funding streams that can directly support apprenticeship or individual apprentices. These funding streams most frequently support other means of human capital development, but they can also support apprenticeship in some circumstances. This section highlights federal funding streams in which the administering departments have issued guidance on how to utilize funds for apprenticeship. It is likely that there are other federal funding streams that could support apprenticeship in certain circumstances.
Workforce Funding through the Workforce Innovation and Opportunity Act
The Workforce Innovation and Opportunity Act (WIOA) authorizes formula grants to state workforce agencies to support job training and career services.38 WIOA funding is administered at the state and local levels by Workforce Development Boards (WDBs), which are partnerships of local employers, training providers, and other workforce stakeholders. State and local WDBs have autonomy to support workforce development through a variety of activities.
Statute and guidance have specified a number of ways in which WDBs can use WIOA funds to support apprenticeship.39 For example, the on-the-job training provisions of WIOA allow WDBs to reimburse apprenticeship sponsors for a portion of wages paid to apprentices. The training provisions of WIOA allow funds to be used for expenses related to an apprenticeship program's related instruction.
In addition to potentially providing direct financial support for apprenticeship programs, WIOA contains several administrative provisions that institutionally integrate local registered apprenticeship programs into state workforce systems. WIOA specifies that there must be a representative from a registered apprenticeship program on each state and local WDB. These boards are responsible for recognizing local workforce programs that meet local needs and approving those programs for WIOA funding. Registered apprenticeship programs are automatically eligible for WIOA funding; they do not need to be approved by a WDB.
GI Bill and Veterans Education Benefits40
Individuals eligible for a GI Bill, including former members of the Armed Forces, can typically use their benefits while pursuing an approved apprenticeship. For example, veterans who use the Post-9/11 GI Bill (the most common education benefit for recent veterans) while pursuing a registered apprenticeship program qualify for a housing allowance while participating in the apprenticeship. The amount of the housing allowance varies by geographic location and other factors. Post-9/11 GI Bill participants in a registered apprenticeship program receive up to 100% of the housing allowance for the first six months of the program. The allowance then declines 20 percentage points every six months until reaching 20%. The declines in the housing allowance are intended to align approximately with scheduled wage increases in the apprenticeship program.41 Post-9/11 GI Bill participants pursuing apprenticeship more than half-time also receive a books and supplies stipend.
In cases where GI Bill-eligible apprentices are required to pay for their related instruction, an apprentice may also be able to use his or her GI Bill benefits to cover tuition and fees associated with related instruction.
Federal Student Aid
In some circumstances, individual apprentices may be able to access federal student aid (FSA) funds such as Pell Grants or subsidized student loans. Eligibility for FSA funds is largely contingent on whether the apprenticeship (or a component of the apprenticeship, such as the related instruction component) is an academic program that is eligible for federal student aid.42 Notably, registration of an apprenticeship program does not necessarily qualify it for federal student aid, and it is possible that there are apprenticeship programs that are not registered by a registration agency but are eligible for FSA funds.
Apprenticeship programs (or components thereof) that are eligible for federal student aid must (1) lead to a degree, diploma, certificate, or other recognized credential; (2) be provided by an eligible institution; and (3) meet program length requirements in terms of credit hours or clock hours.43 For need-based FSA, a student must also meet the financial criteria for a given program.44
The FSA eligibility criteria can be applied separately to the on-the-job training and related instruction portions of an apprenticeship. For example, the related instruction portion of a program may be eligible while the on-the-job training portion is not. The on-the-job training portion of an apprenticeship program can be eligible for FSA if the on-the-job training portion of the program is for qualified credit from an FSA-eligible institution. Guidance specifies that there are no federal limits on the percentage of a qualified program that may consist of on-the-job training, so long as the training is provided by the institution of higher education. Using these criteria, on-the-job training that is either not for credit or is provided by an entity other than an eligible institution (such as an employer) would not qualify for FSA.45
In limited cases, institutions may choose to use Federal Work Study (FWS) funding to cover a portion of an apprentice's wages during on-the-job training.46 If an institution chooses to include apprenticeship employment as part of its FWS program, selected eligible students may receive FWS wages for employment in the apprenticeship, even if the apprenticeship is not part of the student's educational program.47