Conflict Overview
In March 2015, Saudi Arabia and members of a coalition it established (hereinafter referred to as the Saudi-led coalition or the coalition) launched a military operation aimed at restoring the rule of Yemen's internationally recognized president, Abdu Rabbu Mansour Hadi.1 Prior to the start of hostilities, Hadi's government had been gradually supplanted by an alliance composed of the Iran-supported Houthi movement2 and loyalists of the previous President, Ali Abdullah Saleh (hereinafter referred to as Houthi-Saleh forces). In early December 2017, the Houthi-Saleh alliance unraveled, culminating in the killing of former President Saleh on December 4, 2017.
Since Saleh's death, the coalition has made modest military gains along the Saudi-Yemeni border, along the western coastal road (capturing the town of Khoukha between the coalition-controlled port of Mocha and the Houthi-controlled port city of Hodeidah), and in weakening the Houthi siege of Taiz, Yemen's third-largest city.3 Nevertheless, Houthi forces remain ensconced in northern Yemen and have consolidated their hold over the capital, Sana'a. Since Saleh's death, the former ruling party of Yemen has fractured into competing factions.4
Despite multiple attempts by the United Nations to broker a peace agreement, all sides have remained deadlocked. U.N. Special Envoy for Yemen Ismail Ould Cheikh Ahmed has announced that he will step down from his position when his term ends at the end of February 2018. The United Nations estimates that 10,000 people have been killed in the conflict in Yemen since the start of hostilities (March 2015). The actual number of casualties is likely much higher, with more than 2,200 Yemeni deaths from a 2017 cholera outbreak alone.
Prelude to the War
Central governance in Yemen, embodied by the decades-long rule of former President Ali Abdullah Saleh, began to unravel in 2011, when political unrest broke out throughout the Arab world. Popular youth protests in Yemen were gradually supplanted by political elites jockeying to replace then-President Saleh. Ultimately, infighting among various centers of Yemeni political power broke out in the capital, and government authority throughout the country eroded. Soon, militias associated with Al Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula seized territory in one southern province. Concerned that the political unrest and resulting security vacuum were strengthening terrorist elements, the United States, Saudi Arabia, and other members of the international community attempted to broker a political compromise. A transition plan was brokered, and in 2012 former Vice President Abdu Rabbu Mansour Hadi became president.
With the support of the United States, Saudi Arabia, and the United Nations Security Council, President Hadi attempted to reform Yemen's political system. Throughout 2013, key players convened a National Dialogue Conference aimed at reaching broad national consensus on a new political order. However, in January 2014 it ended without agreement.
One antigovernment group in particular, the northern Yemeni Houthi movement, sought to use military force to reshape the political order. Within weeks of the National Dialogue Conference concluding, the Houthis launched a military offensive against various tribal allies of President Hadi. The Houthis were joined by the forces still loyal to former President Saleh, creating an alliance of convenience that was a formidable opponent to President Hadi and his allies.
In 2014, Houthi militants took over the capital and violated several power-sharing arrangements. In 2015, Houthi militants placed President Hadi under house arrest. Although he was able to escape to Aden in southern Yemen, his position became untenable, as Houthi forces advanced from the capital all the way to Aden. In March 2015, after President Hadi, who had fled to Saudi Arabia, appealed for international intervention, Saudi Arabia and a hastily assembled international coalition launched a military offensive aimed at restoring Hadi's rule and evicting Houthi fighters from the capital and other major cities.
The Saudi-led coalition launched air strikes in response to a specific request from President Hadi. In a letter to the heads of state of the Gulf Cooperation Council on March 24, 2017, President Hadi wrote the following:
I urge you, in accordance with the right of self-defence set forth in Article 51 of the Charter of the United Nations, and with the Charter of the League of Arab States and the Treaty on Joint Defence, to provide immediate support in every form and take the necessary measures, including military intervention, to protect Yemen and its people from the ongoing Houthi aggression, repel the attack that is expected at any moment on Aden and the other cities of the South, and help Yemen to confront Al-Qaida and Islamic State in Iraq and the Levant.5
There are a number of reasons as to why Saudi Arabia intervened in Yemen, not all of which are mutually exclusive. Some suggest that the Saudis launched military operations out of fear that Yemen, under Houthi-Saleh rule, would fall under Iranian influence.6 Others charge that Saudi fears of expanding Iranian regional influence are overblown and that the kingdom intervened to secure its southern border.7 Some reports suggest that the Saudis viewed this military campaign as an opportunity to burnish the credentials of the young and then-newly appointed Defense Minister (and now Crown Prince) Prince Mohammed bin Salman.8
The Blockade of Hodeida Port and the Administration's Response
In November 2017, a Houthi missile with alleged Iranian origins landed deep inside Saudi Arabia, leading the coalition to blockade all of Yemen's ports. This exacerbated Yemen's humanitarian crisis and, on November 20, the Famine Early Warning Systems Network (Fews Net) issued an alert, warning that "if all ports remain closed, or re-open but are unable to support large-scale imports of essential goods, Famine is likely in many areas of the country within three to four months. In less accessible areas with the most severe current food insecurity, Famine could emerge even more quickly."9 During the blockade, aid agencies announced that five cities had run out of clean water (Sa'ada, Taiz, Hodeida, Sana'a, and al Bayda).10 Humanitarian agencies decried the closures, asserting that the Saudi-led coalition was violating international law by using starvation as a weapon.11 However, the Saudi-led coalition claimed that it was acting legally, citing Paragraph 14 of UNSCR 2216 (see below), which calls on states to take measures to prevent the supply of military goods to the Houthis.12
The Trump Administration demanded that the coalition ease its entry restrictions while condemning Iran for what the Administration described as a dangerous escalation of the conflict.13 The White House issued four press statements on the conflict between November 8 and December 8, including a statement on December 6 in which President Trump called on Saudi Arabia to "completely allow food, fuel, water, and medicine to reach the Yemeni people who desperately need it. This must be done for humanitarian reasons immediately."14 On December 14, the Administration once again addressed the conflict in Yemen but from within the context of Iran's broader regional activities. In refocusing attention on the Houthi-Iranian dimension of the conflict, U.S. Permanent Representative to the United Nations Nikki Haley presented materials recovered from a missile fired by Houthi forces into Saudi Arabia that reportedly have similarities in design to the Iranian Qiam short-range ballistic missile.15
On December 20, the Saudi-led coalition announced that it would end its blockade of Hodeida port for a 30-day period and permit the delivery of four U.S.-funded cranes to Yemen to increase the port's capability to off-load commercial and humanitarian goods.16 The next day, the White House issued a statement welcoming "Saudi Arabia's announcement of these humanitarian actions in the face of this major conflict."17 Since the end of the blockade, Saudi Arabia also has announced that it would deposit $2 billion in Yemen's Central Bank (located in Aden) in order to shore up Yemen's currency. The kingdom also pledged $1.5 billion toward the United Nations' 2018 Humanitarian Response Plan for Yemen. It is unclear whether the Saudi-led coalition intends to extend the 30-day period and end its blockade indefinitely. On January 2, 2018, in response to a media inquiry on the coalition's continued air campaign against the Houthis, U.S. State Department spokesperson Heather Nauert remarked that "not only have we called on them [Saudi-led coalition] to ease the blockade, we continue to call on them to be very judicious in their use of airpower—also, though, however, understanding that they have—the Saudis—have a legitimate concern about their own security at home. So it's a delicate balance of sorts."18
|
Alleged Iranian Supply of Missiles to the Houthis The degree of Iran's military role in Yemen has long been a subject of much debate. Iran has been caught on multiple occasions attempting to smuggle weapons to the Houthis.19 In repeated public statements by high-level Saudi officials, Saudi Arabia has cited Iran's illicit support for the Houthis as proof that Iran is to blame for the Yemen conflict. Iranian support to the Houthis provides the clerical regime with a relatively low-cost way of countering Saudi influence in Yemen. Saudi officials frequently justify their intervention in Yemen as a defensive action in order to prevent Yemen from being taken over by the Houthis. Recent Houthi missile launches against Saudi Arabia and the UAE have once again raised questions over possible Iranian direct supply of armaments or missile technology know-how to the Houthis. After the November 4 missile attack against King Khalid International Airport in Saudi Arabia, the Saudi-led coalition released photographs of what it said were remnants of an Iranian Qiam missile that had been launched from northern Yemen, an accusation reiterated by U.S. officials.20 In January 2018, reports surfaced that a United Nations Panel of Experts had concluded in an unreleased report that "The panel has identified missile remnants, related military equipment and military unmanned aerial vehicles that are of Iranian origin and were introduced into Yemen after the imposition of the targeted arms embargo.... As a result, the panel finds that the Islamic Republic of Iran is in non-compliance with paragraph 14 of resolution 2216."21 Russia has recently questioned the evidence against Iran, arguing that the U.N. Security Council's Yemen sanctions committee should address the issue of Iranian weapons smuggling.22 |
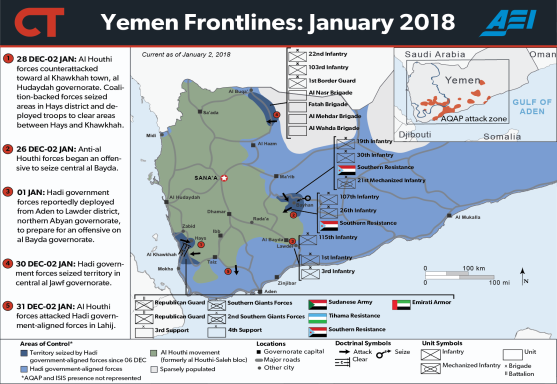 |
|
Source: American Enterprise Institute, Yemen Frontlines: January 2018 |
Yemen's Fragmentation: Conflict in the South
|
Figure 2. Major General Aidarous al Zubaidi First Session of the Southern Transitional Council |
 |
|
Source: Open Source Center, Aden al Ghad (in Arabic), July 5, 2017, Document ID# IMR2017071132888990. |
In Aden, forces allied with President Hadi have repeatedly clashed with southern separatists who have received backing from the United Arab Emirates (UAE), a key member of the Saudi-led coalition. Hadi-UAE tensions are multifaceted, as the sides disagree over how closely to embrace Yemen's main Islamist party (Islah) and how closely to work with southern separatists, many of whom seek either greater southern autonomy or the restoration of an independent state in southern Yemen. In the spring of 2017, the UAE supported General Aidarous al Zubaidi's (see Figure 2) formation of the Southern Transitional Council (STC) after Hadi dismissed him as Aden's governor.
Although President Hadi has relocated Yemen's internationally recognized government to the port city of Aden, the United Arab Emirates (UAE) effectively controls the city through the presence of its own troops or allied tribal militia (known as the Southern Belt or Al Hizam in Arabic). The UAE controls Aden's airport and seaport, and has invested in rebuilding infrastructure. President Hadi's only personally loyal military force in Aden is the Presidential Protection Force, which reportedly is relatively small compared to UAE-allied forces.23
After months of periodic clashes between pro-Hadi forces and UAE-backed forces, the STC issued an ultimatum to Hadi threatening to topple his government unless President Hadi dismissed his cabinet and formed a more representative government. On January 30, 2018, the STC seized control of most of Aden from Hadi's troops in just three days. The UAE and Saudi Arabia may have intervened in order to ensure that the STC remains committed to the larger fight against the Houthis. After the fighting subsided, the STC declared that it would remain committed to the coalition's military operations against the Houthis and handed back military installations to Hadi's forces. Nevertheless, it would appear that Hadi has a government in name only and that, on the ground, power resides in the hands of the STC.
Yemen at the United Nations
As the war in Yemen approaches its fourth year, it has steadily evolved from a contest between competing local elites to a complex conflict involving a combination of Yemeni and foreign forces waging war in an increasingly fragmented landscape. While the conflicts in Syria, Iraq, and Libya seem to have garnered more media attention than Yemen, the Yemen war has been a major focus of various United Nations entities and deliberative bodies since the Saudi coalition's intervention in March 2015.
From the start of hostilities, Saudi Arabia was able to secure the support of the United Nations Security Council, a key development in providing the Saudi-led coalition with international approval for its intervention. On April 14, 2015, the United Nations Security Council adopted Resolution 2216, which imposed sanctions on individuals undermining the stability of Yemen and authorized an arms embargo against the Houthi-Saleh forces. It also demanded that the Houthis withdraw from all areas seized during the current conflict, relinquish arms seized from military and security institutions, cease all actions falling exclusively within the authority of the legitimate Government of Yemen, and fully implement previous council resolutions.
One of the key aspects of United Nations Security Council Resolution (UNSCR) 2216 is that it authorizes member states to prevent the transfer or sale of arms to the Houthis or to former President Saleh and also allows Yemen's neighbors to inspect cargo suspected of carrying arms to Houthi fighters. To implement this authority in UNSCR 2216, some member states (the European Union, Netherlands, New Zealand, the United Kingdom, and the United States) formed the U.N. Verification and Inspection Mechanism (UNVIM), a U.N.-led operation designed to inspect incoming sea cargo to Yemen for illicit weapons. UNVIM can inspect cargo, while also ensuring that humanitarian aid is delivered in a timely manner.
Yemen's Humanitarian Crisis and U.S. Response
Yemen is consistently described as one of the world's worst humanitarian crises. According to UN OCHA, out of a total population estimated at 29 million, 22.2 million Yemenis are in need of assistance and 11.3 million are in acute need. The United Nations often describes Yemen as "the world's largest man-made food security crisis."24 Whereas food is available in markets across the country, the war has hampered distribution networks and 1.25 million public employees have gone nearly a year without receiving salaries, which has contributed to a liquidity crisis in the banking sector. Aid agencies estimate that 17.8 million people are now food insecure.
For 2018, the United Nations' Humanitarian Response Plan calls for $2.96 billion in total humanitarian aid for programs in 86 sectors that will reach an estimated 13 million people. With millions of Yemenis lacking access to basic health care and clean water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH) services, the country is experiencing the world's largest ongoing cholera outbreak. As of January 2018, more than 1 million suspected cholera cases and 2,252 associated Yemeni deaths were reported.
Since March 2015, the United States has been the largest contributor of humanitarian aid to Yemen. Funds were provided to international aid organizations from USAID's Office of Foreign Disaster Assistance (OFDA), USAID's Food for Peace (FFP), and the U.S. Department of State's Bureau of Population, Refugees, and Migration (State/PRM). The United States has provided a total of $767.5 million in humanitarian assistance in FY2017 and FY2018. Overall, the United Nations Yemen 2017 Humanitarian Response Plan is 70% funded with $1.6 billion funded of the $2.3 billion requested.
|
Account |
FY2011 |
FY2012 |
FY2013 |
FY2014 |
FY2015 |
FY2016 |
FY2017 |
|
IDA (USAID/OFDA) |
19.946 |
45.087 |
61.819 |
49.858 |
76.844 |
81.528 |
227.996 |
|
FFP (UDAID/FFP) |
20.013 |
54.803 |
50.208 |
55.000 |
56.672 |
196.988 |
369.629 |
|
MRA (State/PRM) |
22.500 |
19.738 |
18.886 |
8.900 |
45.300 |
48.950 |
38.125 |
|
Total |
62.459 |
119.628 |
130.913 |
113.758 |
178.816 |
327.466 |
635.750 |
Source: Yemen, Complex Emergency—USAID Factsheets.
U.S. Counterterrorism Operations in Yemen
As the Saudi-led coalition's campaign against the Houthis continues and Yemen fragments, the United States not only has sustained counterterrorism operations against Al Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula (AQAP) and various affiliates of the Islamic State, but it has markedly increased the tempo of strikes. According to one source, in 2017, the United States launched more than 120 strikes in Yemen, which was more than in the previous four years combined.25 Repeated U.S. strikes have degraded, but not defeated, groups such as AQAP. According to a spokesperson for U.S. Central Command (CENTCOM), attacks "have put pressure on A.Q.A.P.'s network, severely limiting their freedom of movement, disrupting the organization's ability to recruit and train, and limiting A.Q.A.P.'s ability to plan and execute external operations."26 In a December 2017 war powers resolution letter to Congress on the deployments of United States Armed Forces equipped for combat, the President reported:
A small number of United States military personnel are deployed to Yemen to conduct operations against al-Qa'ida in the Arabian Peninsula (AQAP) and ISIS. The United States military continues to work closely with the Government of Yemen and regional partner forces to dismantle and ultimately eliminate the terrorist threat posed by those groups. Since the last periodic update report, United States forces have conducted a number of airstrikes against AQAP operatives and facilities in Yemen, and supported the United Arab Emirates- and Yemen-led operations to clear AQAP from Shabwah Governorate. In October, United States forces also conducted airstrikes against ISIS targets in Yemen for the first time. United States forces, in a non-combat role, have also continued to provide logistics and other support to regional forces combatting the Houthi insurgency in Yemen.27
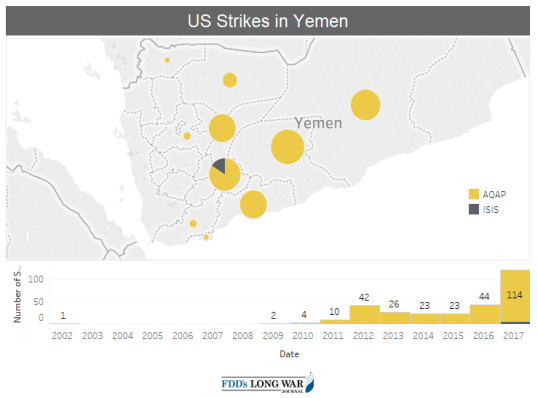 |
|
Source: Long War Journal, Foundation for the Defense of Democracies, 2017: A record year for US counterterrorism strikes, January 3, 2018| Notes: According to the source, "Air strike data has been obtained from press reports from the respective local outlets, US military reports, wire reports (AFP, Reuters, etc.), as well as independent reporting from FDD's Long War Journal." |